2008 GEELY CK battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 38 of 392

31Replacement1. Disconnect all the wire harnesses and the cables on the engine connected to the car body.
2. Detach air filter assembly with hose
3. Disconnect oil pipe and water hose
4. Loose positive and negative cables of the battery.
5. Detach propeller shaft. Detach front exhaust pipe assembly
6. Loose engine left & right rear brackets after hoisting the engine.
7. Disconnect all the other connectors between the engine and the car body.
8. See "Provision 20, Section 2, Chapter 2". Lift the car body and take out the engine assembly.
9. Remove A/C compressor to the crankshaft pulleyV-belt.
10. Remove power steering pump V-belt.
11. Detach water pump fan pulley.
12. Disconnect ignition coil and high voltage cable.
13. Detach cylinder head cover sub-assembly.
14. Detach generator assembly.
15. Detach the camshaft.
16. Detach the throttle body assembly
17. Detach intake manifold stay No. 2.
18. Take out the dipstick
19. Detach No. 1 fuel delivery pipe
20. Detach the wire harness.
21. Detach the steering assisting pump assembly
22. Detach exhaust manifold. See (Figure 71)
23. Pry cylinder head from the dowel pin on the cylinder block.
See (Figure 72)
24. Remove the cylinder head gasket.
25. Install cylinder head gasket
26. Install cylinder head sub-assembly
27. Install exhaust pipe assembly.
(a) Install the new gasket and exhaust manifold with 5
bolts. Torque: 34N. m
(b) Install exhaust manifold stay with 2 bolts.
(c) Install upper heat shield with 4 bolts
Torque: 17N. mFigure 71
Figure 72
Page 48 of 392

41Chapter 4 Fuel System
(MR7131A, MR7151A, MR7161A)Section 1 Check Fuel System Pressure1. Remove the fuel tank from the vehicle
2. Check the fuel pump running
(a) Connect the positive and negative battery terminal to the concerned
fuel pump connector. See (Figure 91).
Notice: Do not start engine
The sound of fuel flowing can be heard if there is pressure.
Check fusible link, fuse, EFI open circuit relay, fuel pump, ECU and
wire connector if there is no pressure.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to "OFF" position.
3. Check fuel pressure
(a) Check battery electrical pressure to be above 12V.
(b) Detach negative terminal cable from the battery.
(c) Install pressure gage from the fuel delivery pipe. See (Figure 92).
(d) Connect battery negative terminal.
(e) Measure fuel pressure
Fuel pressure:
304-343kPa
Check fuel pipe & union, fuel pump, fuel filter if the pressure is too
low.
(f) Start engine. Measure fuel pressure at idle. Fuel pressure: 304-343kPa
(g) Check fuel pressure and retain the pressure for approximately 5min after the engine stopped.
Fuel pressure: 147kPaFigure 91Figure 92
Page 49 of 392

