2008 NISSAN TIIDA low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 280 of 2771
AT-268
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
REPAIR FOR COMPONENT PARTS
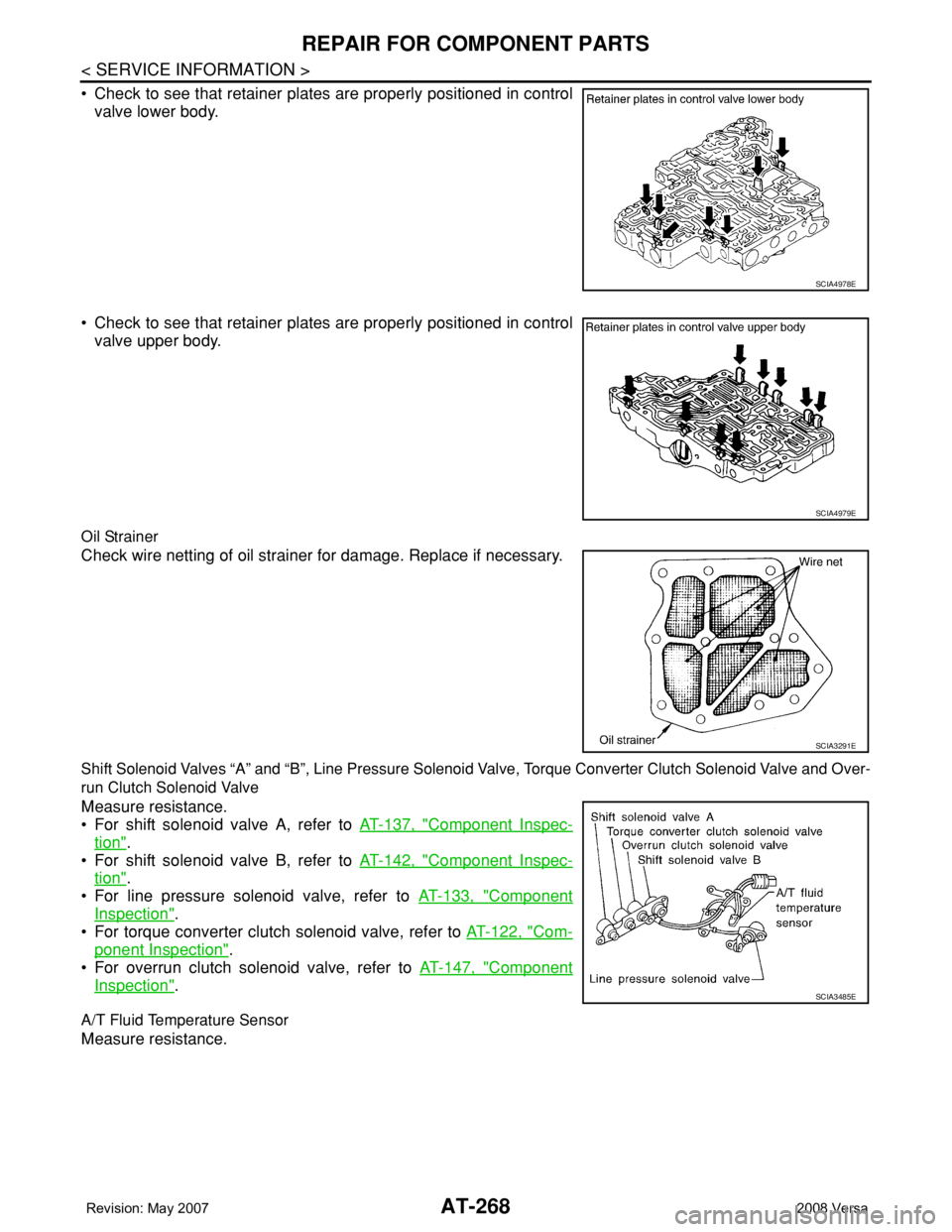
• Check to see that retainer plates are properly positioned in control
valve lower body.
• Check to see that retainer plates are properly positioned in control
valve upper body.
Oil Strainer
Check wire netting of oil strainer for damage. Replace if necessary.
