2007 ISUZU KB P190 Wiring
[x] Cancel search: WiringPage 2088 of 6020
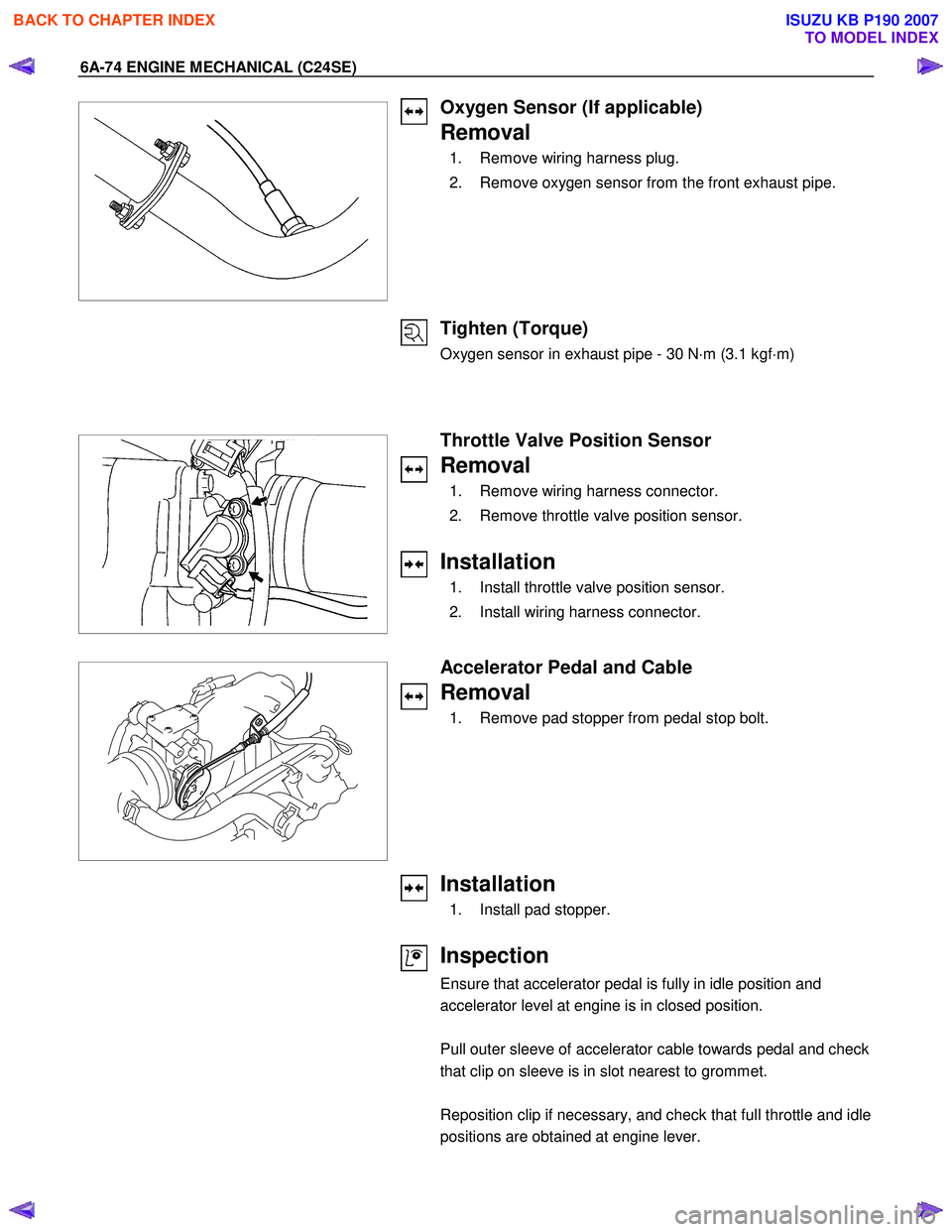
6A-74 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
Oxygen Sensor (If applicable)
Removal
1. Remove wiring harness plug.
2. Remove oxygen sensor from the front exhaust pipe.
Tighten (Torque)
Oxygen sensor in exhaust pipe - 30 N ⋅m (3.1 kgf ⋅m)
Throttle Valve Position Sensor
Removal
1. Remove wiring harness connector.
2. Remove throttle valve position sensor.
Installation
1. Install throttle valve position sensor.
2. Install wiring harness connector.
Accelerator Pedal and Cable
Removal
1. Remove pad stopper from pedal stop bolt.
Installation
1. Install pad stopper.
Inspection
Ensure that accelerator pedal is fully in idle position and
accelerator level at engine is in closed position.
