2007 ISUZU KB P190 Wiring
[x] Cancel search: WiringPage 4337 of 6020
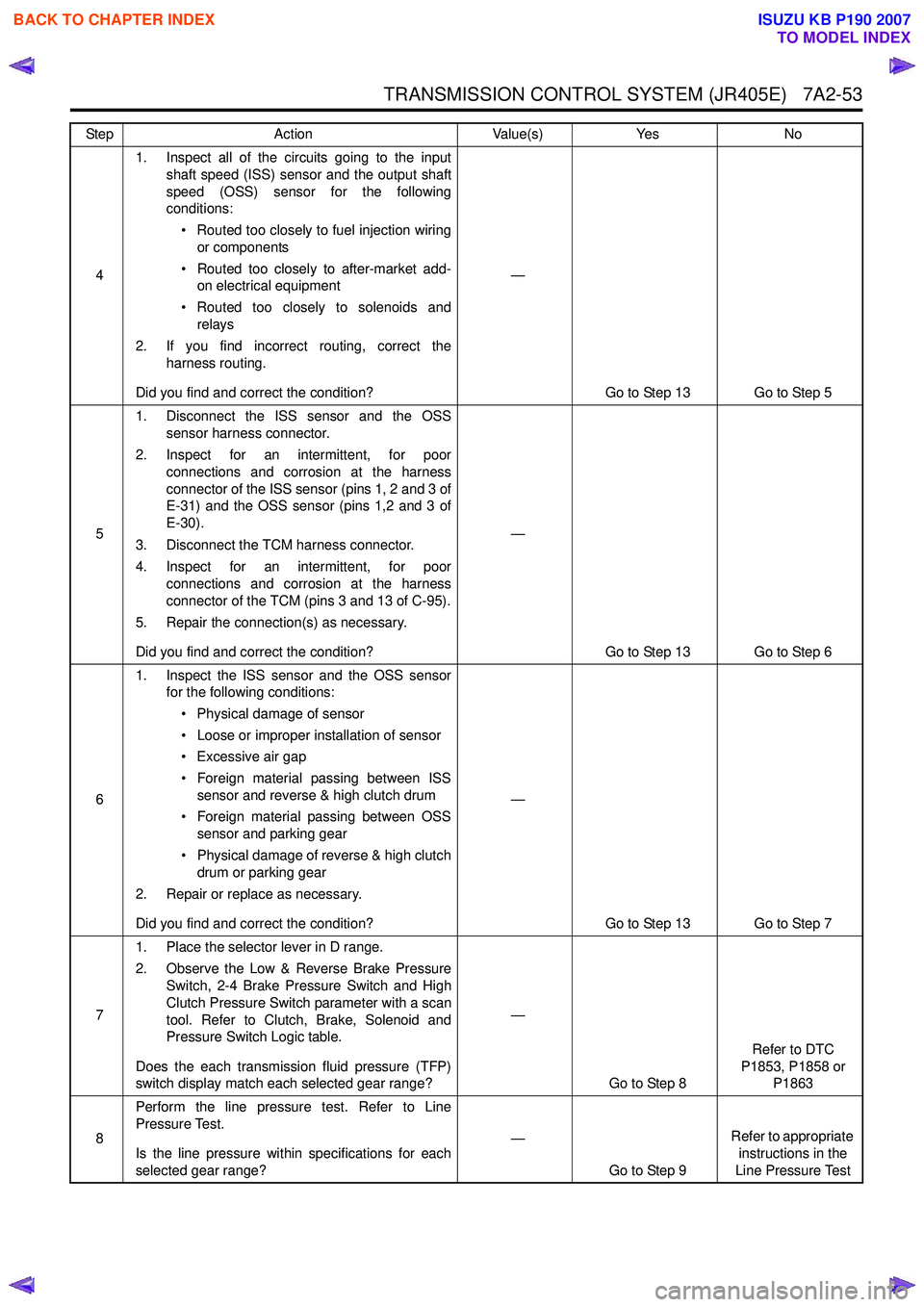
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-53
41. Inspect all of the circuits going to the input
shaft speed (ISS) sensor and the output shaft
speed (OSS) sensor for the following
conditions:
• Routed too closely to fuel injection wiring or components
• Routed too closely to after-market add- on electrical equipment
• Routed too closely to solenoids and relays
2. If you find incorrect routing, correct the harness routing.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 5
5 1. Disconnect the ISS sensor and the OSS
sensor harness connector.
2. Inspect for an intermittent, for poor connections and corrosion at the harness
connector of the ISS sensor (pins 1, 2 and 3 of
E-31) and the OSS sensor (pins 1,2 and 3 of
E-30).
