2010 JAGUAR XFR clutch
[x] Cancel search: clutchPage 532 of 3039

6 Oil temperature sensor 7 High speed CAN from suspension control module 8 CJB (central junction box)
System Operation
ELECTRONIC
DIFFERENTIAL
-
5.0L
SUPERCHARGER
VEHICLES
FROM
2010MY
The
multi-plate
clutch
prevents
excessive
differential
slip and
therefore
maximizes
the
traction
performance
of
the
vehicle.
This
is
fundamentally
different
from
'braked'
traction
control
systems,
which
can
only
counteract
differential
slip when it
occurs.
A
certain
amount
of
differential
slip is
required
to
allow
the
vehicle
to
turn
corners
and
to
remain
stable
under
control
of
the
ABS
(anti-lock
brake
system).
The
system
is
completely
automatic and
does
not
require
any
special
driver
input.
The
multi-plate
clutch
actively
controls
the
torque
flow
through
the
differential
and
optimizes
the
torque
distribution in
the
driveline.
The
clutch
biases
the
torque
from
the
differential
to
the
wheel
with the
higher
grip
and prevents
the
wheel
with the
lower
grip
from
spinning.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 535 of 3039

Thrust race 7 Shim 8 Thrust plate 9 Dished washer 10 Bolt (10 off) 11 Clutch basket 12 Multi-plate clutch and pressure disc 13 Differential case 14 Screw (2 off) 15 Bearing assembly 16 Oil seal 17 Oil slinger inner 18 Oil slinger outer 19 Input flange 20 Pinion nut 21 Collapsible spacer 22 Shim 23 Bearing assembly 24 Pinion shaft 25 Mounting insulator inner (2 off) 26 Mounting insulator rubber (2 off) 27 Mounting insulator outer (2 off) 28 Carrier 29 Oil seal 30 Drain plug 31 Vent 32 Breather cap 33 Shim 34 Bearing assembly 35 Drive gear 36 Shim 37 RH sun gear 38 Circlip 39 Thrust washer (4 off) 40 Planet gear (4 off) 41 Pin (2 off) 42 Shaft 43 LH sun gear 44 Shim 45 Bearing assembly 46 Shim 47 Dowel (2 off) 48 Bolt (4 off) 49 Reduction gear casing 50 Reduction gear 51 Shaft 52 Temperature sensor 53 O-ring seal 54 Motor 55 Screw (4 off) 56 Cover 57 Output actuator locking pin 58 Bolt (9 off)
Page 536 of 3039

60 Oil seal The multi-plate clutch is contained in a clutch basket attached to the differential carrier with the crown wheel securing bolts.
Alternate plates of the clutch pack are keyed to the clutch basket and the LH sun gear. A pressure disc is installed on the outer end of the clutch pack and keyed to the clutch basket. A thrust race on the end of the clutch basket incorporates lugs which
extend through the clutch basket onto the pressure disc.
The actuator assembly is mounted on bearings on the outboard end of the clutch basket, against the thrust race. The actuator
assembly consists of input and output actuators separated by five ball bearings. A locking pin in the cover engages with a slot
in the output actuator to prevent it turning, but allow it to move axially. The input actuator engages with the reduction gearbox
and is free to rotate relative to the cover. Ball bearings locate in curved grooves in the mating faces of the input and
output actuators. The bottom surface of each groove incorporates a ramp. Rotation of the input actuator forces the ball
bearings up the ramps in the grooves and induces an axial movement in the output actuator. The thrust race and pressure disc
transfer the axial movement from the output actuator to the clutch pack.
Item Description 1 Actuator 2 Multi-plate clutch 3 Differential The motor is a 12 V dc motor that adjusts the frictional loading of the multi-plate clutch, via the reduction gearbox and the
actuator assembly, under the control of the DLM. Adjusting the frictional loading of the multi-plate clutch adjusts the locking
torque between the crown wheel drive gear and the sun wheel.