42Section 2 Fuel Pump Inspection1. Fuel pump
(a) Check fuel pump resistance, 0.2~3.0 at 20°. Replace fuel pump if the resistance is not as specified.
See (Figure 93)
(b) Fuel pump running:
Check fuel pump by connecting with battery. Replace fuel pump or wire if the running is not as specified.
See (Figure 94).
The test should be conducted within 10s to prevent coil from damage.
2. Fuel injector assembly
Injection Volume: 40~50cm3/s
Error between each injector: less than 10 cm3Replace injector if the injection volume is not as specified.
(a) Check for leakage: Disconnect the cable from the battery. The fuel drop/min is no more than 1 drop.
Figure 93 Figure 94 Ohmmeter
Battery Ω
Page 60 of 392
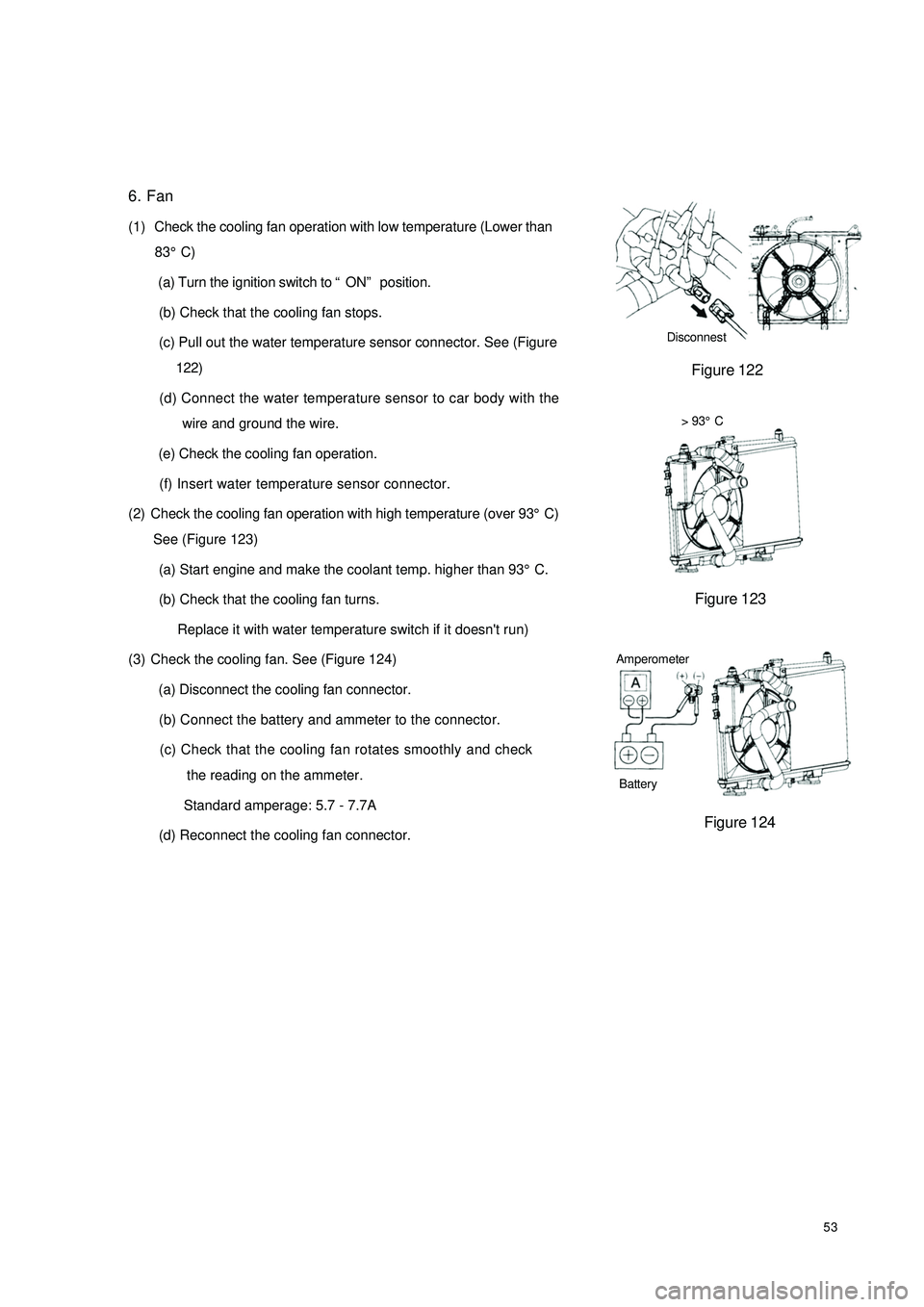
536. Fan
(1) Check the cooling fan operation with low temperature (Lower than
83°C)
(a) Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
(b) Check that the cooling fan stops.
(c) Pull out the water temperature sensor connector. See (Figure
122)
(d) Connect the water temperature sensor to car body with the
wire and ground the wire.
(e) Check the cooling fan operation.
(f) Insert water temperature sensor connector.> 93°C
See (Figure 123)
(a) Start engine and make the coolant temp. higher than 93°C.
(b) Check that the cooling fan turns.
Replace it with water temperature switch if it doesn't run)
(3) Check the cooling fan. See (Figure 124)
(a) Disconnect the cooling fan connector.
(b) Connect the battery and ammeter to the connector.
(c) Check that the cooling fan rotates smoothly and check
the reading on the ammeter.
Standard amperage: 5.7 - 7.7A
(d) Reconnect the cooling fan connector.Disconnest
Figure 123
Figure 124 Figure 122
(2) Check the cooling fan operation with high temperature (over 93°C)Battery Amperometer
Page 67 of 392