Pull outer sleeve of accelerator cable towards pedal and check
that clip on sleeve is in slot nearest to grommet.
Reposition clip if necessary, and check that full throttle and idle
positions are obtained at engine lever.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2147 of 6020
6D2-4 IGNITION SYSTEM
Cleaning Spark Plugs
• Clean spark plugs with a spark plug cleaner.
• Raise the ground electrode to an angle of 45 to 60 degrees.
if electrode is wet, dry it gefore cleaning.
•
After spark plug is thoroughly cleaned, check insulator for
presence of cracks.
• Clean threads and metal body with a wire brush.
• File the electrode tip if electrode is extremely worn.
• Bend the ground electrode to adjust the spark plug gap.
Installation
1. Spark plugs
• Tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Torque: 20 N ⋅m (2.0 kgf ⋅m)
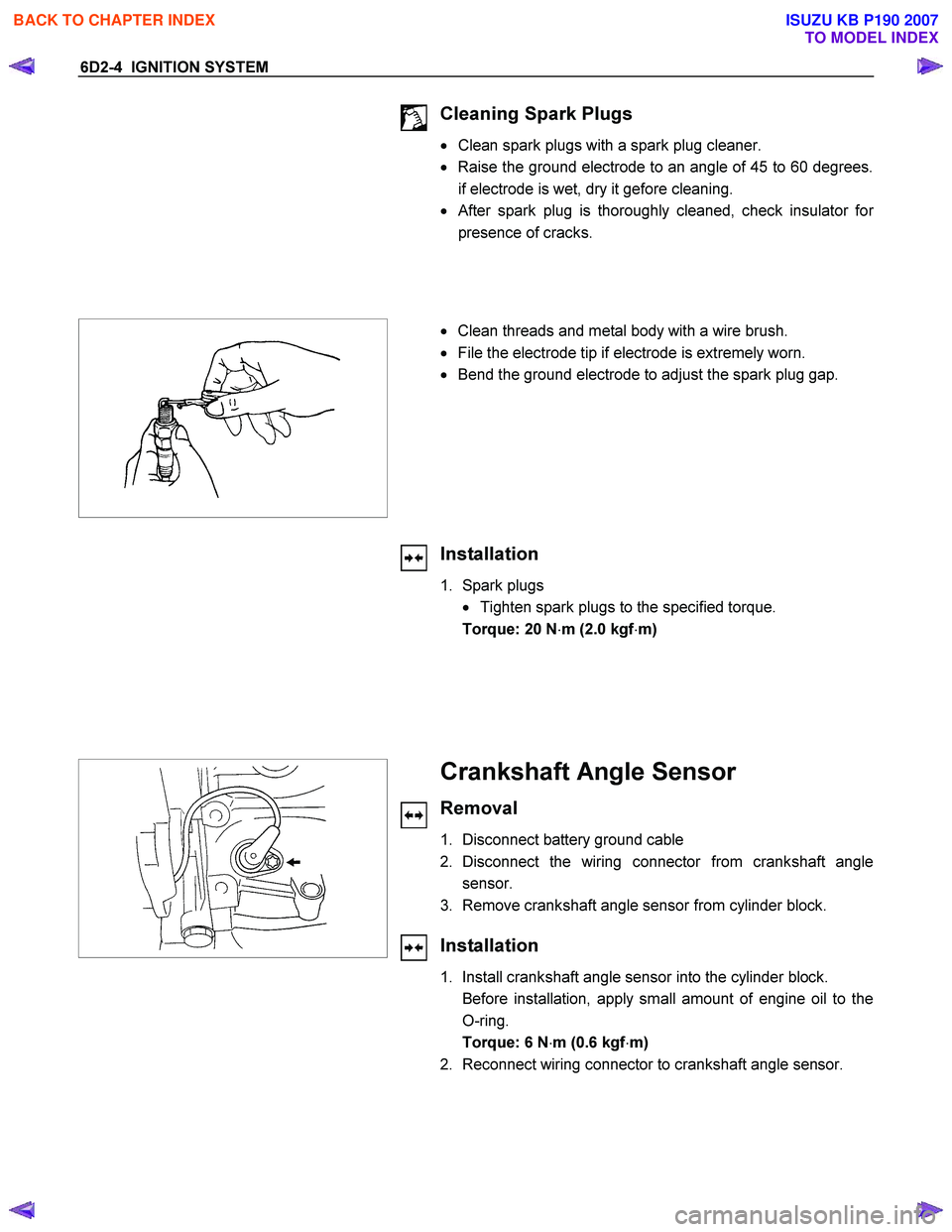
Crankshaft Angle Sensor
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable
2. Disconnect the wiring connector from crankshaft angle sensor.
3. Remove crankshaft angle sensor from cylinder block.
Installation
1. Install crankshaft angle sensor into the cylinder block.
Before installation, apply small amount of engine oil to the O-ring.
Torque: 6 N ⋅m (0.6 kgf ⋅m)
2. Reconnect wiring connector to crankshaft angle sensor.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2150 of 6020
6D3-2 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Starting System
General Description
Cranking Circuit
The cranking system consists of a battery, starter, starter
switch, starter relay, etc. These main components are
connected.
