2007 ISUZU KB P190 DTC CHECK
[x] Cancel search: DTC CHECKPage 3677 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–16
Tech 2 PIM Diagnostic Tests
Tech 2 Limitations
Some DTCs trigger other DTCs to set, which causes Tech 2 to display multiple DTCs. In those situations, Tech 2 may
display more DTCs than is needed to rectify a fault.
W hen Tech 2 displays an output function, it displays only the command given by the PIM. If a connector is disconnected,
that fault will not register in the PIM output function. Tech 2 does not verify the command action.
The service technician must understand the system being diagnosed as well as the correct use and limitations of Tech 2
to be able to perform diagnostic procedures efficiently and successfully.
Tech 2 Intermittent Fault Tests
The following are lists of Tech 2 diagnostic tests that may be used to diagnose intermittent faults:
• W iggle test the suspected PIM wiring harness and connector while observing Tech 2 operating parameters of the
circuit being tested. If Tech 2 read-out fluctuates during this procedure, check the wiring harness circuit for loose
connection.
• Road test the vehicle in conditions that trigger the intermittent fault while an assistant observes the suspected Tech
2 operating parameter data.
• Capture and store data in the Snapshot mode when the fault occurs. The stored data may be replayed at a slower
rate to aid in diagnostics. Refer to Tech 2 User Instructions for more information on the Snapshot function.
• Operate suspected components to test their operation using Tech 2 Output Control Data.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3685 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–24
7 Diagnostics Starting Point
7.1 Diagnostic Requirements, Precautions
and Preliminary Checks
Basic Knowledge Required
A lack of basic understanding of electronics,
electrical wiring circuits and use of electrical
circuit testing tools when performing the PIM