Shift Solenoid Valves “A” and “B”, Line Pressure Solenoid Valve, Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve and Over-
run Clutch Solenoid Valve
Measure resistance.
• For shift solenoid valve A, refer to AT-137, "
Component Inspec-
tion".
• For shift solenoid valve B, refer to AT-142, "
Component Inspec-
tion".
• For line pressure solenoid valve, refer to AT-133, "
Component
Inspection".
• For torque converter clutch solenoid valve, refer to AT-122, "
Com-
ponent Inspection".
• For overrun clutch solenoid valve, refer to AT-147, "
Component
Inspection".
A/T Fluid Temperature Sensor
Measure resistance.
SCIA4978E
SCIA4979E
SCIA3291E
SCIA3485E
Page 281 of 2771

REPAIR FOR COMPONENT PARTS
AT-269
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
N
O
P
• For A/T fluid temperature sensor, refer to AT-156, "Component
Inspection".
Line Pressure Relief Valve Springs and Torque Converter Pressure Holding Spring
• Check each spring for damage or deformation. Also measure free
length and outer diameter. Refer to AT-343, "
Control Valves".
• Replace springs if deformed or fatigued.
ASSEMBLY
1. Install control valve upper, inter and lower body.
a. Place oil circuit of control valve upper body face up. Install steel
balls in their proper positions.
b. Install reamer bolts (F) from bottom of control valve upper body
(1). Using reamer bolts (F) as guides, install separating plate (2)
as a set.
SCIA7533E
SAT138D
SAT871J
SCIA7010E
Page 308 of 2771
AT-296
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
REPAIR FOR COMPONENT PARTS
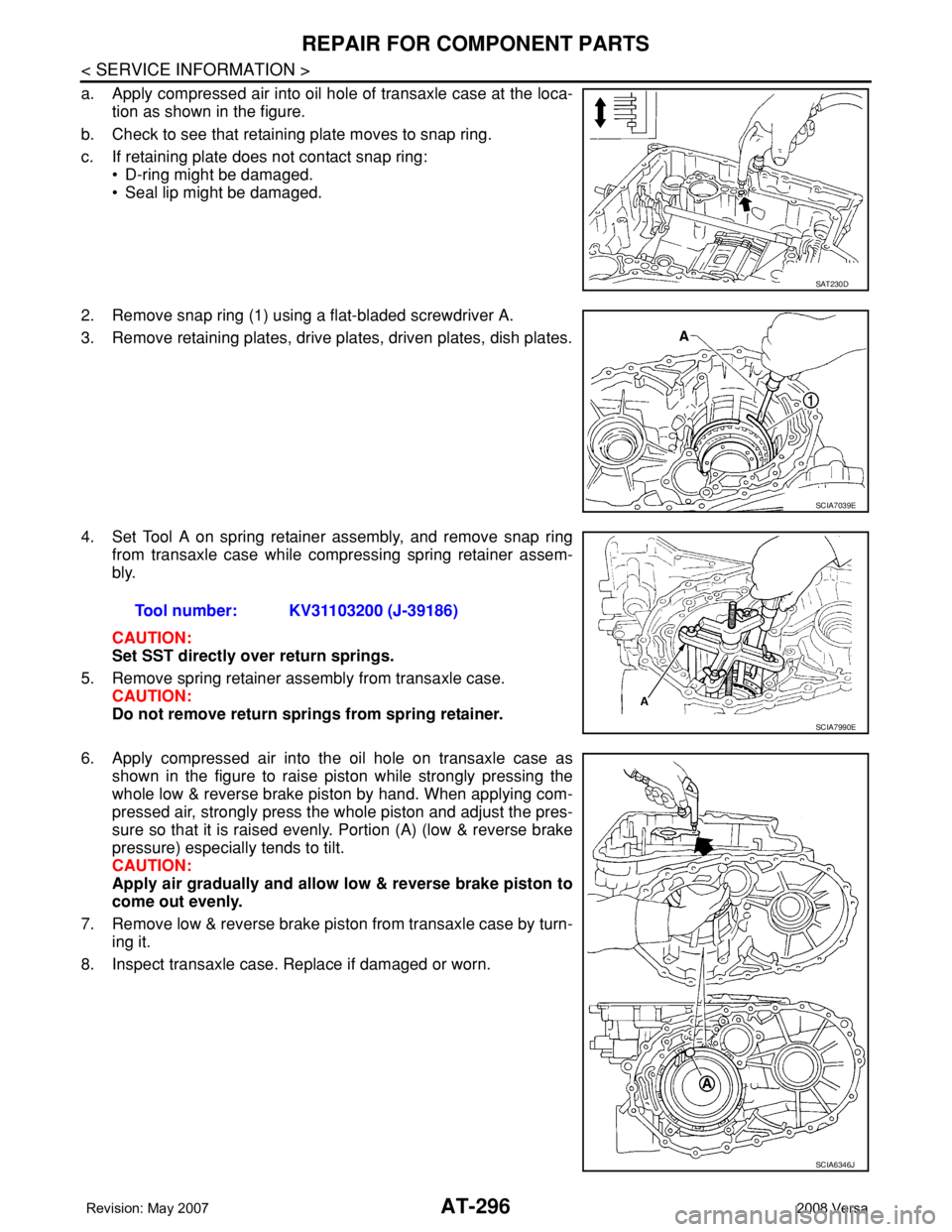
a. Apply compressed air into oil hole of transaxle case at the loca-
tion as shown in the figure.
b. Check to see that retaining plate moves to snap ring.
c. If retaining plate does not contact snap ring:
• D-ring might be damaged.
• Seal lip might be damaged.
2. Remove snap ring (1) using a flat-bladed screwdriver A.