60Section 1 Manual Transaxle Replacement1. Open the engine hood
2. Remove the battery
3. Remove clutch cylinder sub-assembly. See (Figure 140)
4. Detach transmission shift cable assembly. See (Figure 141)
5. Remove the connector and turn on the back-up lamp switch connector.
6. Disconnect vehicle speed sensor
Disconnect vehicle speed sensor connector.
7. Detach the front exhaust pipe
8. Drain transmission oil
9. Detach left & right front wheel hub nut
10. Detach left & right front wheel speed sensor (ABS)
11. Detach front balance rod
12. Detach left & right tie-rod with ball stud pin
13. Detach front balance rod
14. Detach left & right lower swing arm
15. Detach left & right front propeller assembly
16. Hoist the engine from compartment. See "Provision 20, Section 2, Chapter 2"
17. Detach starter assembly
18. Detach engine mounting bracket
19. Detach manual transaxle assembly
20. Install engine mounting bracket
21. Install manual transaxle assembly
22. Connect engine vibration insulating cushions
23. Install starter assembly
24. Install left & right front propeller assembly
25. Connect left & right lower swing arm
26. Connect left & right tie-rod with ball stud pin
27. Connect front balance rod
28. Connect left & right front speed sensor (ABS)
29. Installleft & right front shaft nut
30. Install front exhaust pipe
31. Connect speedometer sensor connector.
32. Connect back-up lamp switch connector.
33. Connect transmission shift cable assembly. See (Figure 141)
34. Install clutch sub-pump assembly. See (Figure 140)Figure 140
Figure 141
Page 71 of 392

64Chapter 9 General Engine Troubles and Their
TroubleshootingSection 1 Overview The wide application of the electronic technologies to the vehicles brings innovation on diagnosis of the
vehicle, many varieties of diagnosis instruments that are very effective and efficient for the vehicle diagnosis
are innovated. Once the fault occurs, the best choice is to go to service station for help. However, even the
most advanced instrument has its limit. For some faults, manual diagnosis is far more convenient and easier
than that of instrument. In case of the crack, distortion and leakage of the components, the manual diagnosis
is even superior to the instrument diagnosis. The faults occurred shall be carefully analyzed and troubleshot
in accordance with the repair manual for normal usage.Section 2 General Engine Fault and TroubleshootingI. Fuel pipeline and circuit fault causing the engine starting failureengine starting failure normally include: starter does not run or starter runs but fails to crank the engine, or
cranks the engine but cranks slowly; starter can crank but fail to start the engine. There are many causes that
result in starting failure, such as failures in starting system, ignition system, fuel injection system and engine
mechanical failure.
1. starter does not run or fails to crank the engine or cranks slowly
(1) Symptom: starter does not run or spongy rotation
(2) Causes:
b. Low battery voltage, excessive battery discharge, damaged generator or failure in charging circuit;
c. Battery terminal rust and backed out;
d. Failure in starting circuit, ECU can not receive STA signal;
e. Damaged starter.
2. engine can not start and crank
(1) Symptom
With the start switch on, starter can crank but fail to start the engine.
(2) Causes
a. Empty fuel tank;
b. Electrical fuel pump inoperative;
c. Injector inoperative;
d. Low fuel pressure;
e. Unreasonable starting operation;
f. Damaged throttle position sensor or no signal is sent to ECU due to the open in throttle position
sensor circuit;
Page 73 of 392

