2009 PORSCHE PANAMERA Pressure
[x] Cancel search: PressurePage 205 of 343

Driving and Driving Safety
203
Advantages of PSM
– Best possible traction and lane-holding ability
in all driving situations – even on road surfaces
with varying friction.
– The system compensates for undesired vehicle reactions (Ferraria effect) when the
driver releases the accelerator pedal or brakes
on bends. This compensation functions up to
the maximum lateral acceleration.
– PSM actively stabilises the vehicle if necessary during dynamic driving maneuvers (e.g. rapid
steering movements, during lane changes, or
on alternating bends).
– Improved braking stability on bends and on different or varying road surfaces.
– Improved brake function and shorter stopping distance in the event of emergency braking. Readiness for operation
PSM is switched on automatically every time you
start the engine.
Function
Sensors at the wheels, brakes, steering system
and engine continuously measure:
–Speed
– Direction of travel (steering angle)
– Lateral acceleration
– Axial acceleration
– Rate of turn about the vertical axis
PSM uses these values to determine the direction
of travel desired by the driver.
PSM intervenes and corrects the course if the
actual direction of motion deviates from the
desired course (steering-wheel position):
It brakes individual wheels as required.
If necessary, PSM also influences the engine
power or the gear-changing characteristic of
Porsche Doppelkupplung (PDK) in order to
stabilise the vehicle. The events below inform the driver of PSM control
operations and warn him to adapt his driving style
to the road conditions:
– PSM warning light on the instrument panel
flashes.
– Hydraulic noises can be heard.
– The vehicle decelerates and steering-wheel forces are altered as PSM controls the brakes.
– Reduced engine power.
– The brake pedal pulsates and its position is changed during braking.
In order to achieve full vehicle deceleration,
foot pressure must be increased after the
brake pedal has begun vibrating.
Examples of PSM control operations
– If the “front wheels of the vehicle drift” on
a bend, the engine power is reduced and the
rear wheel on the inside of the bend is braked
if necessary.
– If the rear of the vehicle swings out on a bend, the front wheel on the outside of the bend is
braked.
Page 206 of 343

204
Driving and Driving Safety
– Brake system prefilling:
The brake system is prepared for possible
subsequent emergency braking if the
accelerator pedal is released suddenly and
quickly. The brake system is prefilled and the
brake pads are already applied gently to the
brake discs.
– Brake booster (Hydraulic Brake Assist): In the event of an emergency braking operation
where the pedal force is insufficient, a brake
booster provides the braking pressure
necessary for maximum deceleration at all
4wheels.
Combined operation of PSM and PTM
In order to ensure optimum stabilisation of the
vehicle, torque distribution between the front and
rear wheels is adapted and the rear differential
lock is controlled on vehicles with PDCC.
In the event of a PTM fault, PSM cannot be
switched off.
If PSM is switched off, it is switched on again
automatically. Automatic brake differential (ABD)
The ABD system controls the front and rear axles
separately. If one wheel of an axle starts to spin,
it is braked so that the other wheel on the same
axle can be driven.
ABD recognizes different driving states, and it
features control strategies adapted to these
states. In situations in which little propulsive power
is required, such as when the vehicle moves off on
a level gravel surface, traction control already
becomes active at low engine speeds. If a large
amount of propulsive power is required, e.g. when
driving off on an uph
ill slope or for rapid
acceleration, the ABD system is adapted
accordingly.
Anti-slip control (ASR)
The anti-slip control system prevents the wheels
from spinning by adjusting the engine power,
thereby ensuring good lane-holding ability and
stable handling.
Engine drag torque control (MSR)
In conditions of excessive slip, the engine
drag torque control system prevents all driven
wheels from locking up when the vehicle is
overrunning. This is also the case for downshifts
on a slippery road.
Switching off PSMf Press button for at least 1 second.
PSM is switched off after a short delay.
The indicator light on the button and the
PSM OFF warning light on the instrument
panel light up.
The warning “PSM off” appears on the
multi-function display in the instrument panel.
