2007 ISUZU KB P190 battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 3732 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–71
11 Service Operations
11.1 Safety and Precautionary Measures
The following safety and precautionary
measures must be followed when servicing
and diagnosing the powertrain interface
module (PIM) System. Otherwise, personal
injury and / or improper braking system
operation may occur:
• W hen using electric welding equipment, disconnect the wiring harness connector from the PIM.
• Never disconnect or reconnect the PIM wiring harness connector when the ignition is switched ON.
• Do not touch the PIM connector pins or soldered components on the PIM circuit board to prevent possible
Electrostatic Discharge damage.
• To avoid wiring connector terminal damage, always use suitable wiring harness test leads (such as those in Tool
No, J35616) when performing tests on the PIM wiring connector.
• The PIM is extremely sensitive to Electro Magnetic Interference (EMI). Ensure the PIM wiring harness is routed
correctly and securely fitted to mounting clips when performing service procedures.
• Due to the sensitive nature of the PIM circuitry, specific wiring repair procedures have been developed. These
procedures and instructions are detailed in 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis and are the only recommended and
approved wiring repair methods.
• Ensure that all wiring harness connectors are seated correctly.
• Never disconnect the battery from the vehicle electrical system while the engine is running.
• Always disconnect the battery from the vehicle electrical system before charging.
• Do not use a fast charger for starting the vehicle.
• Ensure the battery cable terminals are secure.
• Before installing a new PIM, ensure the correct type is fitted. Always refer to the latest spare parts information.
11.2 Powertrain Interface Module
Do not touch the powertrain interface module
pins as Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) damage
may result. For further information on ESD,
refer to 1.2 Warning Caution and Notes.
When replacing the PIM, the PIM must be
reset prior to removal. Failure to perform this
procedure will result in the inability to:
• Test the PIM for warranty purposes.
• Install the PIM into other vehicles.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3735 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–74
12 PIM Security and Programming
12.1 Security and Programming Information
Car Pass Card
W hen performing certain powertrain interface module (PIM) programming functions using Tech 2, you may be prompted
to enter a four digit Security Code (1). This information is found on the car pass card issued with the vehicle when new. If
the card is unavailable, contact the GM Holden Technical Assistance (TAS) centre to obtain the relevant Security Code.
Security Code
The security code is required when performing certain PIM, ICU and ECM programming functions. W hen Tech 2
requests the security code to be entered, and an incorrect code is entered, the PIM will go into a security wait time stage.
This wait time stage will prevent any further attempts to enter the security code until the wait time has elapsed.
Should a second incorrect security code be entered after the initial wait time has elapsed, the PIM will go into a second
wait time stage. The wait time will increase each time an incorrect code is entered. W hen the correct code is entered the
wait time will reset back to its original value of 10 seconds.
NOTE
The ignition switch must be in the ON position
with the battery connected during the wait time
period.
The wait time stages are as follows:
• Stage 1 = 10 seconds.
• Stage 2 = 10 seconds.
• Stage 3 = 10 minutes.
• Stage 4 = 20 minutes.
• Stage 5 = 40 minutes.
• Stage 5 = 80 minutes.
Tech 2 PIM Security Information Data List
The Tech 2 PIM Security Information Data List displays the PIM's current security status.
To view the data list:
1 Connect Tech 2 to the data link connector (DLC) and turn the ignition switch on.
2 On Tech 2 select: Body / Powertrain Interface Module / Security / Security Information .
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3744 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–83
13.5 Security
F0: Immobiliser Link To ECM/PIM
Should the ECM, PIM or ICU be replaced, the modules must be security linked to each other. If this linking
procedure is not performed, the vehicle will not crank nor run. For additional information relating to Tech 2
and the linking procedure, refer to 11A – Immobiliser.
NOTE
After an ECU reset, the ignition switch must be
turned Off for at least 10 seconds and then
turned On for at least one minute, before
attempting communication between Tech 2 and
the ECU.