3. Remove retaining plates, drive plates, driven plates, dish plates.
4. Set Tool A on spring retainer assembly, and remove snap ring
from transaxle case while compressing spring retainer assem-
bly.
CAUTION:
Set SST directly over return springs.
5. Remove spring retainer assembly from transaxle case.
CAUTION:
Do not remove return springs from spring retainer.
6. Apply compressed air into the oil hole on transaxle case as
shown in the figure to raise piston while strongly pressing the
whole low & reverse brake piston by hand. When applying com-
pressed air, strongly press the whole piston and adjust the pres-
sure so that it is raised evenly. Portion (A) (low & reverse brake
pressure) especially tends to tilt.
CAUTION:
Apply air gradually and allow low & reverse brake piston to
come out evenly.
7. Remove low & reverse brake piston from transaxle case by turn-
ing it.
8. Inspect transaxle case. Replace if damaged or worn.
SAT230D
SCIA7039E
Tool number: KV31103200 (J-39186)
SCIA7990E
SCIA6346J
Page 433 of 2771
BCM (BODY CONTROL MODULE)
BCS-17
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
BCS
N
O
P
WORK SUPPORT
Display Item List
CAN Communication Inspection Using CONSULT-III (Self-Diagnosis)INFOID:0000000001704591
1.SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULT CHECK
1. Connect CONSULT–III and select “BCM” on “SELECT SYSTEM” screen.
2. Select “BCM” on “SELECT TEST ITEM” screen, and select “SELF-DIAG RESULTS”.
3. Check display content in self-diagnostic results.
Contents displayed
No malfunction>>Inspection End
Malfunction in CAN communication system>>After printing the monitor items, go to “CAN System”. Refer to
LAN-15, "
Trouble Diagnosis Flow Chart".
ConfigurationINFOID:0000000001806223
DESCRIPTION
CONFIGURATION has three functions as follows:
• READ CONFIGURATION is the function to read (extract) vehicle configuration of current BCM.