diagnostic procedures could result in
incorrect diagnostic results or damage to
components.
In addition, understanding of the Engine Management System is essential to prevent misdiagnosis and component
damage. Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information.
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required
Use of incorrect electrical circuit diagnostic
tools when performing the PIM diagnostic
procedures could result in incorrect
diagnostic results or damage to components.
The following electrical circuit testing tools are required to perform the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Section:
• Tech 2.
• Test lamp, refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for further information.
• Digital multimeter with 10 M Ω impedance, refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for further information.
• Connector test adapter kit Tool No. J35616-A.
Diagnostic Precautions
In addition to the safety and precautionary
measures listed in 11.1 Safety and
Precautionary Measures, the following
diagnostic precautions must be observed
when performing any PIM diagnostic
procedure:
• Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables. Other test equipment may either give incorrect
results or damage serviceable components.
• Do not clear any DTCs unless instructed.
• The fault must be present when using the DTC Diagnostic Tables. Otherwise, misdiagnosis or replacement of
serviceable parts may occur.
• Always use connector adapters such as those contained in connector test adapter kit Tool No. J35616-A to prevent
connector terminal damage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3687 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–26
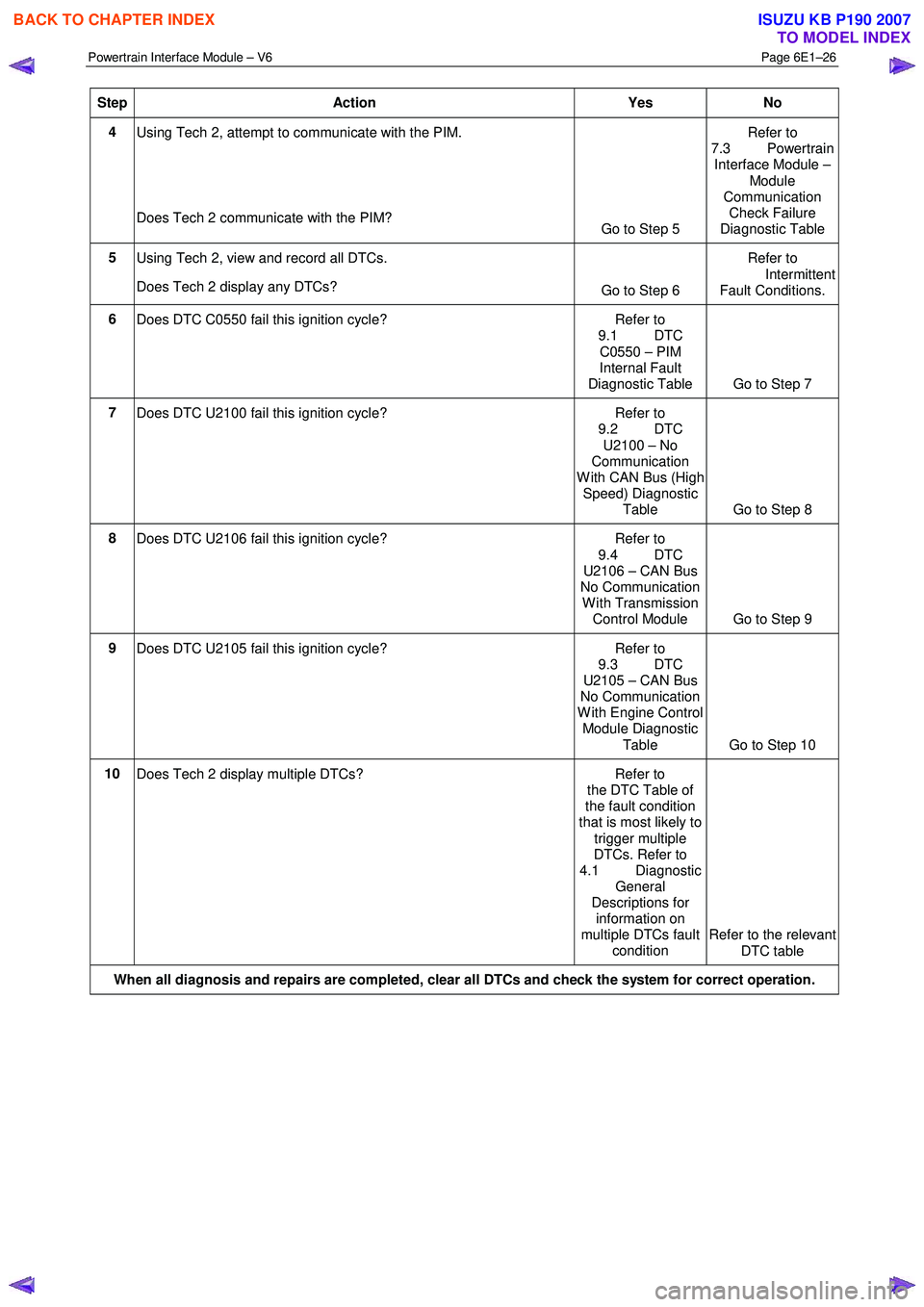
Step Action Yes No
4
Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does Tech 2 communicate with the PIM? Go to Step 5 Refer to
7.3 Powertrain Interface Module –
