2010 GMC SIERRA spare wheel
[x] Cancel search: spare wheelPage 380 of 630

Off-roading can be great fun but has some definite
hazards. The greatest of these is the terrain itself. When
off-road driving, traffic lanes are not marked, curves are
not banked, and there are no road signs. Surfaces can
be slippery, rough, uphill, or downhill.
Avoid sharp turns and abrupt maneuvers. Failure to
operate the vehicle correctly off‐road could result in loss
of vehicle control or vehicle rollover.
Off-roading involves some new skills. That is why it is
very important that you read these driving tips and
suggestions to help make off-road driving safer and
more enjoyable.
Before You Go Off-Roading
.Have all necessary maintenance and service
work done.
.Make sure there is enough fuel, that fluid levels are
where they should be, and that the spare tire is
fully inflated.
.Be sure to read all the information about
four-wheel-drive vehicles in this manual.
.Make sure all underbody shields, if the vehicle has
them, are properly attached.
.Know the local laws that apply to off-roading where
you will be driving or check with law enforcement
people in the area.
.Be sure to get the necessary permission if you will
be on private land.
If you think you will need some more ground clearance
at the front of your vehicle, you can remove the front
fascia lower air dam. The air dam is held in place by
two bolts and 10 snaps accessible from underneath the
front fascia.
To remove the air dam: 1. Remove the two outboard air dam bolts.
2. With a flat‐blade tool, disengage the snaps.
3. After the bolts are removed and the snaps are disengaged, push forward on the air dam until it
is free.
Notice: Operating your vehicle for extended periods
without the front fascia lower air dam installed can
cause improper air flow to the engine. Always be
sure to replace the front fascia air dam when you
are finished off-road driving.
After off-roading, be sure to reinstall the air dam:
1. Line up the snaps and push the air dam rearward to engage the snaps.
2. Install the two outboard bolts.
5-12
Page 448 of 630

Section 6 Service and Appearance Care
Rear Axle. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-48
Four-Wheel Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-50
Front Axle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-52
Noise Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-53
Tampering with Noise Control
System Prohibited . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-53
Headlamp Aiming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-54
Bulb Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-57
Halogen Bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-57
Headlamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-57
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp (CHMSL) and Cargo Lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-58
Pickup Box Identification and Fender Marker Lamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-59
Taillamps, Turn Signal, Stoplamps and Back-up Lamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-60
License Plate Lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-62
Replacement Bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-62
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement . . . . . . . . . . .6-63Tires
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-64
Tire Sidewall Labeling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-65
Tire Terminology and Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-70
Inflation - Tire Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-72
High-Speed Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-74
Dual Tire Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-74
Tire Pressure Monitor System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-75
Tire Pressure Monitor Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-76
Tire Inspection and Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-80
When It Is Time for New Tires . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-82
Buying New Tires . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-83
Different Size Tires and Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-85
Uniform Tire Quality Grading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-85
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-87
Wheel Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-87
Tire Chains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-89
If a Tire Goes Flat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-89
Changing a Flat Tire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-90
Removing the Spare Tire and Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-92
Removing the Flat Tire and Installing the Spare Tire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-97
Secondary Latch System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-103
Storing a Flat or Spare Tire and Tools . . . . . . . . 6-106
Spare Tire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-109
6-2
Page 520 of 630

If you overfill the tire, release air by pushing on
the metal stem in the center of the tire valve.
Recheck the tire pressure with the tire gage.
Be sure to put the valve caps back on the valve
stems. They help prevent leaks by keeping out dirt
and moisture.
High-Speed Operation
{WARNING:
Driving at high speeds, 160 km/h (100 mph) or
higher, puts an additional strain on tires.
Sustained high-speed driving causes excessive
heat build up and can cause sudden tire failure.
You could have a crash and you or others could
be killed. Some high-speed rated tires require
inflation pressure adjustment for high speed
operation. When speed limits and road conditions
are such that a vehicle can be driven at high
speeds, make sure the tires are rated for high
speed operation, in excellent condition, and set to
the correct cold tire inflation pressure for the
vehicle load.Vehicles with P265/70R17 or P275/55R20 size tires
require inflation pressure adjustment when driving the
vehicle at speeds of 100 mph (160 km/h) or higher.
Set the cold tire inflation pressure to 3 psi (20 kPa)
above the recommended cold tire pressure shown on
the Tire and Loading Information label.
When you end this high‐speed driving, return the tires
to the cold inflation pressure shown on the Tire and
Loading Information label. See
Loading the Vehicle
on
page 5‑30and Inflation - Tire Pressure on page 6‑72.
Dual Tire Operation
When the vehicle is new, or whenever a wheel, wheel
bolt or wheel nut is replaced, check the wheel nut
torque after 100, 1,000 and 6,000 miles (160, 1 600 and
10 000 km) of driving. For proper torque and wheel nut
tightening information, see Removing the Spare Tire
and Tools on page 6‑92.
The outer tire on a dual wheel setup generally wears
faster than the inner tire. Your tires will wear more
evenly and last longer if you rotate the tires periodically,
see Tire Inspection and Rotation
on page 6‑80. Also
see Scheduled Maintenance on page 7‑3.
6-74
Page 522 of 630

