2007 ISUZU KB P190 Harness
[x] Cancel search: HarnessPage 2260 of 6020
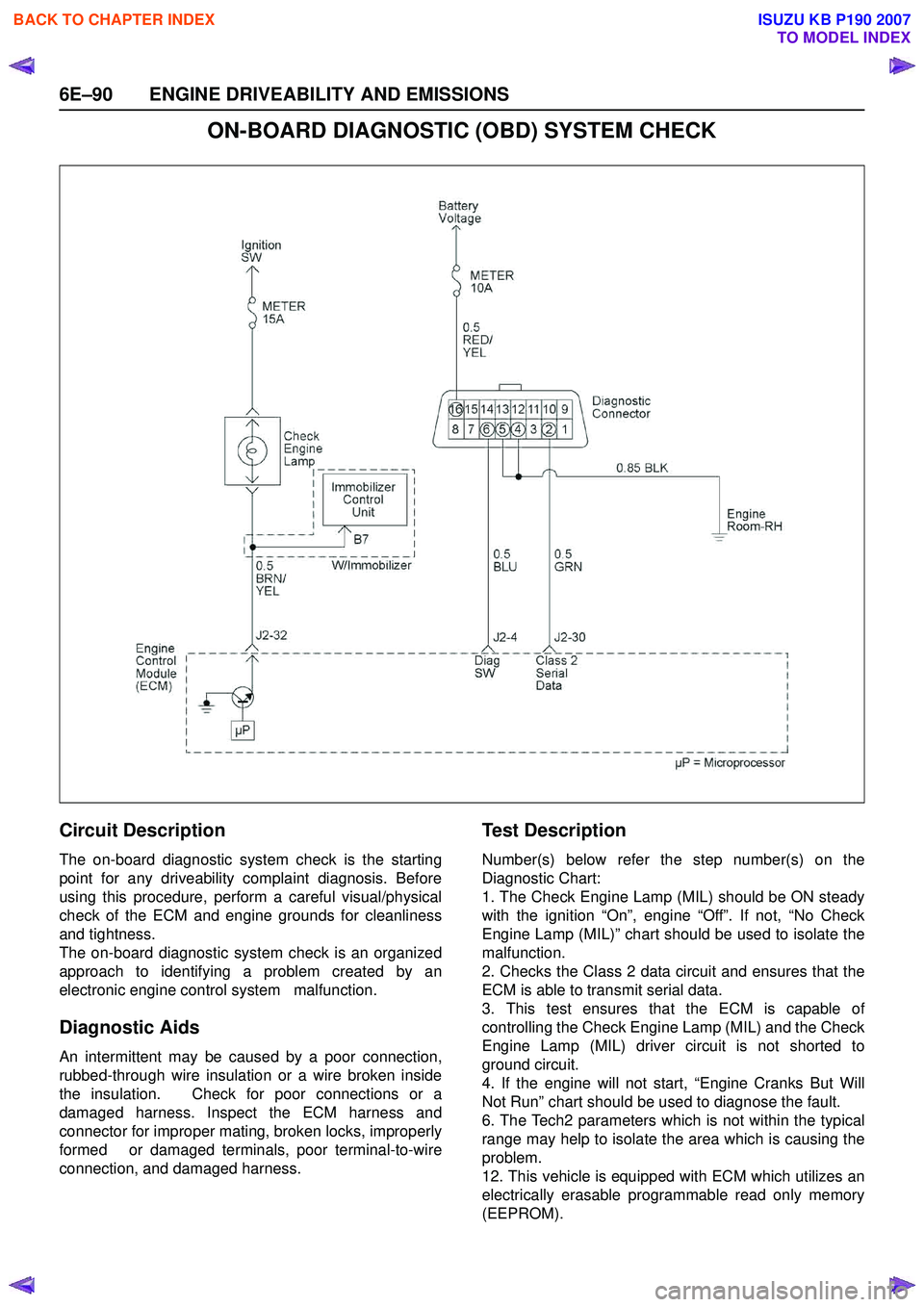
6E–90 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM CHECK
Circuit Description
The on-board diagnostic system check is the starting
point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Before
using this procedure, perform a careful visual/physical
check of the ECM and engine grounds for cleanliness
and tightness.