Starter
The cranking system employs a magnetic type reduction
starter in which the motor shaft is also used as a pinion shaft.
W hen the starter switch is turned on, the contacts of magnetic
switch are closed, and the armature rotates. At the same time,
the plunger is attracted, and the pinion is pushed forward by
the shift lever to mesh with the ring gear.
Then, the ring gear runs to start the engine. W hen the engine
starts and the starter switch is turned off, the plunger returns,
the pinion is disengaged from the ring gear, and the armature
stops rotation. W hen the engine speed is higher than the
pinion, the pinion idles, so that the armature is not driven.
Service Precaution
CAUTION:
Always use the correct fastener in the proper location.
When you replace a fastener, use ONLY the exact part
number for that application. ISUZU will call out those
fasteners that require a replacement after removal. ISUZU
will also call out the fasteners that require thread lockers
or thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do
not use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, or other
corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or fastener
joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings adversely affect
the fastener torque and the joint clamping force, and may
damage the fastener. When you install fasteners, use the
correct tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to parts
and systems.
Diagnosis
Condition Possible cause Correction
Starter does not run Charging failure Repair charging system
Battery Failure Replace Battery
Terminal connection failure Repair or replace terminal connector
and/or wiring harness
Starter switch failure Repair or replace starter switch
Starter failure Repair or replace starter
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2156 of 6020
6D3-8 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
General On-Vehicle Inspection
The operating condition of charging system is indicated by the
charge warning lamp. The warning lamp comes on when the
starter switch is turned to "ON" position. The charging system
operates normally if the lamp goes off when the engine starts.
If the warning lamp shows abnormality or if undercharged or
overcharged battery condition is suspected, perform diagnosis
by checking the charging system as follows:
1. Check visually the belt and wiring connector.
2. W ith the engine stopped, turn the stator switch to "ON" position and observe the warning lamp.
If lamp does not come on:
Disconnect wiring connector from generator, and ground the terminal "L" on connector side.
If lamp comes on:
Repair or replace the generator.
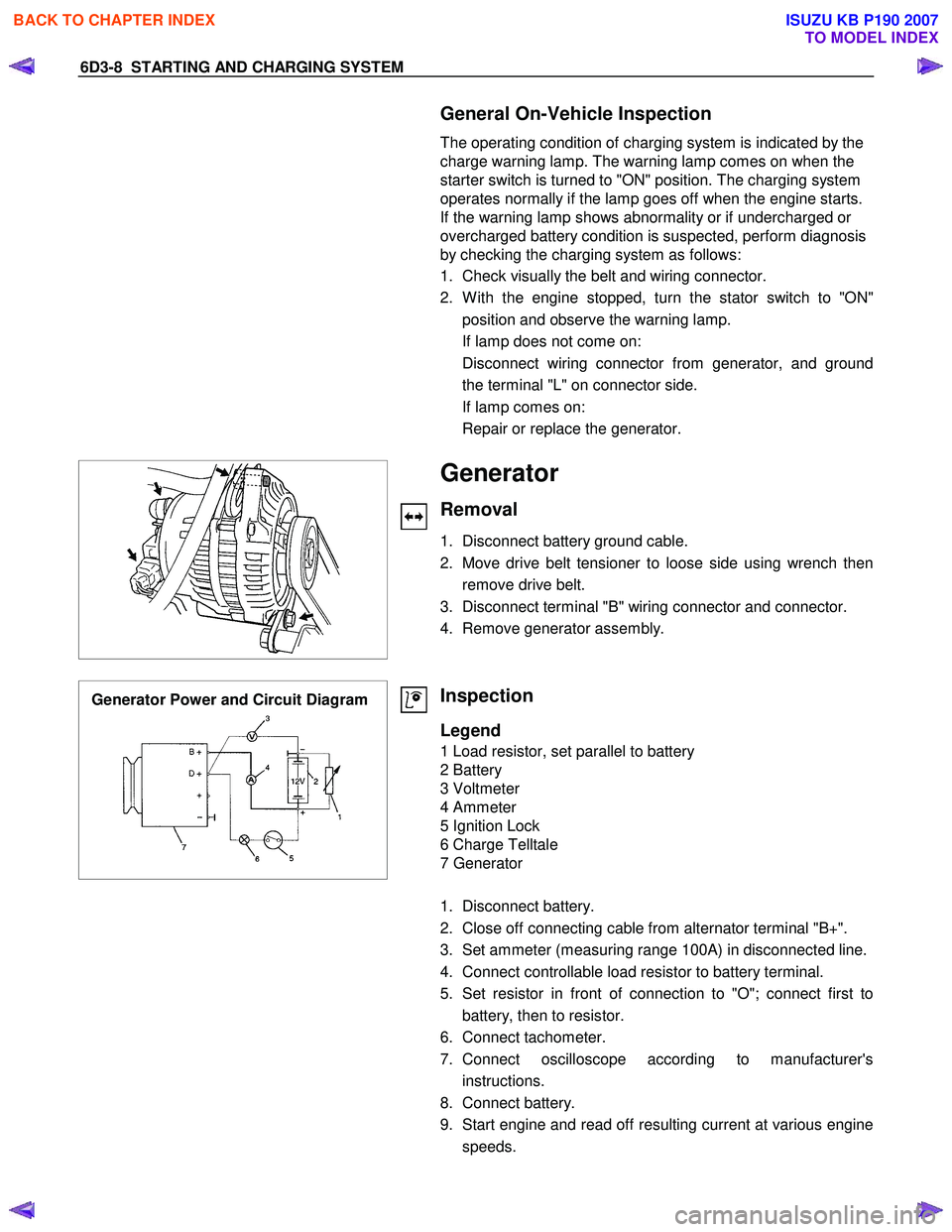
Generator
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Move drive belt tensioner to loose side using wrench then remove drive belt.
3. Disconnect terminal "B" wiring connector and connector.
4. Remove generator assembly.
Generator Power and Circuit Diagram
Inspection
Legend
1 Load resistor, set parallel to battery
2 Battery
3 Voltmeter
4 Ammeter
5 Ignition Lock
6 Charge Telltale
7 Generator
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Close off connecting cable from alternator terminal "B+".
