2010 SKODA OCTAVIA TOUR lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 91 of 199

Seat belts
90
The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy four
times.
The common opinion that it is possible to su pport your body in a minor accident with
your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces acting on the
body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed within the range from 30 km/hour to 50 km/hour, the
forces which are produced on your body in the event of an accident can easily exceed
10.000 N (Newton). This equals a weight of one tonne (1 000 kg).
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the vehicle not wearing a seat belt, are
thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolled way parts of the interior of the vehicle,
such as steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen, page 89, fig. 91 - left. The occu-
pants of a vehicle who have not fastened their seat belts may even be thrown out of
the vehicle. This can result in fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat occupants fasten their seat belts as they will otherwise
be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontr olled manner in the event of an accident
A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the s eat bel t i s a dang er not o nl y to hims elf
but also for those seated at the front page 89, fig. 91 - right.Important safety information regarding the use of seat beltsThe correct use of the seat belts cons iderably reduces the risk of injury!
WARNING
The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twisted,
or chafe against any sharp edges.
It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed if the seat belts are
to offer their maximum protection page 91.
No two persons (also not children) should ever use a single seat belt
together.
The maximum protection which seat belts can offer is only achieved if you
are correctly seated page 86, “Correct seated position”.
The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. specta-
cles, ball-point pens, keys etc.) as this may be a cause of injuries.
Bulky, loose clothing (e.g. a winter coat over a jacket) does not allow you to
be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of the seat belts.
It is prohibited to use clamps or other objects to adjust seat belts (e.g. for
shortening the belts for smaller persons).
The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to protect
and the risk of injury increases.
The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
The belt webbing must always be kept clean. A soiled belt webbing may
impair proper operation of the inertia reel page 135, “Seat belts”.
The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked by paper or similar objects
otherwise the belt tongue will not lock in place properly.
Inspect the seat belts regula rly to ensure they are in good condition. If you
find seat belts which have damage to the seat belt webbing, seat belt connec-
tions, to the inertia reels or to the lock, the relevant safety belt must be replaced
by a specialist garage.
The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not make an
attempt to repair the seat belts yourself.
Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident and
were therefore stretched, must be replaced - this is best done by a specialist
garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The
anchorage points for the belts should also be checked.
In certain countries it is possible to use seat belts which differ in terms of
their operation from the seat belts which are described on the pages which
follow.WARNING (continued)
s2bs.2.book Page 90 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM
Page 92 of 199

Seat belts91
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
How are seat belts correctly fastened?Fastening three-point seat belts
Fasten your seat belt before starting!Fig. 92 Routing of webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt– Correctly adjust the front seat and the head restraint before fastening your seat belt
page 53.
– Slowly pull the belt webbing at the tongue of the lock over your chest and pelvis
.
– Insert the tongue of the lock into the seat belt buckle belonging to the seat until it is heard to lock in place.
– Pull on the seat belt to check that it has also reliably engaged in the lock.
Each three-point seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel. This inertia reel offers you
complete freedom of movement if the belt is unreeled slowly. If the brakes are applied
suddenly, the inertia reel will block. It also blocks the seat belts when the car acceler-
ates, when driving uphill and when cornering.
Expectant mothers must also wear seat belts .
WARNING
The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across your neck but must
run approximately over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the
chest. The lap part of the belt must run across the hip and must never be routed across the stomach. It must always fit snugly
fig. 92 - left. Adjust the belt
webbing as required.
The lap part of the belt should be posi tioned as low as possible at the pelvis
of an expectant mother in order to avoid exerting any pressure on the lower
abdomen fig. 92 - right.
Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctl y adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in
minor accidents.
A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy pr oduced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
Only insert the lock tongue into the lock which is the correct one for your
seat. This will affect the protection which the belt offers and increase the risk of
an injury.
Seat belt height adjusterThe seat belt height adjuster makes it possible for you to adapt the routing of the three-
point seat belt in the area of the shoulder to match your body size.
– Move the height adjuster in the desired direction up or down fig. 93 .
– Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height adjuster has correctly
locked in place.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 93 Front seat: Seat belt height
adjuster
s2bs.2.book Page 91 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM
Page 93 of 199

