2007 SUZUKI SWIFT Signals
[x] Cancel search: SignalsPage 62 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-12 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Electronic Control System DescriptionS7RS0B1101011
The electronic control system consists of 1) various sensors which detect the state of engine and driving conditions, 2)
ECM which controls various devices ac cording to the signals from the sensors and 3) various controlled devices.
Functionally, it is divided into the following sub systems:
• Fuel injection control system
• Ignition control system
• Electric throttle body control system
• Fuel pump control system
• Radiator cooling fan control system
• Evaporative emission control system
• EGR system
• Oxygen sensor heater control system
• A/C control system (A/C model)
• Camshaft position control system
• Immobilizer control system
• Generator control system
• Controller (computer) communication system
Especially, ECM, BCM, combination meter, TCM (A/T model), ABS/ESP ® control module, steering angle sensor
(ESP® model) and keyless start control module (if equipped) intercommunicate by means of CAN communication.
Page 86 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-36 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
O2S B1 S1 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-1,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates activation condition of HO2S-1.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
O2S SENSOR B1 S2 (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
V)
It indicates output voltage of HO2S-2 installed on
exhaust pipe (post-catalyst). It is used to detect catalyst
deterioration.
O2S B1 S2 ACT (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR-2,
ACTIVE / INACTIVE)
This parameter indicates acti vation condition of HO2S-2.
ACTIVE: Activating
INACTIVE: warming up or at stop
FUEL SYSTEM (FUEL SYSTEM STATUS)
Air/fuel ratio feedback loop status displayed as one of
the followings.
OPEN: Open-loop has not yet satisfied conditions to go
closed loop.
CLOSED: Closed-loop using oxygen sensor(s) as
feedback for fuel control.
OPEN-DRIVE COND: Open-loop due to driving
conditions (Power enrichment, etc.).
OPEN SYS FAULT: Open-loop due to detected system
fault.
MAP (MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE, in.Hg,
kPa)
This value indicates how much correction is necessary
to keep the air/fuel mixture stoichiometrical.
It is detected by manifold absolute pressure sensor.
BAROMETRIC PRESS (kPa, in.Hg)
This parameter represents a measurement of barometric
air pressure and is used for al titude correction of the fuel
injection quantity and IAC valve control.
STEP EGR FLOW DUTY (%)
This parameter indicates opening rate of EGR valve
which controls the amount of EGR flow.
FUEL CUT (ON/OFF)
ON: Fuel being cut (output signal to injector is stopped)
OFF: Fuel not being cut
A/C PRESSURE (A/C REFRIGERANT ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE, kPa)
This parameter indicates A/C refrigerant absolute
pressure calculated by ECM.
CLOSED THROTTLE PO S (CLOSED THROTTLE
POSITION, ON/OFF)
This parameter reads ON wh en throttle valve is fully
closed, or OFF when it is not fully closed. CANIST PRG DUTY (EVAP CANISTER PURGE FLOW
DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates valve ON (valve open) time
rate within a certain set cycle of EVAP canister purge
valve which controls the amount of EVAP purge.
IGNITION ADVANCE (IGNITION TIMING ADVANCE
FOR NO.1 CYLINDER,
°)
Ignition timing of No.1 cylinder is commanded by ECM.
The actual ignition timing should be checked by using
the timing light.
BATTERY VOLTAGE (V)
This parameter indicates battery positive voltage
inputted from main relay to ECM.
FUEL PUMP (ON/OFF)
ON is displayed when ECM activates the fuel pump via
the fuel pump relay switch.
ELECTRIC LOAD (ON/OFF)
ON: Headlight or small light ON signal inputted.
OFF: Above electric loads all turned OFF.
BRAKE SW (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the brake switch.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN (RADIATOR COOLING
FAN CONTROL RELAY, ON/OFF)
ON: Command for radiator cooling fan control relay
operation being output.
OFF: Command for relay operation not being output.
BLOWER FAN (ON/OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the blower fan
motor switch.
A/C SWITCH (ON/OFF)
ON: Command for A/C operatio n being output from ECM
to HVAC.
OFF: Command for A/C oper ation not being output.
A/C COMP RELAY (A/C COMPRESSOR RELAY, ON/
OFF)
This parameter indicates the state of the A/C switch.