The on-board diagnostic system check is an organized
approach to identifying a problem created by an
electronic engine control system malfunction.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for poor connections or a
damaged harness. Inspect the ECM harness and
connector for improper mating, broken locks, improperly
formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire
connection, and damaged harness.
Te s t D e s c r i p t i o n
Number(s) below refer the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The Check Engine Lamp (MIL) should be ON steady
with the ignition “On”, engine “Off”. If not, “No Check
Engine Lamp (MIL)” chart should be used to isolate the
malfunction.
2. Checks the Class 2 data circuit and ensures that the
ECM is able to transmit serial data.
3. This test ensures that the ECM is capable of
controlling the Check Engine Lamp (MIL) and the Check
Engine Lamp (MIL) driver circuit is not shorted to
ground circuit.
4. If the engine will not start, “Engine Cranks But Will
Not Run” chart should be used to diagnose the fault.
6. The Tech2 parameters which is not within the typical
range may help to isolate the area which is causing the
problem.
12. This vehicle is equipped with ECM which utilizes an
electrically erasable programmable read only memory
(EEPROM).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2261 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–91
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM CHECK
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”. 2. Check the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp (MIL).
Does the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp turn “On”? — Go to Step 2Go to
No
CHECK
ENGINE Lamp
2 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2 . A t t e m p t t o d i s p l a y “ E n g i n e D a t a ” w i t h t h e T e c h 2 .
Does the Tech 2 display “Engine Data” and “O
2Sensor Data”? — Go to Step 3Go to Step 7
3 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select the “Miscellaneous Test” and perform the“Malfunction Indicator Lamp” in “Lamps”.
3. Operate the Tech 2 in accordance with the Tech 2 instructions.
Does the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp turn “Off”? — Go to Step 4Go to
CHECK
ENGINE LAMP On Steady
4 Attempt to start the engine. Does the engine start and continue to “Run”? —Go to Step 5Go to
Engine
Cranks But Will Not Run
5 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select the “Read DTC Infor By Priority” in“Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
3. Are any DTCs stored? —Go to
DTC
Chart Go to Step 6
6 Compare typical scan data values displayed on the Tech 2 “Engine Data” and “O
2 Sensor Data”.
Are the displayed values within the range? —Refer to
SYMPTOM
DIAGNOSIS Refer to
TYPICAL
SCAN DATA
