2007 ISUZU KB P190 brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 4237 of 6020

7A4–102 UNIT REPAIR (AW30–40LE)
Special Tools
ILLUSTRATIONTOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
5-8840-2152-0 (J–37227)
Holding fixture
5-8840-0003-0 (J –3289 –20)
Holding fixture base
5-8840-2153-0(J–37228)
Oil pan seal cutter
5-8840-0195-0(J –23327 –1)
Spring compressor
5-8840-2256-0(J–9617)
Oil seal installer; oil pump
5-8840-2170-0 (J–37233)
Spring compressor; OD brake piston
5-8840-0093-0(J –29770 –A)
Oil pressure gauge
5-8840-0254-0(J–25048)
Spring compressor
5-8840-2173-0(J–37236)
Reaction sleeve puller; first and reverse brake
5-8840-2174-0(J–37237)
Piston puller; first and reverse brake
5-8840-2169-0 (J –37232 –2)
Oil seal installer;
manual valve shaft seal installer & remover
5-8840-2168-0(J–35467)
Onennway clutch
testing tool; torque converter
ILLUSTRATION
TOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4240 of 6020

CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-1
SECTION 7A1
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION (JR405E)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
Description ................................................................................................................... ...7A1- 3
Construction ...............................................................................................................7A1 - 3
Main Data and Specification .....................................................................................7A1- 4
Number Plate Location ..............................................................................................7A1- 5
Electronic Control Components Location ...............................................................7A1- 6
Transmission Control Module (TCM) Peripheral Circuit .........................................7A1- 7
Structure and Function of Component .........................................................................7A1- 8
Torque Converter (with Lock-up Function) .............................................................7A1- 8
Oil Pump .....................................................................................................................7 A1- 9
Input Shaft ..................................................................................................................7 A1- 10
Output Shaft ...............................................................................................................7A1 - 10
Gear Shifting Mechanism ..........................................................................................7A1- 10
Control Valve ..............................................................................................................7A1 - 14
Oil Passage .................................................................................................................7A 1- 19
Parking Function ........................................................................................................7A1- 2 0