VEHICLE SPEED (km/h, mph)
It is computed based on pulse signals from vehicle
speed sensor.
VVT GAP (TARGET-ACTUAL POSITION, °)
It is calculated using the formula: target valve timing
advance – actual valve timing advance.
TP SENSOR 1 VOLT (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(MAIN) OUTPUT VOLTAGE, V)
The TP sensor (main) reading provides throttle valve
opening information in the form of voltage.
Page 162 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-112 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
System Description
The CMP sensor located on the transmission side of cylinder head consists of the signal generator (magnetic sensor)
and signal rotor (intake camshaft portion).
The signal generator generates reference signal through slits in the slit plate which turns together with the camshaft.
Reference signal
The CMP sensor generates 6 pulses of si gnals each of which has a different waveform length while the camshaft
makes one full rotation. Refer to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
Based on these signals, ECM judges which cylinder pist on is in the compression stroke and the engine speed.
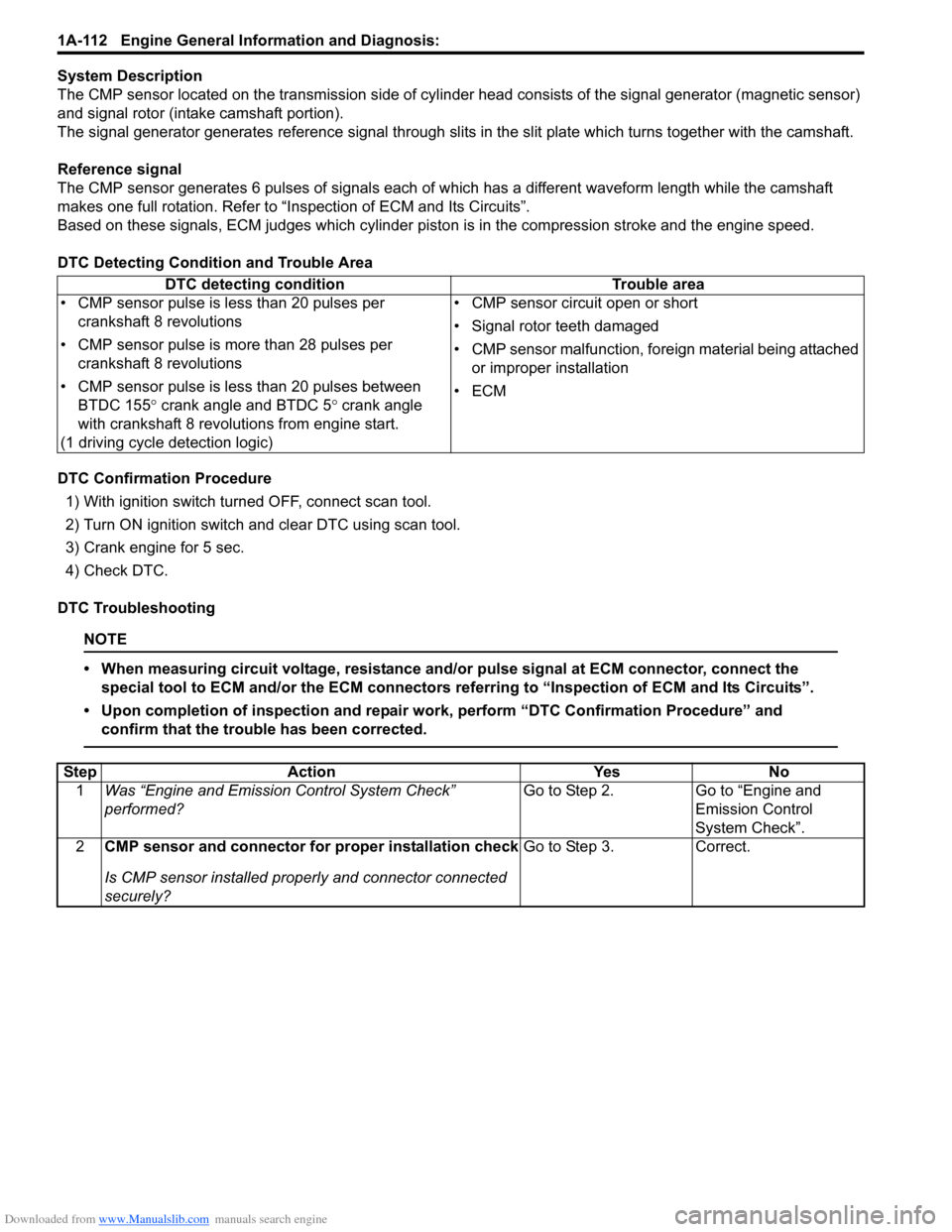
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure 1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Crank engine for 5 sec.
