2010 JAGUAR XFR belt
[x] Cancel search: beltPage 2620 of 3039
position sensor consists of a Hall effect sensor attached to the driver seat frame. While the ignition is on, the RCM supplies the sensor with power, and monitors the return current. When the seat frame moves forwards, the sensor moves over the edge
of the seat track, which changes the reluctance of the sensor. The change of current is detected by the RCM and used as a switching point. The switching point is when the center of the sensor is 3 ± 4 mm from the leading edge of the seat track.
When the driver seat is forward of the switching point, the RCM increases the time delay between firing the two stages of the inflator in the driver airbag. When the driver seat is rearward of the switching point, the RCM uses the normal time delay between firing the two stages.
Safety Belt Sensor
A safety belt switch is installed in the buckle of each front safety belt to provide the RCM with a status signal of the related safety belt(s). When the safety belt is unfastened the switch outputs a low current to the RCM. When the safety belt is fastened the switch outputs a high current to the RCM.
Pretensioners
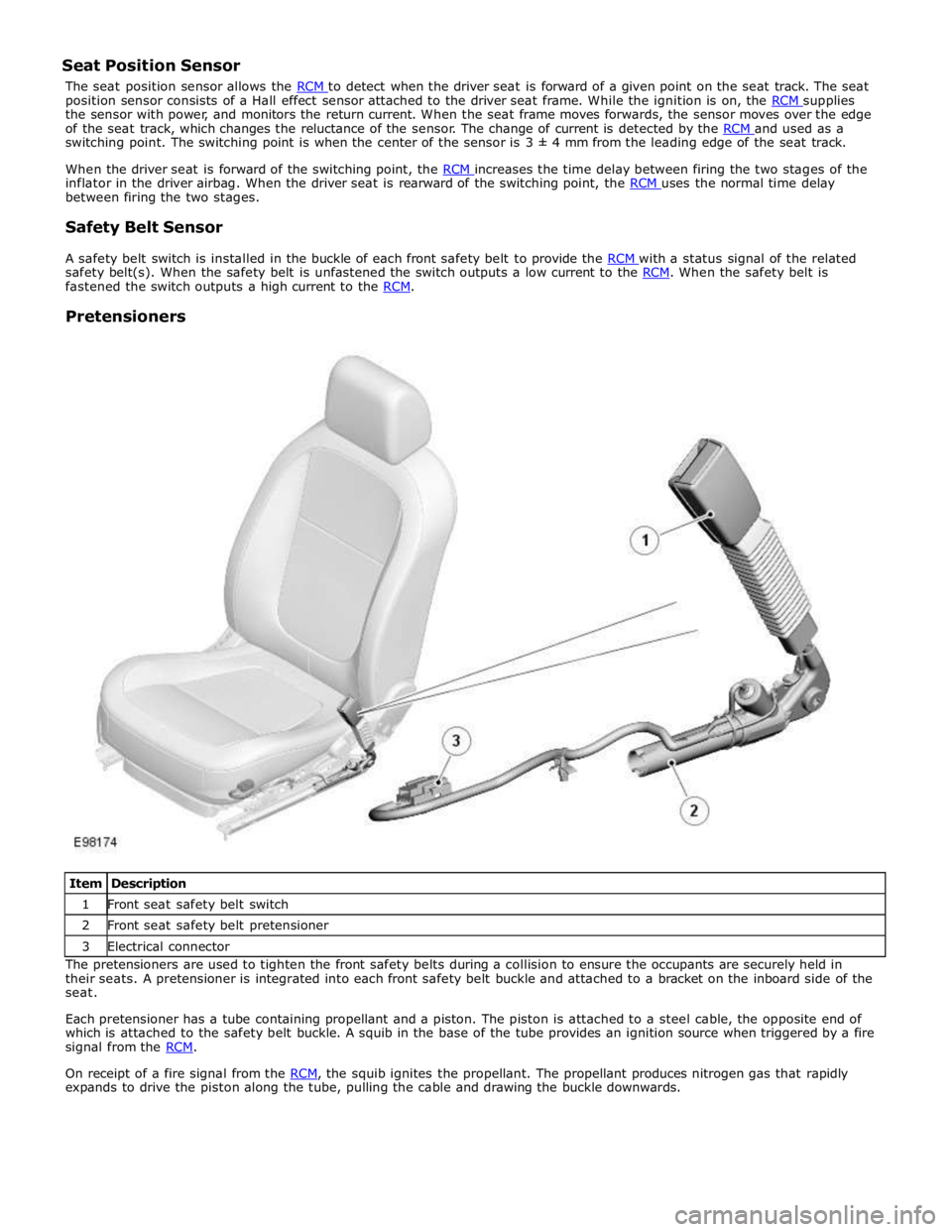
Item Description 1 Front seat safety belt switch 2 Front seat safety belt pretensioner 3 Electrical connector The pretensioners are used to tighten the front safety belts during a collision to ensure the occupants are securely held in
their seats. A pretensioner is integrated into each front safety belt buckle and attached to a bracket on the inboard side of the
seat.