3. Disconnect the TCM harness connector.
4. Inspect for an intermittent, for poor connections and corrosion at the harness
connector of the TCM (pins 3 and 13 of C-95).
5. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 6
6 1. Inspect the ISS sensor and the OSS sensor
for the following conditions:
• Physical damage of sensor
• Loose or improper installation of sensor
• Excessive air gap
• Foreign material passing between ISS sensor and reverse & high clutch drum
• Foreign material passing between OSS sensor and parking gear
• Physical damage of reverse & high clutch drum or parking gear
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 7
7 1. Place the selector lever in D range.
2. Observe the Low & Reverse Brake Pressure Switch, 2-4 Brake Pressure Switch and High
Clutch Pressure Switch parameter with a scan
tool. Refer to Clutch, Brake, Solenoid and
Pressure Switch Logic table.
Does the each transmission fluid pressure (TFP)
switch display match each selected gear range? —
Go to Step 8 Refer to DTC
P1853, P1858 or P1863
8 Perform the line pressure test. Refer to Line
Pressure Test.
Is the line pressure within specifications for each
selected gear range? —
Go to Step 9 Refer to appropriate
instructions in the
Line Pressure Test
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4376 of 6020

7A2-92 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Symptoms - Transmission Controls
Symptoms - Transmission Controls
Important Preliminary Inspections Before Starting
Perform Diagnostic System Check - Transmission
Controls before using the symptom tables, and verify
that all of the following are true:
• The TCM and check trans lamp is operating correctly.
• The scan tool data is within the normal operating range. Refer to Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Verify the customer concern and locate the correct symptom in the table of contents. Inspect the items
indicated under that symptom.
Visual and Physical Inspection
Several of the symptom procedures ask for careful
visual and physical inspection. This step is extremely
important. The visual and physical inspection can lead
to correcting a problem without further inspections, and
can save valuable time. Ensure that:
• The TCM grounds are clean, tight, and in their proper location.
• The transmission harness wiring and terminals are properly connected and are not pinched or cut.
Intermittent
Important: Inspect for improper installation of electrical
components if an intermittent condition exists. Inspect
for aftermarket add-on electrical equipment devices,
lights, and cellular phones. Verify that no aftermarket
equipment is connected to the serial data circuit.
Important: The problem may or may not turn ON the
check trans lamp or store a DTC. Faulty electrical
connections or wiring cause most intermittent
problems.
Perform a careful visual and physical inspection of the
suspect connectors for the following conditions:
• Improperly mated connector halves
• Terminals that are not seated
• Terminals that are damaged or improperly formed
Reform or replace connector terminals in the problem
circuit in order to ensure proper contact tension.
Remove the terminal from the connector body in order
to inspect for poor terminal wire connection.
Road test the vehicle with the DMM connected to the
suspected circuit. An abnormal reading that occurs
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a malfunction in the circuit being monitored.
Use the scan tool in order to help detect intermittent
conditions. Useful features of the Tech 2 includes the
following: • Trigger the Snapshot feature in order to capture
and store transmission parameters when the
malfunction occurs. Review this stored information
in order to see the specific running conditions that
caused the malfunction.
• Use the Plot Function on the scan tool in order to plot selected data parameters. Review this stored
information to aid in locating an intermittent
problem. Refer to the scan tool Users Guide for
more information.
Important: If the intermittent condition exists as a start
and then stall, test for DTCs relating to the vehicle theft
deterrent system. Test for improper installation of
electrical options such as lights, cellular phones, etc.
Any of the following may cause an intermittent check
trans lamp with no stored DTC:
• The TCM grounds are loose or dirty. Refer to Transmission Controls Schematics.
• The check trans lamp circuit intermittently shorted to ground
• Electrical system interference caused by a malfunctioning relay, TCM driven solenoid, or
switch. The electrical component can cause a
sharp electrical surge. Normally, the problem will
occur when the malfunctioning component is
operating.
• There are any open diodes.
Important: The following symptom tables contain
groups of possible causes for each symptom. The
order of these procedures is not important. If the scan
tool readings do not indicate the problems, then
proceed in a logical order, easiest to check or most
likely to cause first. In order to determine if a specific
vehicle is using a particular system or component, refer
to Transmission Controls Schematics for an
application.