4) Check DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/ or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work, perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm that the trouble has been corrected.
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
• CMP sensor pulse is less than 20 pulses per crankshaft 8 revolutions
• CMP sensor pulse is more than 28 pulses per crankshaft 8 revolutions
• CMP sensor pulse is less than 20 pulses between BTDC 155 ° crank angle and BTDC 5 ° crank angle
with crankshaft 8 revolutions from engine start.
(1 driving cycle detection logic) • CMP sensor circuit open or short
• Signal rotor teeth damaged
• CMP sensor malfunction, foreign material being attached
or improper installation
•ECM
Step Action YesNo
1 Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed? Go to Step 2.
Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2 CMP sensor and connector for proper installation check
Is CMP sensor installed properly and connector connected
securely? Go to Step 3.
Correct.
Page 288 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-3 Engine Mechanical:
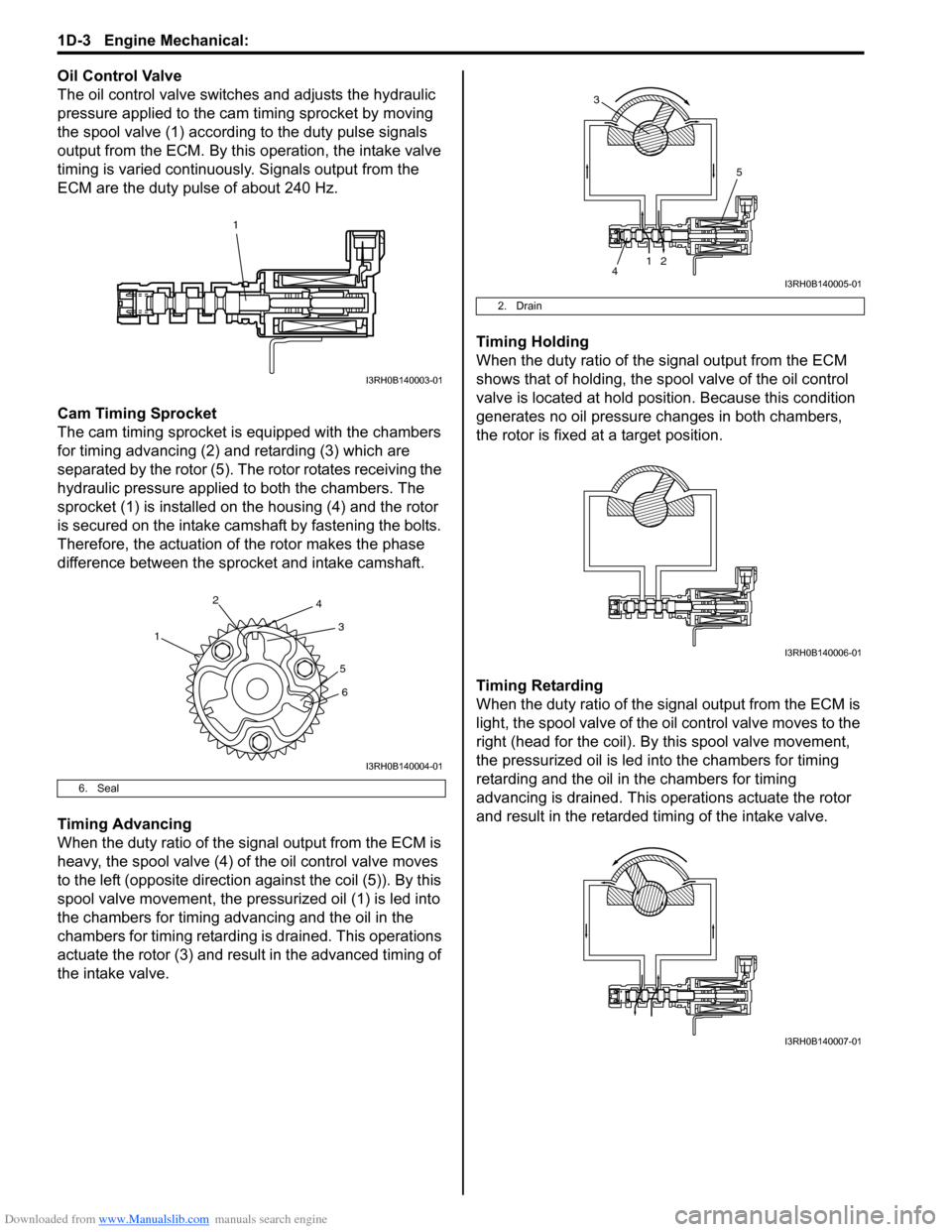
Oil Control Valve
The oil control valve switches and adjusts the hydraulic
pressure applied to the cam timing sprocket by moving
the spool valve (1) according to the duty pulse signals
output from the ECM. By this operation, the intake valve
timing is varied continuously. Signals output from the
ECM are the duty pulse of about 240 Hz.
