2007 ISUZU KB P190 BATTERY
[x] Cancel search: BATTERYPage 2167 of 6020

STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-19
Inspection
Generator
Before any in field testing can be undertaken it is important
that the battery's conditions is established and the terminals
are clean and tight.
Check the condition of the generator drive belt and ensure that
it is adjusted in accordance with the engine manufacturer's
recommnedations.
Battery conditions:
Note: This assessment may be difficult with maintenance free
assemblies.
Test the specific gravity of the individual cells the readings
should be within 10 points of each other, it is recommended
that the average SG should be 1.260 or higher.
A load test should be carried out to determine the ability of the
battery to supply and accept current. This is a good indicator
as to the general condition of the battery.
A load equal to the normal starting current should be placed
across the battery, the duration of this load test should not
exceed 10 seconds, during this time the terminal voltage
across the battery should not drop below 9.6 volts. Observe
each cell for signs of excessive gas liberation, usuall an
indication of cell failure.
If the battery test is clear proceed with the Generator tests as
follows.
Care should be taken when making the following connections.
It is recommended that the battery negative terminal be
disconnected before the test meters are connected, and
reconnecting the negative terminal when the meters are
inserted into the circuit under test. The warning lamp in the D+
circuit should not exceed 2 watts.
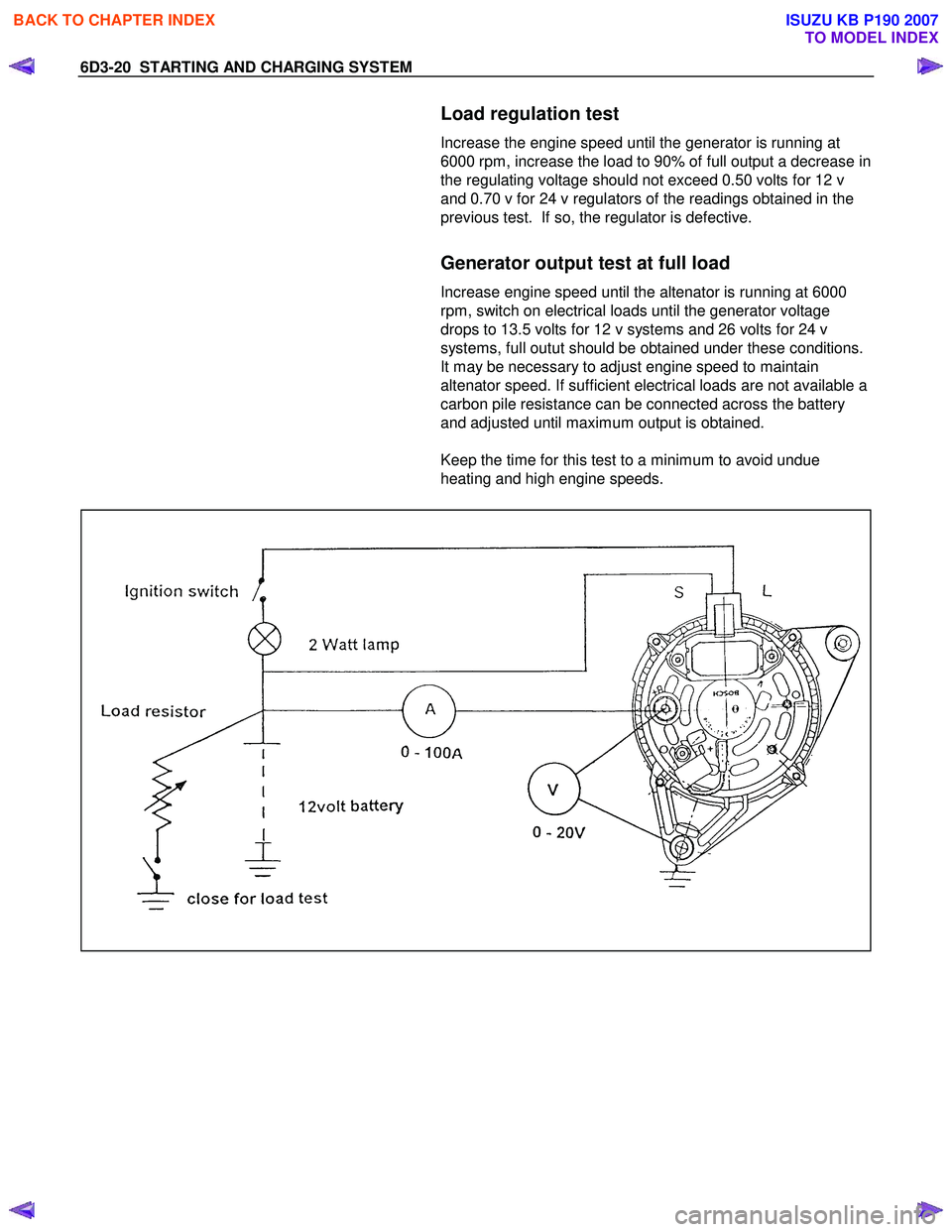
Regulating voltage test on the vehicle.