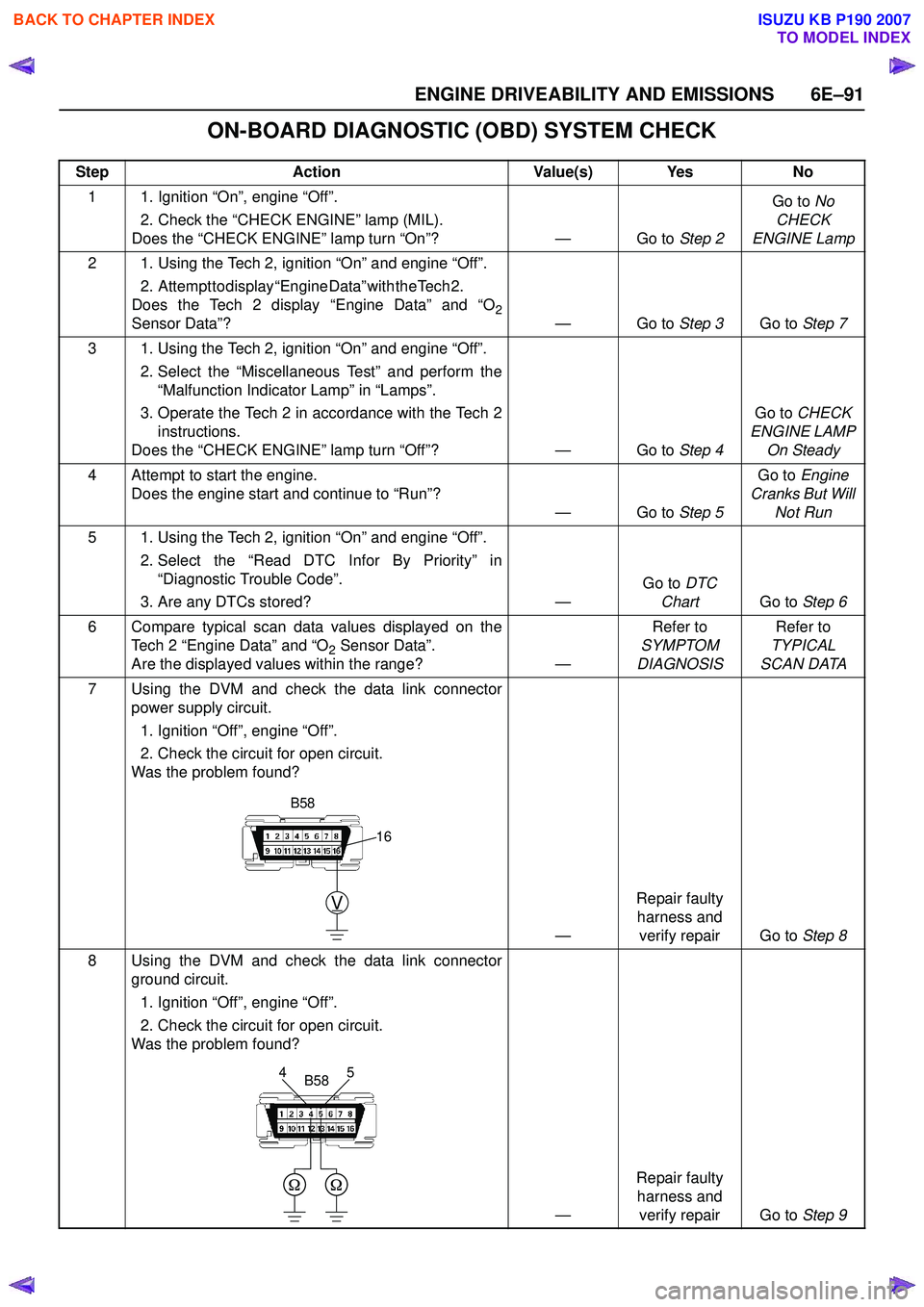
7 Using the DVM and check the data link connector power supply circuit.
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Check the circuit for open circuit.
Was the problem found?
—Repair faulty
harness and verify repair Go to Step 8
8 Using the DVM and check the data link connector ground circuit.
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Check the circuit for open circuit.
Was the problem found?
—Repair faulty
harness and verify repair Go to Step 9
V
16
B58
5
4B58
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2262 of 6020
6E–92 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
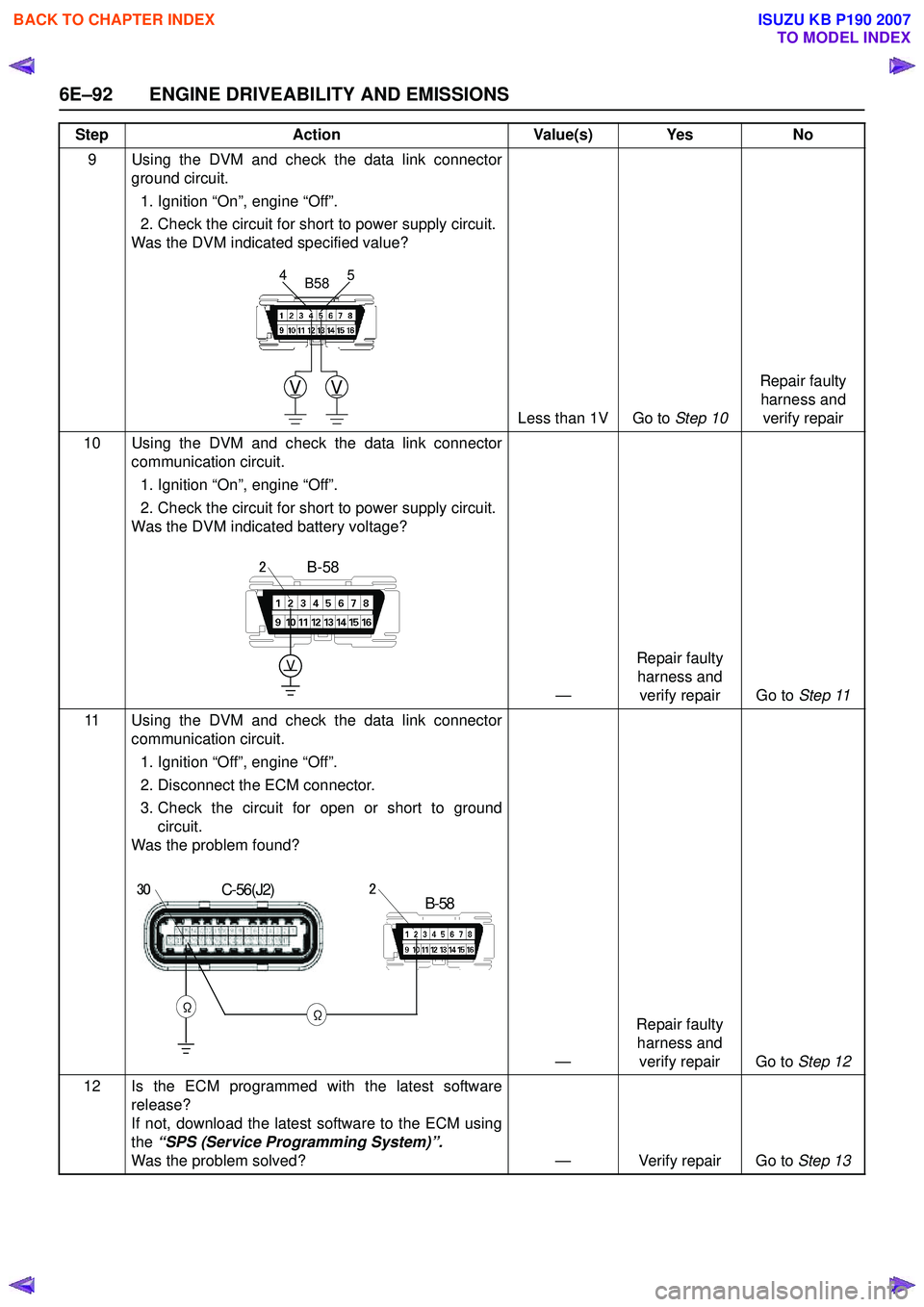
9 Using the DVM and check the data link connectorground circuit.
1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Check the circuit for short to power supply circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
Less than 1V Go to Step 10Repair faulty
harness and verify repair
10 Using the DVM and check the data link connector communication circuit.
1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Check the circuit for short to power supply circuit.
Was the DVM indicated battery voltage?
—Repair faulty
harness and verify repair Go to Step 11
11 Using the DVM and check the data link connector communication circuit.
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the ECM connector.