Use the following tables when diagnosing a symptom
complaint:
• Intermittent Conditions
• Vehicle Does Not Run
• Trouble at Starting
• Faulty Gearshift
• Faulty Shift Pattern
• No or Error Gearshift
• Faulty Operation During Running
• Faulty Operation in Stopping
• Faulty Lock Up
• No Lock Up
• Transmission Fluid Leak
•Others
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4377 of 6020
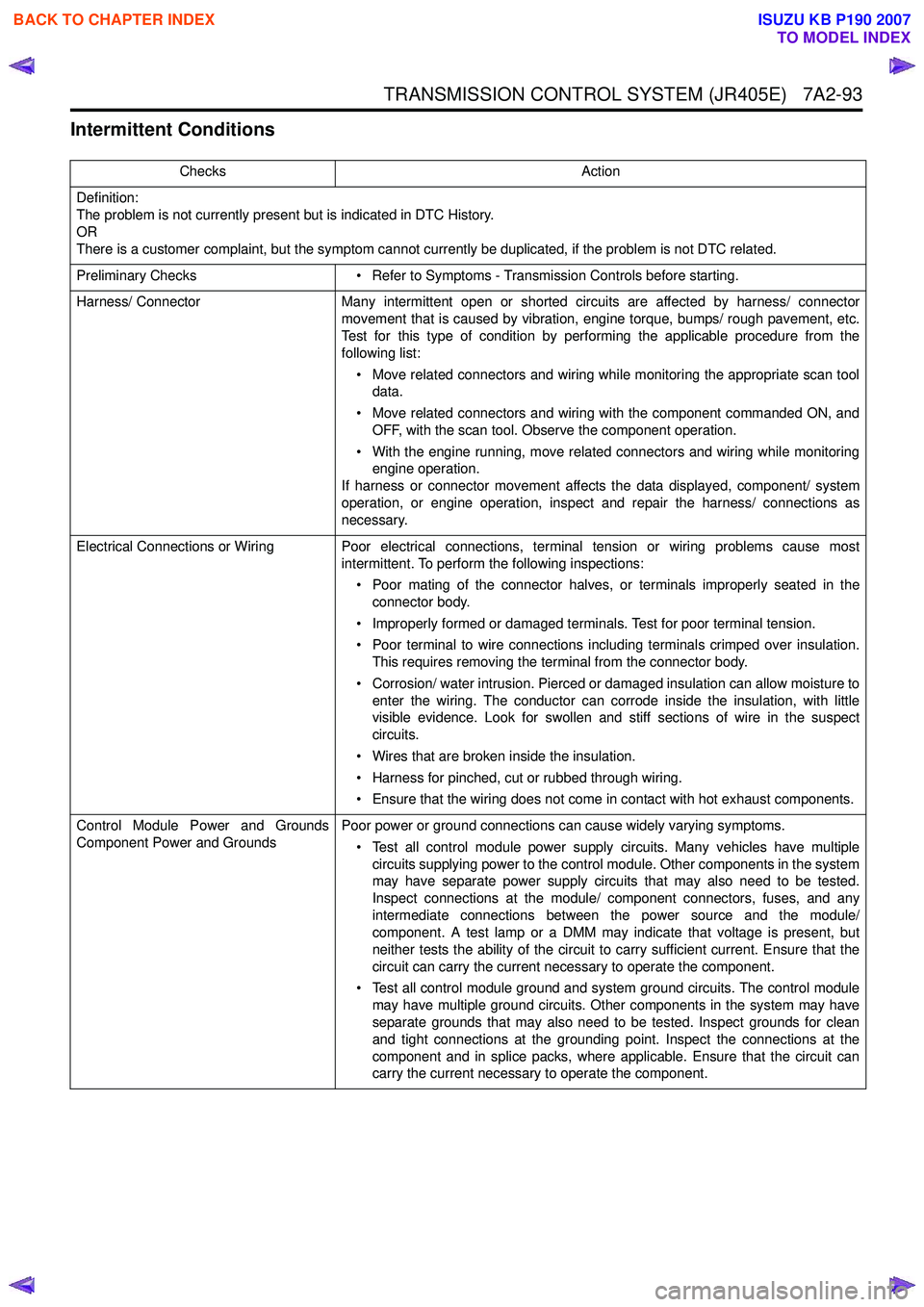
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-93
Intermittent Conditions
ChecksAction
Definition:
The problem is not currently present but is indicated in DTC History.
OR
There is a customer complaint, but the symptom cannot currently be duplicated, if the problem is not DTC related.
Preliminary Checks • Refer to Symptoms - Transmission Controls before starting.
Harness/ Connector Many intermittent open or shorted circuits are affected by harness/ connector
movement that is caused by vibration, engine torque, bumps/ rough pavement, etc.