3. Set ammeter (measuring range 100A) in disconnected line.
4. Connect controllable load resistor to battery terminal.
5. Set resistor in front of connection to "O"; connect first to battery, then to resistor.
6. Connect tachometer.
7. Connect oscilloscope according to manufacturer's instructions.
8. Connect battery.
9. Start engine and read off resulting current at various engine speeds.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2157 of 6020
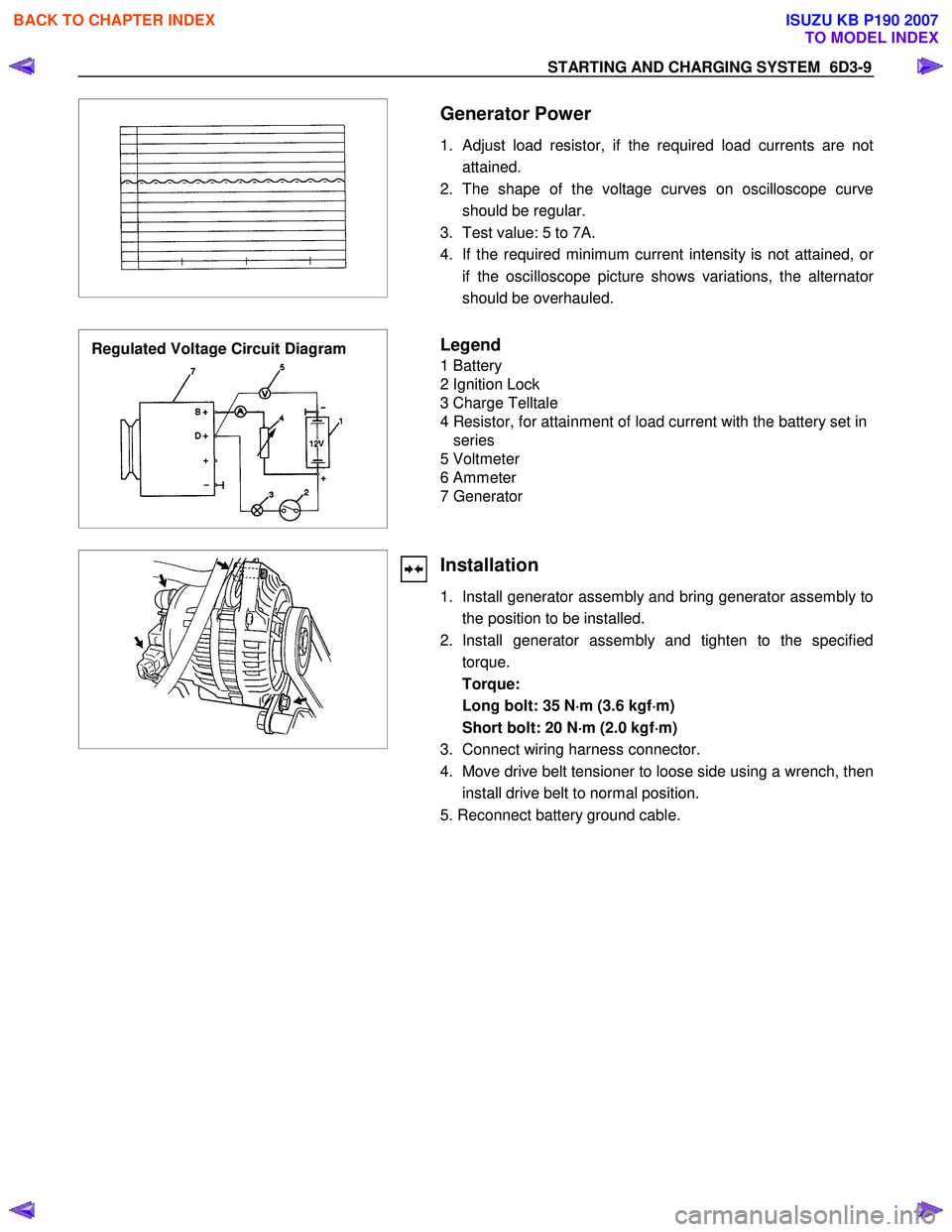
STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-9
Generator Power
1. Adjust load resistor, if the required load currents are not attained.
2. The shape of the voltage curves on oscilloscope curve should be regular.
3. Test value: 5 to 7A.
4. If the required minimum current intensity is not attained, o
r
if the oscilloscope picture shows variations, the alternator
should be overhauled.
Regulated Voltage Circuit Diagram
Legend
1 Battery
2 Ignition Lock
3 Charge Telltale
4 Resistor, for attainment of load current with the battery set in series
5 Voltmeter
6 Ammeter
7 Generator
Installation
1. Install generator assembly and bring generator assembly to the position to be installed.
2. Install generator assembly and tighten to the specified torque.
Torque:
Long bolt: 35 N ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m (3.6 kgf ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m)
Short bolt: 20 N ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m (2.0 kgf ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m)
3. Connect wiring harness connector.
4. Move drive belt tensioner to loose side using a wrench, then install drive belt to normal position.
5. Reconnect battery ground cable.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2160 of 6020

6D3-12 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Diagnosis
The EP regulator incorporates diagnostics which will illuminate
the warning lamp as a result of fault conditions in the generator
and external circuitry.
These conditions include:
1.
An open circuit in the regulator battery sensing wire (S
Terninal)
2. An open circuit or excessive voltage drop in the B+ cable.
3. An open circuit in the generator phase connection.
4. Overcharging of the battery.
5. Regulator output stage short circuit.
6. Open circuit rotor.
The regulator compares the voltage at B+ with the voltage at
the "S" terminal connceted to battery positive. If the voltage
differential exceeds a predetermined threshold, the regulator
will operate in backup mode to limit the output voltage to a safe
level. The warning lamp; will remain illuminated as along as
these conditions prevail.