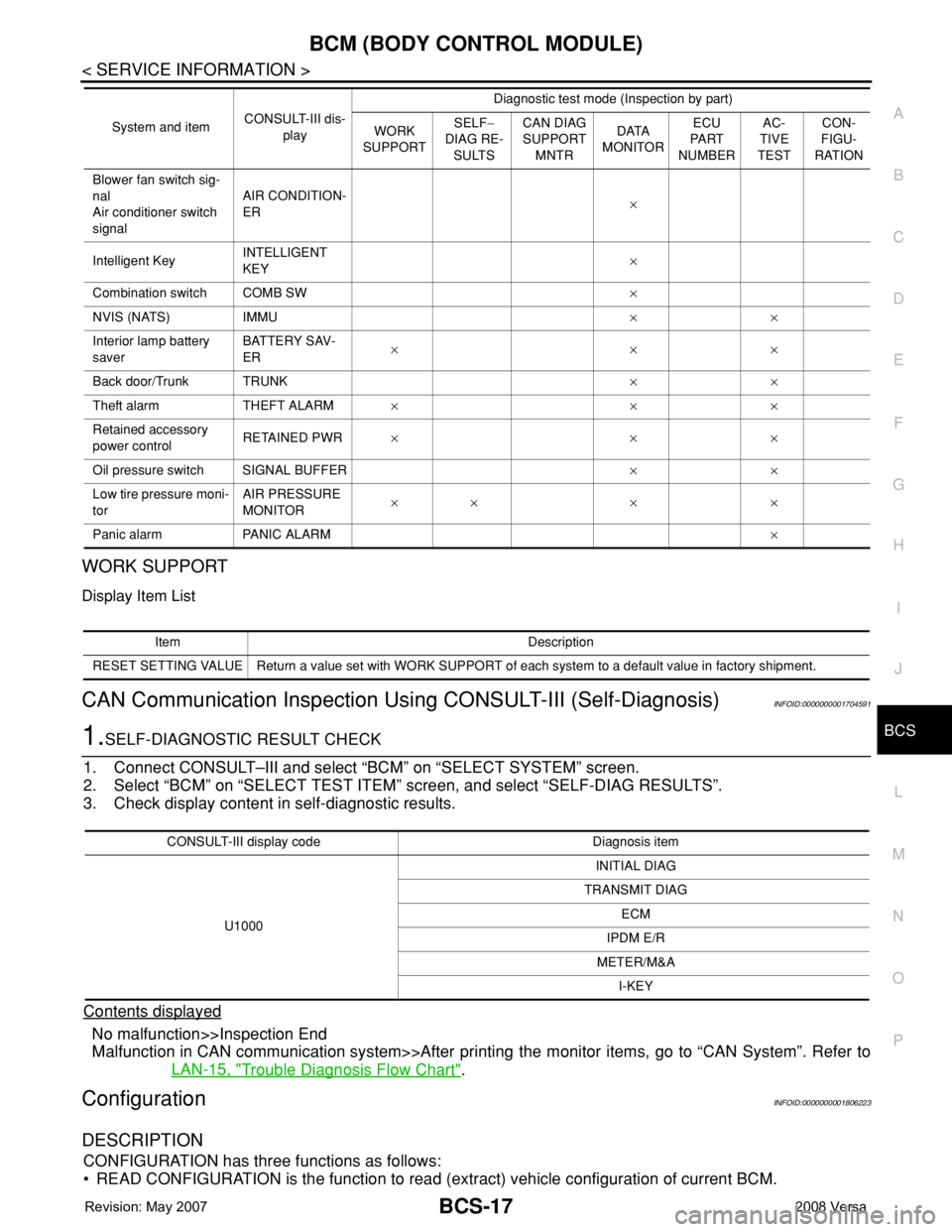
Blower fan switch sig-
nal
Air conditioner switch
signalAIR CONDITION-
ER×
Intelligent KeyINTELLIGENT
KEY×
Combination switch COMB SW×
NVIS (NATS) IMMU××
Interior lamp battery
saverBATTERY SAV-
ER×××
Back door/Trunk TRUNK××
Theft alarm THEFT ALARM×××
Retained accessory
power controlRETAINED PWR×××
Oil pressure switch SIGNAL BUFFER××
Low tire pressure moni-
torAIR PRESSURE
MONITOR×× × ×
Panic alarm PANIC ALARM× System and itemCONSULT-III dis-
playDiagnostic test mode (Inspection by part)
WORK
SUPPORTSELF−
DIAG RE-
SULTSCAN DIAG
SUPPORT
MNTRDATA
MONITORECU
PA R T
NUMBERAC-
TIVE
TESTCON-
FIGU-
RATION
Item Description
RESET SETTING VALUE Return a value set with WORK SUPPORT of each system to a default value in factory shipment.