Four bolts attach the motor to the reduction gearbox, which is located in position on the cover with two dowels, and secured
with four bolts. An O-ring seals the joint between the motor and the reduction gearbox.
The motor is driven by a 12 V dc feed direct from the DLM. The motor also incorporates the following connections with the
DLM:
A motor temperature sensor, to prevent excessive use from damaging the motor.
Two Hall effect motor position sensors, to enable closed loop control of the motor.
The temperature sensor provides a differential oil temperature signal to the DLM, to prevent excessive use from damaging the
multi-plate clutch.
Differential Locking Module (DLM)
The DLM controls operation of the electronic differential. The DLM is attached to a bracket located on the LH side of the luggage compartment, immediately forward of the fender tail lamp, behind the trim.
Page 537 of 3039

bus allows the DLM to communicate with other systems on the vehicle.
A certain amount of differential slip is required to allow the vehicle to turn corners and to remain stable under control of the
ABS. The ADM monitors the driver's demands through primary vehicle controls and automatically sets the slip torque in the differential. The system is completely automatic and does not require any special driver input.
The differential strategy in the ADM includes:
A pre-loading function, increasing locking torque with increased driving torque.
A slip controller to decrease locking torque for optimum comfort, e.g. parking.
The ADM memorizes the position of the motor when the ignition is switched off.
CAN bus messages used by the ADM include wheel speed, steering angle, automatic transmission speed, temperature information, car configuration, axle ratios and mode inputs.
The ADM also sends messages via the CAN bus to tell other control modules on the network the status of the electronic differential. The clutch torque and default mode status are some of the main signals sent out by the ADM.
If the DLM or ADM are replaced, a Jaguar approved diagnostic system must be connected to the vehicle and the differential
self-calibration procedure must be performed. This procedure must also be performed if the motor or electronic differential is
replaced.
If a fault occurs with the electronic differential, the ADM, the DLM, or one of the required input signals, the ADM records an
error code and displays a warning in the message center.
The following messages can be displayed:
Message Description Chime E-DIFF NOT
AVAILABLE Differential temperature has reached the overheat threshold. System deactivated until temperature