Each pretensioner has a tube containing propellant and a piston. The piston is attached to a steel cable, the opposite end of
which is attached to the safety belt buckle. A squib in the base of the tube provides an ignition source when triggered by a fire
signal from the RCM.
On receipt of a fire signal from the RCM, the squib ignites the propellant. The propellant produces nitrogen gas that rapidly expands to drive the piston along the tube, pulling the cable and drawing the buckle downwards.
Page 2621 of 3039
Operation of the airbag warning indicator is controlled by a high speed CAN bus message from the RCM to the instrument cluster. The RCM sends the signal to illuminate the airbag warning indicator if a fault is detected, and for approximately 6 seconds during the bulb check at the beginning of each ignition cycle.
Occupant Monitoring
There are two types of occupant monitoring:
In all markets except NAS & Australia, vehicles have an occupant detection sensor
In NAS markets, vehicles have an occupant classification system
For markets which have an occupant detection sensor, this has no interface with the restraints system and only provides the
belt reminder function.
For markets that have an occupant classification system, this provides the RCM with the occupancy status of the front passenger seat. The restraints control module uses this and the seat buckle status in the evaluation of the firing strategy for
the passenger front airbag, side airbag, and pretensioner.
Safety Belt Sensors
The buckle of each front safety belt incorporates a Hall effect sensor that provides a safety belt status signal to the RCM. The RCM broadcasts the status of the two front safety belts on the high speed CAN bus for use by the instrument cluster. In the event of a front impact the RCM will deploy the pretensioners provided the safety belt buckles are fastened. The safety belt buckle pretensioners have a lower deployment threshold than that required by the airbags. Hence it is possible during a minor
collision, which exceeds the deployment threshold and will deploy only the safety belt buckle pretensioners. Airbag Warning Indicator
Page 2622 of 3039

There is a fault with the passenger airbag firing circuit(s).
The passenger airbag is deactivated with the passenger airbag deactivation switch (where fitted).
Required by passenger seat occupant monitoring (see below).
Passenger Airbag Deactivation Switch (All Except NAS)
The passenger airbag deactivation switch provides a method of manually disabling the passenger airbag. The switch is
installed in the front passenger end of the instrument panel and operated by the ignition key.
When the passenger airbag deactivation switch is operated, it changes a ground connection between two pins in the
connectors of the RCM. When the passenger airbag deactivation switch is selected to OFF, the RCM disables the passenger airbag and, if the front passenger seat is occupied, illuminates the passenger airbag deactivation indicator.
Occupant Detection System
There are two types of occupant monitoring:
In all markets except NAS & Australia, vehicles have an occupant detection sensor
In NAS markets, vehicles have an occupant classification system
For markets which have an occupant detection sensor, this has no interface with the restraints system and only provides the
belt reminder function.
For markets that have an occupant classification system, this provides the RCM with the occupancy status of the front passenger seat. The RCM uses this and the seat buckle status in the evaluation of the firing strategy for the passenger front airbag, side airbag, and pretensioner.
The occupant classification system can determine if the front passenger seat is unoccupied, occupied by a small person, or
occupied by a large person. The occupant classification system consists of:
A pressure pad, installed under the cushion of the front passenger seat, which is connected to a pressure sensor
A safety belt tension sensor, integrated into the anchor point of the front passenger safety belt
An occupant classification module, installed under the front passenger seat.
The pressure pad is a silicone filled bladder. Any load on the pressure pad is detected by the pressure sensor.
The safety belt tension sensor is a strain gauge that measures the load applied by the safety belt anchor to the anchor bolt.
The sensor is located in the lower safety belt anchor point.