Seat belts
92WARNING
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the belt is
positioned approximately across the middle of your shoulder - on no account
across your neck.
Note
It is also possible to adapt the routing of the belt webbing at the front seats by adjusting
the height of the seat.Taking seat belts off– Press the red button in the belt lock fig. 94 . The spring force causes the tongue
of the lock to jump out.
– Guide the seat belt back with your hand to enable the inertia reel to wind up the
belt webbing more easily.
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the be lt tongue in a position which is easy to
get hold of.Three-point safety belt for the middle rear seatYour car is equipped as standard with the three-point seat belt in the middle rear seat.
It i s us ed i n the sam e way as the thre e-poi nt seat belts on the left and right (at front and
rear).
WARNING
The three-point safety belt for the rear middle seat can only fulfil its function
reliably when the backrests are correctly locked into position page 54.Belt tensionersSafety for the driver and front passenger wearing their seat belts is enhanced by the
belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front three-point seat belts, and is a
supplement to the protection afforded by the airbag system.
The three-point seat belts are automatically te nsioned in the event of a frontal collision
of a certain severity. The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the seat belts are not
fastened.
The belt tensioner is deployed in the event of a frontal collision of major severity. A
powder charge is ignited in the inertia re els during deployment. The belt webbing is
pulled into the inertia reels by a mechanical system and the belt is tensioned.
The belt tensioners are not ac tivated in case of minor frontal and rear-end collisions,
in the case of vehicle rollover or accidents, through which no long delays are incurred
to the vehicle. In the case of a side collision, only the belt tensioner of the front seat on
the side on which the collision takes place is deployed.
WARNING
Any work on the belt tensioner and the seat belt, including removal and
installation of system components because of other repair work, must only be
carried out by a specialist garage.
The protective function of the belt tensioner is only adequate for a single
accident. If the belt tensioners have be en deployed, it is then necessary to
replace the entire system.
The Owner's Manual must also be handed over to the new owner if the
vehicle is sold.Note
Smoke is generated when the belt tensione rs are deployed. This is not an indica-
tion of a fire in the vehicle.
Fig. 94 Releasing lock tongue from belt
lock
s2bs.2.book Page 92 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM
Page 96 of 199