Inhibitor Switch ..........................................................................................................7A1- 21
Turbine Sensor ...........................................................................................................7A1- 22
Speed Sensor .............................................................................................................7A1- 22
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor ..........................................................................7A1- 23
Engine Speed Sensor (=CKP Sensor) ......................................................................7A1- 23
Brake Switch ..............................................................................................................7A1- 24
Mode Select Switch ...................................................................................................7A1- 24
Transmission Control Module (TCM) .......................................................................7A1- 25
Control Mechanism ........................................................................................................7A1- 26
Content of Function and Control ..............................................................................7A1- 26
Control Item, Input and Output .................................................................................7A1- 29
Line Pressure Control ................................................................................................7A1- 30
Lock-up Control .........................................................................................................7A1- 3 0
Direct Electric Shift Control (DESC) .........................................................................7A1- 31
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4242 of 6020
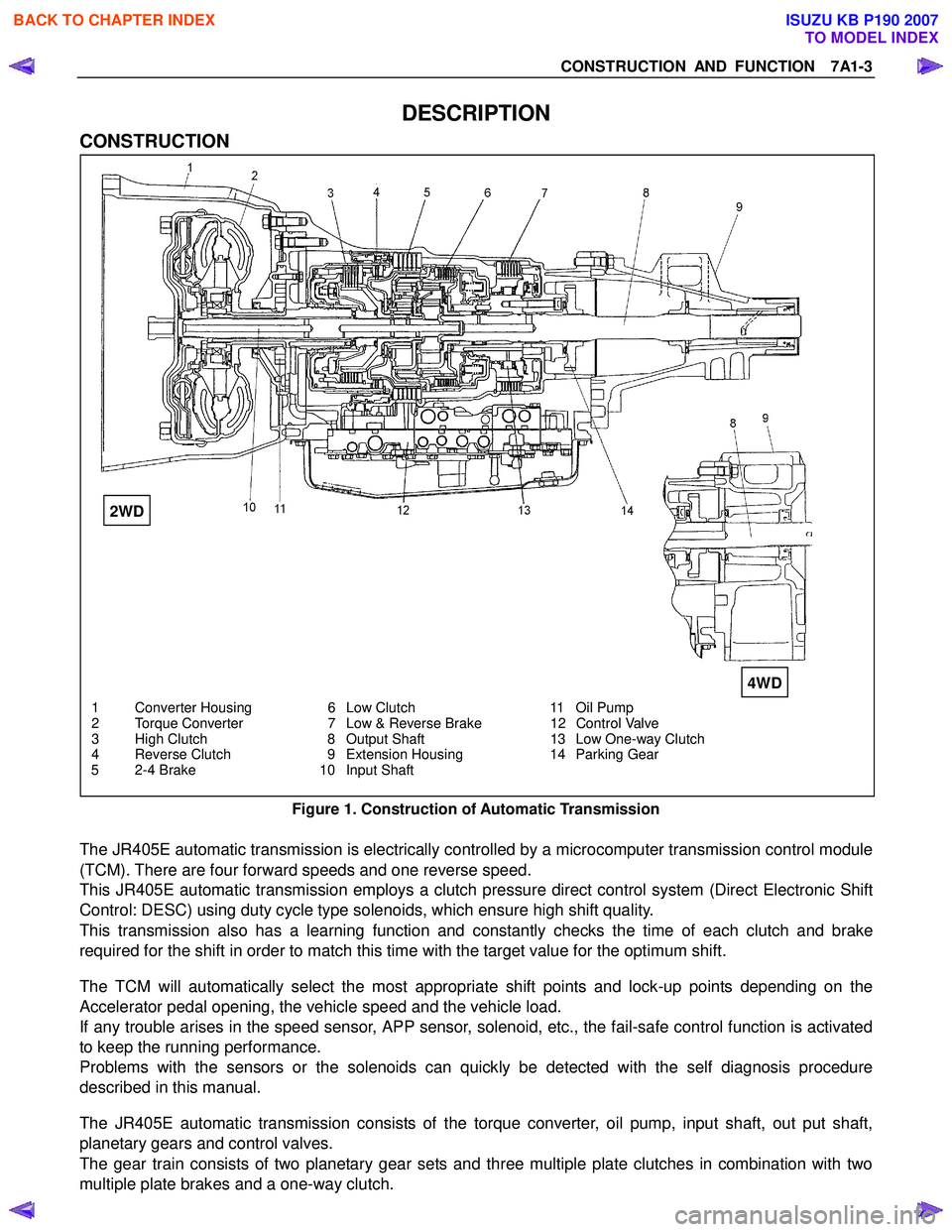
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-3
DESCRIPTION
CONSTRUCTION
1 Converter Housing 6 Low Clutch 11 Oil Pump
2 Torque Converter 7 Low & Reverse Brake 12 Control Valve
3 High Clutch 8 Output Shaft 13 Low One-way Clutch
4 Reverse Clutch 9 Extension Housing 14 Parking Gear
5 2-4 Brake 10 Input Shaft
Figure 1. Construction of Automatic Transmission
The JR405E automatic transmission is electrically controlled by a microcomputer transmission control module
(TCM). There are four forward speeds and one reverse speed.
This JR405E automatic transmission employs a clutch pressure direct control system (Direct Electronic Shift
Control: DESC) using duty cycle type solenoids, which ensure high shift quality.
This transmission also has a learning function and constantly checks the time of each clutch and brake
required for the shift in order to match this time with the target value for the optimum shift.
The TCM will automatically select the most appropriate shift points and lock-up points depending on the
Accelerator pedal opening, the vehicle speed and the vehicle load.
If any trouble arises in the speed sensor, APP sensor, solenoid, etc., the fail-safe control function is activated
to keep the running performance.