Sources of high resistance which will trigger the warning lamp
are:
a. Poor contact in wiring harness connectors.
b. Poor contact between rectifier and regulator.
c. High resistance in fusible link assembly.
Caution:
When bench testing the generator it is important that the
warning lamp wattage of 2 watts is not exceeded.
Reversal of the "S" and "L" on the regulator will damage
the regulator.
The correct plug for the regulator is a 9 122 067 011 for the
Bosch tye and for the Shinagawa connector the number is
X02FW.
See appendix 1 for daignostic matrix.
Before testing or disassembling the generator please observe
the following points.
1. W hen testing the diodes with AC type testers the RMS.
Vlotage output must not exceed 12.0 volts, it is
recommended that the stator should be disconnected
during this test.
2. W here zener power diodes are used, the breakdown voltage should be tested to ensure all diodes have the
same zener voltage.
3. Insulation tests on the rotor and stator should use a voltage not exceeding 110v for a series test lamp. The rectifie
r
must be disconnected from the stator prior to testing.
4. W hen carrying out repairs to the charging system always disconnected the battery negative first, and reconnect it
last.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2171 of 6020

SECTION 6E
TABLE OF CONTENTS
C24SE ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ABBREVIATIONS CHARTS ......................... 6E-6
ECM Circuit Diagram (1/2) ............................ 6E-11
ECM Circuit Diagram (2/2) ............................ 6E-12
GROUND POINT CHART - LHD G.EXP (1/4) 6E-13
GROUND POINT CHART - RHD G.EXP (1/4) 6E-17
LOCATION ................................................... 6E-21
CABLE HARNESS & CONNECTOR LOCATION .............................................. 6E-23
CABLE HARNESS & CONNECTOR LOCATION - LHD ................................... 6E-24
CABLE HARNESS & CONNECTOR LOCATION - RHD ................................... 6E-25
CONNECTOR LIST ...................................... 6E-28
RELAY AND FUSE ....................................... 6E-30
RELAY AND FUSE BOX LOCATION (LHD & RHD) ........................................... 6E-30
FUSE AND RELAY LOCATION (LHD & RHD) 6E-32
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1/9) ..................... 6E-33
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (2/9) ..................... 6E-34
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (3/9) ..................... 6E-35
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (4/9) ..................... 6E-36
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (5/9) ..................... 6E-37
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (6/9) ..................... 6E-38
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (7/9) ..................... 6E-39
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (8/9) ..................... 6E-40
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (9/9) ..................... 6E-41
ECM CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENT & OUTPUT SIGNAL .................................... 6E-42
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ECM AND SENSORS ............................................... 6E-48
Engine Control Module (ECM) ................... 6E-48
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E-48
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) .................. 6E-49
