2010 JAGUAR XFR Ok to crank
[x] Cancel search: Ok to crankPage 140 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action B115B-15
Driver Seat Heater -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Driver seat heater supply
circuit - short to power, open
circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams
and check driver seat heater supply circuit for
short to power, open circuit B1175-13
Driver Door Ajar
Switch - Circuit open
Driver door ajar switch
signal circuit - open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
driver door ajar switch signal circuit for open
circuit B1176-13
Passenger Door Ajar
Switch - Circuit open
Passenger door ajar switch
signal circuit - open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
passenger door ajar switch signal circuit for open
circuit B1177-12
Screenwash Level
Switch - Circuit short
to battery
Screenwash level switch
signal circuit - short to
power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
screenwash level switch signal circuit for short to
power B11C0-13
Driver Side Rear Door
Ajar Switch - Circuit
open
Left rear door ajar switch
signal circuit - open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
left rear door ajar switch signal circuit for open
circuit B11C1-13
Passenger Side Rear
Door Ajar Switch -
Circuit open
Right rear door ajar switch
signal circuit - open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
right rear door ajar switch signal circuit for open
circuit B1222-23
Master Lock/Unlock
Switch - Signal stuck
low
Master lock or unlock switch
digital input circuit - signal
stuck low
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
master lock and unlock switch digital input
circuits for short to ground, open circuit B1237-11
Gear Shift Module
Early Wake-up -
Circuit short to ground
Transmission shift module
wake-up control circuit -
short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams
and check transmission shift module wake-up
control circuit for short to ground B1237-12
Gear Shift Module
Early Wake-up -
Circuit short to battery
Transmission shift module
wake-up control circuit -
short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
transmission shift module wake-up control circuit
for short to power B1237-13
Gear Shift Module
Early Wake-up -
Circuit open
Transmission shift module
wake-up control circuit -
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
transmission shift module wake-up control circuit
for open circuit B123E-13
Crank Enable - Circuit
open
OK to crank signal circuit -
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
OK to crank signal circuit for open circuit B1A85-96 Ambient Light Sensor
- Component internal
failure
Light sensor internal
electronic failure
Check and install a new sensor as required B1C45-13
Front Wiper Park
Position Switch -
Circuit open
Windshield wiper motor park
switch signal circuit - open
circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
windshield wiper motor park switch signal circuit
for open circuit B1C45-23
Front Wiper Park
Position Switch -
Signal stuck low
Signal stuck low
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
front wiper park position switch input circuit for
short, open circuit B1C78-12
Powerwash Relay -
Circuit short to battery
Powerwash relay control
circuit - short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
powerwash relay control circuit for short to power B1C78-14
Powerwash Relay -
Circuit short to ground
or open
Powerwash relay control
circuit - short to ground,
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
powerwash relay control circuit for short to
ground, open circuit www.JagDocs.com
Page 167 of 3039
DTC Description Possible Causes Action P0016-00
Crankshaft Position -
Camshaft Position
Correlation - Bank 1 Sensor A
- No sub type information
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_EX_A -
The relative positions of the
crankshaft position sensor and cam
timing plate teeth are not correct
Engine timing incorrect
Timing chain installed incorrectly
Variable valve timing forced fully
advanced
Check engine timing. Check camshaft
sensor timing plate is installed
correctly. Check timing chain is
installed correctly P0017-00
Crankshaft Position -
Camshaft Position
Correlation - Bank 1 Sensor B
- No sub type information
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_EX_A -
The relative positions of the
crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft timing plate teeth are
not correct
Engine timing incorrect
Timing chain installed incorrectly
Variable valve timing forced fully
advanced
Check for related DTC P0365-00.