Test for this type of condition by performing the applicable procedure from the
following list:
• Move related connectors and wiring while monitoring the appropriate scan tool data.
• Move related connectors and wiring with the component commanded ON, and OFF, with the scan tool. Observe the component operation.
• With the engine running, move related connectors and wiring while monitoring engine operation.
If harness or connector movement affects the data displayed, component/ system
operation, or engine operation, inspect and repair the harness/ connections as
necessary.
Electrical Connections or Wiring Poor electrical connections, terminal tension or wiring problems cause most intermittent. To perform the following inspections:
• Poor mating of the connector halves, or terminals improperly seated in the connector body.
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals. Test for poor terminal tension.
• Poor terminal to wire connections including terminals crimped over insulation. This requires removing the terminal from the connector body.
• Corrosion/ water intrusion. Pierced or damaged insulation can allow moisture to enter the wiring. The conductor can corrode inside the insulation, with little
visible evidence. Look for swollen and stiff sections of wire in the suspect
circuits.
• Wires that are broken inside the insulation.
• Harness for pinched, cut or rubbed through wiring.
• Ensure that the wiring does not come in contact with hot exhaust components.
Control Module Power and Grounds
Component Power and Grounds Poor power or ground connections can cause widely varying symptoms.
• Test all control module power supply circuits. Many vehicles have multiple circuits supplying power to the control module. Other components in the system
may have separate power supply circuits that may also need to be tested.
Inspect connections at the module/ component connectors, fuses, and any
intermediate connections between the power source and the module/
component. A test lamp or a DMM may indicate that voltage is present, but
neither tests the ability of the circuit to carry sufficient current. Ensure that the
circuit can carry the current necessary to operate the component.
• Test all control module ground and system ground circuits. The control module may have multiple ground circuits. Other components in the system may have
separate grounds that may also need to be tested. Inspect grounds for clean
and tight connections at the grounding point. Inspect the connections at the
component and in splice packs, where applicable. Ensure that the circuit can
carry the current necessary to operate the component.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4609 of 6020

MANUAL TRANSMISSION 7B1-3
Service Precaution
WARNING: THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS
COMPONENT AND WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN
ORDER TO DETERMINE WHETHER YOU ARE
PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING. WHEN YOU
ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE
SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFER
TO THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE
AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNECESSARY SRS SYSTEM
REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU/GM will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU/GM will also call
out the fasteners that require thread lockers o
r
thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED,
do not use supplemental coatings (paints, greases,
or other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners
or fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener.
When you install fasteners, use the correct
tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to
parts and systems.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4665 of 6020

MANUAL TRANSMISSION 7B1-59
Service Precaution
WARNING: THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLE MENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS
COMPONENT AND WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN
ORDER TO DETERMINE WHETHER YOU ARE
PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING. WHEN YOU
ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE
SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFER
TO THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE
AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNECESSARY SRS SYSTEM
REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU/GM will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU/GM will also call
out the fasteners that require thread lockers o
r
thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED,
do not use supplemental coatings (paints, greases,
or other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners
or fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener.
When you install fasteners, use the correct
tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to
parts and systems.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4832 of 6020

7D-2 TRANSFER CASE
Service Precaution
WARNING: THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS
COMPONENT AND WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN
ORDER TO DETERMINE WHETHER YOU ARE
PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING. WHEN YOU
ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFER TO
THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE
AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNECESSARY SRS SYSTEM
REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU/GM will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU/GM will also call
out the fasteners that require thread lockers or
thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED,
do not use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases,
or other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners
or fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener. When
you install fasteners, use the correct tightening
sequence and specifications. Following these
instructions can help you avoid damage to parts and
systems.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4876 of 6020

7D1-2 TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM
Service Precaution
WARNING:
THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS COMPONENT AND
WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN ORDER TO DETERMINE
WHETHER YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING.
WHEN YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR
THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFER TO
THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW
WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR OTHERWISE
UNNECESSARY SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.
CAUTION:
Always use the correct fastener in the proper location.
When you replace a fastener, use ONLY the exact part
number for that application. ISUZU/GM will call out those
fasteners that require a replacement after removal.
