Page 1430 of 3039
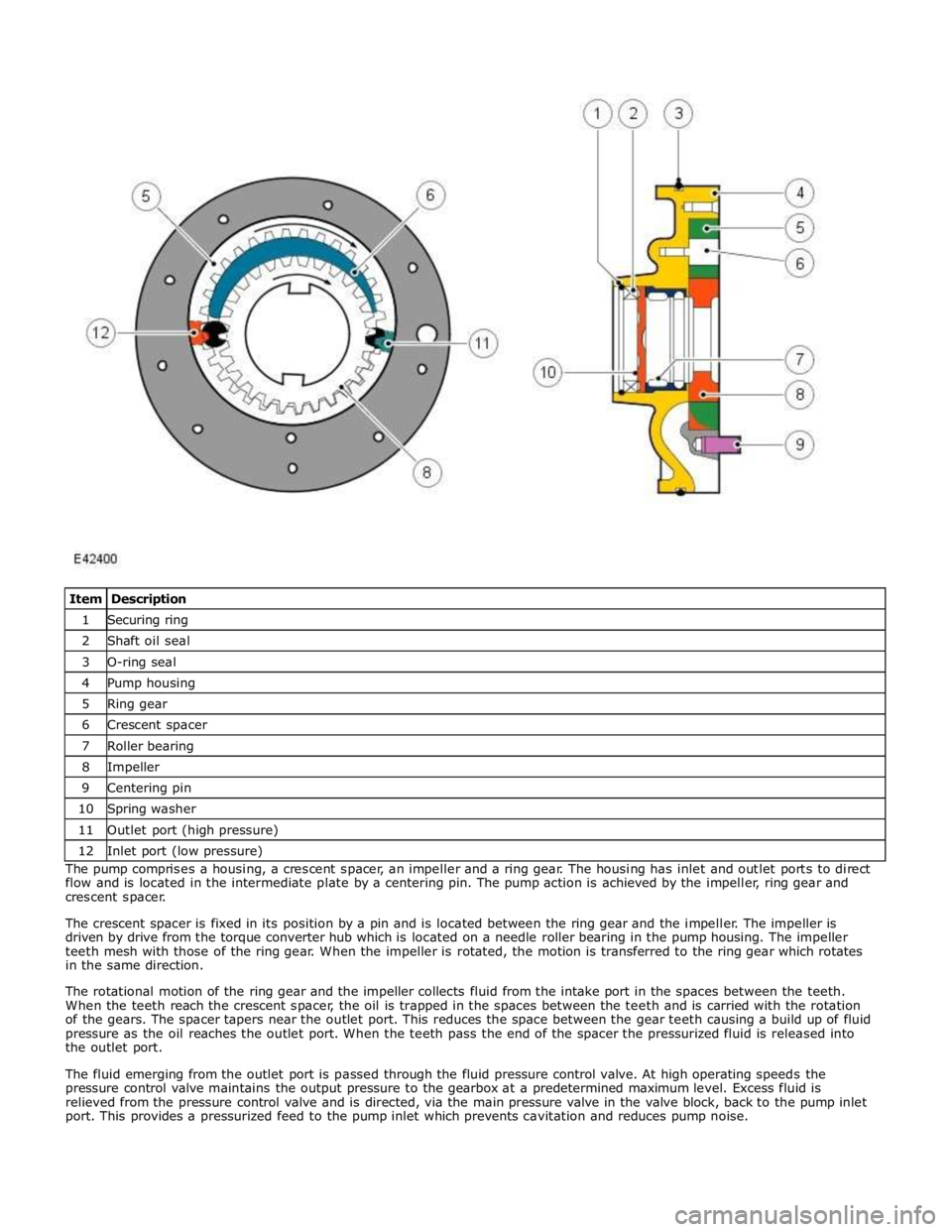
1 Securing ring 2 Shaft oil seal 3 O-ring seal 4 Pump housing 5 Ring gear 6 Crescent spacer 7 Roller bearing 8 Impeller 9 Centering pin 10 Spring washer 11 Outlet port (high pressure) 12 Inlet port (low pressure) The pump comprises a housing, a crescent spacer, an impeller and a ring gear. The housing has inlet and outlet ports to direct
flow and is located in the intermediate plate by a centering pin. The pump action is achieved by the impeller, ring gear and
crescent spacer.
The crescent spacer is fixed in its position by a pin and is located between the ring gear and the impeller. The impeller is
driven by drive from the torque converter hub which is located on a needle roller bearing in the pump housing. The impeller
teeth mesh with those of the ring gear. When the impeller is rotated, the motion is transferred to the ring gear which rotates
in the same direction.