Cam Timing Sprocket
The cam timing sprocket is equipped with the chambers
for timing advancing (2) and retarding (3) which are
separated by the rotor (5). The rotor rotates receiving the
hydraulic pressure applied to both the chambers. The
sprocket (1) is installed on the housing (4) and the rotor
is secured on the intake camshaft by fastening the bolts.
Therefore, the actuation of the rotor makes the phase
difference between the sprocket and intake camshaft.
Timing Advancing
When the duty ratio of the signal output from the ECM is
heavy, the spool valve (4) of the oil control valve moves
to the left (opposite direction against the coil (5)). By this
spool valve movement, the pressurized oil (1) is led into
the chambers for timing advancing and the oil in the
chambers for timing retarding is drained. This operations
actuate the rotor (3) and result in the advanced timing of
the intake valve. Timing Holding
When the duty ratio of the si
gnal output from the ECM
shows that of holding, the sp ool valve of the oil control
valve is located at hold posi tion. Because this condition
generates no oil pressure changes in both chambers,
the rotor is fixed at a target position.
Timing Retarding
When the duty ratio of the sig nal output from the ECM is
light, the spool valve of the o il control valve moves to the
right (head for the coil). By this spool valve movement,
the pressurized oil is led into the chambers for timing
retarding and the oil in the chambers for timing
advancing is drained. This operations actuate the rotor
and result in the retarded timing of the intake valve.
6. Seal
1
I3RH0B140003-01
1 2
3
4
56
I3RH0B140004-01
2. Drain
12
5
4
3
I3RH0B140005-01
I3RH0B140006-01
I3RH0B140007-01
Page 393 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-1
Engine
Ignition System
General Description
Ignition System ConstructionS7RS0B1801001
The ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below.
• ECM
It detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the si gnals from the sensors, determines the most suitable
ignition timing and time for electricity to flow to the primar y coil and sends a signal to the ignitor (power unit) in the
ignition coil assembly.
• Ignition coil assembly (including an ignitor)
The ignition coil assembly has a built -in ignitor which turns ON and OFF the current flow to the primary coil
according to the signal from ECM. When the current flow to the primary coil is turned OFF, a high voltage is induced
in the secondary coil.
• High-tension cords and spark plugs
• CMP sensor (Camshaft position sensor) and CKP sensor (Crankshaft position sensor)
Using signals from these sensors, ECM identifies the specific cylinder whose piston is in the compression stroke,
detects the crank angle and adjusts in itial ignition timing automatically.
• TP sensor, ECT sensor, MAP sensor, MAF sensor, IAT sensor, knock sensor and other sensors / switches
Although this ignition system does not have a distributor, it has two ignition coil assemblies (one is for No.1 and No.4
spark plugs and the other is for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs). W hen an ignition signal is sent from ECM to the ignitor in
the ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs, a high voltage is induced in the secondary coil and that
passes through the high-tension cords and causes No.1 and No.4 spark plugs to spark simultaneously. Likewise,
when an ignition signal is sent to the ignitor in the ot her ignition coil assembly, No.2 and No.3 spark plugs spark
simultaneously.
Page 397 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-5
6Ignition coil assembly power supply and ground circuit
check
1) Check ignition coil assembly power supply and ground
circuits for open and short.