66f. The idle control valve is faulty;
g. The water temperature sensor is damaged;
h. The vacuum pressure sensor is damaged;
i. The air filter is blocked;
j. The injector leaks;
k. The compression pressure in the cylinder is too low;
l. The intake temperature sensor is damaged.
(3) Diagnosis and Troubleshooting
a. Check high pressure spark, check whether the high pressure spark on the ignition coil high pressure
bus and extension are OK, if the bus spark is week, replace the ignition coil, if the bus spark is OK
while the extension spark is too week, replace the ignition coil also; In addition, excessive spark
plug clearance will influence the starting feature, the clearance of the spark plug shall be adjusted
to normal value (0.8±0.1mm);
b. If there is low fuel pressure, check whether the battery voltage is OK, otherwise it shall be
troubleshot or replaced; check fuel pump check valve for leakage, check fuel filter and fuel pipe for
block, if there are leakage or block, replace or troubleshoot them;
c. If there is leakage for fuel pressure regulator, intake manifold is likely to be mixed with gasoline and
it is hard to start, troubleshoot or replace them;
d. Idle control valve can not be opened to maximum position due to mechanical wear, aging or control
circuit failure, the idle control valve shall be replaced and the control circuit failure shall be troubleshot;
e. If the water temperature sensor data is not accurate, it may cause small injection, check the water
temperature sensor based on the standard data and calibrate the data;
f. There is big time lag for intake pressure temperature sensor that makes it somewhat insensitive at
low speed and result in inaccurate injection, adjustment or replacement shall be made;
g. If the air cleaner filter is too dirty, the air flow resistance is excessively big, resulting in hard start,
as a result of it, the filter shall be replaced.
In a word, there are many factors causing the starting failure of the engine, analysis shall be made based on
the severe conditions of the faults. Generally speaking, check the ignition system first, then check intake
system, fuel system, control system, at last check the cylinder pressure, check the DTC before checking the
trouble. The diagnosis and troubleshooting procedures for starting failure of the engine are shown in (Figure
148).
Page 90 of 392

83ECU microcomputer consists of microprocessor, memory, clock generator, timer, I/O interface and input
level A/D converter that are integrated in a large scale integrated circuit chip, that is SCM (Single Chip
Microcomputer).
1. Input level
The input signals from the sensor are pre-processed by the input level. The input signals are sent to protected
circuit first, sometimes through the signal converter and amplifier, and then sent to microcomputer.
The sensor signal is separated into switch type and analog type. Ignition on/off signal, camshaft position
signal, vehicle speed signal and A/C signal are switch type; Signals such as battery voltage, engine temperature,
intake temperature, airflow, intake manifold absolute pressure, throttle opening, excessive air coefficient,
knock, A/C refrigerant pressure are analog type. Analogy signal can only be processed by the digital micro-
computer after being converted into digital signal by A/D converter. Hence, data collection shall be made
first for analog signal, and the sampling shall be maintained also.
Speed and crankshaft position reference signal from the sensor is processed in a dedicated circuit to restrain
the interference pulse.
2. Microcomputer
The microcomputer of the engine electronic control unit is integrated in a single chip microcomputer, consist-
ing of the following:
(1) Microprocessor, microprocessor is also called as central processing unit (CPU), consisting of the following
three parts:
Arithmetic logic unit.
Register group.
Controller.
(2) System assembly, The data transferred among the internal sections of the single chip microcomputer
(SCM) is performed on the internal bus, while that between the SCM and other components is performed
on the external bus. The external bus is also called system bus. It is separated into data bus, address bus
and control bus.
(3) Memory, the memory is designed to store the binary data. The primary components of the memory are:
Memory.
Data register.
Address register, address decoder.
a. Memory controller
(4) A/D converter
(5) I/O interface.
(6) Clock generator.
(7) Timer
(8) CAPCOM unit.
(9) Watchdog timer.
(10) Interrupt system.