The rotational motion of the ring gear and the impeller collects fluid from the intake port in the spaces between the teeth.
When the teeth reach the crescent spacer, the oil is trapped in the spaces between the teeth and is carried with the rotation
of the gears. The spacer tapers near the outlet port. This reduces the space between the gear teeth causing a build up of fluid
pressure as the oil reaches the outlet port. When the teeth pass the end of the spacer the pressurized fluid is released into
the outlet port.
The fluid emerging from the outlet port is passed through the fluid pressure control valve. At high operating speeds the
pressure control valve maintains the output pressure to the gearbox at a predetermined maximum level. Excess fluid is
relieved from the pressure control valve and is directed, via the main pressure valve in the valve block, back to the pump inlet
port. This provides a pressurized feed to the pump inlet which prevents cavitation and reduces pump noise.
Page 1432 of 3039
DRIVE CLUTCHES
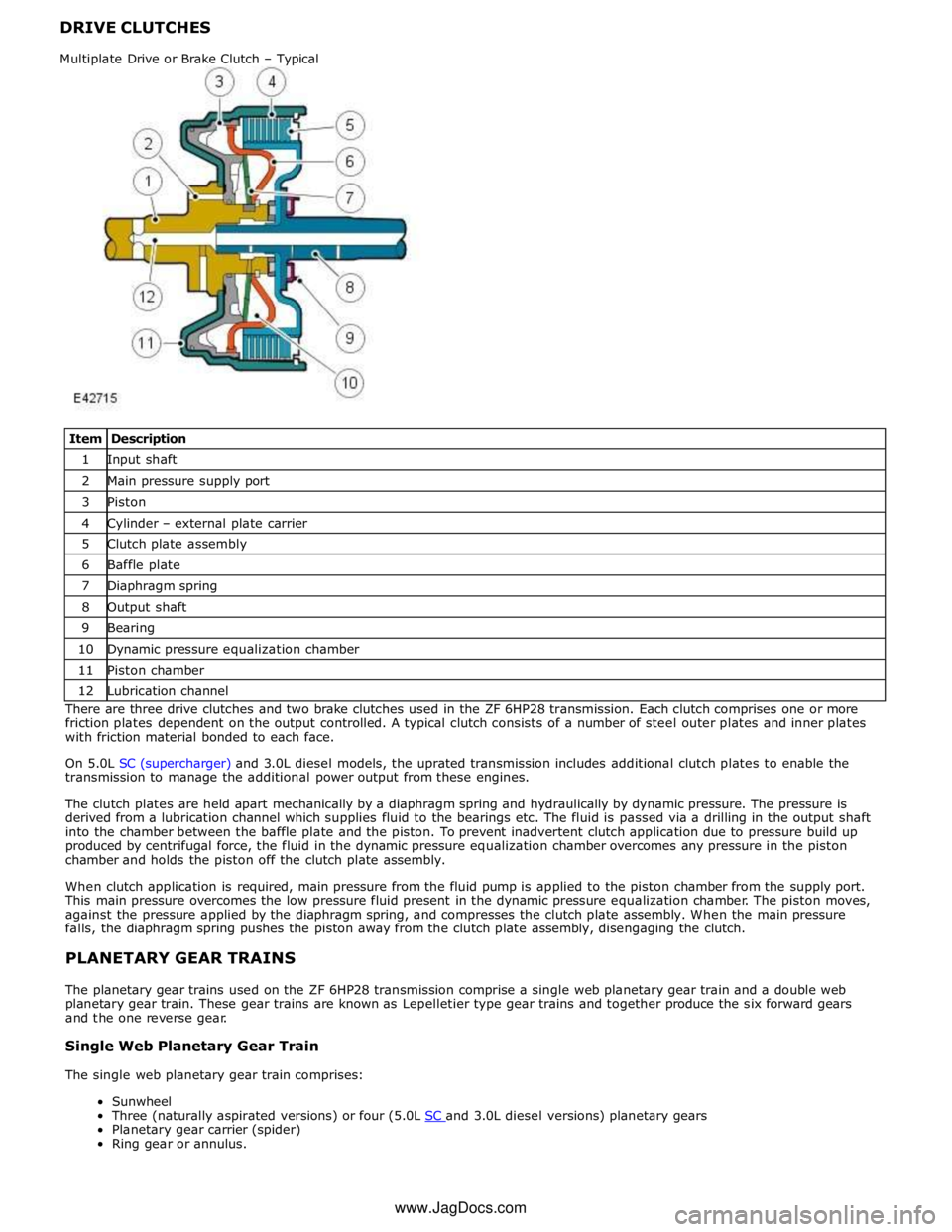
Item Description 1 Input shaft 2 Main pressure supply port 3 Piston 4 Cylinder – external plate carrier 5 Clutch plate assembly 6 Baffle plate 7 Diaphragm spring 8 Output shaft 9 Bearing 10 Dynamic pressure equalization chamber 11 Piston chamber 12 Lubrication channel There are three drive clutches and two brake clutches used in the ZF 6HP28 transmission. Each clutch comprises one or more
friction plates dependent on the output controlled. A typical clutch consists of a number of steel outer plates and inner plates
with friction material bonded to each face.