Are circuits in good condition? Go to Step 7.
Repair or replace.
7 Ignition coil assembly check
1) Check ignition coil for resistance referring to “Ignition
Coil Assembly (Including ignitor) Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 8.
Replace ignition coil
assembly.
8 CKP sensor check
1) Check CKP sensor referring to “CKP Sensor Inspection
in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 9.
Tighten CKP sensor
bolt, replace CKP
sensor or CKP sensor
plate.
9 CMP sensor check
1) Check CMP sensor referring to “Camshaft Position
(CMP) Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 10. Tighten CMP sensor
bolt, replace CMP
sensor or intake
camshaft.
10 Ignition trigger signal circuit check
1) Check ignition trigger signal wire for open, short and
poor connection.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 11. Repair or replace.
11 A known-good ignition coil assembly substitution
1) Substitute a known-good ignition coil assembly and then
repeat Step 2.
Is check result of Step 2 satisfactory? Go to Step 12. Substitute a known-
good ECM and then
repeat Step 2.
12 Knock sensor check
1) Confirm that knock sensor circuit is in good condition
referring to “DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High in Section 1A”.
2) Check oscilloscope waveform of knock sensor signal
referring to “Reference waveform No.25” and
“Reference waveform No.26” under “Inspection of ECM
and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 13. Substitute a known-
good knock sensor and
recheck.
13 Ignition timing check
1) Check initial ignition timing and ignition timing advance
referring to “Ignition Timing Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? System is in good
condition.
Check CMP sensor,
CMP sensor rotor tooth
of camshaft, CKP
sensor, CKP sensor
plate and/or input
signals related to this
system.
Step
Action YesNo
Page 577 of 1496
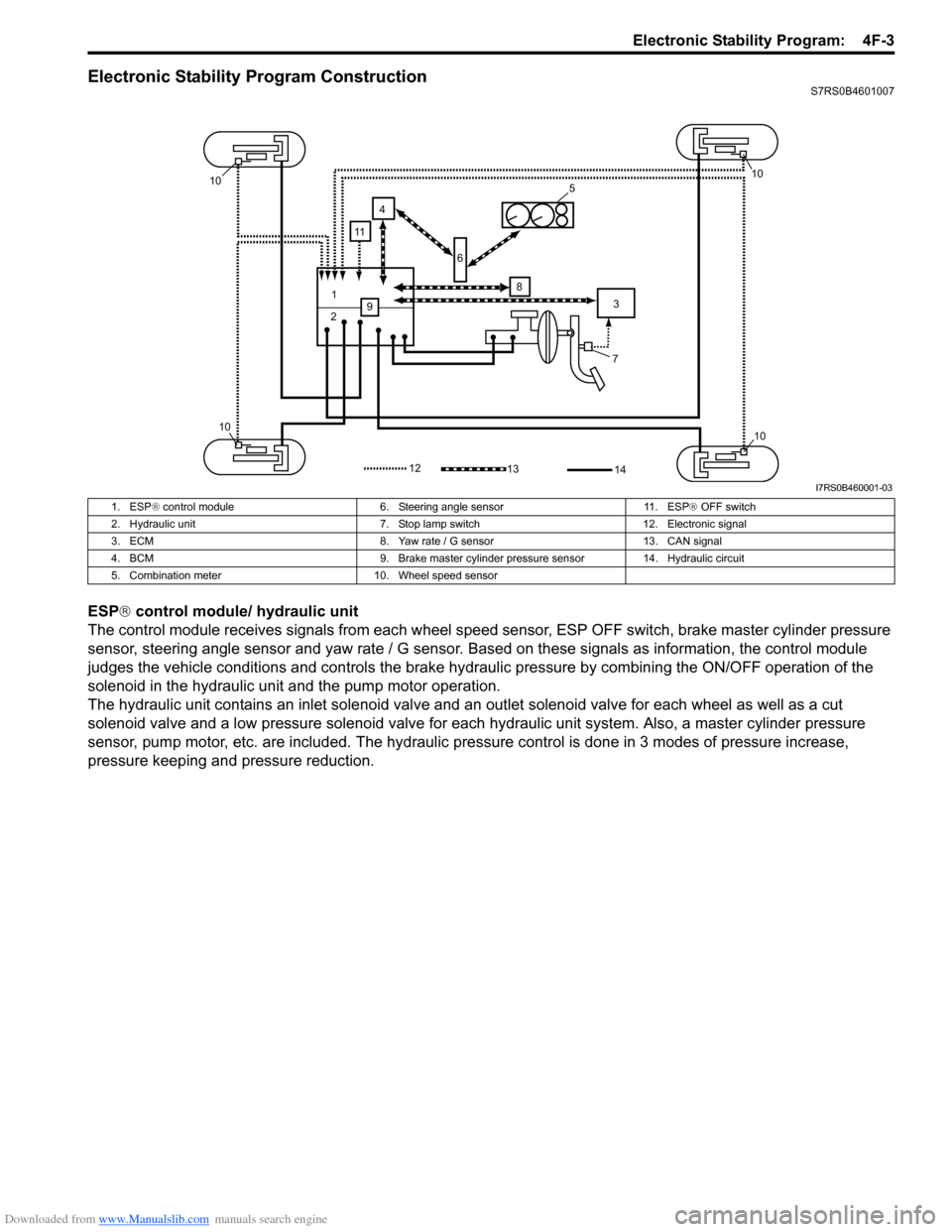
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-3