Check engine timing. Check camshaft
sensor timing plate is installed
correctly. Check timing chain is
installed correctly
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check exhaust (B)
camshaft position actuator (Bank 1)
for open circuit, short circuit to
ground, short circuit to power P0018-00
Crankshaft Position -
Camshaft Position
Correlation - Bank 2 Sensor A
- No sub type information
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_IN_B -
The relative positions of the
crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft timing plate teeth are
not correct
Engine timing incorrect
Timing chain installed incorrectly
Variable valve timing forced fully
advanced
Check engine timing. Check camshaft
sensor timing plate is installed
correctly. Check timing chain is
installed correctly P0019-00
Crankshaft Position -
Camshaft Position
Correlation - Bank 2 Sensor B
- No sub type information
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_EX_B -
The relative positions of the
crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft timing plate teeth are
not correct
Engine timing incorrect
Timing chain installed incorrectly
Variable valve timing forced fully
advanced
Check engine timing. Check camshaft
sensor timing plate is installed
correctly. Check timing chain is
installed correctly P0020-13
Intake (A) Camshaft Position
Actuator (Bank 2) - Circuit
open
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_IN_B -
Intake valve solenoid 2 open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check intake valve
solenoid 2 for open circuit P0023-13
Exhaust (B) Camshaft
Position Actuator (Bank 2) -
Circuit open
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_EX_B -
Exhaust (B) Camshaft Position
actuator (Bank 2) circuit, open
circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check exhaust (B)
camshaft position actuator (Bank 2)
circuit for open circuit P0026-72
Intake Valve Control
Solenoid Circuit
Range/Performance (Bank 1)
- Actuator stuck open
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_IN_A -
Intake valve solenoid 1 angle less
than target
Intake valve solenoid 1 slow or not
operating
Check operation of intake valve
solenoid 1. Check and install a new
intake valve solenoid 1 as required.
Refer to the warranty policy and
procedures manual, or determine if
any prior approval programme is in
operation, prior to the installation of
a new module/component P0026-77
Intake Valve Control
Solenoid Circuit
Range/Performance (Bank 1)
- Commanded position not
reachable
NOTE: - Circuit VFS_IN_A -
Intake valve solenoid 1 angle
greater than target
Intake valve solenoid 1 not
returning to target in time
Check operation of intake valve
solenoid 1. Check and install a new
intake valve solenoid 1 as required.
Refer to the warranty policy and
procedures manual, or determine if
any prior approval programme is in
operation, prior to the installation of
Page 240 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action U0300-00
Internal Control Module
Software
Incompatibility - No
sub type information
Invalid configuration
message is received
Re-configure the speed control module using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Clear
DTCs and re-test. If DTC still logged, suspect
incorrect speed control module installed. Check and
install a new module as required, refer to new
module/component installation note at top of DTC
Index U0300-55
Internal Control Module
Software
Incompatibility - Not
configured
RJB - at least one of the
car configuration
parameters is not
configured
Re-configure the RJB using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system U0401-00
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A - No
sub type information
ECM did not respond
properly to speed control
cancel or auto brake
cancel request
Check ECM for related DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index U0401-67
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A -
Signal incorrect after
event
ECM did not respond
properly to speed control
resume request
Check ECM for related DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index U0401-81
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A -
Invalid serial data
received
Invalid data received
from engine control
module
Bus signal/message
failure
Speed control inhibited
by ECM
Check the Engine Control Module for related DTCs
and refer to relevant DTC Index. If U040181 is
logged as historic but no other DTCs have logged in
the engine control module at the same time and
distance, it may be caused by cranking with low
voltage conditions. Check battery and charging
system according to instructions in the battery care
manual. Install the latest Engine Control Module
software using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, contact Dealer Technical Support before
replacing components U0415-53
Invalid Data Received
From Anti-Lock Braking
System (ABS) Control
Module - De-activated
Event information
Deactivated
Check the Anti-Lock Braking System Module for
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0415-81
Invalid Data Received
From Anti-lock Brake
System (ABS) Control
Module - Invalid serial
data received
Stability assist fault
Check ABS module for related DTCs and refer to
relevant DTC Index U0417-67
Invalid Data Received
From Park Brake
Control Module - Signal
incorrect after event
Parking brake module did
not respond properly to
apply request
Check parking brake module for related DTCs and
refer to relevant DTC Index U0417-81
Invalid Data Received
From Park Brake
Control Module -
Invalid serial data
received
Speed control inhibited
by parking brake module
Check parking brake module for related DTCs and
refer to relevant DTC Index U0418-68
Invalid Data Received
From Brake System
Control Module - Event
information
Event information
Check the Anti-Lock Braking System Module for
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0421-81
Invalid Data Received
From Suspension
Control Module 'A' -
Invalid serial data
received
Invalid serial data
received
Check the Suspension Control Module for related
DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0423-81
Invalid Data Received
From Instrument Panel
Control Module -
Invalid serial data
received
Speed control inhibited
by instrument cluster
Check instrument cluster, CJB and RJB for related
DTCs and refer to relevant DTC Index U1A00-88
Private Communication
Network - Bus off
Bus off
The module setting this code has disabled CAN
transmission. Check for other bus off codes. Check
the module and circuits. Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams. Clear all DTCs and road test the vehicle. If
the concern reoccurs contact Dealer Technical
Page 547 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Rear Drive Axle/Differential - Differential Front Bushing TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol
Removal and Installation
Special Tool(s)
204-274
Bush install and removal tool
204-275
Bush install and removal tool
204-335
Bush install and removal tool
204-601
Bush install tool
303-1121
Installer, Crankshaft Seal Removal
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Refer to: Differential Case - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (205-02 Rear Drive Axle/Differential, Removal and Installation).