Preconditions: TIS approval (TIS 2000 Security Access) must be obtained, the four digit security number
entered into Tech 2 and the theft deterrent system disarmed. Then the ignition must be turned ‘On’, using a
programmed remote coded key.
F1: Reset PIM
This function erases the security link between the Engine Control Module (ECM) and the Powertrain Interface Modules (PIM). If this procedure is performed, the engine will not crank nor run. A ICU Link to ECM/PIM
procedure will need to be performed. For additional information relating to the ICU Link to ECM/PIM
procedure, refer to 11A – Immobiliser.
NOTE
After an ECU reset, the ignition switch must be
turned Off for at least 10 seconds and then
turned On for at least one minute, before
attempting communication between Tech 2 and
the ECU.
Preconditions: The four digit security code must be entered into Tech 2 and the ignition switched ‘On’ with a
programmed remote coded key.
F2: Security Information
The security code is required when performing certain PIM, ICU and ECM programming functions. W hen Tech 2 requests the security code to be entered, and an incorrect code is entered, the PIM will go into a
security wait time stage. This wait time stage will prevent any further attempts to enter the security code until
the wait time has elapsed.
Should a second incorrect security code be entered after the initial wait time has elapsed, the PIM will go into a second wait time stage. The wait time will increase each time an incorrect code is entered. W hen the
correct code is entered the wait time will reset back to its original value of 10 seconds.
NOTE
The ignition switch must be in the ON position
with the battery connected during the wait time
period.
The wait time stages are as follows: • Stage 1 = 10 seconds.
• Stage 2 = 10 seconds.
• Stage 3 = 10 minutes.
• Stage 4 = 20 minutes.
• Stage 5 = 40 minutes.
• Stage 5 = 80 minutes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3753 of 6020

Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 5
Service Notes
1. Vehicles fitted with catalytic converters should not be operated with leaded petrol. Lead will contaminate
the ceramic monolith.
2. Do not drop the catalytic converter as it will damage the ceramic monolith.
3. Replace the catalytic converter if it is damaged.
4. Do not allow water, oil or fuel to enter the converter as the ceramic monolith will be contaminated.
5. Do not use engine and/or fuel additives unless approved by General Motors. Many additives contain phosphorous that will contaminate the ceramic monolith.
6. The vehicle must not be started by pushing or towing, as unburned fuel could reach the catalytic converter and destroy the ceramic monolith. Always use jumper leads to start a vehicle that has a flat or
defective battery.
7. W hen carrying out a compression test, for V6 engines use Tech 2 to ensure the output control Engine Compression Test is set to enable, refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical. This prevents fuel injection and
ignition during engine cranking.
8. Do not drive the vehicle with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected, as the catalytic converter will overheat.
9. Do not coast downhill with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected.
10. The catalytic converter is serviceable as part of the front exhaust assembly only. Refer to the service operations in this section for details of front exhaust pipe assembly removal and reinstallation.
11. The exhaust flange gaskets must be replaced whenever a new exhaust pipe, muffler or catalytic converter is installed.