returns within limits. Single E-DIFF FAULT Fault has occurred with electronic differential. System deactivated until fault rectified. Single
Page 779 of 3039
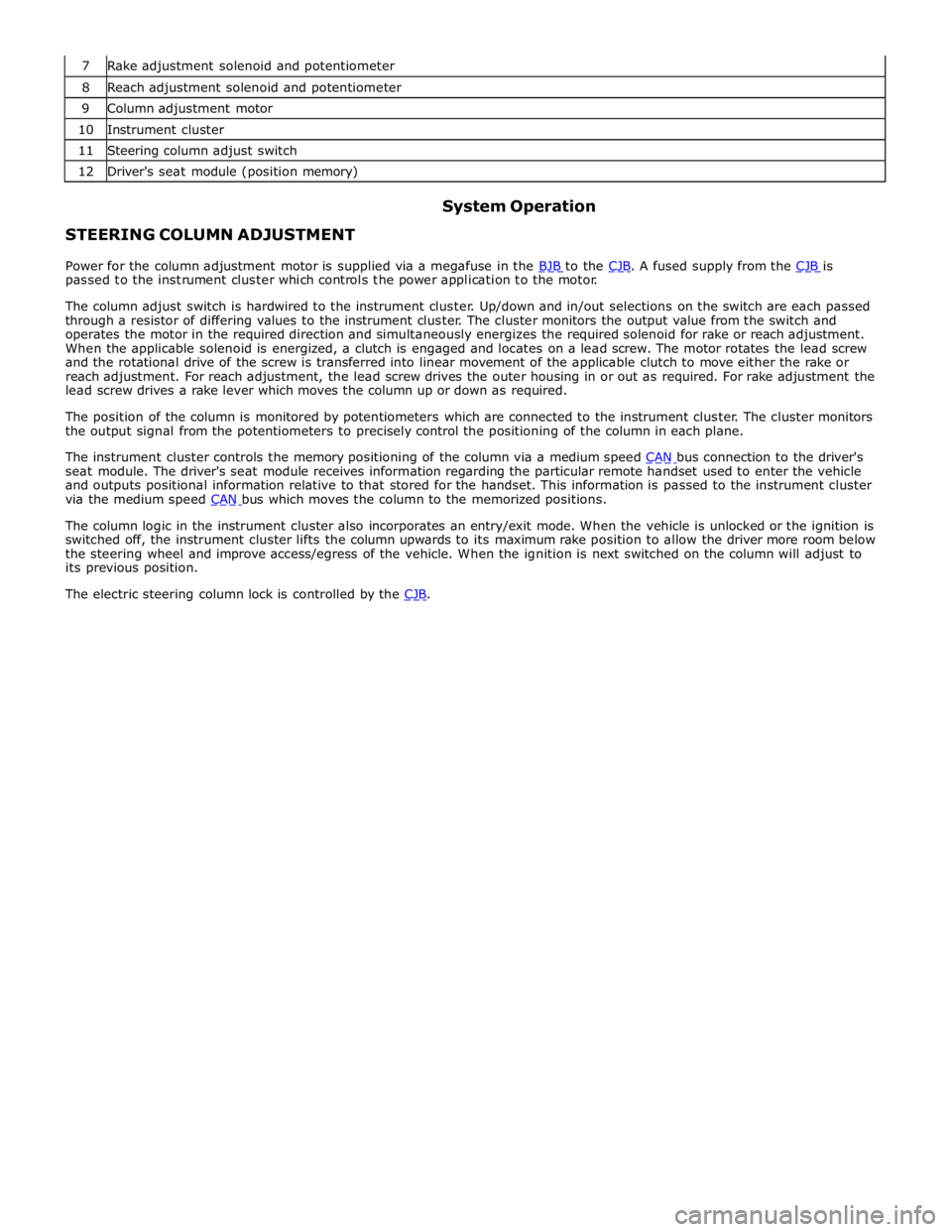
8 Reach adjustment solenoid and potentiometer 9 Column adjustment motor 10 Instrument cluster 11 Steering column adjust switch 12 Driver's seat module (position memory)
STEERING COLUMN ADJUSTMENT System Operation
Power for the column adjustment motor is supplied via a megafuse in the BJB to the CJB. A fused supply from the CJB is passed to the instrument cluster which controls the power application to the motor.
The column adjust switch is hardwired to the instrument cluster. Up/down and in/out selections on the switch are each passed
through a resistor of differing values to the instrument cluster. The cluster monitors the output value from the switch and
operates the motor in the required direction and simultaneously energizes the required solenoid for rake or reach adjustment.
When the applicable solenoid is energized, a clutch is engaged and locates on a lead screw. The motor rotates the lead screw
and the rotational drive of the screw is transferred into linear movement of the applicable clutch to move either the rake or
reach adjustment. For reach adjustment, the lead screw drives the outer housing in or out as required. For rake adjustment the
lead screw drives a rake lever which moves the column up or down as required.
The position of the column is monitored by potentiometers which are connected to the instrument cluster. The cluster monitors
the output signal from the potentiometers to precisely control the positioning of the column in each plane.
The instrument cluster controls the memory positioning of the column via a medium speed CAN bus connection to the driver's seat module. The driver's seat module receives information regarding the particular remote handset used to enter the vehicle
and outputs positional information relative to that stored for the handset. This information is passed to the instrument cluster
via the medium speed CAN bus which moves the column to the memorized positions.
The column logic in the instrument cluster also incorporates an entry/exit mode. When the vehicle is unlocked or the ignition is
switched off, the instrument cluster lifts the column upwards to its maximum rake position to allow the driver more room below
the steering wheel and improve access/egress of the vehicle. When the ignition is next switched on the column will adjust to
its previous position.