Page 638 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Rear Disc Brake - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Brake
Pads Vehicles With: High Performance Brakes
Removal and Installation
Special Tool(s)
206-080
Brake caliper piston retractor tool
206-081
Brake caliper piston retractor tool
303-588
Remover, Crankshaft Pulley/Damper Removal
WARNINGS:
Failure to release the tension and calibrate the electric parking brake during rear parking brake related service procedures,
could cause the parking brake to function incorrectly or become inoperative.
Do not allow dirt or foreign liquids to enter the reservoir. Use only new brake fluid of the correct specification from
airtight containers. Do not mix brands of brake fluid as they may not be compatible.
Brake pads must be renewed in axle sets only, otherwise braking efficiency may be impaired.
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage paint finished surfaces. If spilled, immediately remove the fluid and clean the area
with water.
NOTES:
Only extraction bolt from special tool 303-588 is used.
Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
Page 813 of 3039

Component Tests
Engine Oil Leaks
NOTE: Before installing new gaskets or oil seals, make sure that the fault is clearly established.
If the oil leak cannot be identified clearly by a visual inspection, carry out an Ultraviolet test:
Fluorescent Oil Additive Method
1. Clean the engine with a suitable cleaning fluid (brake cleaner).
2. Drain the engine oil and refill with recommended oil, premixed with Diesel Engine Oil Dye or equivalent. Use a minimum
14.8 ml (0.5 ounce) to a maximum 29.6 ml (1 ounce) of fluorescent additive to all engines. If oil is not premixed,
fluorescent additive must first be added to the crankcase.
3. Run engine for 15 minutes. Stop the engine and inspect all seal and gasket areas for leaks using a 12 Volt Master UV
Diagnostic Inspection Kit or equivalent. A clear bright yellow or orange area will identify leak. For extremely small
leaks, several hours may be required for the leak to appear.
4. As necessary, pressurize the main oil gallery system to locate leaks due to incorrectly sealed, loose or cocked plugs. If
the flywheel bolts leak oil, look for sealer on the threads.
5. Repair all leaks as necessary.
Compression Test General Remarks
NOTES:
Removing fuses and disconnecting electrical components may cause the Engine Control Module (ECM) to log Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs). After the measurements have been carried out, DTCs should be cleared from memory by connecting to
the Manufacturer Approved Diagnostic System.
Only check the compression pressure with the valves set to the prescribed clearance (if this can be adjusted).
The compression pressure should be checked with the engine at normal operating temperature.
Check the Compression Pressure
WARNING: Move gear selector lever to 'P' position. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
1. Remove the fuel pump relay.
2. Start the engine - the engine will start, run for a few seconds then stall.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Install the compression tester.
5. Install an auxiliary starter switch in the starting circuit. With the ignition switch OFF, using the auxiliary starter switch,
crank the engine a minimum of five compression strokes and record the highest reading. Note the approximate number
of compression strokes required to obtain the highest reading.
6. Repeat the test on each cylinder, cranking the engine approximately the same number of compression strokes.
7. Install the removed components in reverse order, observing the specified tightening torques.
8. Clear all DTCs from the ECM.
Interpretation of the Results
NOTE: Due to the possibility of loose carbon that has become trapped between the valve face and seat effecting the
pressure readings, when carrying out a compression test and cylinders are found to have low pressures, install the spark plugs,
road test the vehicle and re-test the suspect cylinders. If the correct pressures are restored, no further action is required.