On 5.0L SC (supercharger) and 3.0L diesel models, the uprated transmission includes additional clutch plates to enable the
transmission to manage the additional power output from these engines.
The clutch plates are held apart mechanically by a diaphragm spring and hydraulically by dynamic pressure. The pressure is
derived from a lubrication channel which supplies fluid to the bearings etc. The fluid is passed via a drilling in the output shaft
into the chamber between the baffle plate and the piston. To prevent inadvertent clutch application due to pressure build up
produced by centrifugal force, the fluid in the dynamic pressure equalization chamber overcomes any pressure in the piston
chamber and holds the piston off the clutch plate assembly.
When clutch application is required, main pressure from the fluid pump is applied to the piston chamber from the supply port.
This main pressure overcomes the low pressure fluid present in the dynamic pressure equalization chamber. The piston moves,
against the pressure applied by the diaphragm spring, and compresses the clutch plate assembly. When the main pressure
falls, the diaphragm spring pushes the piston away from the clutch plate assembly, disengaging the clutch.
PLANETARY GEAR TRAINS
The planetary gear trains used on the ZF 6HP28 transmission comprise a single web planetary gear train and a double web
planetary gear train. These gear trains are known as Lepelletier type gear trains and together produce the six forward gears
and the one reverse gear.
Single Web Planetary Gear Train
The single web planetary gear train comprises:
Sunwheel
Three (naturally aspirated versions) or four (5.0L SC and 3.0L diesel versions) planetary gears Planetary gear carrier (spider)
Ring gear or annulus. Multiplate Drive or Brake Clutch – Typical www.JagDocs.com
Page 1459 of 3039
3. CAUTION: Make sure the torque converter is fully
located into the oil pump drive.
4. Refer to: Transmission - TDV6 3.0L Diesel (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Installation).
5. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
Page 1481 of 3039
7. CAUTION: Make sure the torque converter is fully
located into the oil pump drive.
8. CAUTION: Make sure that the torque converter
remains in the transmission.
NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Raise the powertrain assembly jack and transmission
assembly.
Page 1497 of 3039
5. CAUTION: Make sure the torque converter is fully
located into the oil pump drive.
6. CAUTION: Make sure that the torque converter
remains in the transmission.
NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Raise the powertrain assembly jack and transmission
assembly. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1520 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Transmission/Transaxle Cooling - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Transmission Cooling - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
System Operation
Fluid from the pump in the automatic transmission flows through the feed hose and pipe to the transmission fluid cooler. The
fluid then flows through the transmission fluid cooler, and the return hose and pipe, to the sump of the automatic
transmission.
Page 1565 of 3039
Published: 01-Aug-2012
Fuel System - General Information - Fuel System Pressure Release V8 5.0L
Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol
General Procedures
Draining
1. Remove the fuel pump fuse.
2. Remove the fuel filler cap.
3. CAUTION: When depressurising the fuel system, make sure that
there is no throttle input. Failure to follow this instruction may cause
damage to the vehicle.
Start the engine and allow it to idle until the engine stalls.
4. Crank the engine for approximately five seconds to make sure that the
fuel rail pressure is released.
Filling
1. NOTE: Make sure all repairs have been carried out before
proceeding to the following steps.
Install the fuel pump fuse.
2. Install the fuel filler cap.
3. Read and clear stored DTC fault codes.
Page 1580 of 3039
Fuel system Electronic returnless fuel system (ERFS) Fuel tank Multi layer plastic Fuel tank sender unit Mounted on the body of the fuel pump Fuel filter Located in the fuel tank Fuel pump Electric,located in the fuel tank System pressure 4.5 bar - 65 lbf/in2 Capacities Liters Fuel tank capacity 71.1 (total) / 69.5 (useable) Torque Specifications
Item Nm lb-ft lb-in Fuel tank filler pipe bracket retaining nut 9 - 80 Fuel tank filler pipe bracket retaining bolt 9 - 80 Fuel tank support strap retaining bolts 35 26 - Fuel / vapor tube bracket retaining bolt in engine compartment 5 - 44 Fuel / vapor tube bracket to underbody retaining bolts 7 - 62 Fuel pump and sender unit locking ring 250 184 -