The electric steering column lock is controlled by the CJB.
Page 780 of 3039

STEERING COLUMN Component Description
Item Description 1 Rake housing 2 Electric steering column lock 3 Mounting plate 4 Rake lever 5 Crash tube 6 Distance keeper 7 Steering wheel mounting splines 8 Steering angle sensor ring 9 Crash adaptor 10 Rake lever pivot bearing (2 off) 11 Flanged locknut (4 off) - mounting to cross-beam 12 Rake solenoid 13 Rake clutch 14 Spindle 15 Reach solenoid 16 Reach clutch 17 Column adjustment motor 18 Outer clamping yoke 19 Clamp bolt 20 Inner tube yoke
WARNING: Do not attempt to dismantle the steering column. The crash safety of the unit will be compromised.
The steering column is attached to the in-vehicle cross-beam and secured with 4 flanged lock nuts onto 4 studs integral with
the cross-beam.
Page 782 of 3039
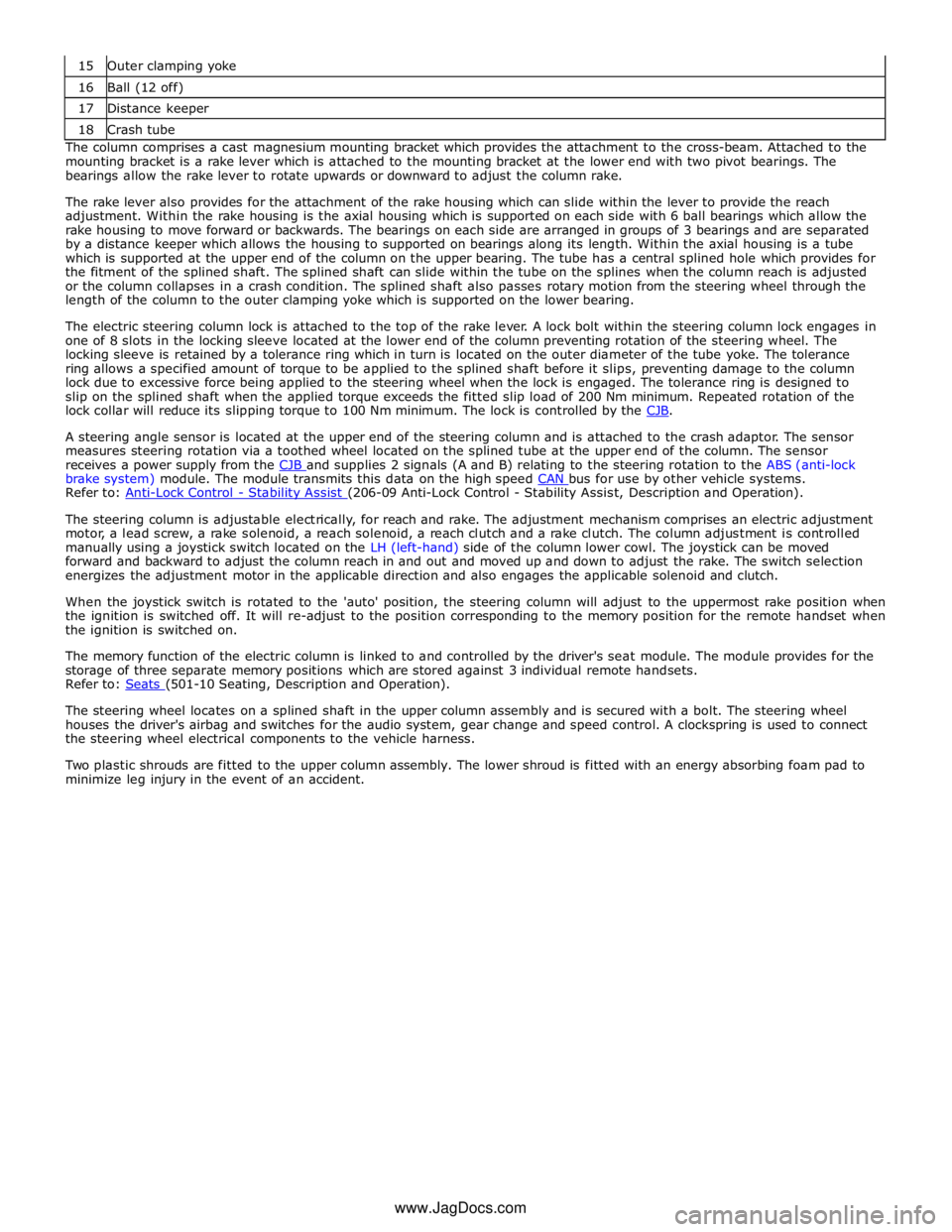
16 Ball (12 off) 17 Distance keeper 18 Crash tube The column comprises a cast magnesium mounting bracket which provides the attachment to the cross-beam. Attached to the
mounting bracket is a rake lever which is attached to the mounting bracket at the lower end with two pivot bearings. The
bearings allow the rake lever to rotate upwards or downward to adjust the column rake.