3. Check the circuit for open or short to ground circuit.
Was the problem found?
—Repair faulty
harness and verify repair Go to Step 12
12 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
VV
5
4B58
V
B-582
C-56(J2)
ΩΩ
B-58230
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2264 of 6020
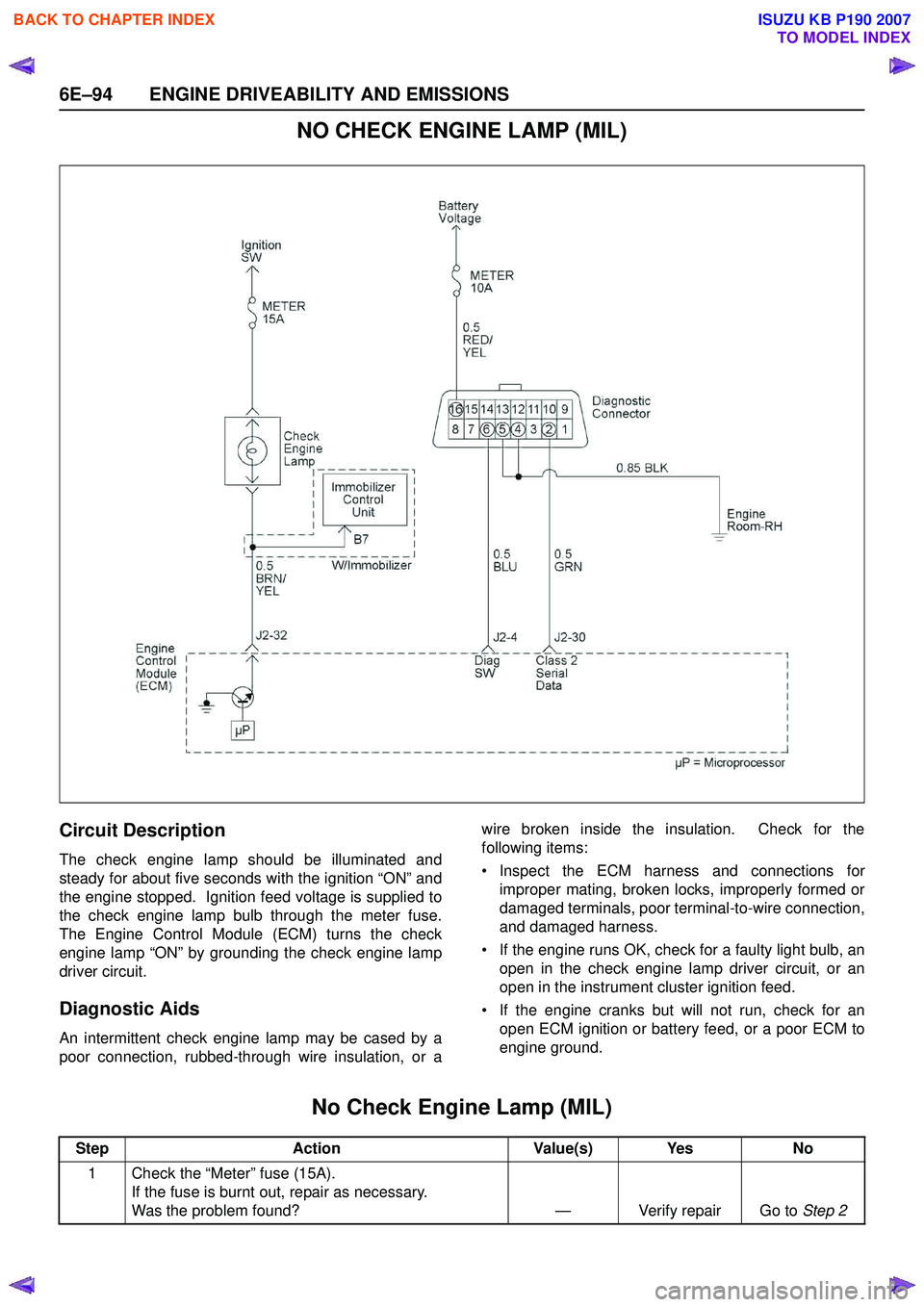
6E–94 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
NO CHECK ENGINE LAMP (MIL)
Circuit Description
The check engine lamp should be illuminated and
steady for about five seconds with the ignition “ON” and
the engine stopped. Ignition feed voltage is supplied to
the check engine lamp bulb through the meter fuse.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) turns the check
engine lamp “ON” by grounding the check engine lamp
driver circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent check engine lamp may be cased by a
poor connection, rubbed-through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside the insulation. Check for the
following items:
• Inspect the ECM harness and connections for improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection,
and damaged harness.
• If the engine runs OK, check for a faulty light bulb, an open in the check engine lamp driver circuit, or an
open in the instrument cluster ignition feed.
• If the engine cranks but will not run, check for an open ECM ignition or battery feed, or a poor ECM to
engine ground.