1.3 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
1.1 Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3755 of 6020
Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 7
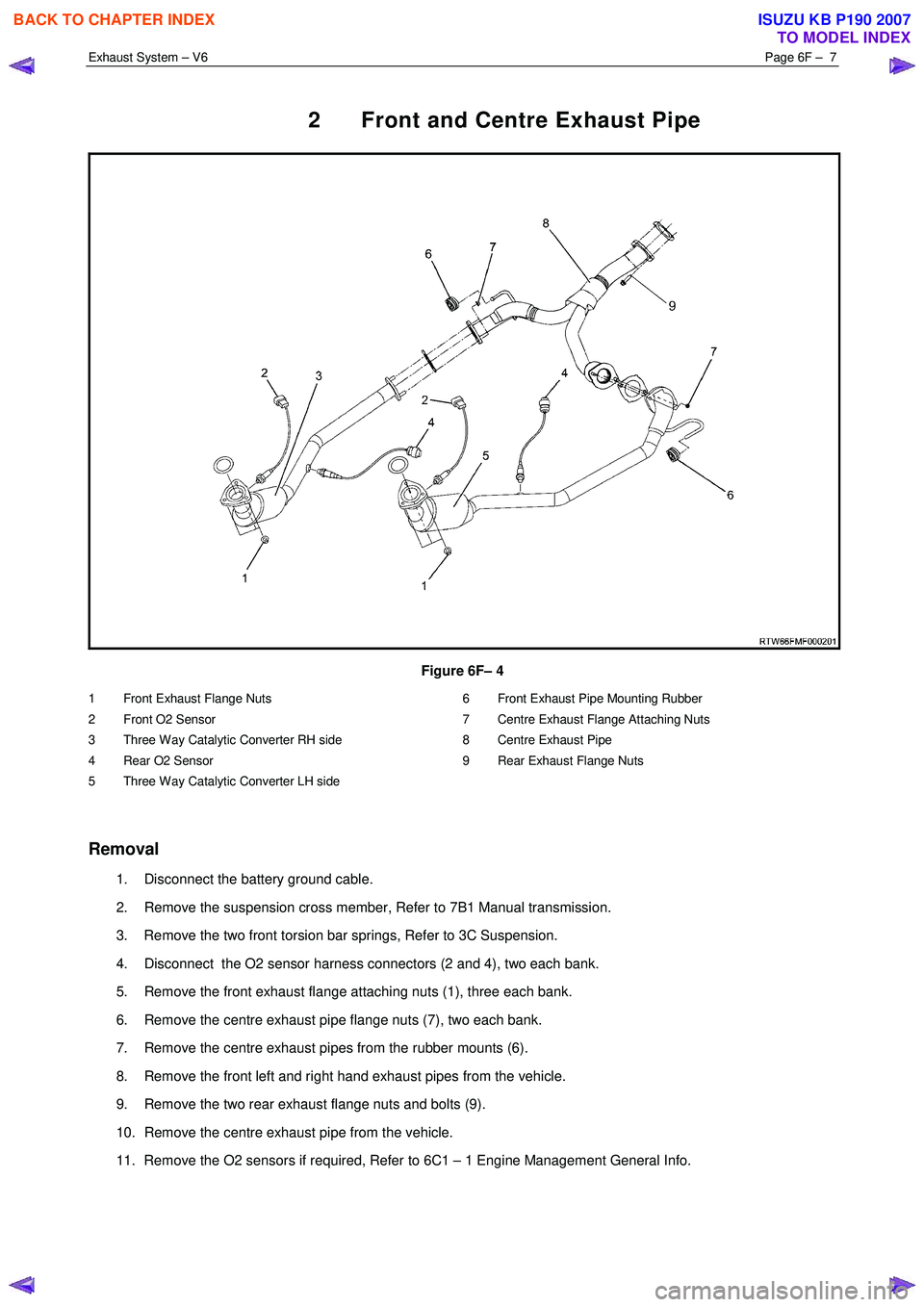
2 Front and Centre Exhaust Pipe
Figure 6F– 4
1 Front Exhaust Flange Nuts
2 Front O2 Sensor
3 Three Way Catalytic Converter RH side
4 Rear O2 Sensor
5 Three Way Catalytic Converter LH side 6 Front Exhaust Pipe Mounting Rubber
7 Centre Exhaust Flange Attaching Nuts
8 Centre Exhaust Pipe
9 Rear Exhaust Flange Nuts
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Remove the suspension cross member, Refer to 7B1 Manual transmission.
