2009 SKODA ROOMSTER ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 133 of 263
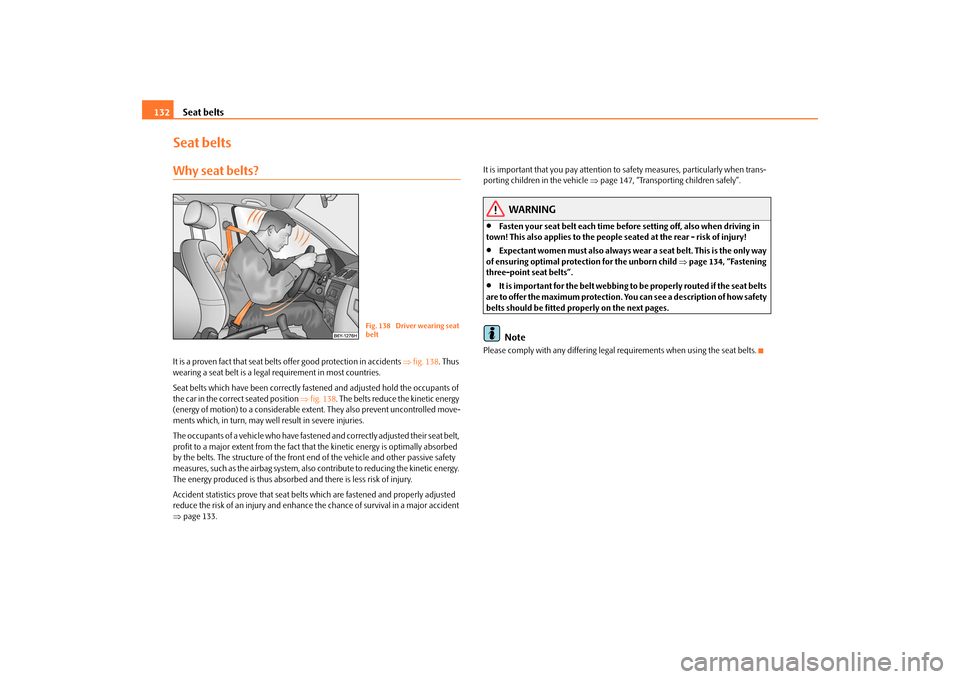
Seat belts 132Seat beltsWhy seat belts?It is a proven fact that seat belts offer good protection in accidents ⇒fig. 138. Thus
wearing a seat belt is a legal requirement in most countries.
Seat belts which have been correctly fastened and adjusted hold the occupants of
the car in the correct seated position ⇒fig. 138. The belts reduce the kinetic energy
(energy of motion) to a considerable extent. They also prevent uncontrolled move-
ments which, in turn, may well result in severe injuries.
The occupants of a vehicle who have fastened and correctly adjusted their seat belt,
profit to a major extent from the fact that the kinetic energy is optimally absorbed
by the belts. The structure of the front end of the vehicle and other passive safety
measures, such as the airbag system, also contribute to reducing the kinetic energy.
The energy produced is thus absorbed and there is less risk of injury.
Accident statistics prove that seat belts which are fastened and properly adjusted
reduce the risk of an injury and enhance the chance of survival in a major accident
⇒page 133.It is important that you pay attention to safety measures, particularly when trans-
porting children in the vehicle ⇒page 147, “Transporting children safely”.
WARNING
•
Fasten your seat belt each time before setting off, also when driving in
town! This also applies to the people seated at the rear - risk of injury!
•
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way
of ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child ⇒page 134, “Fastening
three-point seat belts”.
•
It is important for the belt webbing to be properly routed if the seat belts
are to offer the maximum protection. You can see a description of how safety
belts should be fitted properly on the next pages.Note
Please comply with any differing legal requirements when using the seat belts.
Fig. 138 Driver wearing seat
belt
s29g.4.book Page 132 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM
Page 134 of 263

Seat belts133
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Praktik
Technical Data
The physical principle of a frontal collisionThe physical principle of a frontal accident can be explained quite simply:
Motion energy, so-called kinetic energy, is produced as soon as the vehicle is
moving, both for the vehicle and its occupants. The magnitude of this kinetic energy
depends essentially on the speed at which the vehicle is travelling and on the
weight of the vehicle and the occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an acci-
dent.
The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy
four times.