When the malfunction indicator is illuminated, the
system may not be able to detect or signal low tire
pressure as intended. TPMS malfunctions may occur
for a variety of reasons, including the installation of
replacement or alternate tires or wheels on the vehicle
that prevent the TPMS from functioning properly.
Always check the TPMS malfunction telltale after
replacing one or more tires or wheels on your vehicle to
ensure that the replacement or alternate tires and
wheels allow the TPMS to continue to function properly.
SeeTire Pressure Monitor Operation
on page 6‑76for
additional information.
Federal Communications Commission
(FCC) and Industry and Science Canada
See Radio Frequency Statementon page 8‑19for
information regarding Part 15 of the Federal
Communications Commission (FCC) Rules and
RSS-210/211 of Industry and Science Canada.
Tire Pressure Monitor Operation
This vehicle may have a Tire Pressure Monitor System
(TPMS). The TPMS is designed to warn the driver when
a low tire pressure condition exists. TPMS sensors are
mounted onto each tire and wheel assembly, excluding
the spare tire and wheel assembly. The TPMS sensors monitor the air pressure in the vehicle's tires and
transmits the tire pressure readings to a receiver
located in the vehicle.
When a low tire pressure
condition is detected, the
TPMS will illuminate the
low tire pressure warning
symbol located on the
instrument panel cluster.
At the same time a message to check the pressure in a
specific tire appears on the Driver Information Center
(DIC) display. The low tire pressure warning light and
the DIC warning message come on at each ignition
cycle until the tires are inflated to the correct inflation
pressure. If your vehicle has DIC buttons, tire pressure
levels can be viewed by the driver. For additional
information and details about the DIC operation and
displays see DIC Operation and Displays (With DIC
Buttons)
on page 4‑51or DIC Operation and Displays
(Without DIC Buttons)on page 4‑58and DIC Warnings
and Messages on page 4‑65.
6-76
Page 526 of 630

Tire Inspection and Rotation
We recommend that you regularly inspect your
vehicle's tires, including the spare tire, for signs of
wear or damage. SeeWhen It Is Time for New
Tires
on page 6‑82for more information.
Tires should be rotated every 5,000 to 8,000 miles
(8 000 to 13 000 km). See Scheduled Maintenance
on page 7‑3.
The purpose of a regular tire rotation is to achieve
a uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. This will
ensure that your vehicle continues to perform
most like it did when the tires were new.
Any time you notice unusual wear, rotate your
tires as soon as possible and check wheel
alignment. Also check for damaged tires or
wheels. See When It Is Time for New Tires
on
page 6‑82
and Wheel Replacementon page 6‑87.
If your vehicle has dual rear wheels, also see
Dual Tire Operation
on page 6‑74.
If your vehicle has single rear wheels and the
tread design for the front tires is the same as the
rear tires, use the rotation pattern shown here
when rotating the tires.
6-80
Page 528 of 630

Make certain that all wheel nuts are properly
tightened. See“Wheel Nut Torque” under
Capacities and Specifications
on page 6‑126.
{WARNING:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to
which it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after time. The wheel could
come off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the
vehicle. In an emergency, you can use a
cloth or a paper towel to do this; but be sure
to use a scraper or wire brush later,
if needed, to get all the rust or dirt off.
See Changing a Flat Tire
on page 6‑90.
If your vehicle has a Tire Pressure Monitor
System (TPMS), reset the TPMS sensors after
rotating the tires. See Tire Pressure Monitor
Operation
on page 6‑76. Make sure the spare tire, if your vehicle has one,
is stored securely. Push, pull, and then try to
rotate or turn the tire. If it moves, tighten the
cable. See
Storing a Flat or Spare Tire and Tools
on page 6‑106.
When It Is Time for New Tires
Various factors, such as maintenance, temperatures,
driving speeds, vehicle loading, and road conditions,
influence when you need new tires.
One way to tell when it is
time for new tires is to
check the treadwear
indicators, which appear
when your tires have only
1/16 inch (1.6 mm) or less
of tread remaining. Some
commercial truck tires
may not have treadwear
indicators.
6-82
Page 531 of 630