Problems with the sensors or the solenoids can quickly be detected with the self diagnosis procedure
described in this manual.
The JR405E automatic transmission consists of the torque converter, oil pump, input shaft, out put shaft,
planetary gears and control valves.
The gear train consists of two planetary gear sets and three multiple plate clutches in combination with two
multiple plate brakes and a one-way clutch.
2WD
4WD
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4243 of 6020
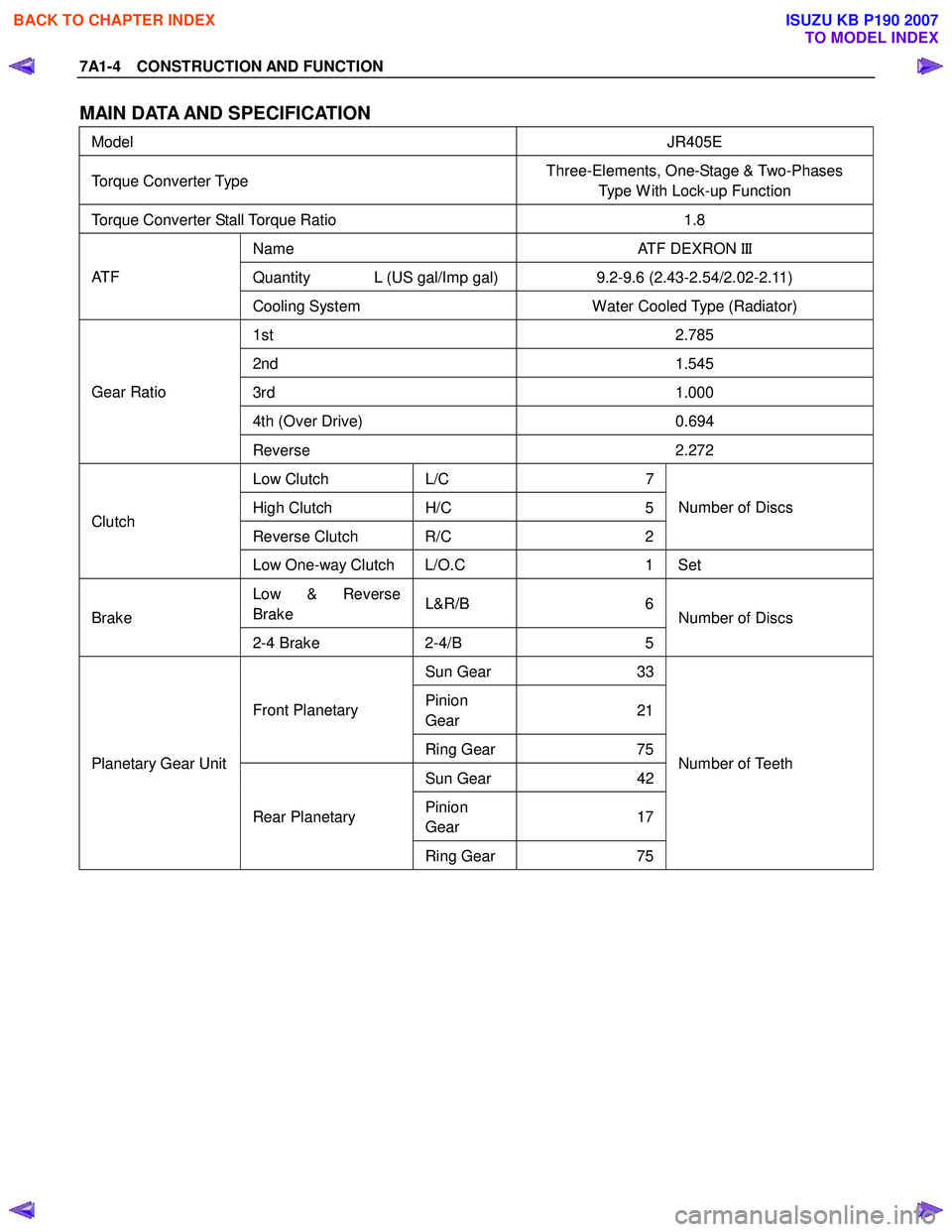
7A1-4 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATION
Model JR405E
Torque Converter Type Three-Elements, One-Stage & Two-Phases
Type W ith Lock-up Function
Torque Converter Stall Torque Ratio 1.8
Name ATF DEXRON III
Quantity L (US gal/Imp gal) 9.2-9.6 (2.43-2.54/2.02-2.11) AT F
Cooling System Water Cooled Type (Radiator)
1st 2.785
2nd 1.545
3rd 1.000
4th (Over Drive) 0.694
Gear Ratio
Reverse 2.272
Low Clutch L/C 7
High Clutch H/C 5
Reverse Clutch R/C 2Number of Discs Clutch
Low One-way Clutch L/O.C 1 Set
Low & Reverse
Brake L&R/B 6
Brake
2-4 Brake 2-4/B 5 Number of Discs
Sun Gear
33
Pinion
Gear 21Front Planetary
Ring Gear 75
Sun Gear 42
Pinion
Gear 17
Planetary Gear Unit
Rear Planetary Ring Gear 75 Number of Teeth
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4245 of 6020
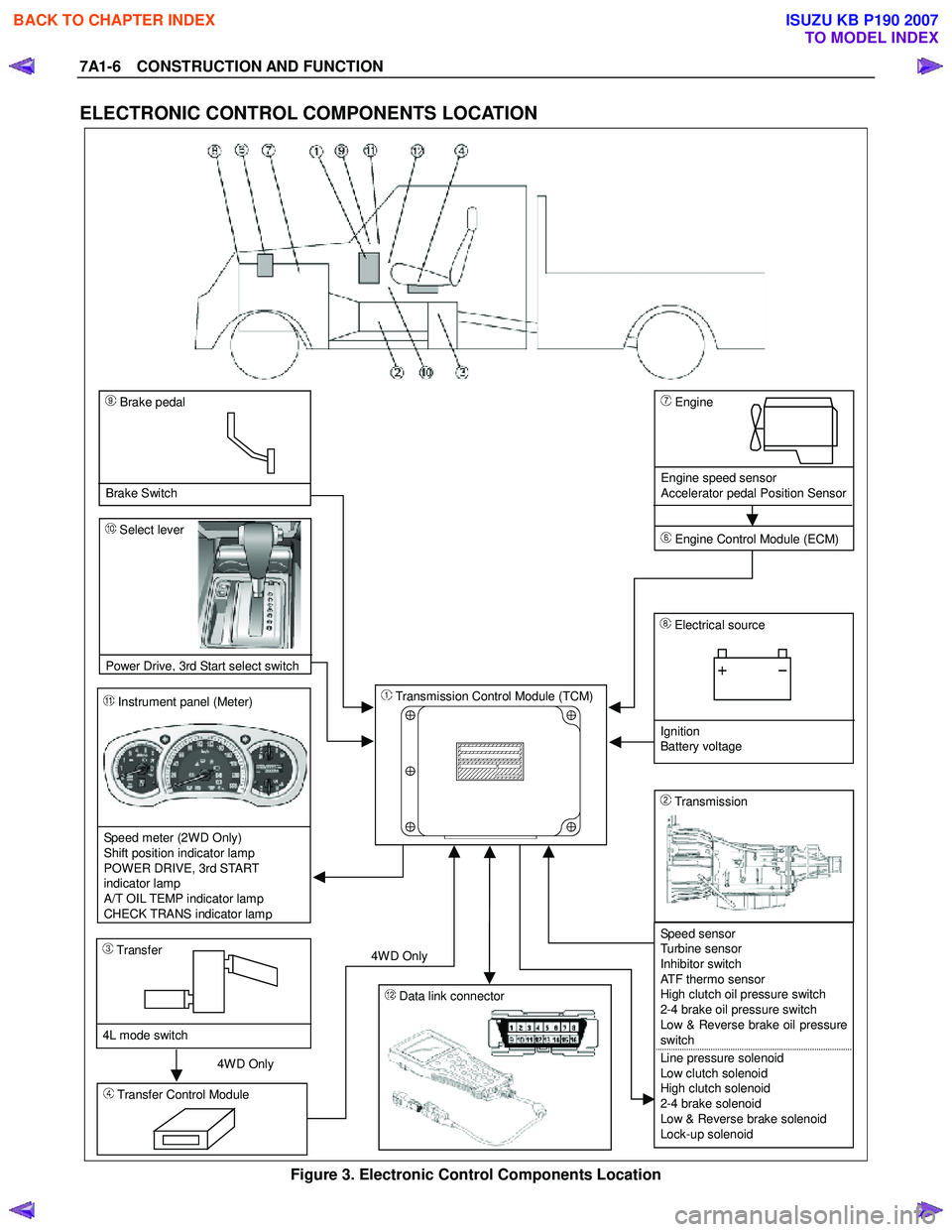
7A1-6 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS LOCATION