Module
Communication Check Failure
Diagnostic Table
5 Using Tech 2, view and record all DTCs.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to Step 6 Refer to
Intermittent Fault Conditions.
6 Does DTC C0550 fail this ignition cycle? Refer to
9.1 DTC
C0550 – PIM
Internal Fault
Diagnostic Table Go to Step 7
7 Does DTC U2100 fail this ignition cycle? Refer to
9.2 DTC
U2100 – No
Communication
W ith CAN Bus (High Speed) Diagnostic
Table Go to Step 8
8 Does DTC U2106 fail this ignition cycle? Refer to
9.4 DTC
U2106 – CAN Bus
No Communication
W ith Transmission Control Module Go to Step 9
9
Does DTC U2105 fail this ignition cycle? Refer to
9.3 DTC
U2105 – CAN Bus
No Communication
W ith Engine Control Module Diagnostic
Table Go to Step 10
10 Does Tech 2 display multiple DTCs? Refer to
the DTC Table of
the fault condition
that is most likely to
trigger multiple
DTCs. Refer to
4.1 Diagnostic General
Descriptions for information on
multiple DTCs fault condition Refer to the relevant
DTC table
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3688 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–27
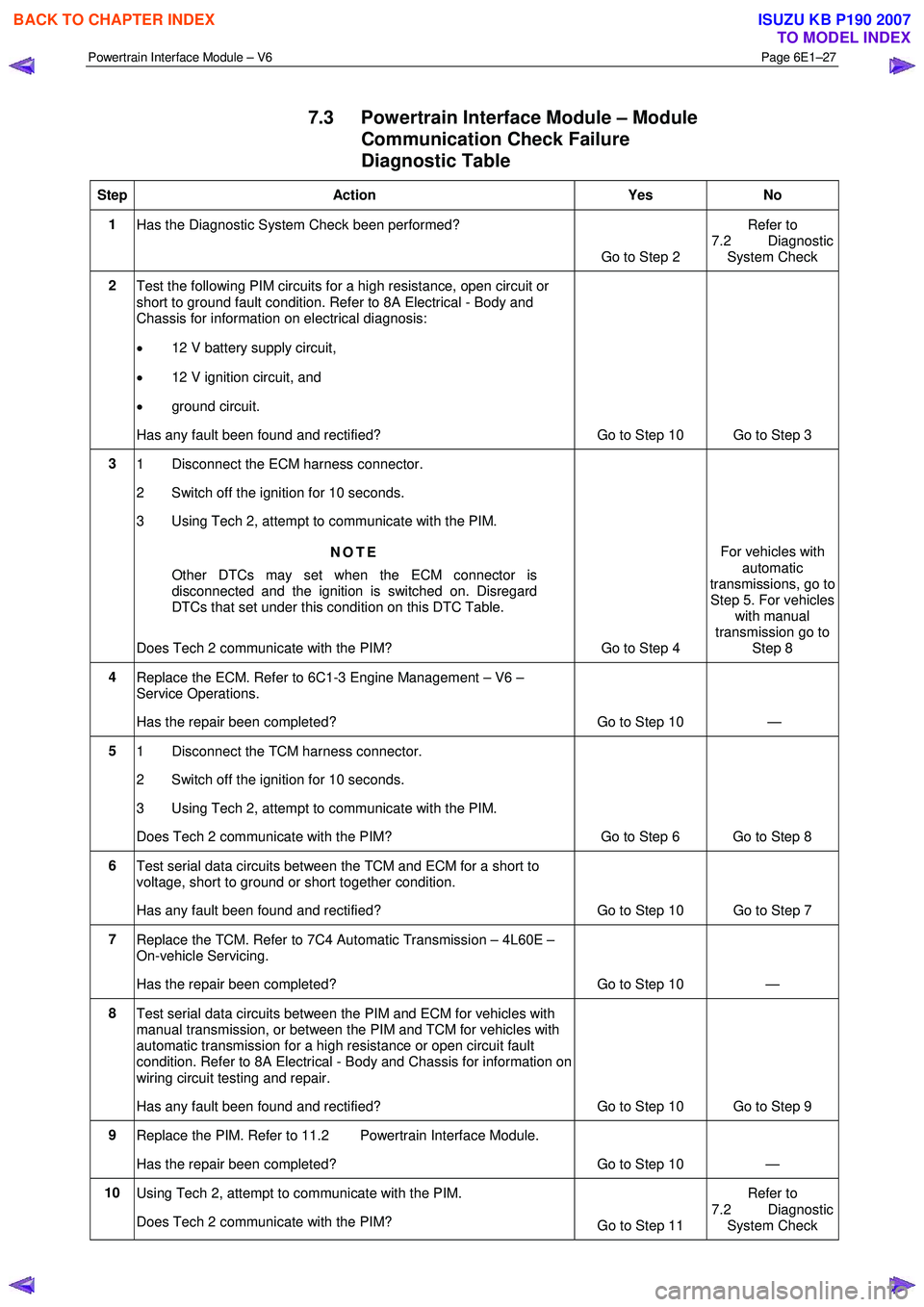
7.3 Powertrain Interface Module – Module
Communication Check Failure
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
7.2 Diagnostic System Check
2 Test the following PIM circuits for a high resistance, open circuit or
short to ground fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and
Chassis for information on electrical diagnosis:
• 12 V battery supply circuit,
• 12 V ignition circuit, and
• ground circuit.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 3
3 1 Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
2 Switch off the ignition for 10 seconds.
3 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
NOTE
Other DTCs may set when the ECM connector is
disconnected and the ignition is switched on. Disregard
DTCs that set under this condition on this DTC Table.