3. Remove the two front torsion bar springs, Refer to 3C Suspension.
4. Disconnect the O2 sensor harness connectors (2 and 4), two each bank.
5. Remove the front exhaust flange attaching nuts (1), three each bank.
6. Remove the centre exhaust pipe flange nuts (7), two each bank.
7. Remove the centre exhaust pipes from the rubber mounts (6).
8. Remove the front left and right hand exhaust pipes from the vehicle.
9. Remove the two rear exhaust flange nuts and bolts (9).
10. Remove the centre exhaust pipe from the vehicle.
11. Remove the O2 sensors if required, Refer to 6C1 – 1 Engine Management General Info.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3756 of 6020

Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 8
NOTE:
• Support the exhaust system at all times.
• Clean the threads of the attaching bolts, nuts,
studs and flanges with a suitable cleaning
solvent.
• Apply a high temperature anti-seize
compound to the manifold front pipe flange
joint studs, then align the flange over the
studs.
Reinstallation
1. Install any removed O2 sensors, Refer to 6C1 – 1 Engine Management General Info.
2. Position the centre exhaust pipe into location under the vehicle.
3. Install the two rear exhaust flange nuts and bolts (9).
4. Position the front exhaust pipes into location under the vehicle.
5. Install the centre exhaust pipes into the rubber mounts (6).
6. Install the exhaust flange fixing nuts (1), three each bank.
7. Install the rear exhaust pipe flange nuts (7), two each bank.
8. Reconnect the O2 sensor harness connectors (4), two each bank.
9. Install the two front torsion bar springs, Refer to 3C Suspension.
10. Install the suspension cross member, Refer to 7B1 Manual transmission.
11. Reconnect the battery ground cable.
O2 Sensor
tightening torque.....................................................50 Nm
Front Exhaust Flange Nuts
tightening torque.......................................40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Centre Exhaust Flange Nuts
tightening torque.....................................................43 Nm
Rear Exhaust Flange Nuts
tightening torque.....................................................43 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3757 of 6020
Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 9