4WD Only 4W D Only
Instrument panel (Meter)
Speed meter (2WD Only)
Shift position indicator lamp
POWER DRIVE, 3rd START
indicator lamp
A/T OIL TEMP indicator lamp
CHECK TRANS indicator lam
p
Brake pedal
Brake Switch
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Electrical source
Ignition
Battery voltage
Speed sensor
Turbine sensor
Inhibitor switch
ATF thermo sensor
High clutch oil pressure switch
2-4 brake oil pressure switch
Low & Reverse brake oil pressure
switch
Line pressure solenoid
Low clutch solenoid
High clutch solenoid
2-4 brake solenoid
Low & Reverse brake solenoid
Lock-up solenoid
Transmission
Transfer Control Module
Transfer
4L mode switch
Engine
Engine speed sensor
Accelerator pedal Position Sensor
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Data link connector
Select lever
Power Drive
, 3rd Start select switch
Figure 3. Electronic Control Components Location
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4249 of 6020

7A1-10 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
INPUT SHAFT
• The input shaft has some oil holes, through which lubricating ATF is supplied to the torque converter, the
bearings, etc.
• The input shaft is fitted to the turbine runner in the torque converter, the reverse & high clutch drum and
the rear sun gear by means of the spline. Therefore, the engine driving force received by the torque
converter is transmitted to the reverse & high clutch drum and rear sun gear.
OUTPUT SHAFT
• The output shaft has some oil holes, through which the lubricating ATF is supplied to the bearings, the
planetary gear unit, etc.
• The output shaft transmits the engine driving force from the planetary gear to the propeller shaft.
• The front internal gear is fitted with the rear carrier assembly by spline. The parking gear is also fitted by
spline. By fixing this gear mechanically, the output shaft is fixed as required when parking the vehicle.
GEAR SHIFTING MECHANISM
• The JR405E consists of two sets of planetary gears, three multiple plate clutches, two multiple plate
brakes and a one-way clutch. They are activated in different combinations in any of four forward and one
reverse gear positions.
Principle of gear shifting (Figure 12) • Planetary gears have the advantage of a compact configuration because of the way they are constructed
with a single central shaft.
• Also, unlike the manual transmission gears that require changing of the gear mesh, the gear ratio of the
planetary gears can be changed more easily by locking, releasing or rotating only some of their parts.
• A planetary gear is made up of a sun gear (1) at its center, and pinion gears (2) each of which rotates
about its own center and around the sun gear, as shown. They are all contained within the internal gear
(3).
• Also, since the pinion gears are further supported by the planetary carrier (4), they rotate as a unit in the
same direction, and at the same rate.