The common opinion that it is possible to support your body in a minor accident
with your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces
acting on the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed within the range from 30 km/hour to 50 km/hour,
the forces which are produced on your body in the event of an accident can easily
exceed 10.000 N (Newton). This equals a weight of one tonne (1 000 kg).
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt, are
thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolled way parts of the interior of the car,
such as steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen,⇒fig. 139. The occupants of a
vehicle who have not fastened their seat belts may even be thrown out of the
vehicle. This can result in fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat occupants fasten their seat belts as they will other-
wise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the event of an
accident A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the seat belt is a danger not
only to himself but also for those seated at the front ⇒fig. 140.
Important safety information regarding the use of seat beltsThe correct use of the seat belts considerably reduces the risk of
injury!
WARNING
•
The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or
twisted, or chafe against any sharp edges.
•
It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed if the seat belts
are to offer their maximum protection ⇒page 134, “How are seat belts
correctly fastened?”.
Fig. 139 The driver is thrown
forward if not wearing a beltFig. 140 The rear seat occu-
pant is thrown forward if not
wearing a belt
s29g.4.book Page 133 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM
Page 156 of 263

Intelligent Technology155
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Praktik
Technical Data
Driving TipsIntelligent TechnologyElectronic stability programme (ESP)*GeneralGeneral
The ESP aids you maintain control of your vehicle in situations in borderline driving
situations such as when negotiating a curve too fast. The risk of skidding is reduced
and your vehicle thus offers greater driving stability depending on the conditions of
the road surface. This occurs at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:•
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL);
•
Traction control system (TCS);
•
Antilock brake system (ABS);
•
Brake Assist.Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts a
self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It also
processes additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive
sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehicle about its vertical axis, the lateral accel-
eration of the vehicle, the braking pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the steering
angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual
behaviour of the vehicle. If differences exist, such as the vehicle beginning to skid,
the ESP will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel is braked.
Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front wheel of
a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle to break
away) while occurs this is on the inner rear wheel of a vehicle which tends to under-
steer (tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied
by noises.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 159, “Antilock brake system
(ABS)*”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also does not operate.
The ESP warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on the
ESP
⇒page 35.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the button
⇒fig. 165. The ESP warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when the ESP is
switched off
⇒page 35.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain
exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip, to switch off the
system.
Examples:
Fig. 165 ESP switch
s29g.4.book Page 155 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM
Page 157 of 263

Intelligent Technology 156•
when driving with snow chains;
•
when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface;
•
when it is necessary to rock a vehicle when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the ESP again.
WARNING
It is also not possible for the ESP to overcome the physical limits of the
vehicle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still always adapt your
style of driving to the condition of the road surface and the traffic situation.
This particularly applies when driving on slippery and wet roads. The
increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than other-
wise - risk of an accident!
Note
•
All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve problem-
free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can lead to an
undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP ⇒page 204,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Traction control system (TCS)*
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels from spinning
when accelerating.General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, accelerate
and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts a
self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the
ABS sensors. If the wheels are spinning, the force transmitted to the road surface is
automatically adapted by reducing the engine speed. This occurs at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 159, “Antilock brake system
(ABS)*”. The TCS will not function if a fault exists in the ABS system.
The TCS warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a fault on the
TCS
⇒page 34.
Switching off
You can switch the TCS off and on again as you wish by pressing the button
⇒fig. 166. The TCS warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when the TCS is
switched off
⇒page 34.
Fig. 166 TCS switch
s29g.4.book Page 156 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM
Page 158 of 263

Intelligent Technology157
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Praktik
Technical Data The TCS should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice in certain
exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip, to switch off the
system.
Examples:
•
when driving with snow chains;
•
when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface;
•
when it is necessary to rock a vehicle when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the TCS again.
WARNING
You should always adjust your style of driving to the conditions of the road
surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety offered must not tempt
you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an accident!
Note
•
All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve problem-
free operation of the TCS. Differing rolling circumferences of the tyres can lead to
an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the TCS ⇒page 204,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)*
The electronic differential lock prevents an individual wheel from
slipping.Models fitted with ESP are equipped with electronic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off, accelerate
and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface are unfavourable.Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part of the
driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the ABS sensors.
Should only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery surface there will be an
appreciable difference in the speed of the driven wheels. The EDL function brakes
the slipping wheel and the differential transmits a greater driving force to the other
driven wheel. This control process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in order to
avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel which is being
braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the same characteristics as a
vehicle not fitted with EDL.
The EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down.
WARNING
•
Carefully depress the accelerator when accelerating on uniformly slip-
pery road surfaces, such as ice and snow. The driven wheels might still spin
despite the EDL and affect the stability of the vehicle - risk of an accident!
•
You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition of road
surface and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle is fitted with EDL.
The increased safety offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than
otherwise - risk of an accident!Note
•
If the ABS or TCS or ESP warning light comes on, this may also indicate a fault in
the EDL. Please have the vehicle inspected as soon as possible by a specialist
garage.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the EDL ⇒page 204,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
s29g.4.book Page 157 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM
Page 160 of 263

Intelligent Technology159
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Praktik
Technical Data
WARNING
•
Never switch off the engine before the vehicle is stationary.
•
The brake booster only operates when the engine is running. Greater
physical effort for braking is required when engine is switched off. Because
if you do not stop as normal, this can cause an accident and severe injuries.
Antilock brake system (ABS)*ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking.General
The ABS contributes significantly to enhancing the active safety of your vehicle.
Compared to a vehicle not fitted with the ABS brake system, you are able to retain
optimal steering ability even during a full brake application on a slippery road
surface because the wheels do not lock up.
You must not expect, however, that the braking distance will be shorter under all
circumstances as a result of the ABS. The braking distance for example on gravel
and fresh snow, when you should anyway be driving slowly and cautiously, will be
longer.
Operating principle
As soon as the vehicle speed has increased to about 20 km/hour an automatic test
procedure is conducted during which you will be able to hear a pumping noise for
about 1 second.
The brake pressure will be reduced on a wheel which is rotating at a speed which is
too low for the speed of the vehicle and tending to lock. This control cycle is notice-
able from a pulsating movement of the brake pedal which is accompanied by
noises. This is consciously intended to provide the driver with the information that
the wheels are tending to lock (ABS control range). You must always keep the brake
pedal depressed to enable the ABS to optimally control the brake application in this
braking range. Never interrupt the application of the brakes!
WARNING
•
The ABS can also not overcome the physical limits of your vehicle. Please
do not forget this, particularly when driving on icy or wet road surfaces. If the
ABS is operating within the control range, adapt your speed immediately to
the conditions of the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased
safety offered by the ABS must not tempt you to take greater risks than
otherwise - risk of an accident!
•
The normal braking system is still fully functional if there is an ABS fault.
Visit a specialist garage as quickly as possible and adjust your style of driving
to take account of the ABS fault in the meantime since you will not know the
extent of the fault and in how far the braking efficiency is affected.Note
•
A warning light comes on if a fault occurs in the ABS system
⇒page 35.
•
Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or another combi-
nation of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ABS ⇒page 204,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Brake Assist*During a severe brake application (e.g. if a hazard exists), the Brake Assist increases
the braking force and thus makes it possible to rapidly produce the pressure
required in the brake system.
The majority of drivers do apply the brakes in good time in dangerous situations,
but do not depress the brake pedal with sufficient pressure. Consequently, it is not
possible for the vehicle to achieve its maximum deceleration and the vehicle covers
a greater distance than necessary.
The Brake Assist is activated by the very quick operation of the brake pedal. In such
cases, a much greater braking pressure exists than during a normal brake applica-
tion. This makes it possible, even with a relatively low resistance of the brake pedal,
to produce an adequate pressure in the brake system in the shortest possible time,
which is required for maximum deceleration of the vehicle. You must apply the
s29g.4.book Page 159 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM
Page 161 of 263
Intelligent Technology 160brake pedal firmly and hold it in this position in order to achieve the shortest
possible braking distance.
The Brake Assist is able to help you achieve a shorter braking distance in emergency
situations by rapidly producing the pressure required in the brake system. It fully
exploits the attributes of the ABS. After you release the brake pedal, the function of
the Brake Assist is automatically switched off and the brakes operate in the normal
way.
The Brake Assist is part of the ESP system. If a fault occurs in the ESP, the Brake Assist
function is also not available. Further information on the ESP ⇒page 155.
WARNING
•
The Brake Assist is also not able to overcome the physical limits of your
vehicle in terms of the braking distance required.
•
Adapt your speed to the conditions of the road surface and to the traffic
situation.
•
The increased safety offered by the Brake Assist must not tempt you to
take a greater safety risk than otherwise.
Electrohydraulic power steeringThe power steering enables you to steer the vehicle with less physical force.