ISUZU/GM will also call out the fasteners that require
thread lockers or thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE
SPECIFIED, do not use supplemental coatings (Paints,
greases, or other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded
fasteners or fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such
coatings adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener. When you
install fasteners, use the correct tightening sequence and
specifications. Following these instructions can help you
avoid damage to parts and systems.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4885 of 6020
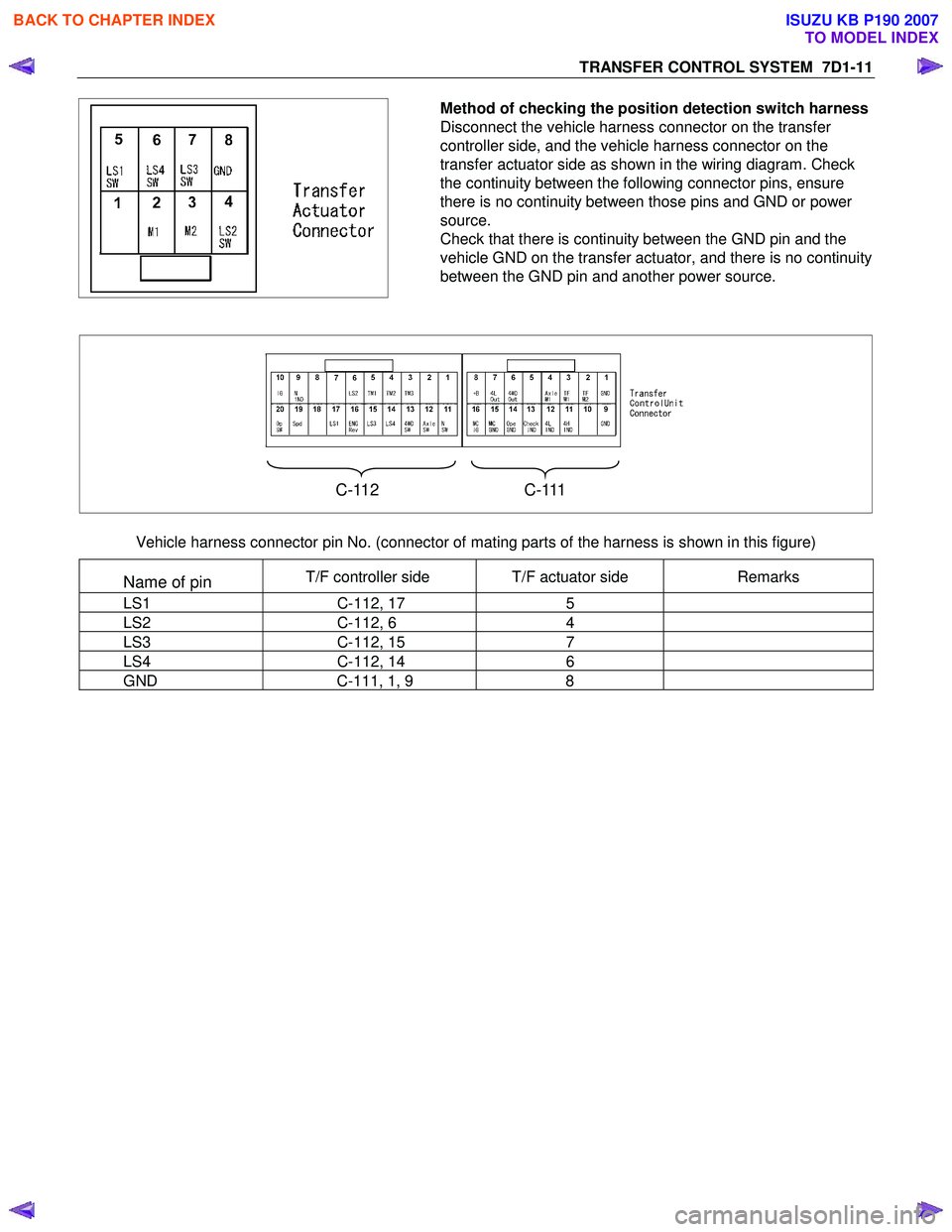
TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM 7D1-11
Method of checking the position detection switch harness
Disconnect the vehicle harness connector on the transfer
controller side, and the vehicle harness connector on the
transfer actuator side as shown in the wiring diagram. Check
the continuity between the following connector pins, ensure
there is no continuity between those pins and GND or power
source.
Check that there is continuity between the GND pin and the
vehicle GND on the transfer actuator, and there is no continuity
between the GND pin and another power source.
C-112 C-111
Vehicle harness connector pin No. (connector of mating parts of the harness is shown in this figure)
Name of pin T/F controller side T/F actuator side Remarks
LS1 C-112, 17 5
LS2 C-112, 6 4
LS3 C-112, 15 7
LS4 C-112, 14 6
GND C-111, 1, 9 8
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007