2010 JAGUAR XFR brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 1848 of 3039
information from other systems:
ABS (anti-lock brake system) module - Road speed signal
TCM (transmission control module) - Reverse gear engaged signal
Trailer module - Trailer attached to vehicle
The module also outputs messages on the medium speed CAN bus which are received by the integrated audio module. The integrated audio module processes these messages and converts them into Media Orientated System Transport (MOST) signals
which are passed to the audio system power amplifier. These signals are then used by the power amplifier to emit the
applicable warning tones from the front or rear audio speakers when an object is detected by the front or rear parking aid
sensors. A warning tone can also be emitted to alert the driver to a fault in the parking aid system.
The control module has a diagnostic connection via the medium speed CAN bus to enable faults to be retrieved using the
Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment. Additionally an on-board diagnostic routine within the control module constantly
monitors the system and alerts the driver to a system fault by emitting a 3 second continuous tone through the rear audio
system speakers when the ignition is switched on. If front parking aid sensors are fitted, the control switch LED will also flash
6 times.
Parking Aid Sensors
Four ultrasonic sensors are located in the front (if fitted) and rear bumpers.
Each sensor has a three pin connector which mates with a bumper harness, which in turn is connected to the main body
harness. Three pins provide for power supply, ground and signal lines to and from the parking aid module.
The parking aid module controls the operation of each sensor using a digital output on the signal line. The module controls the
sensor in one of two modes; combined transmitter and receiver mode or receiver mode only.
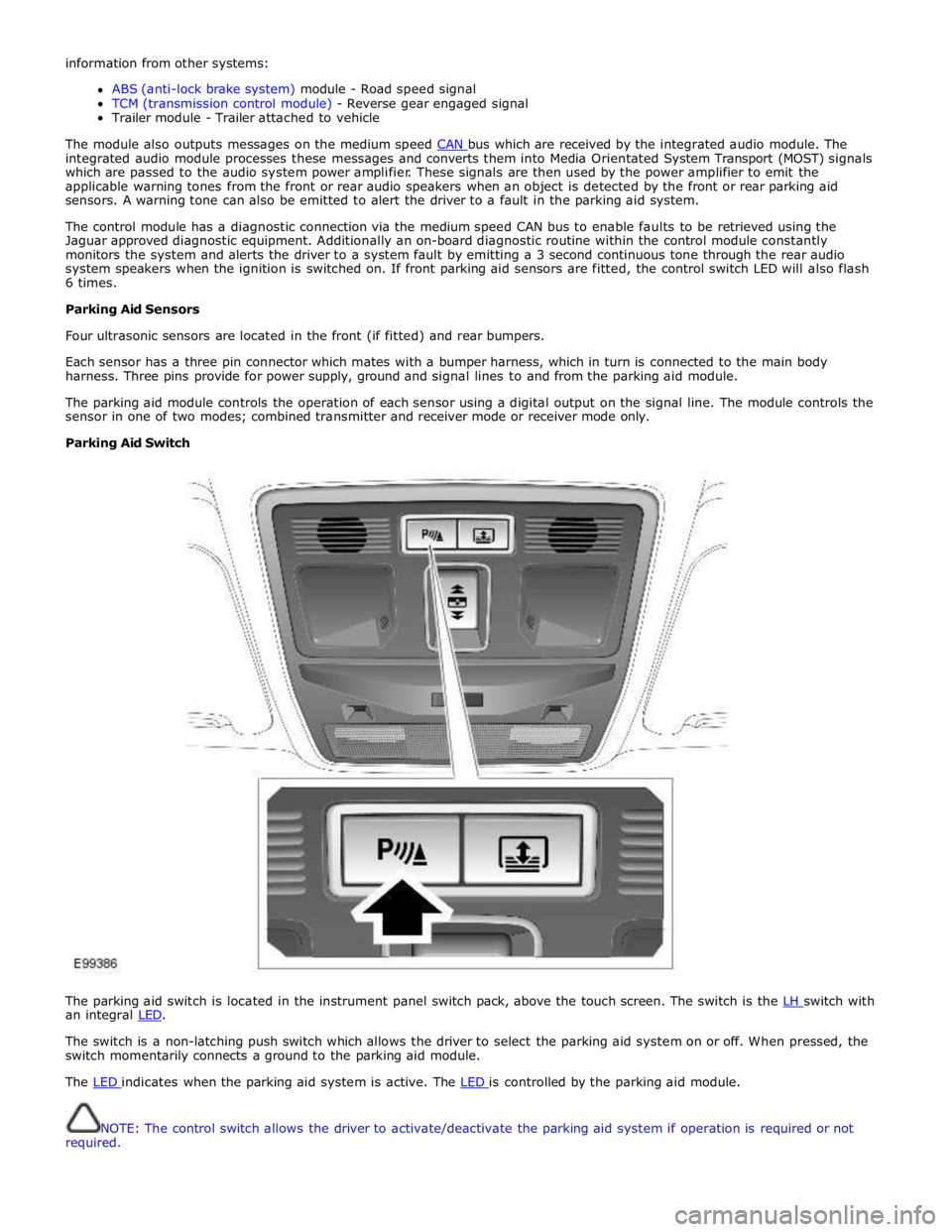
Parking Aid Switch
The parking aid switch is located in the instrument panel switch pack, above the touch screen. The switch is the LH switch with an integral LED.