Does Tech 2 communicate with the PIM? Go to Step 4 For vehicles with
automatic
transmissions, go to
Step 5. For vehicles with manual
transmission go to Step 8
4 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 10 —
5 1 Disconnect the TCM harness connector.
2 Switch off the ignition for 10 seconds.
3 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does Tech 2 communicate with the PIM? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6 Test serial data circuits between the TCM and ECM for a short to
voltage, short to ground or short together condition.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 7
7 Replace the TCM. Refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 10 —
8 Test serial data circuits between the PIM and ECM for vehicles with
manual transmission, or between the PIM and TCM for vehicles with
automatic transmission for a high resistance or open circuit fault
condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on
wiring circuit testing and repair.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9 Replace the PIM. Refer to 11.2 Powertrain Interface Module.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does Tech 2 communicate with the PIM? Go to Step 11 Refer to
7.2 Diagnostic System Check
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3689 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–28
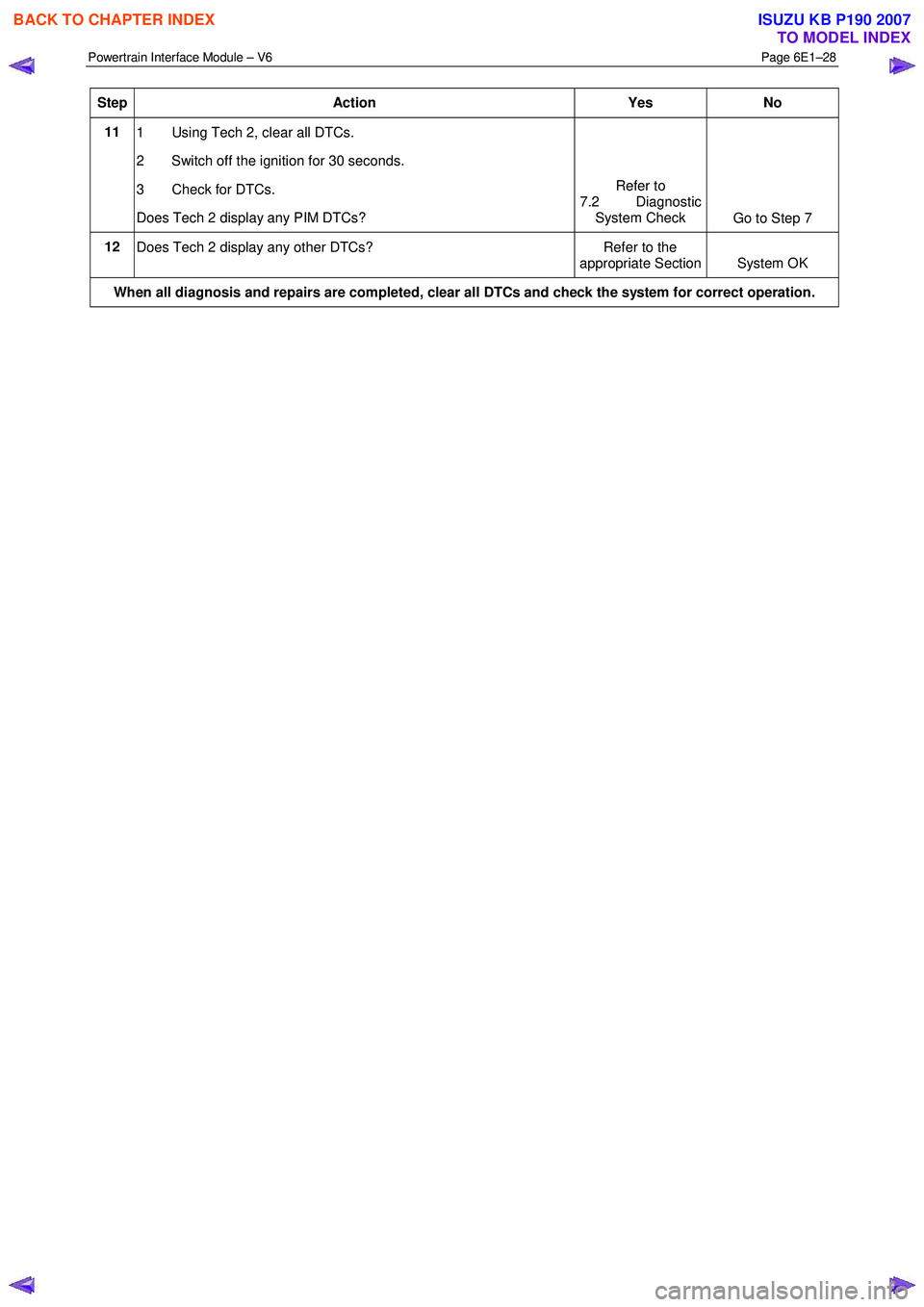
Step Action Yes No
11
1 Using Tech 2, clear all DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Check for DTCs.
Does Tech 2 display any PIM DTCs? Refer to
7.2 Diagnostic System Check Go to Step 7
12
Does Tech 2 display any other DTCs? Refer to the
appropriate Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3690 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–29
Intermittent Fault Conditions
8.1 Intermittent Conditions Diagnostic Table
Description
A fault condition is intermittent if one of the following conditions exists:
• The fault condition is not always present.
• The fault condition cannot be presently duplicated.
• There is no Current DTC but a History DTC is stored.
Diagnostic Table
Checks Actions
Preliminary
• Perform the Preliminary Checks, refer to 7.1 Diagnostic Requirements,
Precautions and Preliminary Checks.
• Gather information from the customer regarding the conditions that trigger the
intermittent fault such as:
• At what engine or ambient temperature range does the fault occur?
• Does the fault occur when operating aftermarket electrical equipment inside