• As shown below, each planetary gear is constructed of three elements; a sun gear, pinion gears, an
internal gear and a planetary carrier. Gear shifting is achieved by conditioning two of the three elements,
namely the sun gear, the internal gear and planetary carrier.
• The planetary gears are locked by the clutch, brake and one-way clutch according to the gear shifting.
1. Sun Gear
2. Pinion Gear
3. Internal Gear
4. Planetary Carrier
Figure 12. Planetary Gear
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4250 of 6020
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-11
• The JR405E consists of two sets of planetary gears, which are called front planetary gear and rear
planetary gear.
• The sun gear of the front planetary gear is fixed to the drive plates of 2-4 brake and reverse clutch.
• The planetary carrier of the front planetary gear is fixed to the drum of the low clutch, the drive plates of
the low & reverse brake, and the hub of the high clutch.
• The internal gear of the front planetary gear, and the planetary carrier of the rear planetary gear, are
connected as one and fixed to the output shaft.
• The sun gear of the rear planetary gear is fixed to the input shaft.
• The internal gear of the rear planetary gear is fixed to the hub of the low clutch.
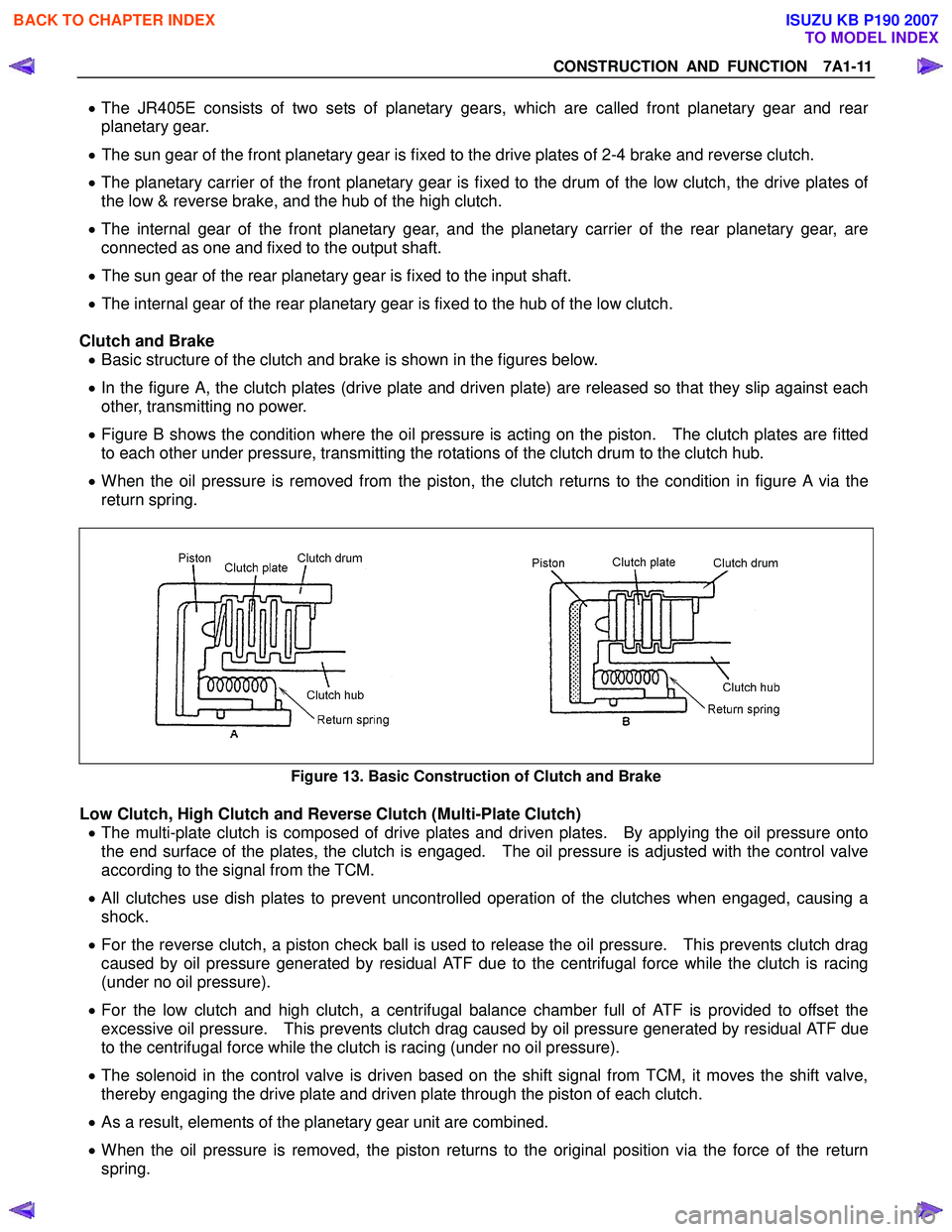
Clutch and Brake • Basic structure of the clutch and brake is shown in the figures below.