The switch is a non-latching push switch which allows the driver to select the parking aid system on or off. When pressed, the
switch momentarily connects a ground to the parking aid module.
The LED indicates when the parking aid system is active. The LED is controlled by the parking aid module.
NOTE: The control switch allows the driver to activate/deactivate the parking aid system if operation is required or not
required.
Page 1872 of 3039

MODEL SHUT DOWN PERIOD (minutes) TYPICAL VALUES BATTERY DRAIN (mA) XJ6 4.0 60 <38.6 XJS 60 <43.9 XJ6 (X300) (1995MY) 60 <43 XJ8 (X300) 60 <30 XK8 (X100) 60 <30 S-Type (X200) 60 <30 X-Type (X400) 30 <30 XJ6 (X350) 40 <30 XJ8 (X350) 40 <30 XK (X150) - From 2006MY <20 (after lock/arm condition) ² <30 33 (unlocked) <30 XF (X250) - From 2008MY <20 (after lock/arm condition) ² <30 33 (unlocked) <30 XF (X250) - From 2013MY <10 (after lock/arm condition) ² <25 XF SportBrake (X250) - From 2013MY <10 (after lock/arm condition) ² <25 <20 (unlocked) <25 XJ (X351) - From 2010MY - 2012MY 10 (afterlock/arm condition) ² <20 30 (unlocked) <20 XJ (X351) - From 2013MY 10 (afterlock/arm condition) ² <20 <20 (unlocked) <20 F - Type (X152) - From 2013MY 10 (afterlock/arm condition) ² <20 <20 (unlocked) <20
NOTE:
1. The total current drain will be higher if certain approved accessories are fitted (for example: tracker, trailer module, etc.)
2. Applies to vehicles without Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS). Vehicle shut-down period with TPMS is approximately 15
minutes.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1879 of 3039

The dual battery system comprises the following components:
Dual Battery Module (DBM).
Dual Battery Junction Box (DBJB).
Gateway Module (GWM).
Primary battery.
Secondary battery.
The GWM hosts most of the software required to control the dual battery system and components. The GWM monitors the
components and can store fault related DTC's.
The GWM also controls the charging system software in conjunction with the ECM, RJB, CJB and ABS (anti-lock brake system) control module via the high speed and medium speed CAN (controller area network) bus. The GWM software will monitor the
status of the stop/start system and determine when a stop/start event can occur. It can also intervene to maintain vehicle
systems by keeping the engine running or initiating a restart due to, for example, climate control system requirements or
request for restart from the ECM. A brake pressure signal is received from the ABS control module which will indicate to the
GWM that an engine restart is required from driver operation of the foot brake.
The GWM contains the intelligent power management system and the BMS software. Monitoring of the primary battery
condition for stop/start is controlled by the GWM and the BMS control module.