Page 209 of 343

Driving and Driving Safety
207
ABS Brake System
(Anti-Lock Brake System)
Warning!
In spite of the advantages of ABS, it is still the
driver’s responsibility to adapt his driving style and
maneuvers in line with road and weather
conditions, as well as the traffic situation.
The increased safety that is provided should not
induce you to take greater risks with your safety.
The limits set by the physic s of driving cannot be
overcome, even with ABS.
Risk of accidents due to inappropriate speed
cannot be reduced by ABS.
ABS ensures
– Full steering control
The vehicle remains steerable
– Good driving stability
No skidding due to locked wheels
– Optimum braking distance
Shorter stopping distance in most cases
– Prevention of wheel locking
No flat spots on the tires Function
The decisive advantage of ABS lies in the driving
stability and maneuverability of the vehicle in
hazardous situations.
ABS prevents locking of
the wheels during full
braking, on almost all road surfaces, until just
before the vehicle stops.
ABS begins to control the braking process as
soon as a wheel shows a tendency to lock.
This controlled braking process is comparable
with extremely rapid cadence braking.
The pulsating brake pedal and a “juddering noise”
warn the driver to adapt his driving speed to the
road conditions.
f If full braking is necessary, press the brake
pedal fully during the whole braking operation,
even though the pedal is pulsating. Do not
reduce brake pressure. If the ABS warning light lig
hts up on the instrument
panel while the engine is running, the ABS has
switched off because of a fault.
The warning message “ABS failure” appears on
the multi-function display in the instrument panel.
For information on warning messages on the
multi-function display:
f Please see the chapter “OVERVIEW OF
WARNING MESSAGES” on page 152.
In this case, the brake system will operate without
lock prevention, as on vehicles without ABS.
f Adapt your driving style to the changed
braking behavior.
The ABS must be checked by your authorized
Porsche dealer in order to prevent the
occurrence of further faults with unpredictable
consequences.
Please contact a qualified specialist workshop.
We recommend that you have an authorized
Porsche dealer to do this work as they have
trained workshop personnel and the necessary
parts and tools.
The ABS control unit is adjusted for the approved
tire dimensions.
The use of tires with no n-approved dimensions can
lead to different wheel speeds, causing ABS to
switch off. Warning light USA
Warning light Canada
Page 214 of 343

212
Driving and Driving Safety
“Sport” and “Sport Plus” Mode FunctionThe selectable chassis settings mean that the
vehicle can offer various modes for a sportier
overall setup.
When “Sport” or “Sport Plus” mode is selected, all
the vehicle’s control systems are intentionally
shifted towards greater agility and driving
performance:
– PASM (Porsche Active Suspension Management) is automa tically changed to
“PASM Sport” or “PASM Sport Plus” mode,
resulting in a stiffer suspension setup.
The vehicle switches to Low Level in “PASM
Sport Plus” mode.
f Please see the chapter “PORSCHE ACTIVE
SUSPENSION MANAGEMENT (PASM)” on
page 208.
– Just like PASM, PDCC is switched to the corresponding “Sport” or “Sport Plus” mode,
whereby the rolling movements of the vehicle
are reduced further, depending on the
selected mode.
f Please see the chapter “PORSCHE DYNAMIC
CHASSIS CONTROL (PDCC)” on page 211.
– The PDK transmission switches to a sporty gear-changing map and shortens the gear
shifting times when Sport mode is activated.
Gear changes take place faster. f
Please see the chapter ““SPORT” AND “SPORT
PLUS” MODE” on page 195.
– The electronic accelerator pedal reacts sooner, and the engine is more responsive to
throttle inputs. When Sport mode is switched
on and the vehicle is travelling at a speed of
less than 25 mph (40 km/h), this function is
activated only after the driver has floored the
accelerator pedal or released it briefly.
– The rpm limiter characteristic is “harder”. In other words: the engine is immediately
throttled when the performance limits are
reached (only in manual selection mode on
vehicles with PDK).