Page 2624 of 3039

Published: 10-Jul-2014
Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the supplemental restraints system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section in the workshop manual. REFER to: (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System)
Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation), Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation), Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNING: TO AVOID ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY, THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY MUST
BE DEPLETED BEFORE REPAIRING OR REPLACING ANY AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) COMPONENTS. TO
DEPLETE THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY ENERGY, DISCONNECT THE BATTERY GROUND CABLE AND WAIT ONE MINUTE. FAILURE
TO FOLLOW THIS INSTRUCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Given the legal implications of a restraints system failure, harness repairs to Air Bag module circuits are not
acceptable. Where the text refers to "REPAIR the circuit", this will normally mean the replacement of a harness.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation). Electrical
Battery condition, state of charge
Make sure all electrical connector(s) are engaged correctly on the air bag circuits
Wiring harness
Air bag module(s)
Make sure the restraints control module (RCM) is correctly installed
Fuse(s)
Sensor(s)
Pretensioner(s)
Warning lamp bulb(s) Visual Inspection
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2706 of 3039
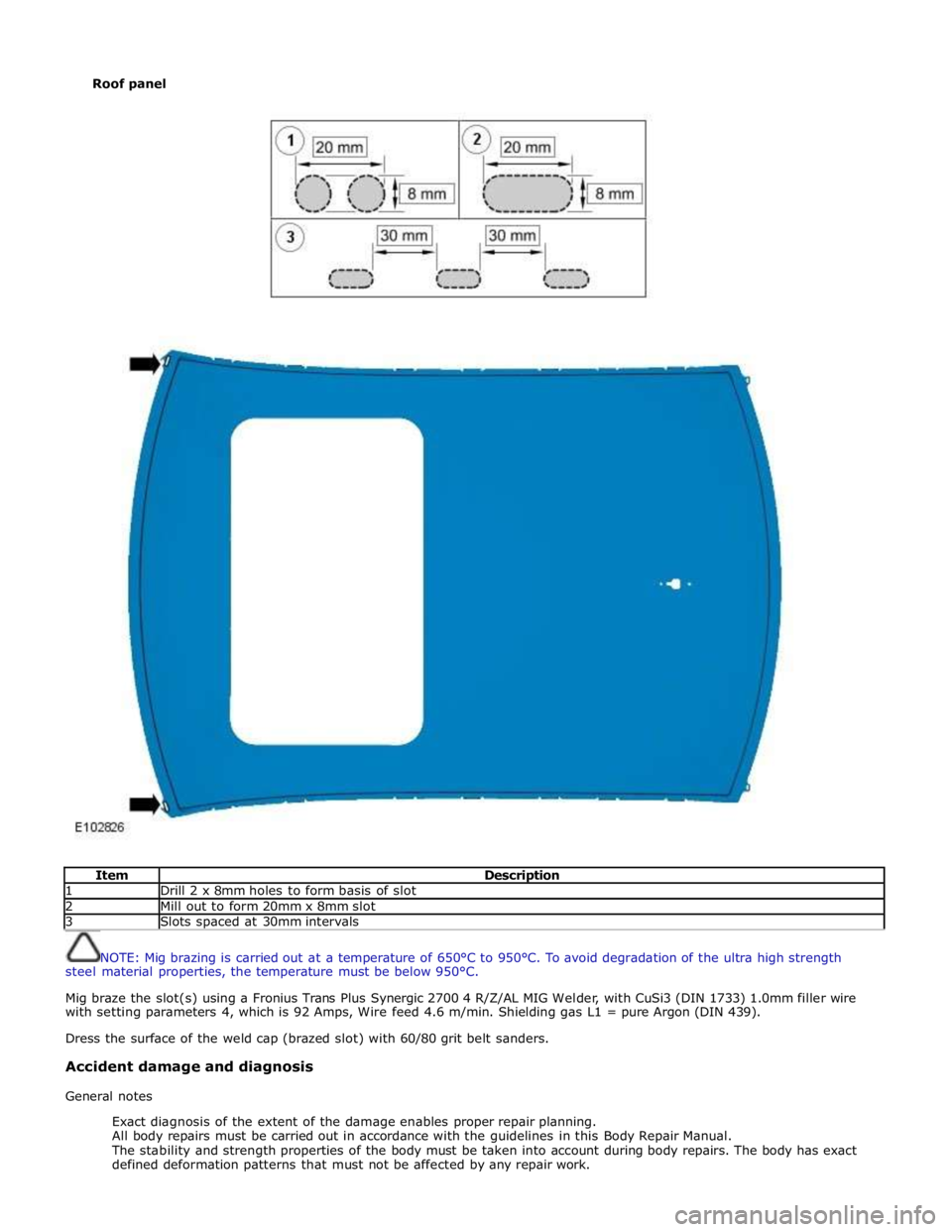
Item Description 1 Drill 2 x 8mm holes to form basis of slot 2 Mill out to form 20mm x 8mm slot 3 Slots spaced at 30mm intervals
NOTE: Mig brazing is carried out at a temperature of 650°C to 950°C. To avoid degradation of the ultra high strength
steel material properties, the temperature must be below 950°C.