Page 1881 of 3039
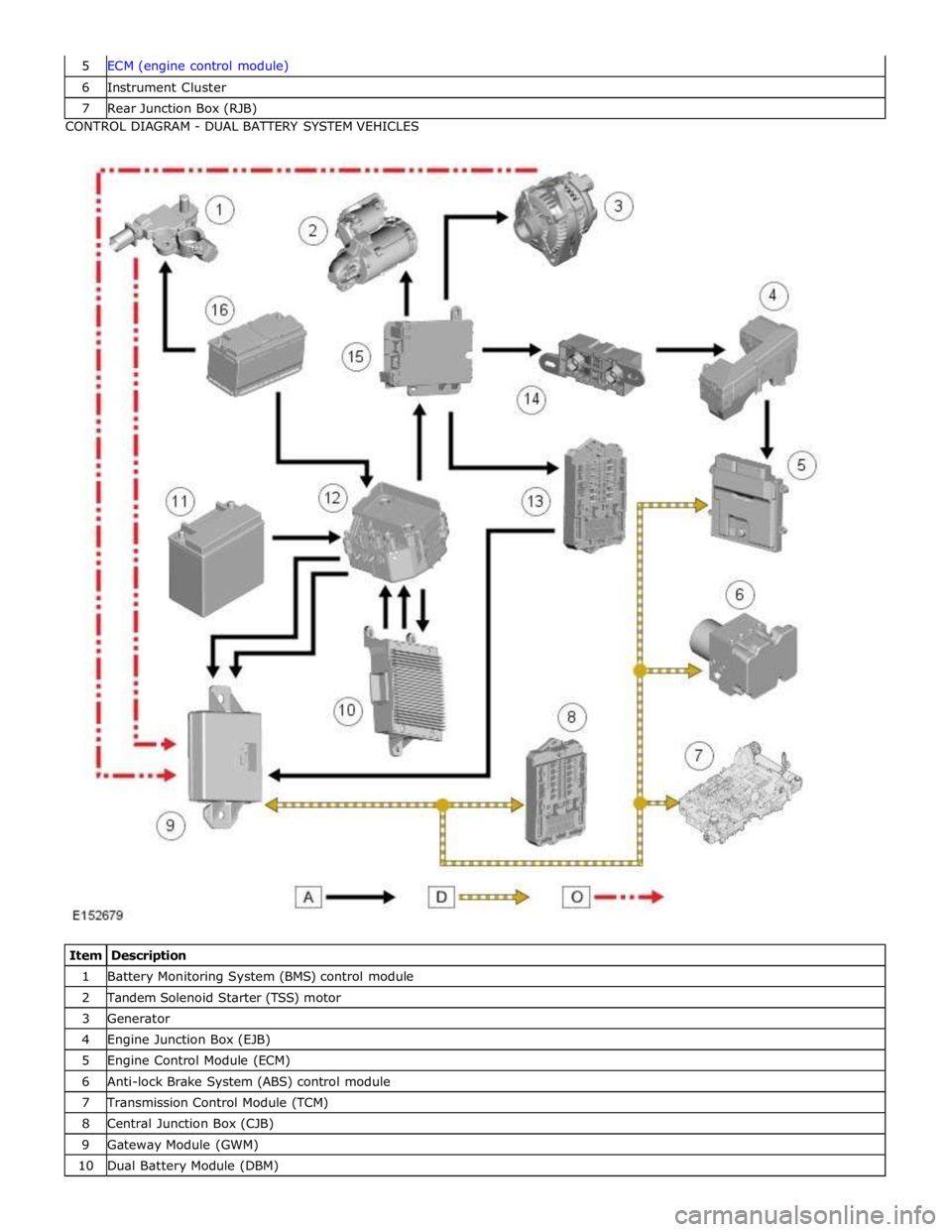
6 Instrument Cluster 7 Rear Junction Box (RJB) CONTROL DIAGRAM - DUAL BATTERY SYSTEM VEHICLES
Item Description 1 Battery Monitoring System (BMS) control module 2 Tandem Solenoid Starter (TSS) motor 3 Generator 4 Engine Junction Box (EJB) 5 Engine Control Module (ECM) 6 Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) control module 7 Transmission Control Module (TCM) 8 Central Junction Box (CJB) 9 Gateway Module (GWM) 10 Dual Battery Module (DBM)
Page 1885 of 3039

is operated to crank the engine. The GWM is connected to the ABS (Anti-lock Brake System) control module via the high speed
CAN bus. With the vehicle stationary and the engine off after an ECO engine stop, when the driver releases the brake pedal
the ABS control module senses the reduction in brake pressure. This change of brake pressure state is sent as a high speed
CAN message which is received by the GWM and the ECM. The GWM reacts within 105ms to instruct the DBM via the LIN bus
to operate the two contactors in the DBJB to supply the sensitive loads from the secondary battery and supply the TSS motor
direct from the primary battery.