Electronic Stability Program ConstructionS7RS0B4601007
ESP® control module/ hydraulic unit
The control module receives signals from each wheel speed sensor, ESP O FF switch, brake master cylinder pressure
sensor, steering angle sensor and yaw rate / G sensor. Ba sed on these signals as information, the control module
judges the vehicle conditions and controls the brake hydraulic pressure by combining the ON/OFF operation of the
solenoid in the hydraulic unit and the pump motor operation.
The hydraulic unit contains an inlet so lenoid valve and an outlet solenoid valve for each wheel as well as a cut
solenoid valve and a low pressure solenoid valve for each hydraulic unit system. Also, a master cylinder pressure
sensor, pump motor, etc. are included. The hydraulic pre ssure control is done in 3 modes of pressure increase,
pressure keeping and pressure reduction.
7
1
2 3
4
5
6
8
9
10
1010
10
1312
11
14
I7RS0B460001-03
1. ESP ® control module 6. Steering angle sensor 11. ESP ® OFF switch
2. Hydraulic unit 7. Stop lamp switch 12. Electronic signal
3. ECM 8. Yaw rate / G sensor 13. CAN signal
4. BCM 9. Brake master cylinder pre ssure sensor 14. Hydraulic circuit
5. Combination meter 10. Wheel speed sensor
Page 579 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-5
Yaw rate / G sensor
The yaw rate / G sensor consists of the yaw rate (angular velocity in the vehicle turning direction) sensor and right-left
G (acceleration in right-left direction) sensor and is mounted to the P/S controller B/K at the lower part of the center
console. It detects the angular velocity in the vehicle turn ing direction and movement in the right-left direction, and
then it sends that information to ESP ® control module.
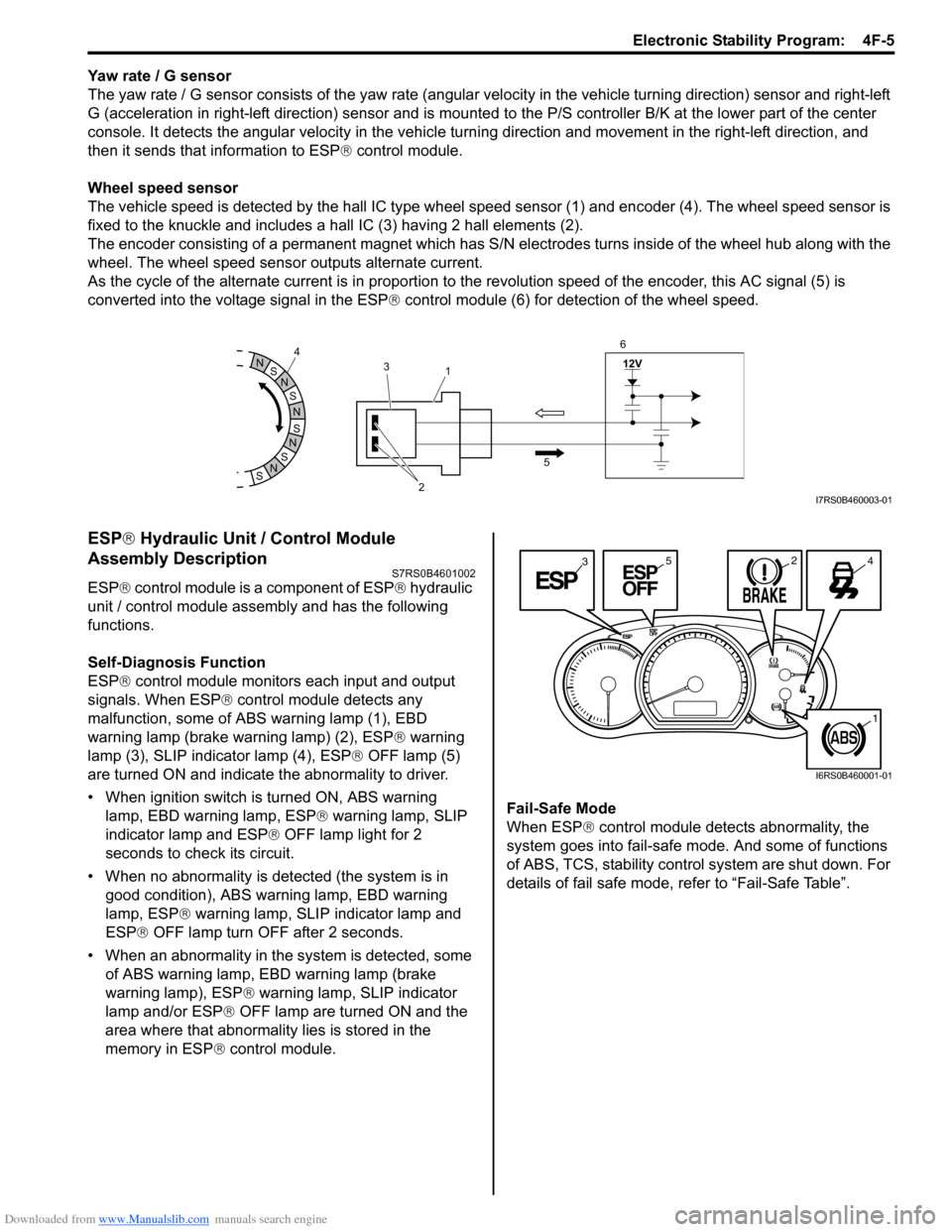
Wheel speed sensor
The vehicle speed is detected by the hall IC type wheel speed sensor (1) and encoder (4). The wheel speed sensor is
fixed to the knuckle and includes a hall IC (3) having 2 hall elements (2).