– The turbo overboost briefly increases the engine boost pressure in the engine speed
range from 2,500 rpm to approx. 4,000 rpm.
As a result, torque in this speed range is
increased by 70 Nm (52 ftlb.). This
considerably improves acceleration and
flexibility, particularly in the medium engine
speed range. This does not affect the
maximum power. Quickly flooring the
accelerator pedal acti vates turbo overboost
in the engine control system. Overboost has
an effective operating time of approx.
10 seconds. After this time, it can be re-
activated by quickly flooring the accelerator
pedal again. – PSM (Porsche Stability Management) control is
more sporty in “Sport Plus” mode. PSM
interventions are later than in Normal mode.
The driver can maneuver the vehicle with
greater agility at it s performance limits,
without having to dispense with the assistance
of PSM in emergency situations. This helps to
achieve optimal lap times, particularly on race
circuits with a dry road surface.
f Please see the chapter “PORSCHE STABILITY
MANAGEMENT (PSM)” on page 202.
– Adaptive cruise control regulates speed and distance more dynamically.
– The Auto Start Stop function is deactivated.
f Please see the chapter “AUTO START STOP
FUNCTION” on page 169.
– The rear spoiler extends earlier and retracts later (“Sport Plus” mode only).
f Please see the chapter “RETRACTABLE REAR
SPOILER” on page 214.
– The system switches from High Level.
f Please see the chapter “HIGH LEVEL” on
page 209.
Page 230 of 343

228
Storage, Luggage Compartment and Roof Transport System
Stowing Loads
Danger!
Danger of injury. An unsecured or incorrectly
positioned load can slip out of place or
endanger the vehicle occupants during
braking, direction changes or in accidents.
Never transport objects that are not secured.
f Always transport loads in the luggage
compartment, never in the passenger
compartment (e.g. on or in front of the seats).
f Support the load against the seat backrests
wherever possible. Always lock the backrests
into place.
f Only transport heavy objects with the rear seat
backrests upright and engaged.
f Place the load behind unoccupied seats
whenever possible.
f Stow heavy objects as far forward as possible
on the floor, with lightweight objects behind
them.
f Never load the vehicle higher than the top
edge of the seat backrest.
f Always protect the passenger compartment
with a luggage compartment cover. Do not
drive with objects on top of the luggage
compartment cover. f
If the rear seats are not occupied, the
backrests can be addition ally secured with the
seat belts. Simply cro ss the outer seat belts
and insert each into the opposite buckle.
f Make sure that the load cannot damage the
heating filaments and the TV antenna in the
rear window.
Tie-down belts
f Do not use elastic belt s or straps to tie
down a load.
f Do not route belts and straps over
sharp edges.
f Observe the directions for use and information
for the tie-down equipment.
f Use only belts with a tear strength of at least
1543 lbs (700 kg) and a maximum width of
1 in. (25 mm).
f Cross the belts over the load. Driving
f
Vehicle handling changes depending on the
vehicle load. Adapt your driving style to the
changed driving behavior.
f Do not exceed the maximum gross weight
and axle load.
This information can be found under “Technical
data” in this Owner’s Manual:
f Please see the chapter “WEIGHTS” on
page 328.
f Never drive with the tailgate open. Exhaust
gases can enter the passenger compartment.
f Adapt the tire pressure to the load.
After you change the tire pressure, you must
also update the setting for Tire Pressure
Monitoring.
For information on setting Tire Pressure
Monitoring on the multi-function display:
f Please see the chapter “OVERVIEW OF
WARNING MESSAGES” on page 152.
Information on tire pressures for partially and fully
loaded vehicles can be found under “Technical
data” in this Owner’s Manual:
f Please see the chapter “TIRE PRESSURE FOR
COLD TIRES (68 °F/20 °C)” on page 326.
Page 238 of 343

236
Storage, Luggage Compartment and Roof Transport System
Loading InformationDefinitionsThe rear-axle load is the vehicle weight on the
rear axle plus the weight of the transported load.