Different Size Tires and Wheels
If you add wheels or tires that are a different size than
your original equipment wheels and tires, this could
affect the way your vehicle performs, including its
braking, ride and handling characteristics, stability, and
resistance to rollover. Additionally, if your vehicle has
electronic systems such as anti‐lock brakes, rollover
airbags, traction control, and electronic stability control,
the performance of these systems can be affected.
{WARNING:
If you add different sized wheels, your vehicle
may not provide an acceptable level of
performance and safety if tires not recommended
for those wheels are selected. You may increase
the chance that you will crash and suffer serious
injury. Only use GM specific wheel and tire
systems developed for your vehicle, and have
them properly installed by a GM certified
technician.
See Buying New Tires
on page 6‑83andAccessories
and Modificationson page 6‑4for additional
information.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
Quality grades can be found where applicable on
the tire sidewall between tread shoulder and
maximum section width. For example:
Treadwear 200 Traction AA
Temperature A
The following information relates to the system
developed by the United States National
Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA),
which grades tires by treadwear, traction, and
temperature performance. This applies only to
vehicles sold in the United States. The grades are
molded on the sidewalls of most passenger car
tires. The Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG)
system does not apply to deep tread, winter-type
snow tires, space-saver, or temporary use
spare tires, tires with nominal rim diameters of
10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm), or to some
limited-production tires.
6-85
Page 538 of 630
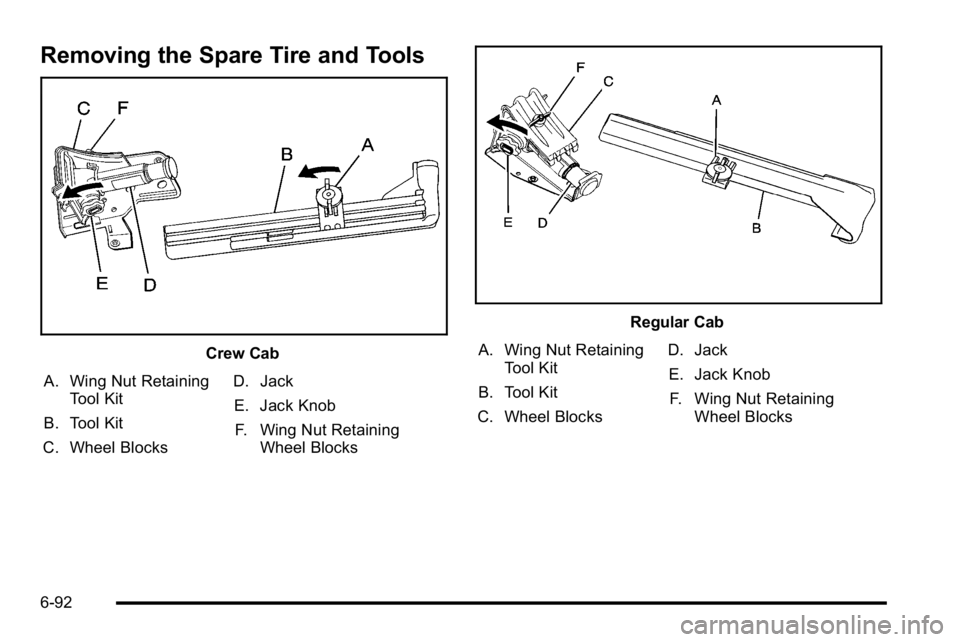
Removing the Spare Tire and Tools
Crew Cab
A. Wing Nut Retaining Tool Kit
B. Tool Kit
C. Wheel Blocks D. Jack
E. Jack Knob F. Wing Nut Retaining Wheel Blocks
Regular Cab
A. Wing Nut Retaining Tool Kit
B. Tool Kit
C. Wheel Blocks D. Jack
E. Jack Knob F. Wing Nut Retaining Wheel Blocks
6-92