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve ....................... 6E-49
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor ............ 6E-50
Knock Sensor (KS) .................................... 6E-50
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E-50
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor ........ 6E-51
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) .................... 6E-51
Heated Oxygen (O
2) Sensor ..................... 6E-51
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR FUEL METERING .............................................. 6E-52 Battery Voltage Correction Mode ............... 6E-52
Clear Flood Mode ...................................... 6E-52
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) Mode .... 6E-52
Engine Speed/ Vehicle Speed/ Fuel Disable Mode ........................................................ 6E-52
Acceleration Mode ..................................... 6E-52
Fuel Cutoff Mode ....................................... 6E-52
Starting Mode ............................................ 6E-52
Run Mode .................................................. 6E-52
Fuel Metering System Components .......... 6E-53
Fuel Injector ............................................... 6E-53
Fuel Pressure Regulator ............................ 6E-53
Fuel Rail ..................................................... 6E-53
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit ....................... 6E-53
Thottle Body Unit ....................................... 6E-53
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ELECTRIC IGNITION SYSTEM ................................. 6E-54
Spark Plug ................................................. 6E-54
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM ............................... 6E-57
EVAP Emission Control System Purpose .. 6E-57
EVAP Emission Control System Operation 6E-57
System Fault Detection .............................. 6E-57
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV) SYSTEM .................................................. 6E-59
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose .... 6E-59
A/C CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS ........................ 6E-60
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation ...................... 6E-60
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose ........................ 6E-60
A/C Request Signal ................................... 6E-60
ISUZU STRATEGY BASED DIAGNOSTICS 6E-61
Overview .................................................... 6E-61
STRATEGY BASED DIAGNOSTICS CHART 6E-61 Diagnostic Thought Process ...................... 6E-62
1. Verify the Complaint .............................. 6E-62
2. Perform Preliminary Checks .................. 6E-62
3. Check Bulletins and Troubleshooting Hints 6E-63
4. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Checks 6E-63
5a and 5b. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Procedures .............................................. 6E-63
5c. Technician Self Diagnoses .................. 6E-63
5d. Intermittent Diagnosis .......................... 6E-64
6 E –1
E N GINE DRIV EABILITY AND E M IS SIONS
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2203 of 6020
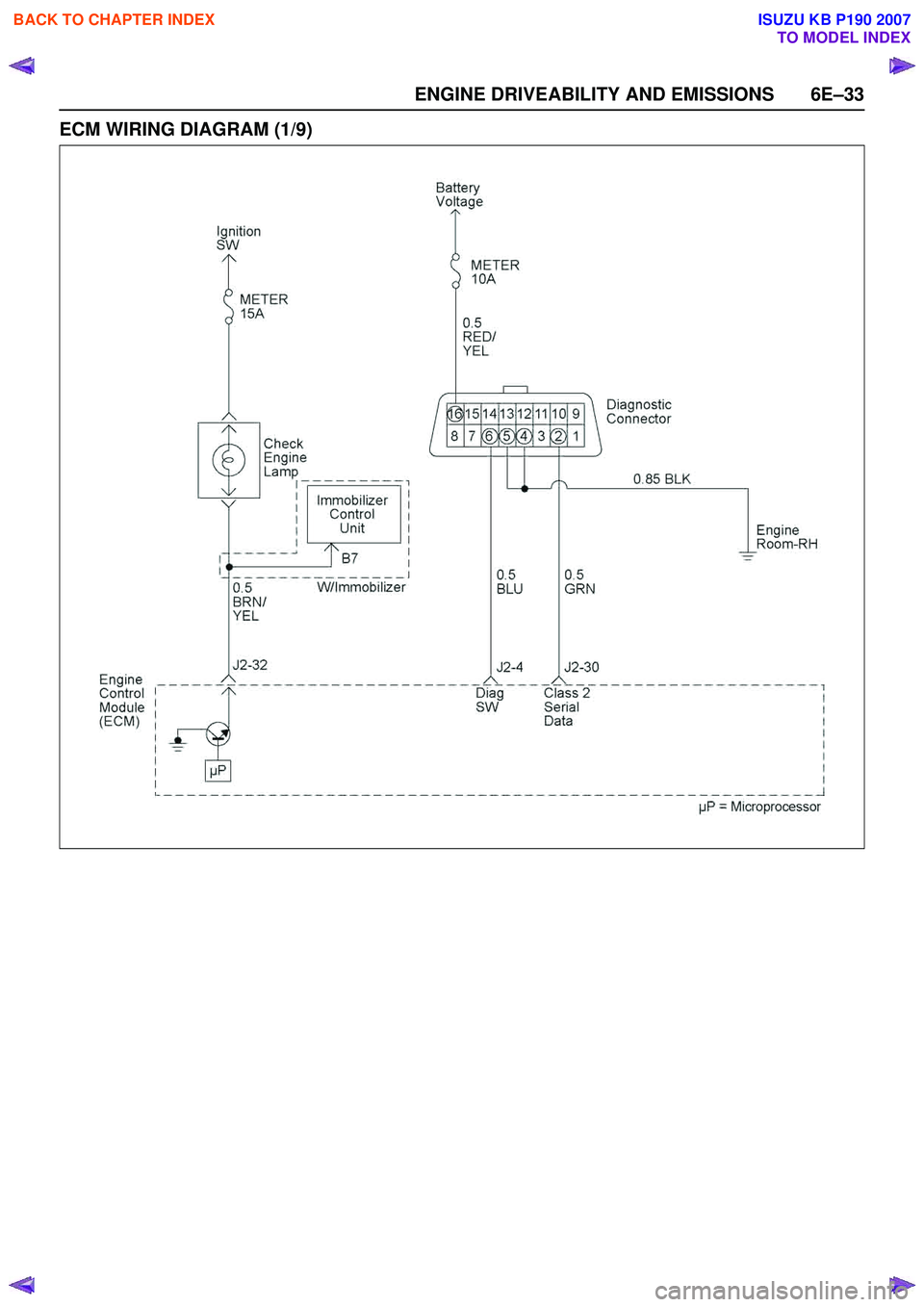
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–33
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1/9)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007