When the engine is running and the generator is supplying power to the vehicle systems, the GWM again instructs the DBM to
operate the two contactors in the DBJB to supply all vehicle systems from the primary battery and the generator and to isolate
the secondary battery.
Secondary Battery Charging
The DBM also controls the charging of the secondary battery. The GWM contains electrical load management software and
monitors both batteries for their state of charge. The primary battery is monitored by the BMS control module which is
connected to the DBM via the LIN bus. The DBM communicates the primary battery condition to the GWM via a LIN bus
connection. The GWM sends a signal to the DBM via the LIN bus to instruct it to apply charging from the generator to the
secondary battery when required. The contactor 2 is closed by the DBJB to complete the secondary battery circuit, and the
generator output is applied to the secondary battery to charge it.
The generator output is controlled by the GWM which monitors and controls the electrical load management system. The
generator is connected to the GWM by a LIN bus allowing the GWM to control the output of the generator to maintain electrical
system load requirements and battery charging.
Electrical Load Management
The electrical load management is controlled by the GWM and the BMS control module.
The GWM will monitor the vehicle system power loads before and during an ECO engine stop.
Before an ECO engine stop, the GWM will transmit a signal to system control modules on the CAN bus to request a power save
on all electrical loads and set a minimum electrical value override. The GWM monitors the vehicle electrical loads and will
inhibit a ECO engine stop until the load current is at a value low enough to be supported by the secondary battery.
If the electrical loads cannot be reduced sufficiently, the GWM will inhibit the ECO engine stop.
When the engine is stopped after an ECO engine stop, the GWM will continue to monitor the primary battery state of charge.
If the primary or secondary battery voltage falls below 11.0V, a level which will result in degraded starting performance or
possible primary battery damage, the GWM will initiate an engine start.
System Inhibits
The ECO stop/start system is inhibited if the dual battery system is not be capable of preventing electrical loads on the
vehicle being subject to unacceptably low voltage levels during ECO stop/start operations due to a fault.
ECO stop/start inhibit monitoring of the primary battery is performed by the BMS control module. If the primary battery voltage
is too low to support an ECO stop/start, then the BMS control module will send a message to the GWM on the LIN bus to
suspend ECO stop/start.
The GWM monitors the secondary battery and the dual battery system components. Any fault found will cause the GWM to
inhibit ECO stop/start and the GWM will record a DTC (diagnostic trouble code).
Fault Diagnosis
The GWM performs passive and active diagnostics on the dual battery system to determine the status of the system
components.
Passive diagnostics can detect faults in the DBJB and can check for stuck open or closed contactors and failure of DBM
contactor command signals.
Active diagnostics is a routine to test the capability of the contactors to respond to open or close command signals sent from
the GWM to the DBM. This routine also checks the FET's (Field Effect Transistors) activate as required. (Refer to Dual Battery
Junction Box below for description of FET operation)
The GWM will also check the dual battery system components for faults in a controlled environment when the generator is
providing a charging output. This will ensure that the detection of a fault will not result in sensitive electrical loads being
subjected to low voltage which may occur during an ECO stop/start with a fault present.
The GWM will illuminate the charge warning indicator in the instrument cluster if fault is detected in the dual battery system
which will result in a degraded power supply.
If a fault is detected the GWM transmits a CAN message to inhibit ECO stop/start operation. In some cases it will record a
DTC, display a warning message in instrument cluster and also illuminate charge warning indicator.
PRIMARY BATTERY - ALL VEHICLES Component Description
The primary battery is located in a plastic tray under the luggage compartment floor in the right side of the luggage
compartment, adjacent to the spare wheel. The battery is vented via a tube which is connected with a T piece to the vent from
Page 1948 of 3039

3 Satellite Radio digital receiver (Optional - NAS only) 4 Telephone control module (Optional) 5 Touch-screen 6 TV tuner (Optional) 7 Power amplifier (Not fitted to the Jaguar Sound System) 8 IAM (integrated audio module) 9 Portable audio module (Optional) 10 ICM (information control module)
AUDIO SYSTEM OPERATION System Operation
The components of the audio/infotainment system are all connected on the MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring.
The MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring is a fibre optic communications bus for multimedia applications. Audio
and control information is passed around the MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring and can be picked up by any of
the systems units. For example, radio station tuning/selection input by the vehicle user into the Touch-screen is sent along the
MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring and collected by the IAM (integrated audio module) which then selects the
requested radio station.