Mig braze the slot(s) using a Fronius Trans Plus Synergic 2700 4 R/Z/AL MIG Welder, with CuSi3 (DIN 1733) 1.0mm filler wire
with setting parameters 4, which is 92 Amps, Wire feed 4.6 m/min. Shielding gas L1 = pure Argon (DIN 439).
Dress the surface of the weld cap (brazed slot) with 60/80 grit belt sanders.
Accident damage and diagnosis
General notes
Exact diagnosis of the extent of the damage enables proper repair planning.
All body repairs must be carried out in accordance with the guidelines in this Body Repair Manual.
The stability and strength properties of the body must be taken into account during body repairs. The body has exact
defined deformation patterns that must not be affected by any repair work. Roof panel
Page 2711 of 3039
Body saws are particularly versatile and are therefore very suitable for making severance cuts on body parts.
Reciprocating saw
In addition to the short stroke saw, the reciprocating saw can be used. With this, it is possible to make narrow and straight
cuts to an exact depth.
Carrying out the repairs
Butt joint
NOTE: The severance cut should always be kept as short as possible on sectional replacement. Only cut at the severance
lines shown in the repair chapters.
Do not make any cuts near reinforcements or pre-determined folding lines.
Prepare parts remaining on the vehicle/new parts.
NOTE: Do not use a welding torch to remove paint residue (the heat could cause the metal to deform).
- Reshape the adjoining surface of any dented body parts that are to remain on the vehicle using a hammer and a
counterhold (Make sure that the old part matches the shape of the new part). Grind off left over spot welds or
seams with an angle grinder.
- Cut the new parts to shape.
- If necessary punch or drill holes for mig plug welding.
- Grind all joining flanges to bare metal on both sides. Do not use an angle grinder for this purpose (this could
weaken the metal and damage the zinc layer). Suitable tools: rotating wire brush, belt sander or plastic disc.
- Apply welding primer liberally to all weld flanges.
- The primer must be well stirred before use.
NOTE: When using aerosols, take care not to contaminate adjacent parts with spray mist.
Fit the new part.
It must be Make sured that the new part fits exactly to the specified dimensions. Suitable equipment:
- Alignment jig.
- Universal measuring system.
- Jig system.
- Ruler or tape measure.
- Compass.
- Frame dimensions can be found in the model-specific repair manuals.
Page 2714 of 3039

- Disadvantage: Scarring and hardening of the surface.
Flattening using a copper electrode.
- Small, sharp dents that face outwards can be worked on with a copper electrode.
Flattening using a flame and body files.
NOTE: When applied correctly, this method can be used with all the attached parts still in place (roof headlining,
wiring harnesses etc.).
- Small, soft dents (only slight stretching): Working at the edges of the dent in an inward spiral pattern, the dent
is heated with an oxyacetylene torch (torch size 1 - 2 mm, excess gas flame) to approx. 250° C.
- Working rapidly with a body file extracts heat from the edge area until the dent is flattened. Preferably alternate
between two files. This increases the amount of heat that can be extracted.
Safety measures
The electronic control modules (ECM) fitted to vehicles make it advisable to follow suitable precautions prior to carrying
out welding repair operations. Harsh conditions of heat and vibration may be generated during these operations which
could cause damage to the modules. In particular, it is essential to follow the appropriate precautions when
disconnecting or removing the airbag RCM.
Do not allow electronic modules or lines to come into contact with the ground connection or the welding electrode.
Seat belt anchorages are a safety critical. When making repairs in these areas, it is essential to follow design
specifications. Note that extra strength low alloy steel may be used for seat belt anchorages. Where possible, the
original production assembly should be used, complete with its seat belt anchorages, or the cut line should be so
arranged that the original seat belt anchorage is not disturbed.
All welds within 250mm (9.842) of seat belt anchorages must be carefully checked for weld quality, including spacing of
spot welds.
Remove the battery before carrying out welding work in its vicinity.