The indicated compression pressures are considered within specification if the lowest reading cylinder is within 75% of the
highest reading.
If the cylinder pressures are found to be low, carry out a leakdown test to determine the location of the fault (if any leakback
can be heard through the engine breather system suspect the piston rings, if any leakback can be heard through the inlet
system suspect the inlet valve or seat, if any leakback can be heard through the exhaust manifold suspect the exhaust valve
or seat. If the measurements for two cylinders next to each other are both too low then it is very likely that the cylinder head
gasket between them is burnt through. This can also be recognized by traces of engine oil in the coolant and/or coolant in the
Page 814 of 3039

engine oil).
Oil Consumption Test
The amount of oil an engine uses will vary with the way the vehicle is driven in addition to normal engine-to-engine variation.
This is especially true during the first 16,100 km (10,000 miles) when a new engine is being broken in or until certain internal
components become conditioned. Vehicles used in heavy-duty operation may use more oil. The following are examples of
heavy-duty operation:
Trailer towing applications
Severe loading applications
Sustained high speed operation
Engines need oil to lubricate the following internal components:
Cylinder block cylinder walls
Pistons and piston rings
Intake and exhaust valve stems
Intake and exhaust valve guides
All internal engine components
When the pistons move downward, a thin film of oil is left on the cylinder walls. As the vehicle is operated, some oil is also
drawn into the combustion chambers past the intake and exhaust valve stem seals and burned.
The following are examples of conditions that can affect oil consumption rates:
Engine size
Operator driving habits
Ambient temperatures
Quality and viscosity of oil
Engine is being run in an overfilled condition (check the oil level at least five minutes after a hot shutdown with the
vehicle parked on a level surface. The oil level should not be above the top of the cross-hatched area and the letter "F"
in FULL).
Operation under varying conditions can frequently be misleading. A vehicle that has been run for several thousand miles on
short trips or in below-freezing ambient temperatures may have consumed a "normal" amount of oil. However, when checking
the engine oil level, it may measure up to the full mark on the oil level indicator due to dilution (condensation and fuel) in the
engine crankcase. The vehicle then might be driven at high speeds on the highway where the condensation and fuel boil off.
The next time the engine oil is checked it may appear that a liter of oil was used in about 160 km (100 miles). Oil
consumption rate is about one liter per 2,400 km (1,500 miles).
Make sure the selected engine oil meets Jaguar specification and the recommended API performance category "SG" and SAE
viscosity grade as shown in the vehicle Owner's Guide. It is also important that the engine oil is changed at the intervals
specified for the typical operating conditions.
The following diagnostic procedure is used to determine the source of excessive oil consumption.
NOTE: Oil use is normally greater during the first 16,100 km (10,000 miles) of service. As mileage increases, oil use
decreases. High speed driving, towing, high ambient temperature and other factors may result in greater oil use.
1. Define excessive consumption, such as the number of miles driven per liter of oil used. Also determine customers
driving habits, such as sustained high speed operation, towing, extended idle and other considerations.
2. Verify that the engine has no external oil leaks as described under Engine Oil Leaks in this section.
3. Carry out an oil consumption test:
Run the engine to normal operating temperature. Switch engine OFF and allow oil to drain back for at least five
minutes .
With vehicle parked on level surface, check the engine oil level.
If required, add engine oil to set level exactly to the FULL mark.
Record the vehicle mileage.
Instruct the customer to return for a level check after driving the vehicle as usual for 1,610 km (1000 miles).
Check the oil level under the same conditions and at the same location as the initial check.
NOTE: If the oil consumption rate is unacceptable go to Step 4.
4. Check the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system. Make sure the system is not plugged.
5. Check for plugged oil drain-back holes in the cylinder head and cylinder block.
6. If the condition still exists after carrying out the above tests go to step 9.
7. Carry out a cylinder compression test. Refer to the Compression Test procedure in this section. This can help determine
the source of oil consumption such as valves, piston rings or other areas.
8. Check valve guides for excessive guide clearance. Install new valve stem seals after verifying valve guide clearance.
9. Worn or damaged internal engine components can cause excessive oil consumption. Small deposits of oil on the tips of
the spark plugs can be a clue to internal oil consumption.