• In the figure A, the clutch plates (drive plate and driven plate) are released so that they slip against each
other, transmitting no power.
• Figure B shows the condition where the oil pressure is acting on the piston. The clutch plates are fitted
to each other under pressure, transmitting the rotations of the clutch drum to the clutch hub.
• When the oil pressure is removed from the piston, the clutch returns to the condition in figure A via the
return spring.
Figure 13. Basic Construction of Clutch and Brake
Low Clutch, High Clutch and Reverse Clutch (Multi-Plate Clutch) • The multi-plate clutch is composed of drive plates and driven plates. By applying the oil pressure onto
the end surface of the plates, the clutch is engaged. The oil pressure is adjusted with the control valve
according to the signal from the TCM.
• All clutches use dish plates to prevent uncontrolled operation of the clutches when engaged, causing a
shock.
• For the reverse clutch, a piston check ball is used to release the oil pressure. This prevents clutch drag
caused by oil pressure generated by residual ATF due to the centrifugal force while the clutch is racing
(under no oil pressure).
• For the low clutch and high clutch, a centrifugal balance chamber full of ATF is provided to offset the
excessive oil pressure. This prevents clutch drag caused by oil pressure generated by residual ATF due
to the centrifugal force while the clutch is racing (under no oil pressure).
• The solenoid in the control valve is driven based on the shift signal from TCM, it moves the shift valve,
thereby engaging the drive plate and driven plate through the piston of each clutch.
• As a result, elements of the planetary gear unit are combined.
• When the oil pressure is removed, the piston returns to the original position via the force of the return