CONSULT-III display code Diagnosis item
U1000INITIAL DIAG
TRANSMIT DIAG
ECM
IPDM E/R
METER/M&A
I-KEY
Page 805 of 2771

CL-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
NVH Troubleshooting ChartINFOID:0000000001703116
Use the chart below to help you find the cause of the symptom. The numbers indicate the order of the inspec-
tion. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
Reference pageCL-5CL-8EM-72CL-11CL-13EM-93
SUSPECTED PARTS (Possible cause)
CLUTCH PEDAL (Inspection and adjustment)
CLUTCH LINE (Air in line)
ENGINE MOUNTING (Loose)
CSC (Concentric slave cylinder) (Worn, dirty or damaged)
CLUTCH DISC (Out of true)
CLUTCH DISC (Runout is excessive)
CLUTCH DISC (Lining broken)
CLUTCH DISC (Dirty or burned)
CLUTCH DISC (Oily)
CLUTCH DISC (Worn out)
CLUTCH DISC (Hardened)
CLUTCH DISC (Lack of spline grease)
DIAPHRAGM SPRING (Damaged)
DIAPHRAGM SPRING (Out of tip alignment)
PRESSURE PLATE (Distortion)
FLYWHEEL (Distortion)
SymptomClutch grabs/chatters 1 2 2 2 2 2
Clutch pedal spongy 1
Clutch noisy 1
Clutch slips 1 2 2 3 4 5
Clutch does not disengage 12 55555 5667
Page 830 of 2771
RADIATOR
CO-13
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
CO
N
P O
Checking Radiator CapINFOID:0000000001702533
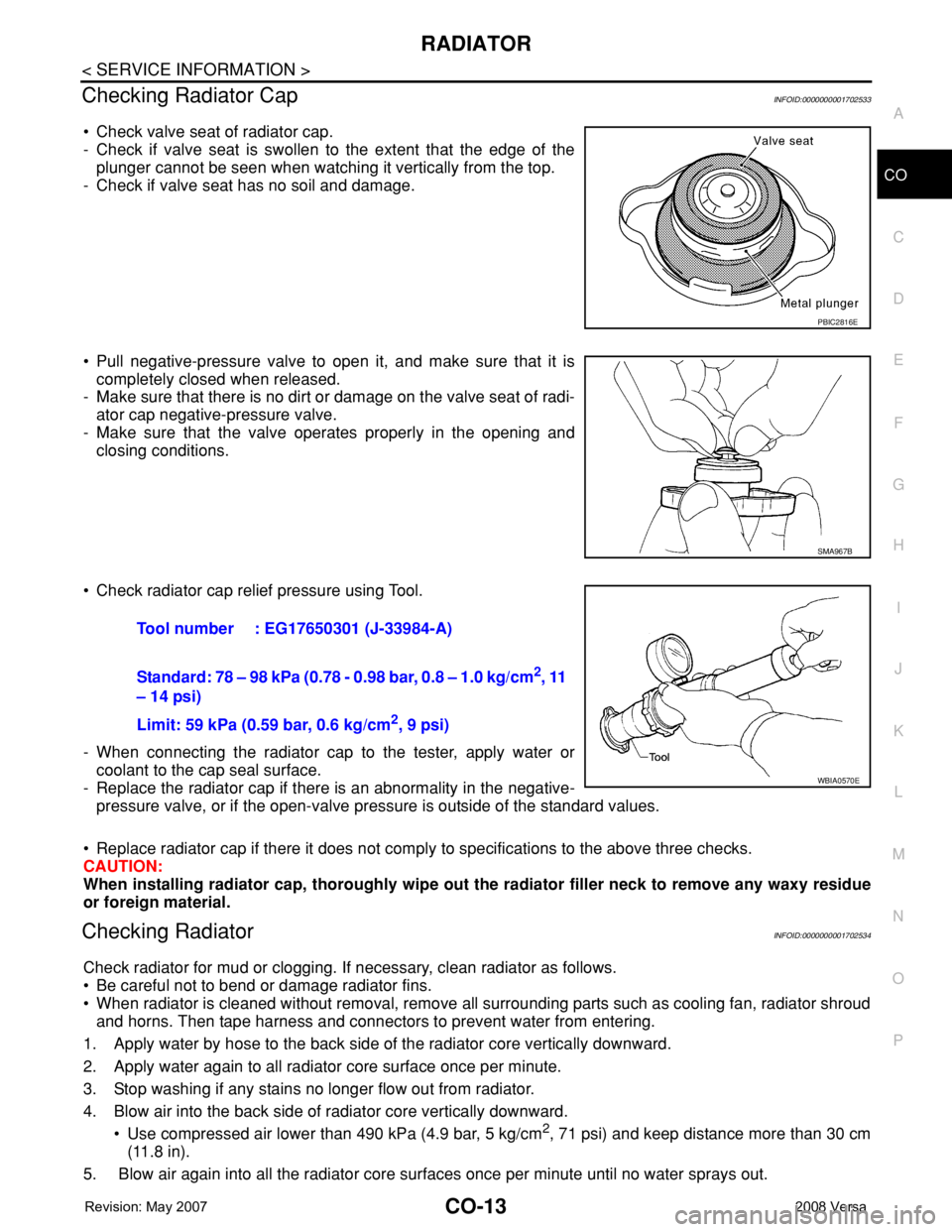
• Check valve seat of radiator cap.