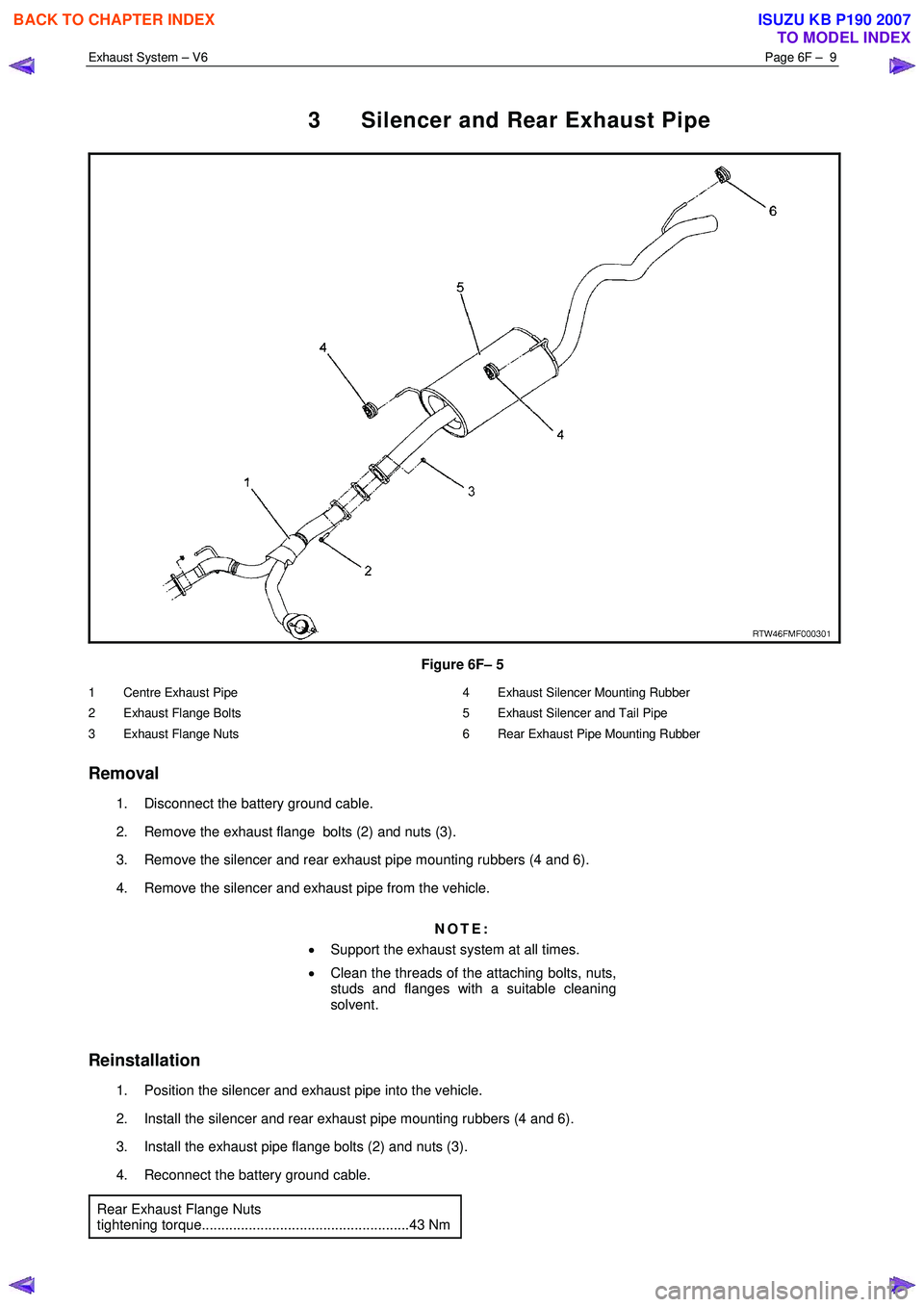
3 Silencer and Rear Exhaust Pipe
Figure 6F– 5
1 Centre Exhaust Pipe
2 Exhaust Flange Bolts
3 Exhaust Flange Nuts 4 Exhaust Silencer Mounting Rubber
5 Exhaust Silencer and Tail Pipe
6 Rear Exhaust Pipe Mounting Rubber
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Remove the exhaust flange bolts (2) and nuts (3).
3. Remove the silencer and rear exhaust pipe mounting rubbers (4 and 6).
4. Remove the silencer and exhaust pipe from the vehicle.
NOTE:
• Support the exhaust system at all times.
• Clean the threads of the attaching bolts, nuts,
studs and flanges with a suitable cleaning
solvent.
Reinstallation
1. Position the silencer and exhaust pipe into the vehicle.
2. Install the silencer and rear exhaust pipe mounting rubbers (4 and 6).
3. Install the exhaust pipe flange bolts (2) and nuts (3).
4. Reconnect the battery ground cable.
Rear Exhaust Flange Nuts
tightening torque.....................................................43 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3797 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–11
Figure 7C2 – 2
The TCM is an electronic control module receiving input or providing output to control the operation of the 4L60E
automatic transmission.
The TCM receives the following inputs from the engine control module (ECM):
• engine speed and torque values,
• engine intake air temperature (IAT), accelerator pedal position (APP) information,
• engine coolant temperature (ECT),
• driver selected shift mode, and
• air-conditioning (A/C) status.
The ECM provides this data to the TCM through the databus.
Other TCM inputs are:
• battery and ignition voltage,
• brake switch status,
• transmission fluid temperature (TFT), and
vehicle speed sensor (VSS).
The TCM provides the following outputs to control the automatic transmission:
• shift solenoids to control transmission shifting,
• torque converter clutch (TCC) pulse width modulated (PW M) solenoid operation to control the apply and release of
the torque converter clutch assembly, and
• pressure control (PC) solenoid to regulate the transmission line pressure.
Other TCM outputs provided to the ECM / PIM are:
• MIL illumination request,
• vehicle speed,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007