MOST (media orientated systems transport) technology uses a plastic optical fibre which forms a network connecting the audio
and multimedia system components. Each component in the ring is connected to the plastic optical fibre through a device
known as a FOT (fibre optical transceiver). Each FOT (fibre optical transceiver) has two optical connections; one connection is
sensitive to light and is the input, the second connection forms the light source and is the output. The system operates by
connecting the output from one FOT (fibre optical transceiver) to the input of another FOT (fibre optical transceiver).
The light signals are sent in one direction only and are formed in the following way:
Electrical signals are converted into an electrical current
The current then drives an LED (light emitting diode) in the FOT (fibre optical transceiver) to produce a high intensity
red light
The LED transmits the light through a fibre optic cable A photo diode in the FOT (fibre optical transceiver) at the opposite end of the fibre optic cable detects the light.
The following components may be connected to the MOST ring dependant on the vehicle equipment level:
IAM (integrated audio module)
Touch-screen
ICM (information control module)
DAB (digital audio broadcasting) radio receiver (Optional - Europe only)
Satellite radio digital receiver (Optional - NAS only)
Power amplifier (Not fitted to the Jaguar Sound System)
Portable audio module (Optional)
Telephone control module (Optional)
Navigation computer (Optional)
TV tuner (Optional)
NOTE: Do not view the red light directly
MOST is a synchronous network. A timing master supplies the clock information and all other devices on the network
synchronize their operation to this clock. The timing master for the MOST (media orientated systems transport) network on this
vehicle is the ICM (information control module). This unit also controls and manages the MOST (media orientated systems
transport) ring and the system components.
An Optical Bus tester is used in conjunction with the Jaguar diagnostic system to diagnose the MOST (media orientated
systems transport) system. The Optical Bus tester emits a visible, high intensity red light which can be connected into the ring
at any point to test the ring integrity. Disconnecting a MOST (media orientated systems transport) connector will reveal if the
high intensity red light is visible.
If a break occurs in the MOST (media orientated systems transport) ring fault codes are stored in the ICM (information control
module) which can be retrieved using the Jaguar diagnostic system equipment.
With reference to the audio system information and signal transfer the instrument cluster is the gateway between the high
and medium speed CAN bus communication protocols. The ICM (information control module) is the gateway between medium speed CAN and the MOST (media orientated systems transport) systems.
A typical example of information transfer is vehicle speed information from the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module used to
control the automatic volume control function. The vehicle speed information from the ABS module is sent on the high speed CAN network and collected by the instrument panel gateway. The signal is passed to the medium speed CAN network and onto the ICM (information control module) gateway. The ICM (information control module) calculates the volume adjustment
required. The corrected audio volume level signal is sent on the MOST (media orientated systems transport) network to the
IAM (integrated audio module) or Power amplifier (dependant on vehicle equipment level) for output to the speaker system.
Page 1949 of 3039

systems.
A typical example of information transfer is vehicle speed information from the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module used to
control the automatic volume control function. The vehicle speed information from the ABS module is sent on the high speed
CAN network and collected by the instrument panel gateway. The signal is passed to the medium speed CAN network and onto the ICM gateway. The ICM calculates the volume adjustment required. The corrected audio volume level signal is sent on the
MOST network to the IAM or Power amplifier (dependant on vehicle equipment level) for output to the speaker system.
AUDIO SYSTEM USER CONTROLS
Touch-Screen
Item Description 1 Touch-screen 2 Home menu button 3 Touch-screen on/off button The Touch-screen forms the basis of the audio system. It communicates with the rest of the audio/infotainment system on the
MOST ring and allows control of the audio system and other infotainment systems from a single point.
The Touch-screen communicates with the IAM on the MOST ring and provides the primary user interface and display of the
audio system controls. No configuration procedure is required if the touch-screen is replaced.
Calibration of the Touch-screen using the Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment enables updates to be downloaded as new
technology becomes available or any fault concerns require software updates.