- Check if valve seat is swollen to the extent that the edge of the
plunger cannot be seen when watching it vertically from the top.
- Check if valve seat has no soil and damage.
• Pull negative-pressure valve to open it, and make sure that it is
completely closed when released.
- Make sure that there is no dirt or damage on the valve seat of radi-
ator cap negative-pressure valve.
- Make sure that the valve operates properly in the opening and
closing conditions.
• Check radiator cap relief pressure using Tool.
- When connecting the radiator cap to the tester, apply water or
coolant to the cap seal surface.
- Replace the radiator cap if there is an abnormality in the negative-
pressure valve, or if the open-valve pressure is outside of the standard values.
• Replace radiator cap if there it does not comply to specifications to the above three checks.
CAUTION:
When installing radiator cap, thoroughly wipe out the radiator filler neck to remove any waxy residue
or foreign material.
Checking RadiatorINFOID:0000000001702534
Check radiator for mud or clogging. If necessary, clean radiator as follows.
• Be careful not to bend or damage radiator fins.
• When radiator is cleaned without removal, remove all surrounding parts such as cooling fan, radiator shroud
and horns. Then tape harness and connectors to prevent water from entering.
1. Apply water by hose to the back side of the radiator core vertically downward.
2. Apply water again to all radiator core surface once per minute.
3. Stop washing if any stains no longer flow out from radiator.
4. Blow air into the back side of radiator core vertically downward.
• Use compressed air lower than 490 kPa (4.9 bar, 5 kg/cm
2, 71 psi) and keep distance more than 30 cm
(11.8 in).
5. Blow air again into all the radiator core surfaces once per minute until no water sprays out.
PBIC2816E
SMA967B
Tool number : EG17650301 (J-33984-A)
Standard: 78 – 98 kPa (0.78 - 0.98 bar, 0.8 – 1.0 kg/cm
2, 11
– 14 psi)
Limit: 59 kPa (0.59 bar, 0.6 kg/cm
2, 9 psi)
WBIA0570E
Page 864 of 2771

CVT SYSTEM
CVT-25
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
CVT
N
O
P Lock-up and Select Control System Diagram
Lock-up Released
In the lock-up released state, the torque converter clutch control valve is set into the unlocked state by the
torque converter clutch solenoid and the lock-up apply pressure is drained.
In this way, the torque converter clutch piston is not coupled.
Lock-up Applied
In the lock-up applied state, the torque converter clutch control valve is set into the locked state by the torque
converter clutch solenoid and lock-up apply pressure is generated.
In this way, the torque converter clutch piston is pressed and coupled.
Select Control
When shifting between “N” (“P”)⇔“D” (“R”), optimize the operating pressure on the basis of the throttle posi-
tion, the engine speed, and the secondary pulley (output) revolution speed to lessen the shift shock.
Control ValveINFOID:0000000001703445
FUNCTION OF CONTROL VALVE
SCIA2374E
Name Function
Torque converter regulator valve Optimizes the supply pressure for the torque converter depending on driving conditions.