The encoder consisting of a permanent ma gnet which has S/N electrodes turns inside of the wheel hub along with the
wheel. The wheel speed sensor outputs alternate current.
As the cycle of the alternate current is in proportion to the revolution speed of the encoder, this AC signal (5) is
converted into the voltage signal in the ESP ® control module (6) for detection of the wheel speed.
ESP ® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Description
S7RS0B4601002
ESP ® control module is a component of ESP ® hydraulic
unit / control module assembly and has the following
functions.
Self-Diagnosis Function
ESP ® control module monitors each input and output
signals. When ESP ® control module detects any
malfunction, some of ABS warning lamp (1), EBD
warning lamp (brake warning lamp) (2), ESP ® warning
lamp (3), SLIP indicator lamp (4), ESP ® OFF lamp (5)
are turned ON and indicate the abnormality to driver.
• When ignition switch is turned ON, ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP
indicator lamp and ESP ® OFF lamp light for 2
seconds to check its circuit.
• When no abnormality is detected (the system is in good condition), ABS warning lamp, EBD warning
lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator lamp and
ESP ® OFF lamp turn OFF after 2 seconds.
• When an abnormality in the system is detected, some of ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp (brake
warning lamp), ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator
lamp and/or ESP ® OFF lamp are turned ON and the
area where that abnormality lies is stored in the
memory in ESP ® control module. Fail-Safe Mode
When ESP
® control module detects abnormality, the
system goes into fail-safe mode. And some of functions
of ABS, TCS, stability control system are shut down. For
details of fail safe mode, re fer to “Fail-Safe Table”.
S
N
S
N
S
N
N
S
N
S
12V
2
3
1
5
4
6I7RS0B460003-01
3245
1
I6RS0B460001-01