spring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4252 of 6020
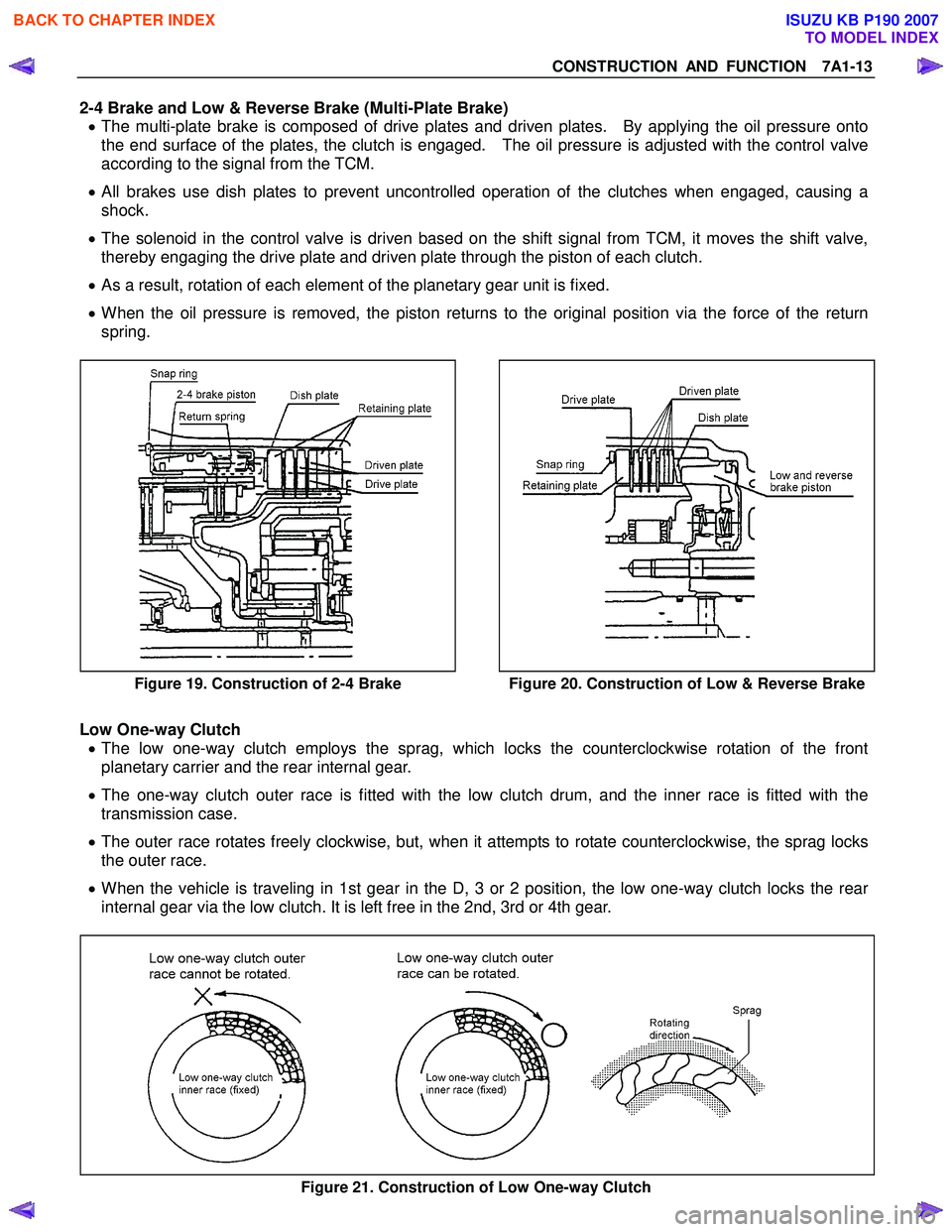
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-13
2-4 Brake and Low & Reverse Brake (Multi-Plate Brake) • The multi-plate brake is composed of drive plates and driven plates. By applying the oil pressure onto
the end surface of the plates, the clutch is engaged. The oil pressure is adjusted with the control valve
according to the signal from the TCM.
• All brakes use dish plates to prevent uncontrolled operation of the clutches when engaged, causing a
shock.
• The solenoid in the control valve is driven based on the shift signal from TCM, it moves the shift valve,
thereby engaging the drive plate and driven plate through the piston of each clutch.
• As a result, rotation of each element of the planetary gear unit is fixed.
• When the oil pressure is removed, the piston returns to the original position via the force of the return
spring.
Figure 19. Construction of 2-4 Brake
Figure 20. Construction of Low & Reverse Brake
Low One-way Clutch
• The low one-way clutch employs the sprag, which locks the counterclockwise rotation of the front
planetary carrier and the rear internal gear.
• The one-way clutch outer race is fitted with the low clutch drum, and the inner race is fitted with the
transmission case.
• The outer race rotates freely clockwise, but, when it attempts to rotate counterclockwise, the sprag locks
the outer race.
• When the vehicle is traveling in 1st gear in the D, 3 or 2 position, the low one-way clutch locks the rear
internal gear via the low clutch. It is left free in the 2nd, 3rd or 4th gear.
Figure 21. Construction of Low One-way Clutch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007