Pressure regulator valve Optimizes the discharge pressure from the oil pump depending on driving conditions.
TCC control valve• Activates or deactivate the lock-up.
• Lock-up smoothly by opening lock-up operation excessively.
TCC solenoid valve Controls the TCC control valve or select control valve.
Shift control valveControls flow-in/out of line pressure from the primary pulley depending on the stroke dif-
ference between the stepping motor and the primary pulley.
Secondary valve Controls the line pressure from the secondary pulley depending on operating conditions.
Clutch regulator valve Adjusts the clutch operating pressure depending on operating conditions.
Secondary pressure solenoid valve Controls the secondary valve.
Line pressure solenoid valve Controls the line pressure control valve.
Step motor Controls the pulley ratio.
Manual valveTransmits the clutch operating pressure to each circuit in accordance with the selected
position.
Select control valve Engages forward clutch, reverse brake smoothly depending on select operation.
Select switch valveSwitches torque converter clutch solenoid valve control pressure use to torque converter
clutch control valve or select control valve.
Lock-up select solenoid valve Controls the select switch valve.
Page 868 of 2771

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
CVT-29
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
CVT
N
O
P
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
DTC Inspection Priority ChartINFOID:0000000001703451
If some DTCs are displayed at the same time, perform inspections one by one based on the following priority
chart.
NOTE:
If DTC “U1000 CAN COMM CIRCUIT” is displayed with other DTCs, first perform the trouble diagnosis
for “DTC U1000 CAN COMMUNICATION LINE”. Refer to CVT-56
.
Fail-SafeINFOID:0000000001703452
The TCM has an electrical fail-safe mode. This mode makes it possible to operate even if there is an error in a
main electronic control input/output signal circuit.
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION
If any malfunction occurs in a sensor or solenoid, this function controls the CVT to make driving possible.
Output Speed Sensor (Secondary Speed Sensor)
The shift pattern is changed in accordance with throttle position when an unexpected signal is sent from the
output speed sensor (secondary speed sensor) to the TCM. The overdrive-off mode is inhibited, and the tran-
saxle is put in “D”.
Input Speed Sensor (Primary Speed Sensor)
The shift pattern is changed in accordance with throttle position and secondary speed (vehicle speed) when
an unexpected signal is sent from the input speed sensor (primary speed sensor) to the TCM. The sport mode
is inhibited, and the transaxle is put in “D”.
PNP Switch
If an unexpected signal is sent from the PNP switch to the TCM, the transaxle is put in “D”.
CVT Fluid Temperature Sensor
If an unexpected signal is sent from the CVT fluid temperature sensor to the TCM, the gear ratio in use before
receiving the unexpected signal is maintained or the gear ratio is controlled to keep engine speed under 3500
rpm.
Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor A (Secondary Pressure Sensor)
• If an unexpected signal is sent from the transmission fluid pressure sensor A (secondary pressure sensor) to
the TCM, the secondary pressure feedback control is stopped and the offset value obtained before the non-
standard condition occurs is used to control line pressure.
• If transmission fluid pressure sensor A (secondary pressure sensor) error signal is input to TCM, secondary
pressure feedback control stops, but line pressure is controlled normally.
Pressure Control Solenoid A (Line Pressure Solenoid)
If an unexpected signal is sent from the solenoid to the TCM, the pressure control solenoid A (line pressure
solenoid) is turned OFF to achieve the maximum fluid pressure.
Pressure Control Solenoid B (Secondary Pressure Solenoid)
If an unexpected signal is sent from the solenoid to the TCM, the pressure control solenoid B (secondary pres-
sure solenoid) is turned OFF to achieve the maximum fluid pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
If an unexpected signal is sent from the solenoid to the TCM, the torque converter clutch solenoid is turned
OFF to cancel the lock-up.
Ste p M oto r
If an unexpected signal is sent from the step motor to the TCM, the step motor coil phases “A” through “D” are
all turned OFF to hold the gear ratio used right before the non-standard condition occurred.
CVT Lock-up Select Solenoid
Priority Detected items (DTC)
1 U1000 CAN communication line
2 Except above