The touch-screen provides user control of the following systems:
System Functions Audio Radio display AM/FM or DAB, auxiliary and portable audio, digital TV or CD (compact disc) Climate
control Air conditioning, distribution, seats, heated steering wheel, automatic air recirculation Telephone Digit dialer, phone book, last ten calls (made, received, missed) Navigation Destination, stored locations, navigation setup, route options Vehicle
Security, parking, valet mode, trip computer, clock, brightness, contrast, system settings, vehicle settings, display settings
Page 1974 of 3039
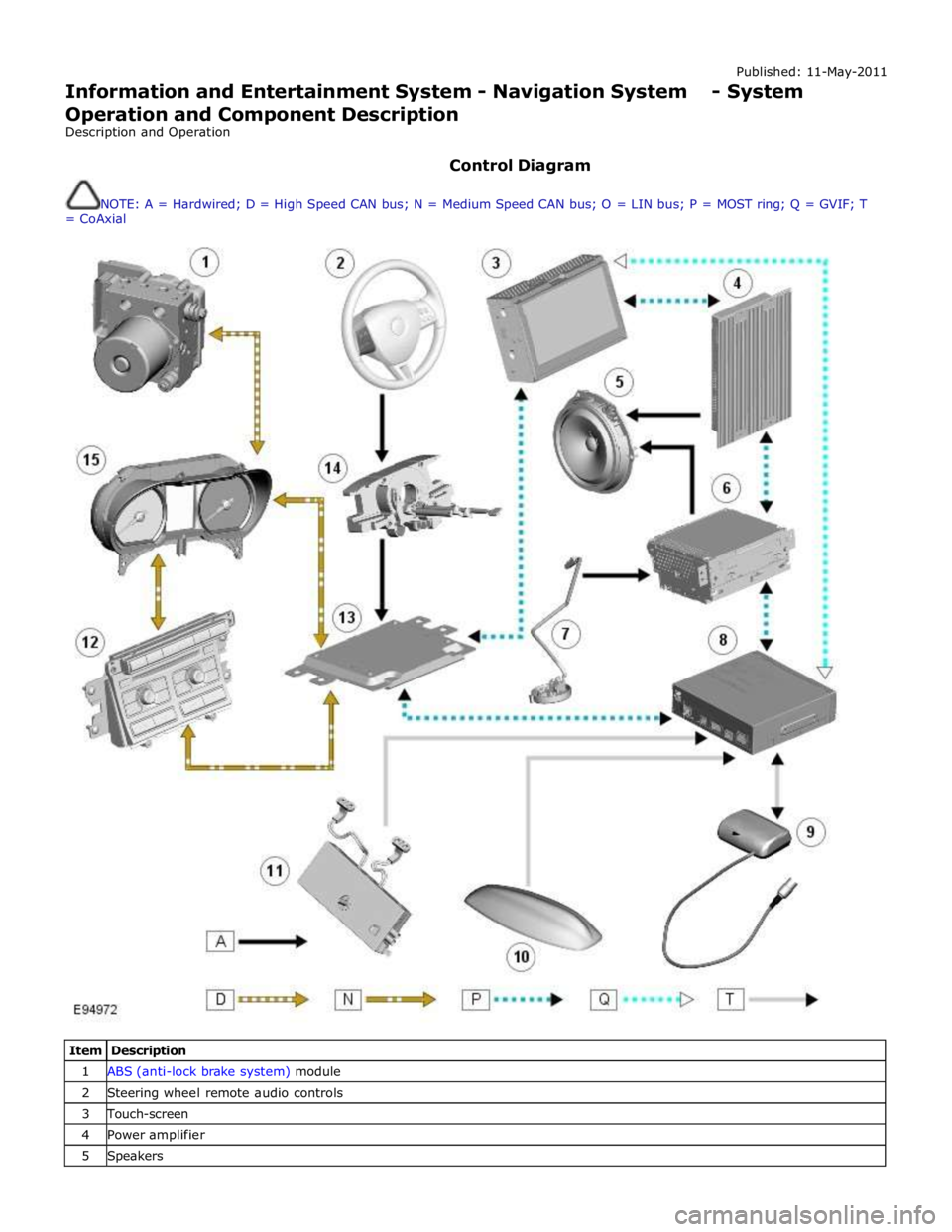
Published: 11-May-2011
Information and Entertainment System - Navigation System - System
Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired; D = High Speed CAN bus; N = Medium Speed CAN bus; O = LIN bus; P = MOST ring; Q = GVIF; T
= CoAxial
Item Description 1 ABS (anti-lock brake system) module 2 Steering wheel remote audio controls 3 Touch-screen 4 Power amplifier 5 Speakers