The rake lever also provides for the attachment of the rake housing which can slide within the lever to provide the reach
adjustment. Within the rake housing is the axial housing which is supported on each side with 6 ball bearings which allow the
rake housing to move forward or backwards. The bearings on each side are arranged in groups of 3 bearings and are separated
by a distance keeper which allows the housing to supported on bearings along its length. Within the axial housing is a tube
which is supported at the upper end of the column on the upper bearing. The tube has a central splined hole which provides for
the fitment of the splined shaft. The splined shaft can slide within the tube on the splines when the column reach is adjusted
or the column collapses in a crash condition. The splined shaft also passes rotary motion from the steering wheel through the
length of the column to the outer clamping yoke which is supported on the lower bearing.
The electric steering column lock is attached to the top of the rake lever. A lock bolt within the steering column lock engages in
one of 8 slots in the locking sleeve located at the lower end of the column preventing rotation of the steering wheel. The
locking sleeve is retained by a tolerance ring which in turn is located on the outer diameter of the tube yoke. The tolerance
ring allows a specified amount of torque to be applied to the splined shaft before it slips, preventing damage to the column
lock due to excessive force being applied to the steering wheel when the lock is engaged. The tolerance ring is designed to
slip on the splined shaft when the applied torque exceeds the fitted slip load of 200 Nm minimum. Repeated rotation of the
lock collar will reduce its slipping torque to 100 Nm minimum. The lock is controlled by the CJB.
A steering angle sensor is located at the upper end of the steering column and is attached to the crash adaptor. The sensor
measures steering rotation via a toothed wheel located on the splined tube at the upper end of the column. The sensor
receives a power supply from the CJB and supplies 2 signals (A and B) relating to the steering rotation to the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module. The module transmits this data on the high speed CAN bus for use by other vehicle systems. Refer to: Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist, Description and Operation).
The steering column is adjustable electrically, for reach and rake. The adjustment mechanism comprises an electric adjustment
motor, a lead screw, a rake solenoid, a reach solenoid, a reach clutch and a rake clutch. The column adjustment is controlled
manually using a joystick switch located on the LH (left-hand) side of the column lower cowl. The joystick can be moved
forward and backward to adjust the column reach in and out and moved up and down to adjust the rake. The switch selection
energizes the adjustment motor in the applicable direction and also engages the applicable solenoid and clutch.
When the joystick switch is rotated to the 'auto' position, the steering column will adjust to the uppermost rake position when
the ignition is switched off. It will re-adjust to the position corresponding to the memory position for the remote handset when
the ignition is switched on.
The memory function of the electric column is linked to and controlled by the driver's seat module. The module provides for the
storage of three separate memory positions which are stored against 3 individual remote handsets.
Refer to: Seats (501-10 Seating, Description and Operation).