Airbag system95
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
When are the airbags deployed?The airbag system is designed in such a wa y that the driver and front passenger airbag
are deployed in the event of a violent frontal collision.
In the case of a violent side collision , the side airbag* on the side of the vehicle at
which the collision occurs, is deployed to gether with the relevant head airbag*.
In special accident scenarios, the front as well as the relevant side and head airbags
may be deployed together.
The airbags are not deployed in the case of minor frontal and side collisions, in the
case of rear-end collisi ons and vehicle rollover.
Deployment factors
It is not possible to state globally which deployment conditions apply to the airbag
system in every situation as the circumstances which exist in the case of accidents vary
greatly. An important role in this case is played by factors such as the type of object
against which the vehicle impacts (hard, soft ), the angle of impact, the relative speed
during the accident etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which occurs
during a collision. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates the
relevant restraint system. If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is measured
during the collision remains below the prescribed reference values specified in the
control unit, the airbags are no t deployed although the vehicle may well suffer severe
damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The airbags are not deployed if:
ignition off,
a minor frontal collision,
a minor side collision,
a rear-end collision,
Rollover of the vehicle.Note
A grey white, non harmful gas is released when airbag is inflated. This is perfectly
normal and is not an indicati on of a fire in the vehicle.
In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed:
The interior lighting comes on (if the switch for the interior light is in the door
contact position),
The hazard warning light is switched on,
All the doors are unlocked,
the fuel supply to the engine is interrupted.
Front airbagsDescription of the front airbags
The airbag system is not a su bstitute for the seat belt!Fig. 95 Driver airbag in the steering whee l/front passenger airbag in the dash panelThe front airbag for the driver is housed in the steering wheel fig. 95 - left. The front
airbag for the front passenger* is housed in the dash panel above the storage compart-
ment fig. 95 - right. The installation positions are each marked with the “AIRBAG”
logo.
The front airbag system is complementary to the three-point seat belts and offers addi-
tional protection for the head and chest area of the driver and passenger in the event
of a frontal collision. page 96
The airbag is not a substitute for the seat belt, but is part of the complete passive
vehicle safety concept. Please note that an airbag can only offer you optimal
protection in combination with a seat belt which is fastened .
s2bs.2.book Page 95 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM
Page 109 of 199
Transporting children safely
108
The shoulder part of the seat belt mu st run approximately across the middle
of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest. It must on no account run
across the neck. The lap part of the seat belt must run across the pelvis and fits
snugly; it must not run over the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if
necessary.
Please comply with any differing nati onal legal regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
Child safety seats in Group 3For children of about 7 years of age weighing between 22 and 36 kg and of a height of
less than 150 cm, the optimal solution is a ch ild safety seat (seat bolster) in combina-
tion with the three-point seat belt fig. 108 .
Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the vehicle
without a seat bolster.
WARNING
When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please comply with
the appropriate national regu lations regarding the use of child safety seats. If
required, the front passenger ai rbag has to be deactivated,
in a specialist garage
or by using the key-operated swit ch for the front passenger airbag*
page 101, “Switch for switching off the front passenger airbag*”.
The shoulder part of the seat belt mu st run approximately across the middle
of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest. It must on no account run
across the neck. The lap part of the seat belt must run across the pelvis and fits
snugly; it must not run over the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if
necessary.
Please comply with any differing nati onal legal regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
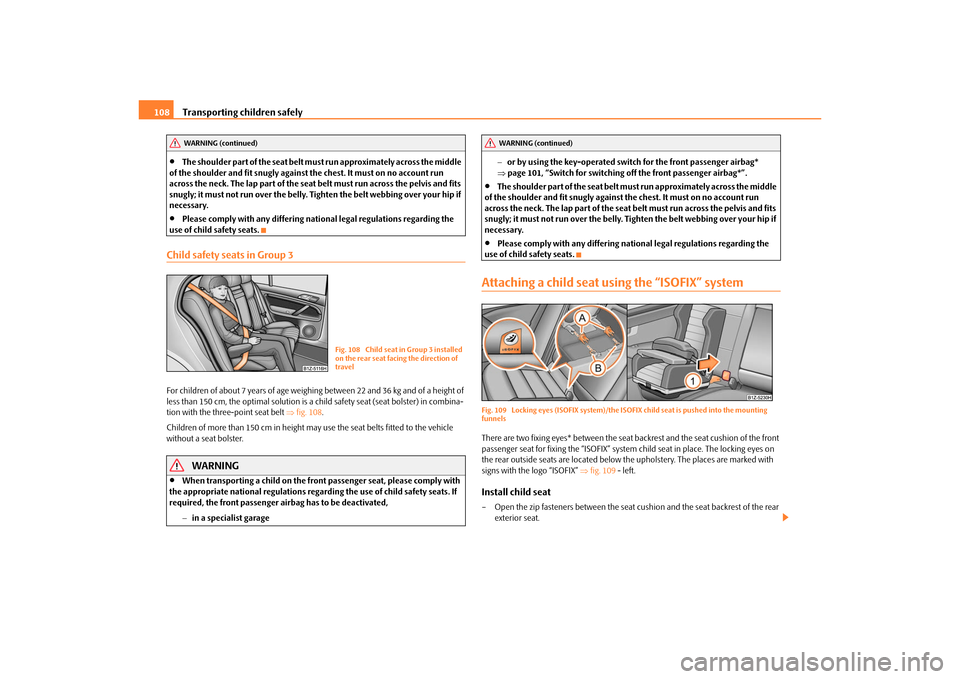
Attaching a child seat using the “ISOFIX” systemFig. 109 Locking eyes (ISOFIX system)/the ISOF IX child seat is pushed into the mounting
funnelsThere are two fixing eyes* between the seat backrest and the seat cushion of the front
passenger seat for fixing the “ISOFIX” system child seat in place. The locking eyes on
the rear outside seats are located below th e upholstery. The places are marked with
signs with the logo “ISOFIX” fig. 109 - left.Install child seat– Open the zip fasteners between the seat cushion and the seat backrest of the rear
exterior seat.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 108 Child seat in Group 3 installed
on the rear seat facing the direction of
travel
WARNING (continued)
s2bs.2.book Page 108 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM
Page 110 of 199