The steering characteristics can be changed by a specialist garage.
You will place great stresses on the power steering system if the steering is turned
to full lock when the vehicle is stationary. Turning the steering to full lock in such a
situation will be accompanied by noises.
It is still possible to fully steer the vehicle if the power steering fails or if the engine
is not running (vehicle being towed in). The only difference is that greater physical
effort is required.
It is possible that the hydraulic pump of the power steering will not run due to the
low vehicle network voltage if the battery has gone flat and the engine must started
with the help off jump leads. This condition will be indicated by lighting up of the
warning light.The power steering operates again if the battery is charged to a specific range when
engine is running. It also operates again, if the engine can be started with its own
battery.
If there is a fault in the power steering, the warning light lights up in the instrument
cluster
⇒page 29.
Caution
Do not leave the steering at full lock for more than 15 seconds when the engine is
running - risk of damaging the power steering!
Note
Have the steering inspected as soon as possible by a specialist garage if there is a
leak or fault in the system.Tyre inflation pressure-control system*The tyre inflation pressure-control system compares with the aid of the ABS sensors
the speed and also the rolling circumference of the individual wheels. If the tyre
inflation pressure is significantly changed and thus the rolling circumference of a
wheel, the warning light
lights up in the instrument cluster ⇒page 35. The tyre
inflation pressure-control system functions late or too sensitively if:
Fig. 167 Button for setting
the tyre inflation pressure
control value
s29g.4.book Page 160 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM
Page 180 of 263

Taking care of your vehicle and cleaning the vehicle179
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Praktik
Technical Data
Removing stains
– Remove fresh stains which are water-based (e.g. coffee, tea, juices,
blood etc.) with an absorbent cloth or household paper or use the
cleaner from the care set for a stain which has already dried in.
– Remove fresh stains on a fat base (e.g. butter, mayonnaise, chocolate
etc.) with an absorbent cloth or household cleaning paper or with the
cleaner from the care set if the stain has not yet penetrated into the
surface.
– Use a grease dissolver for grease stains which have dried in.
–Eliminate special stains (e.g. ball-point pens, felt pen, nail varnish,
dispersion paint, shoe cream etc.) with a special stain remover suit-
able for leather.
Leather care
– Treat the leather every six months with the leather care product avail-
able from specialist garages.
– Apply only a small amount of the care product.
– Dry the leather off with a soft clothWe recommend that you consult a specialist garage if you have any questions
regarding cleaning and care of the leather interior in your vehicle.
Caution
•
You must on no account treat the leather with solvents (e.g. gasoline, turpen-
tine), floor wax, shoe cream or such like.
•
Avoid leaving your vehicle for lengthy periods in bright sunlight in order to
avoid bleaching the leather. If you leave your vehicle parked in the open for lengthy
periods, protect the leather from the direct rays of the sun by covering it over.
•
Sharp-edged objects on items of clothing such as zip fasteners, rivets, sharp-
edged belts may leave permanent scratches or signs of rubbing on the surface.
Note
•
Use a care cream with light blocker and impregnation effect regularly and each
time after cleaning the leather. The cream nourishes the leather, allows it to breathe
and keeps it supple and also provides moisture. It also creates surface protection.
•
Clean the leather every 2 to 3 months, remove fresh soiling each time this
occurs.
•
Remove fresh stains such as those from ball-point pens, ink, lipstick, shoe
cream etc., as quickly as possible.
•
Care also for the leather dye. Refreshen areas which have lost their colour with
a special coloured leather cream as required.
•
The leather is a natural material with specific properties. During the use of the
vehicle, minor optical changes can occur on the leather parts of the covers (e. g
wrinkles or creases as a result of the stress of the covers).
Seat belts– Keep the seat belts clean!
– Wash seat belts which have become soiled using a mild soapy solu-
tion.
– Inspect the seat belts regularly to ensure they are in good condition.Belt webbing which has become severely soiled may prevent the inertia reel from
reeling up the belt properly.
WARNING
•
The seat belts must not be removed for cleaning.
•
Never clean the seat belts chemically as dry cleaning may destroy the
fabric. The seat belts must also not be allowed to come into contact with
corrosive liquids (such as acids etc.).
•
Seat belts which have damage to the webbing, the connections, the
inertia reel or the lock should be replaced by a specialist garage.
s29g.4.book Page 179 Wednesday, June 17, 2009 9:54 AM