The Curb weight - actual weight of your vehicle -
vehicle weight including standard and optional
equipment, fluids, and emergency tools. This
weight does not include passengers and cargo.
The Gross Vehicle Weight is the sum of the curb
weight and the weight of passengers and cargo
combined.
The Gross Vehicle Weight Rating is the
maximum total weight of vehicle, passengers,
luggage, hitch, trailer tongue load and optional
equipment.
The Gross Axle Weight Rating is the maximum
load limit for the front or the rear axle. This
information is located on the safety comliance
sticker located in the dr iver’s side door jamb.
For determining the compat ibility of the tire and
vehicle load capabilities:
f Please see the chapter “TIRES AND WHEELS”
on page 280. The load capacity coefficient (e.g. “106”) is a
minimum requirement. For more information:
f
Please see the chapter “INSCRIPTION ON
RADIAL TIRE” on page 288.
The Gross Combined Weight Rating is the
maximum total weight rating of vehicle,
passengers and cargo.
The Vehicle Capacity Weight - Load Limit - is
the maximum total weight limit specified of the
load (passengers and cargo) for the vehicle. This
is the maximum weight of passengers and cargo
that can be loaded into the vehicle. This infor-
mation can be found on the tire pressure plate.
The maximum loaded vehicle weight is the
sum of curb weight, acce ssory weight, vehicle
capacity weight and production options weight.
The load rating is the maximum load that a tire
is rated to carry for a given inflation pressure.
The maximum load rating is the load rating for
a tire at the maximum permissible inflation
pressure.
The cargo capacity is the permissible weight of
cargo, the subtracted weight of passengers from
the load limit.
f Never exceed the permissible limits.
Danger!
Risk of personal injury or death.
Injuries are much more likely in an accident
if persons ride in the cargo area.
f Persons must ride only on the seats provided
for this purpose.
f Make sure that everybody fastens their safety
belts.
Risk of loss of control, damage to the vehicle
and serious personal injury or death.
f Never exceed the specified axle loads.
Overloading can shorten the service life of the
tires and car, as well as lead to dangerous
vehicle reactions and long braking distances.
Damage due to overloading is not covered by the vehicle warranty.
Page 239 of 343
Storage, Luggage Compartment and Roof Transport System
237
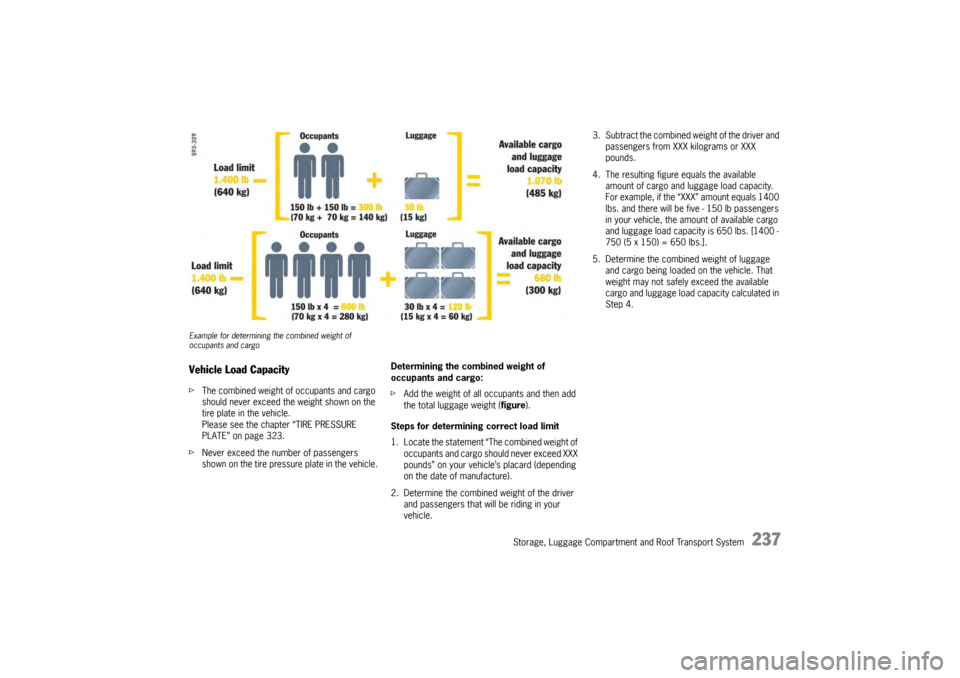
Example for determining the combined weight of
occupants and cargoVehicle Load CapacityfThe combined weight of occupants and cargo
should never exceed the weight shown on the
tire plate in the vehicle.