Page 825 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Engine System - General Information - Cylinder Bore Out-of-Round
General Procedures
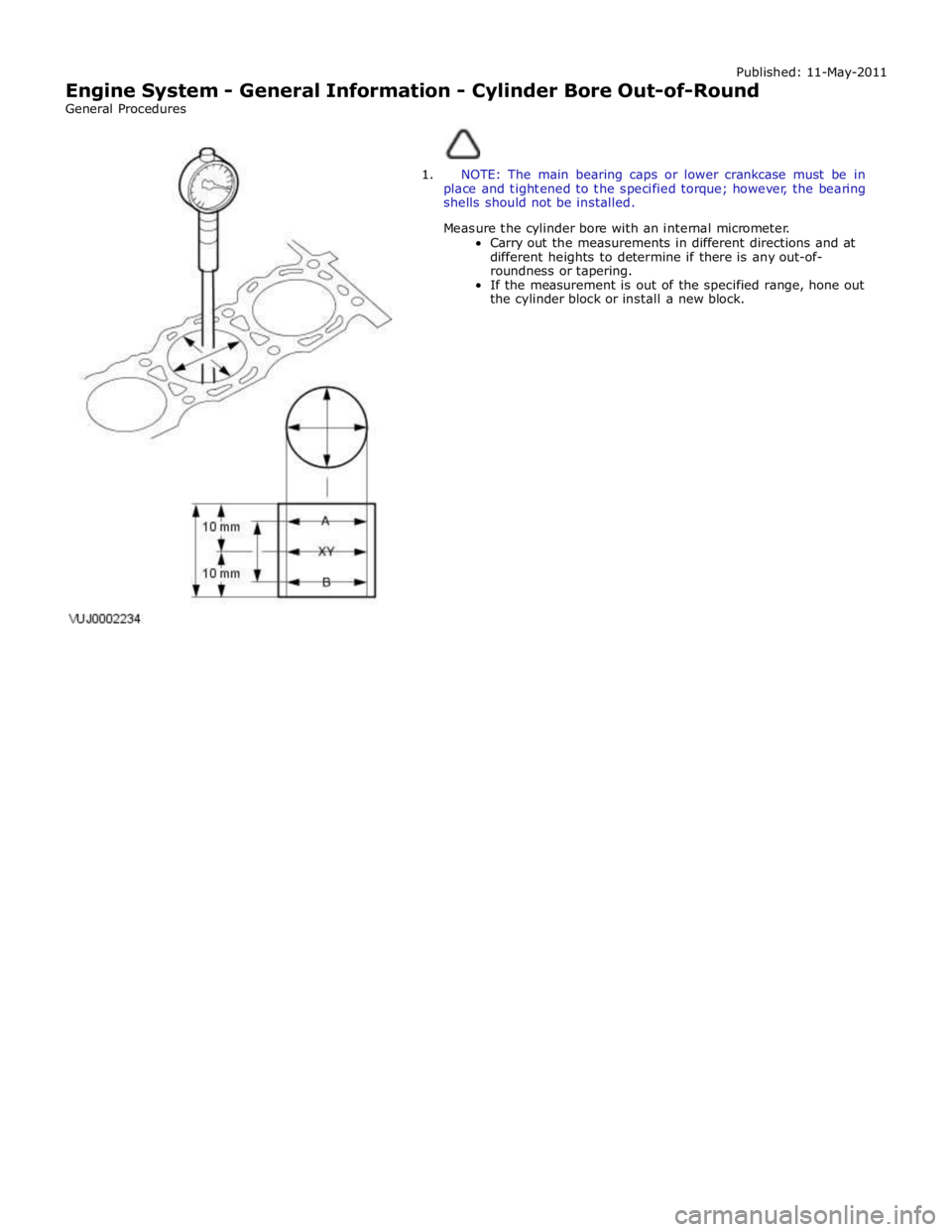
1. NOTE: The main bearing caps or lower crankcase must be in
place and tightened to the specified torque; however, the bearing
shells should not be installed.
Measure the cylinder bore with an internal micrometer.
Carry out the measurements in different directions and at
different heights to determine if there is any out-of-
roundness or tapering.
If the measurement is out of the specified range, hone out
the cylinder block or install a new block.