No Check Engine Lamp (MIL)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Check the “Meter” fuse (15A). If the fuse is burnt out, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 2
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2266 of 6020
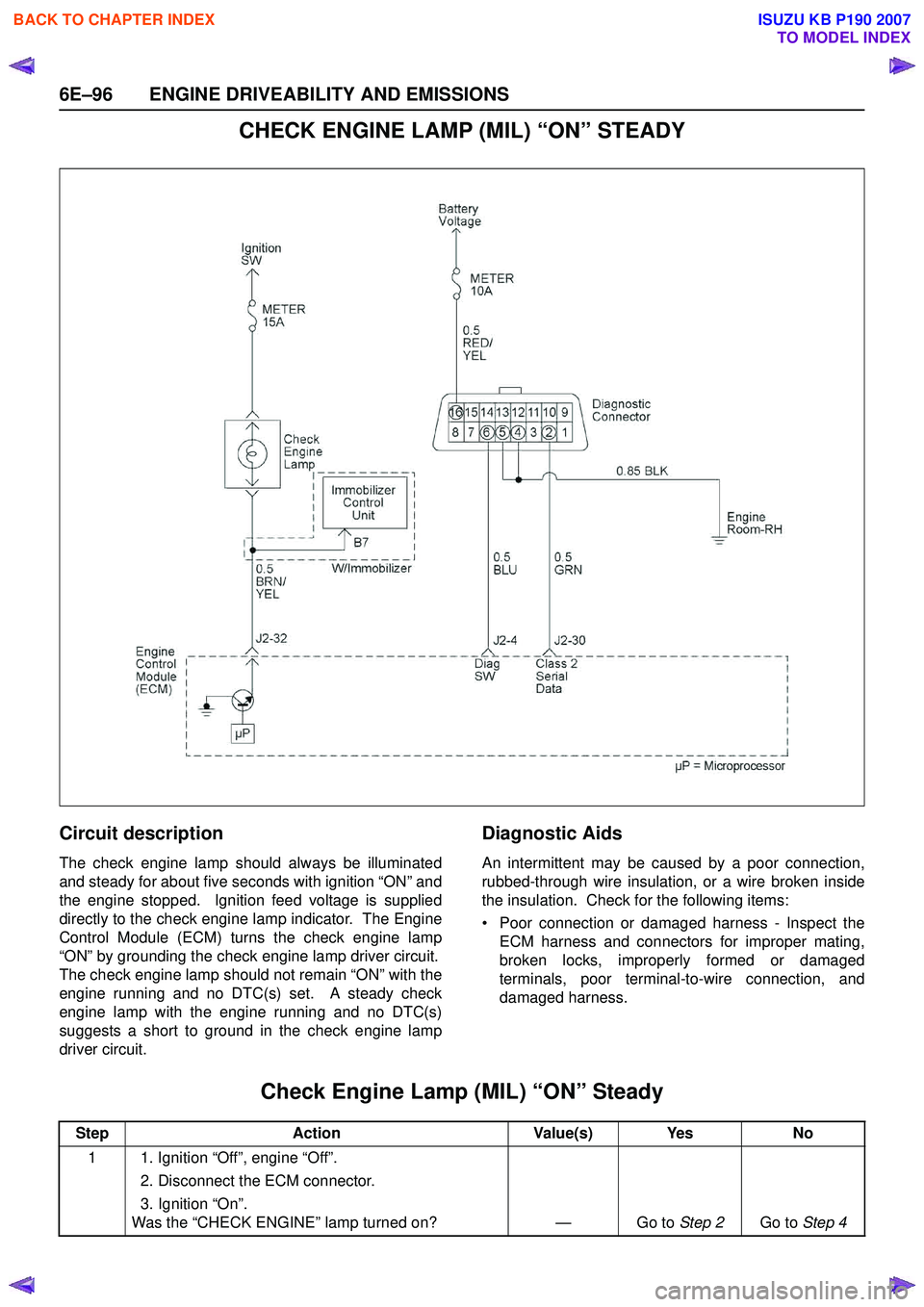
6E–96 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CHECK ENGINE LAMP (MIL) “ON” STEADY
Circuit description
The check engine lamp should always be illuminated
and steady for about five seconds with ignition “ON” and
the engine stopped. Ignition feed voltage is supplied
directly to the check engine lamp indicator. The Engine
Control Module (ECM) turns the check engine lamp
“ON” by grounding the check engine lamp driver circuit.
The check engine lamp should not remain “ON” with the
engine running and no DTC(s) set. A steady check
engine lamp with the engine running and no DTC(s)
suggests a short to ground in the check engine lamp
driver circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
• Poor connection or damaged harness - Inspect the ECM harness and connectors for improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection, and
damaged harness.
Check Engine Lamp (MIL) “ON” Steady
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”. 2. Disconnect the ECM connector.
3. Ignition “On”.
Was the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp turned on? — Go to Step 2Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2270 of 6020
6E–100 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Injector Coil Test Procedure (Steps 1-6) and Injector Balance Test Procedure (Steps 7-11)
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed? — Go to Step 2Go to
OBD
System Check
2 1. Turn the engine OFF. NOTE: In order to prevent flooding of a single cylinder
and possible engine damage, relieve the fuel pressure
before performing the fuel injector coil test procedure.
2. Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to Test Description Number 2.
3. Connect the 5-8840-2618-0 Fuel Injector Tester to B+ and ground, and to the 5-8840-2589-0 Injector
Adapter Cable.
4. Remove the harness connector of the Fuel Injector and connect the 5-8840-2589-0 Injector
Adapter Cable for F/I check.
5. Set the amperage supply selector switch on the fuel injector tester to the “Coil Test” 0.5 amp
position.
6. Connect the leads from the 5-8840-2392-0 Digital Voltmeter (DVM) to the fuel injector tester. Refer
to the illustrations associated with the test
description.
7. Set the DVM to the tenths scale (0.0).
8. Observe the engine coolant temperature.
Is the engine coolant temperature within the specified
values? 10°C (50°F)
to
35°C (95°F) Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
3 1. Set the injector adapter cable to injector #1. 2. Press the “Push to Start Test” button on the fuelinjector tester.
3. Observe the voltage reading on the DVM.
Important: The voltage reading may rise during the
test.
4. Record the lowest voltage observed after the first second of the test.
5. Set the injector adapter cable to the next injector and repeat steps 2, 3, and 4.
Did any fuel injector have an erratic voltage reading
(large fluctuations in voltage that did not stabilize) or a
voltage reading outside of the specified values? 5.7-6.6V Go to Step 4Go to Step 7
4 Replace the faulty fuel injector(S). Refer to Fuel
Injector .
Is the action complete? — Go to Step 7—
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2272 of 6020
6E–102 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
9 1. Connect the 5-8840-0378-0 Fuel Injector Testerand 5-8840-2589-0 Injector Adapter Cable to the
fuel injector harness connector.
2. Set the amperage supply selector switch on the fuel injector tester to the “Balance Test” 0.5-2.5
amp position.
3. Using the Scan Tool turn the fuel pump ON then OFF in order to pressurize the fuel system.
4. Record the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge after the fuel pressure stabilizes.
This is the first pressure reading.
5. Energize the fuel injector by depressing the “Push to Start Test” button on the fuel injector tester.
6. Record the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge after the fuel pressure gauge
needle has stopped moving. This is the second
pressure reading.
7. Repeat steps 1 through 6 for each fuel injector.
8. Subtract the second pressure reading from the first pressure reading for one fuel injector. The
result is the pressure drop value.
9. Obtain a pressure drop value for each fuel injector.
10. Add all of the individual pressure drop values. This is the total pressure drop.
11. Divide the total pressure drop by the number of fuel injectors. This is the average pressure drop.
Does any fuel injector have a pressure drop value that
is either higher than the average pressure drop or
lower than the average pressure drop by the specified
value? 10kPa
(1.5psi) Go to Step 10Go to
OBD
System Check
10 Re-test any fuel injector that does not meet the specification. Refer to the procedure in Step 11.
NOTE: Do not repeat any portion of this test before
running the engine in order to prevent the engine from
flooding.
Does any fuel injector still have a pressure drop value
that is either higher than the average pressure drop or
lower than the average pressure drop by the specified
value? 10kPa
(1.5psi) Go to Step 11Go to
Symptoms
11 1. Replace the faulty fuel injector(s). Refer to Fuel
Injector .