Please see the chapter “TIRE PRESSURE
PLATE” on page 323.
f Never exceed the number of passengers
shown on the tire pressure plate in the vehicle. Determining the combined weight of
occupants and cargo:
f
Add the weight of all occupants and then add
the total luggage weight ( figure).
Steps for determining correct load limit
1. Locate the statement “The combined weight of occupants and cargo should never exceed XXX
pounds” on your vehicle’s placard (depending
on the date of manufacture).
2. Determine the combined weight of the driver and passengers that will be riding in your
vehicle.
3. Subtract the combined weight of the driver and passengers from XXX kilograms or XXX
pounds.
4. The resulting figure equals the available amount of cargo and luggage load capacity.
For example, if the “XXX” amount equals 1400
lbs. and there will be five - 150 lb passengers
in your vehicle, the am ount of available cargo
and luggage load capacity is 650 lbs. [1400 -
750 (5 x 150) = 650 lbs.].
5. Determine the combined weight of luggage and cargo being loaded on the vehicle. That
weight may not safely exceed the available
cargo and luggage load ca pacity calculated in
Step 4.
Page 256 of 343

254
Maintenance and Car Care
Engine OilIt is important to perform oil changes regularly in
accordance with the intervals specified in your
Maintenance Schedule.Engine oil consumptionIt is normal for your engine to consume oil.
The rate of oil consumption depends on the quality
and viscosity of oil, the speed at which the engine
is operated, the climate, road conditions as well
as the amount of dilution and oxidation of the
lubricant.
If the vehicle is used for repeated short trips, and
consumes a normal amount of oil, the engine oil
measurement may not show any drop in the oil
level at all, even afte r 600 miles (1000 km) or
more. This is because the oil is gradually
becoming diluted with fuel or moisture, making it
appear that the oil level has not changed.
The diluting ingredients evaporate out when the
vehicle is driven at high speeds, as on an
expressway, making it then appear that oil is
excessively consumed after driving at high
speeds.
If the conditions you drive your vehicle in are
dusty, humid, or hot, the frequency of the oil
change intervals should be greater. If the vehicle is driven at a high rate of speed,
climatic conditions are warm, and the load is high,
the oil should be checked more frequently, as
driving conditions will de
termine the rate of oil
consumption.
– The engine in your vehicle depends on oil to lubricate and cool all of its moving parts.
Therefore, the engine oil should be checked
regularly and kept at the required level.
– Make it a habit to have the engine oil level checked with every refueling.
– The oil pressure warning light is not an oil level indicator.
The oil pressure warning light indicates serious
engine damage may be occuring when lit, if
engine rpm is above idle speed.
Checking Engine-Oil Levelf Check the oil level on the multi-function display
at regular intervals before refuelling.
f Please see the chapter “OIL LEVEL DISPLAY
AND MEASUREMENT OF THE ENGINE OIL
LEVEL” on page 121.
Warning!
Engine oil is hazardous to your health and
may be fatal if swallowed.
f Keep engine oil out of children's reach.
Used engine oil contains chemicals that have
caused cancer in laboratory animals.
f Always protect your skin by washing thoroughly with soap and water.
Top-up quantity
The difference between the minimum and
maximum marks on the segment display is
approx. 1.06 US quearts (1 liter).
One segment of the display corresponds to
a top-up quantity of approx. 0.26 US quarts
(0.25 liters).
f Never add more engine oil than required to
reach the maximum mark.