The steering wheel locates on a splined shaft in the upper column assembly and is secured with a bolt. The steering wheel
houses the driver's airbag and switches for the audio system, gear change and speed control. A clockspring is used to connect
the steering wheel electrical components to the vehicle harness.
Two plastic shrouds are fitted to the upper column assembly. The lower shroud is fitted with an energy absorbing foam pad to
minimize leg injury in the event of an accident.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 800 of 3039

path is completed and a signal voltage is returned to the instrument cluster via a resistor. The returned reference voltage is
detected by the instrument cluster and performs the requested trip function.
RIGHT HAND MULTIFUNCTION SWITCH
The instrument cluster outputs 4 separate reference voltages to the following switch functions:
Wash/wipe switch
Intermittent wipe switch
Master wiper switch
Flick wipe switch.
Wash/Wipe Switch
The reference voltage is supplied to one of two resistors connected in parallel. When the switch is not being operated the
current flows through one resistor and the returned signal voltage is monitored by the instrument cluster. When the wash/wipe
switch is operated, a connection is made and the current flows through the second resistor. The change in signal voltage is
detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the wash/wipe function.
Intermittent Delay/Auto Wipe Switch
The reference voltage is supplied to the switch and can pass through up to 7 resistors, connected in series, for intermittent
delay selections and the auto wipe function.
When the rotary switch is in the auto position the reference voltage flows through 1 resistor. The returned signal voltage is
detected by the instrument cluster which determines auto wipe is selected. The instrument cluster outputs a message on the
medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the auto wipe function.
With the rotary switch in one of the intermittent positions, the reference voltage is routed through up to 7 of the resistors
depending on the delay period selected. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which determines
selected delay period. The instrument cluster outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the selected intermittent wipe function.
NOTE: The delay period for the intermittent selections can vary according to vehicle speed.
Master Wiper Switch
The reference voltage supplied from the instrument cluster to the master wiper switch. The voltage can pass through up to 4
resistors connected in series.
When the switch is in the off position, the reference voltage passes through 4 resistors and the returned voltage is monitored
by the instrument cluster. The instrument cluster outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that no wiper selections have been requested.
With the switch in the intermittent, slow wipe or fast wipe position, the reference voltage passes through 3, 2 or 1 resistors
respectively. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which determines selected delay period. The
instrument cluster outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the selected wipe function. Flick Wipe Switch
The reference voltage is supplied to one of two resistors connected in parallel. When the switch is not being operated the
current flows through one resistor and the returned signal voltage is monitored by the instrument cluster. When the flick wipe
switch is operated, a connection is made and the current flows through the second resistor. The change in signal voltage is
detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the flick wipe function.
STEERING COLUMN ADJUSTMENT SWITCH
The instrument cluster supplies 2 reference voltages to the column adjustment switch.
The first reference voltage is supplied to the joystick switch. When the switch is moved to one of its 4 positions, the switch
contact is completed and the reference voltage is passed through one of 4 different resistors with different values. The
returned signal voltage is measured by the instrument cluster which determines the selected column adjust request. The
instrument cluster outputs a supply to the steering column adjustment motor and energizes the applicable clutch solenoid to
move the column to the desired position.
The second reference voltage is supplied to the auto/manual selection of the switch. When the switch is in the auto position,
the reference voltage passes directly through the switch contacts and is measured by the instrument cluster. The instrument
cluster outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the driver seat module which responds with the recorded memory position setting. The instrument cluster then activates the column adjustment motor and clutch solenoids to move the column
to the memorized position. When the switch is in the manual position the reference circuit is broken. The instrument cluster
detects the broken circuit and allows manual operation of the column adjustment switch to move the column.
HEATED STEERING WHEEL
The heated steering wheel receives a battery power supply via the CJB. The heated steering wheel is controlled by the driver using a selection on the TSD. When the driver selects the heated steering wheel to be active, the request is passed from the
TSD on the MOST ring to the information and entertainment module. The information and entertainment module converts the