the vehicle?
• Does the fault occur on rough roads or in wet road conditions?
• If the intermittent fault is a start and then stall condition, check immobiliser system.
Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Harness / Connector Install Tech 2 and perform the Tech 2 Intermittent Fault Tests. Refer to 4.1 Diagnostic General Descriptions for information on Tech 2 ECU diagnostic
tests.
W arning Indicator The following conditions may cause an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp fault with
no DTC listed:
• Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid, switch or other external source.
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• theft deterrent alarms,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• Loose PIM ground connections.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3692 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–31
9 DTC Tables
9.1 DTC C0550 – PIM Internal Fault
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC C0550 – EEPROM Error.
• DTC C0550 – Internal Control Module Read Only Memory (ROM Error).
• DTC C0550 – Internal Control Module Random Access Memory (RAM) Error.
Circuit Description
The powertrain interface module (PIM) is the control centre for the communication language conversion between GM
LAN serial data and keyword 2000 serial data. If there is an internal microprocessor integrity fault condition with the PIM,
DTC C0550 will set.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector Chart for the following information:
• PIM connector illustration and terminal assignment, and
• PIM wiring diagram.
• For intermittent fault conditions, refer to Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault conditions in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Conditions for running the DTC are:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
An internal PIM fault exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The action taken when any of these DTCs set will depend on the severity of the error. This may vary from no visual or
audible warnings to a Malfunction Indicator Lamp and / or Service Vehicle Soon warning lamp displayed on the
instrument cluster.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
Refer to 4.1 Diagnostic General Descriptions for information on the conditions for clearing DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 This step checks if the DTC is current, and if so, indicates the PIM has an internal problem.