Utmost care must be taken when welding near the fuel tank or other components that contain fuel. If the tank filler
neck or a fuel line must be detached to allow access for welding work, then the fuel tank must be drained and removed.
Never weld, on components of a filled air conditioning system. The same applies if there is a risk of the air conditioning
system heating up.
Connect the ground connection of the electrical welder directly to the part that is to be welded. Make sure that there
are no electrically insulating parts between the ground connection and the welding point.
Adjacent vehicle parts and adjacent vehicles must be shielded against flying sparks and heat.
Pedestrian protection system
The pedestrian protection system is designed to mitigate injuries in a pedestrian collision with the vehicle. It does this by
utilizing a pair of pyrotechnic actuators to lift the hood away from the engine, creating a cushioned impact between the
pedestrian and the vehicle. It is essential that any repair or replacement operations do not affect the safe working of the
system.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection System (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Description and Operation).
Resistance spot welding
Where resistance spot welds have been used in production, they must be reproduced with new spot welds in replacement
where possible. All such reproduction spot welds should be spaced 25 to 30mm apart.
Setting up the equipment and co-ordinating the welding parameters.
Equipment:
- Follow the equipment manufacturer's instructions for the equipment settings.
- Select the correct electrode arms (as short as possible).
- Align the electrode arms and tips exactly.
- Electrode tips should be convex (rough shaping with a file, fine shaping with a sanding block).
Body:
- Make sure that the flanges to be joined lie perfectly flat to one another.
- Prepare a bare metal joint surface (inside and outside).
Notes on technique/method:
- Carry out a test weld on a sample piece of the material coated in welding paste.
- If any metal parts are located between the electrode arms then there will be a loss of induction and therefore
power (adjust current setting).
- The power needs to be adjusted for high-strength low alloy steel.
- Repeated welding on old welding points often leads to poor quality welds.
- Keep the electrode tips as near as possible to an angle of 90° to the contact surface.
- Keep the pressure on the electrodes for a short period after finishing the weld.
- The electrodes work best if their shape is convex. Clean the contact surface of the electrodes regularly.
Resistance spot welding panels where the total thickness is 3 mm or more
For all repairs to modern Jaguar vehicles, spot-welding equipment should be suitable for reliable welding of zinc-plated,
high-strength and high-tensile steels in three or more layers, up to 5 mm total thickness. If these requirements are not
fulfilled, plug welding must be used for safety reasons. The electrical specifications (current, resistance, heat) of the
spot-welding equipment have different validity, depending upon the type of equipment. Therefore, it is essential that the
manufacturer's instructions are observed with regard to the actual welding performance.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2731 of 3039