Transporting children safely109
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
– Insert the mounting funnels onto the
locking eyes between the seat back-
rest and the seat cushion fig. 109 .
– Push the notched arms of the child seat in to the locking eyes in direction of arrow
, until they are heard to lock in place fig. 109 .
– Pull on both sides of the child seat!
One can mount a child safety seat using the “I SOFIX” system quickly, easily and reliably.
Please pay close attention to instructions from the manufacturer of the child safety
seat when installing and removing the seat.
Child seats fitted with the “ISOFIX” system can only be mounted and fixed in a vehicle
fitted with an “ISOFIX” system when these child seats have been released for this type
of vehicle according to the ECE-R 44 standard.
You can obtain child seats with the “ISOFIX” attachment system from specialist garages
who will also installed it as well.
Complete installation instructions are enclosed with the child safety seat.
WARNING
The locking eyes have just been deve loped for child safety seats which use
the “ISOFIX” system. You should therefore never attach other child safety seats,
seat belts or objects to the locking eyes - hazard!
Ask an authorised Škoda Service Part ner whether a child seat which you
bought for another vehicle is recommended for use in a Škoda before using an
“ISOFIX” system.
Certain child seats which use the “ISO FIX” system can be attached with
standard three-point seat belts. Please pay close attention to instructions from
the manufacturer of the child safety seat when installing and removing the seat.Note
Child seats which use the “ISOFIX” system are currently available for children
weighing from 9 up to 18 kg. This correspond s to an age range of from 9 months to 4
years.
The child seats can also be fitted with the “Top Tether” system page 109.
Attaching child seat using the “Top Tether”* systemIn certain countries national legal provisions also require the equipment of the rear
seat with fixing eyes for child seat using the “Top Tether” system fig. 110 .
Always perform the installation and removal of the child seat using the “Top Tether”
system as stated in the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat.
WARNING
Attach the child seats with the “Top Tether” system only to the points
provided for this purpose fig. 110 .
On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other
anchorage points.
Pay attention to the important safety information regarding the use of child
seats.Note
Store the remaining part of the belt for the “Top Tether” system in a textile pocket,
which is located at the child seat.
AA
AB
A1
Fig. 110 Rear seat: Top Tether
s2bs.2.book Page 109 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM
Page 112 of 199

Intelligent Technology111
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Driving TipsIntelligent TechnologyElectronic stability programme (ESP)*GeneralThe ESP aids you in maintaining control of your vehicle in situations in which the
vehicle is driving at its dynamic limits, such as entering a curve fast. The risk of skidding
is reduced and your vehicle thus offers greater driving stability depending on the
conditions of the road surface. The system operates at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
Traction control system (TCS),
active driver-steering recommendation (DSR),
Antilock brake system (ABS),
Brake Assist,
Uphill-Start off-Assist.
The ESP system cannot be switched off, only the TCS system can be switched off by
pressing the button fig. 111 , the warning light
lights up. Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts a
self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It also proc-
esses additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive sensors: the
rotational velocity of the vehicle about its ve
rtical axis, the lateral acceleration of the
vehicle, the braking pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the steering
angle and the speed of the vehicle and is co nstantly compared with the actual behav-
iour of the vehicle. If differences exist, such as the vehi cle beginning to skid, the ESP will
automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces wh ich take effect when the wheel is braked.
Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front wheel of a
vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle to break away)
while occurs this is on the inner rear wh eel of a vehicle which tends to understeer
(tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied by
noises.
During an intervention of the system, the warning light
flashes quickly in the instru-
ment cluster page 26.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS page 115, “Antilock brake system
(ABS)”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also does not operate.
The ESP warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on the
ESP
page 26.WARNING
It is also not possible for the ESP to overcome the physical limits of the vehicle.
Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still always adapt your style of
driving to the condition of the road surfac e and the traffic situation. This partic-
ularly applies when driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety
Fig. 111 ESP switch
s2bs.2.book Page 111 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM
Page 113 of 199

Intelligent Technology
112
offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an acci-
dent!
Note
All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve problem-free
operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circum ferences of the tyres can lead to an unde-
sirable reduction in the engine output.
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on th e brakes, on chassis or another combina-
tion of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP page 157, “Accesso-
ries, changing and replacing parts”.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)*
The electronic differential lock prev ents an individual wheel from slip-
ping.Models fitted with ESP ar e equipped with electronic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, accelerate
and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automaticall y, that is without any action on the part of the driver.
It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sensors. Should
only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery surface there will be an appreciable
difference in the speed of the driven wheels. The EDL function brakes the slipping
wheel and the differential transmits a greate r driving force to the other driven wheel.
This control process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatica lly if unusually severe stresses exist in order to avoid
excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel which is being braked. The
vehicle can continue to be driven and has the same characteristics as a vehicle not
fitted with EDL. The EDL switches on again automatically
as soon as the brake has cooled down.
WARNING
Carefully depress the accelerator when accelerating on uniformly slippery
road surfaces, such as ice and snow. Th e driven wheels might still spin despite
the EDL and affect the stability of the vehicle - risk of an accident!
You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition of road
surface and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle is fitted with EDL.
The increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than
otherwise - risk of an accident!Note
If the ABS or ESP warning light comes on, this may also indicate a fault in the EDL.
Please have the vehicle inspected as soon as possible by a specialist garage.
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combina-
tion of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the EDL page 157, “Accesso-
ries, changing and replacing parts”.
Traction control system (TCS)
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels from spinning
when accelerating.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 112 TCS switch
s2bs.2.book Page 112 Monday, September 27, 2010 9:53 AM