3 This step checks the PIM ground and 12 V battery supply.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3693 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–32
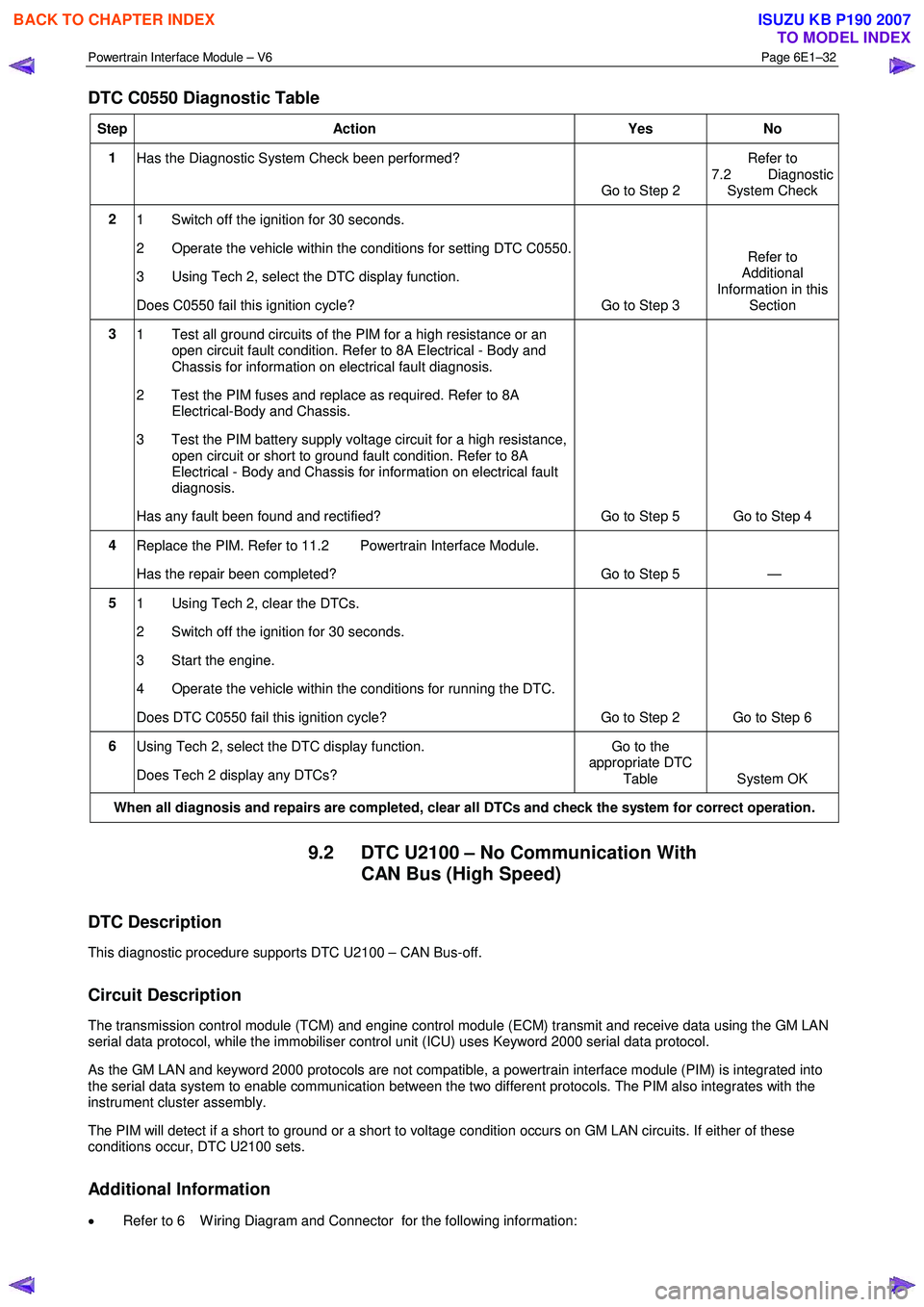
DTC C0550 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
7.2 Diagnostic System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for setting DTC C0550.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does C0550 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to
Additional
Information in this Section
3 1 Test all ground circuits of the PIM for a high resistance or an
open circuit fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and
Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
2 Test the PIM fuses and replace as required. Refer to 8A Electrical-Body and Chassis.
3 Test the PIM battery supply voltage circuit for a high resistance, open circuit or short to ground fault condition. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 Replace the PIM. Refer to 11.2 Powertrain Interface Module.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 5 —
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC C0550 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
9.2 DTC U2100 – No Communication With CAN Bus (High Speed)
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC U2100 – CAN Bus-off.
Circuit Description
The transmission control module (TCM) and engine control module (ECM) transmit and receive data using the GM LAN
serial data protocol, while the immobiliser control unit (ICU) uses Keyword 2000 serial data protocol.
As the GM LAN and keyword 2000 protocols are not compatible, a powertrain interface module (PIM) is integrated into
the serial data system to enable communication between the two different protocols. The PIM also integrates with the
instrument cluster assembly.
The PIM will detect if a short to ground or a short to voltage condition occurs on GM LAN circuits. If either of these
conditions occur, DTC U2100 sets.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector for the following information:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007