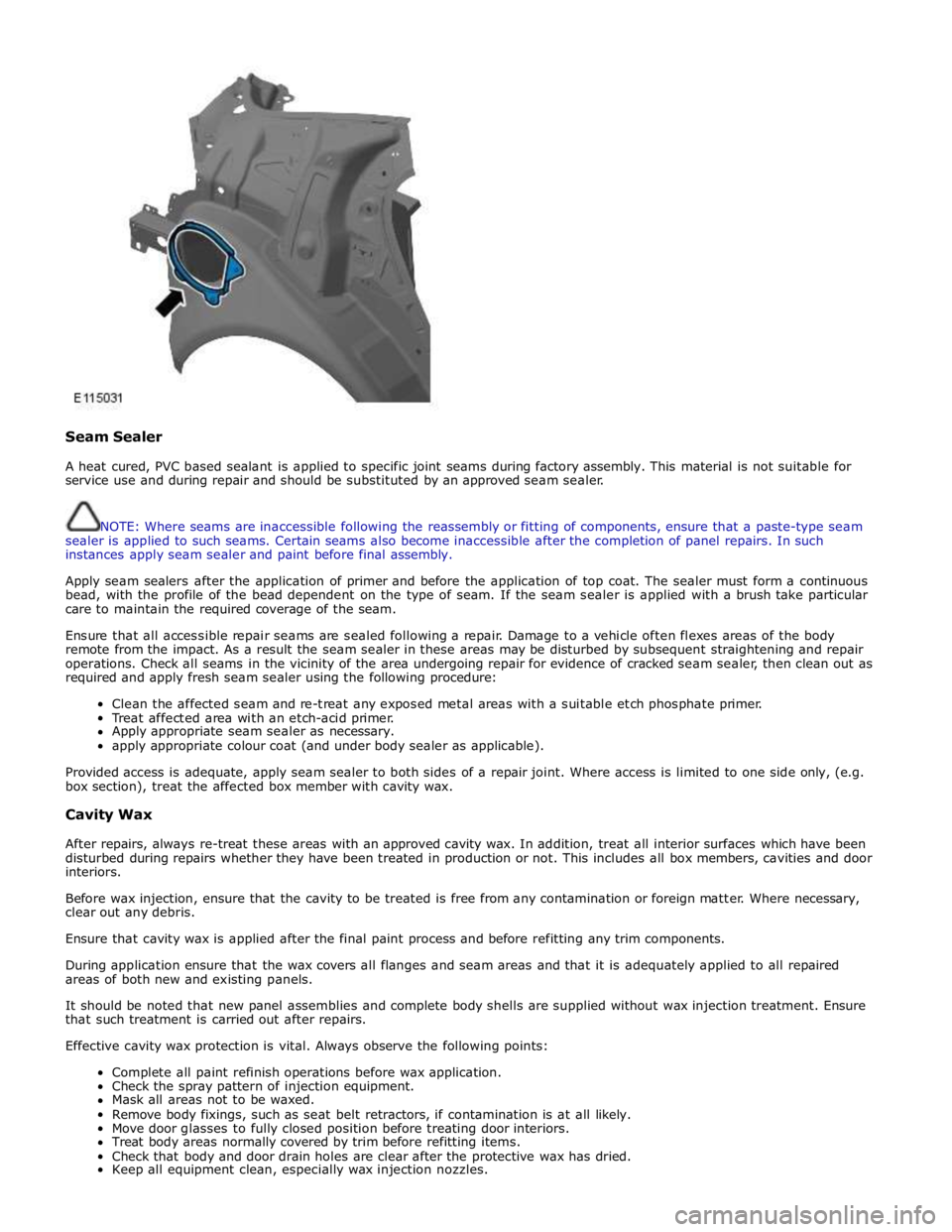
Seam Sealer
A heat cured, PVC based sealant is applied to specific joint seams during factory assembly. This material is not suitable for
service use and during repair and should be substituted by an approved seam sealer.
NOTE: Where seams are inaccessible following the reassembly or fitting of components, ensure that a paste-type seam
sealer is applied to such seams. Certain seams also become inaccessible after the completion of panel repairs. In such
instances apply seam sealer and paint before final assembly.
Apply seam sealers after the application of primer and before the application of top coat. The sealer must form a continuous
bead, with the profile of the bead dependent on the type of seam. If the seam sealer is applied with a brush take particular
care to maintain the required coverage of the seam.
Ensure that all accessible repair seams are sealed following a repair. Damage to a vehicle often flexes areas of the body
remote from the impact. As a result the seam sealer in these areas may be disturbed by subsequent straightening and repair
operations. Check all seams in the vicinity of the area undergoing repair for evidence of cracked seam sealer, then clean out as
required and apply fresh seam sealer using the following procedure:
Clean the affected seam and re-treat any exposed metal areas with a suitable etch phosphate primer.
Treat affected area with an etch-acid primer.
Apply appropriate seam sealer as necessary.
apply appropriate colour coat (and under body sealer as applicable).
Provided access is adequate, apply seam sealer to both sides of a repair joint. Where access is limited to one side only, (e.g.
box section), treat the affected box member with cavity wax.
Cavity Wax
After repairs, always re-treat these areas with an approved cavity wax. In addition, treat all interior surfaces which have been
disturbed during repairs whether they have been treated in production or not. This includes all box members, cavities and door
interiors.
Before wax injection, ensure that the cavity to be treated is free from any contamination or foreign matter. Where necessary,
clear out any debris.
Ensure that cavity wax is applied after the final paint process and before refitting any trim components.
During application ensure that the wax covers all flanges and seam areas and that it is adequately applied to all repaired
areas of both new and existing panels.
It should be noted that new panel assemblies and complete body shells are supplied without wax injection treatment. Ensure
that such treatment is carried out after repairs.
Effective cavity wax protection is vital. Always observe the following points:
Complete all paint refinish operations before wax application.
Check the spray pattern of injection equipment.
Mask all areas not to be waxed.
Remove body fixings, such as seat belt retractors, if contamination is at all likely.
Move door glasses to fully closed position before treating door interiors.
Treat body areas normally covered by trim before refitting items.
Check that body and door drain holes are clear after the protective wax has dried.
Keep all equipment clean, especially wax injection nozzles.