2. Disconnect the 5-8840-2589-0 Injector Adapter Cable for F/I check and re-connect the original F/I
check connector.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2273 of 6020
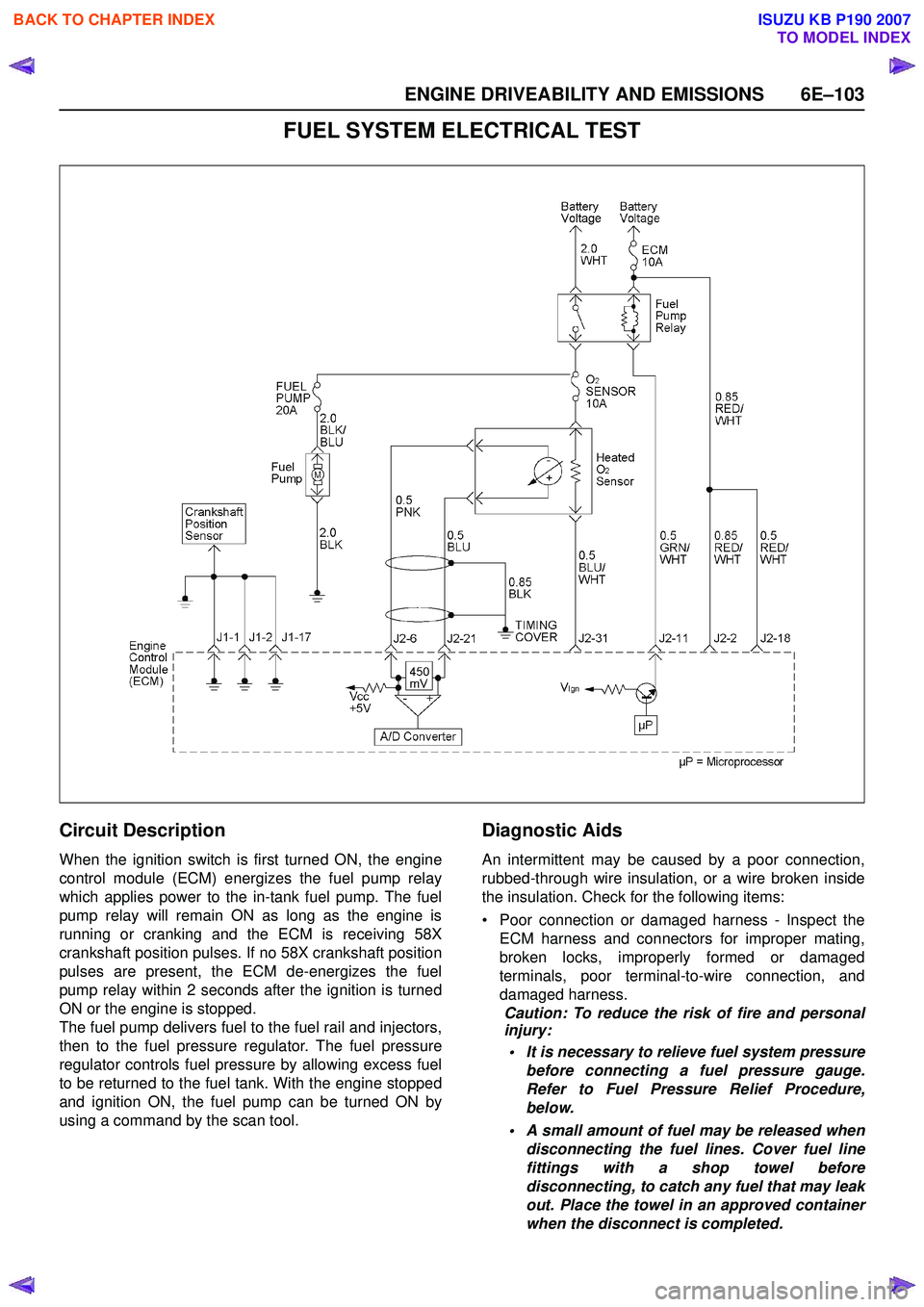
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–103
FUEL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL TEST
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is first turned ON, the engine
control module (ECM) energizes the fuel pump relay
which applies power to the in-tank fuel pump. The fuel
pump relay will remain ON as long as the engine is
running or cranking and the ECM is receiving 58X
crankshaft position pulses. If no 58X crankshaft position
pulses are present, the ECM de-energizes the fuel
pump relay within 2 seconds after the ignition is turned
ON or the engine is stopped.
The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel rail and injectors,
then to the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure
regulator controls fuel pressure by allowing excess fuel
to be returned to the fuel tank. With the engine stopped
and ignition ON, the fuel pump can be turned ON by
using a command by the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
• Poor connection or damaged harness - Inspect the ECM harness and connectors for improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection, and
damaged harness. Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
• It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure before connecting a fuel pressure gauge.
Refer to Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure,
below.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before
disconnecting, to catch any fuel that may leak
out. Place the towel in an approved container
when the disconnect is completed.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007