Connect a voltmeter to the generator, the positive lead to the
B+ terminal and the nagative lead to the generator casing.
Select the voltage range to suit the system, i.e. 20v for 12 volt
sysytems or 40v for 24 volt systems. Connect an ammeter in
series with the main output cable from the B+ terminal on the
generator, the range selected must be capable of reading the
maximum output from the generator.
Note the voltmeter reading before starting the engine. This
reading should increase when the engine is running indicating
generator output, start the engine and increase the engine
speed until the generator is running at 4000 rpm, switch on
vehicle loads of 5-10 A is indcated on the ammeter, the
voltmeter shoud read 14.0-14.2 v for a 12 volt system, for a 24
volt system the readings should be 5-10 A and 27.7-28.5 volts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2168 of 6020
6D3-20 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Load regulation test
Increase the engine speed until the generator is running at
6000 rpm, increase the load to 90% of full output a decrease in
the regulating voltage should not exceed 0.50 volts for 12 v
and 0.70 v for 24 v regulators of the readings obtained in the
previous test. If so, the regulator is defective.
Generator output test at full load
Increase engine speed until the altenator is running at 6000
rpm, switch on electrical loads until the generator voltage
drops to 13.5 volts for 12 v systems and 26 volts for 24 v
systems, full outut should be obtained under these conditions.
It may be necessary to adjust engine speed to maintain
altenator speed. If sufficient electrical loads are not available a
carbon pile resistance can be connected across the battery
and adjusted until maximum output is obtained.
Keep the time for this test to a minimum to avoid undue
heating and high engine speeds.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2169 of 6020
STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-21
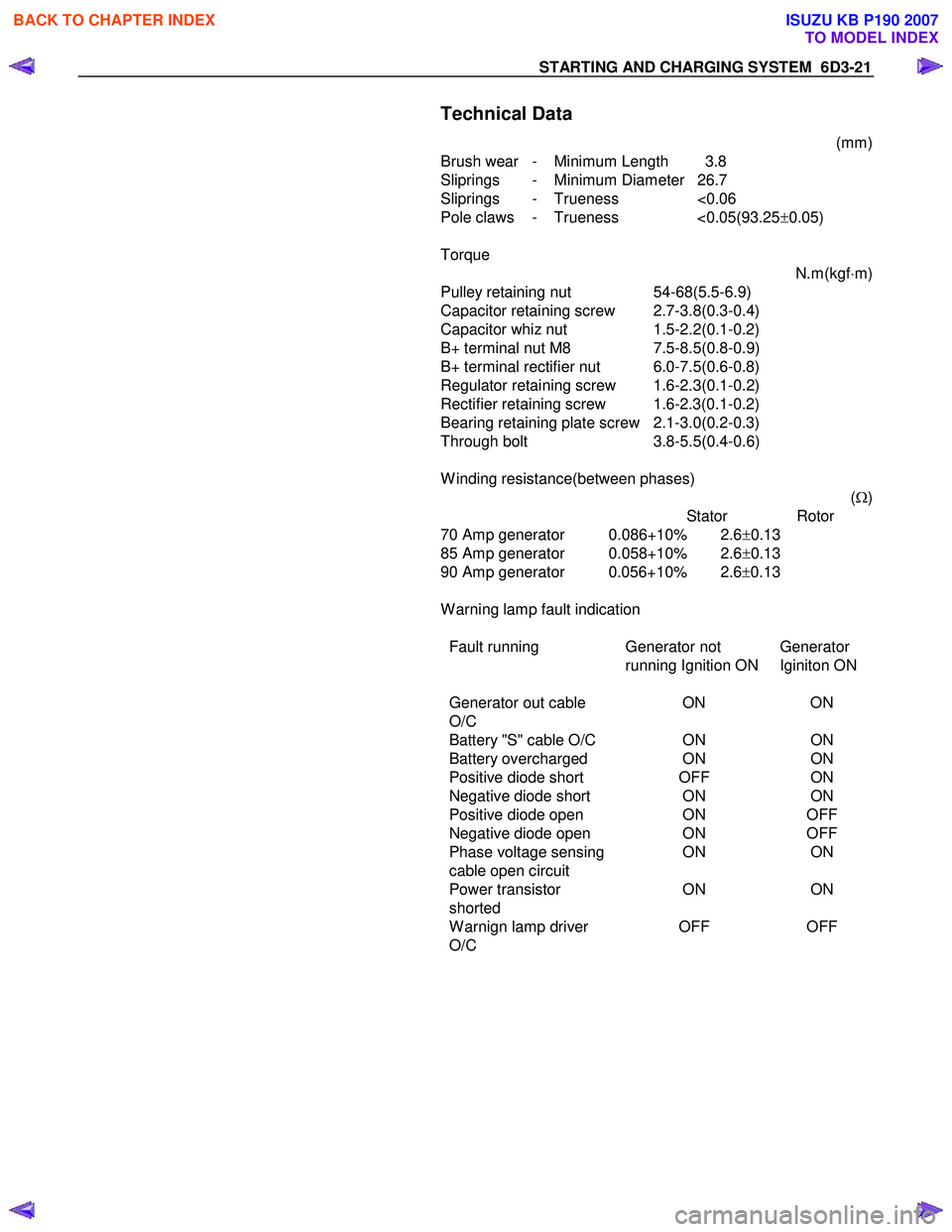
Technical Data
(mm)
Brush wear - Minimum Length 3.8
Sliprings - Minimum Diameter 26.7
Sliprings - Trueness <0.06
Pole claws - Trueness <0.05(93.25 ±0.05)
Torque N.m(kgf⋅m)
Pulley retaining nut 54-68(5.5-6.9)
Capacitor retaining screw 2.7-3.8(0.3-0.4)
Capacitor whiz nut 1.5-2.2(0.1-0.2)
B+ terminal nut M8 7.5-8.5(0.8-0.9)
B+ terminal rectifier nut 6.0-7.5(0.6-0.8)
Regulator retaining screw 1.6-2.3(0.1-0.2)
Rectifier retaining screw 1.6-2.3(0.1-0.2)
Bearing retaining plate screw 2.1-3.0(0.2-0.3)
Through bolt 3.8-5.5(0.4-0.6)
W inding resistance(between phases) (Ω )
Stator Rotor
70 Amp generator 0.086+10% 2.6 ±0.13
85 Amp generator 0.058+10% 2.6 ±0.13
90 Amp generator 0.056+10% 2.6 ±0.13
W arning lamp fault indication
Fault running Generator not
running Ignition ON Generator
Iginiton ON
Generator out cable
O/C ON
ON
Battery "S" cable O/C ONON
Battery overcharged ONON
Positive diode short OFFON
Negative diode short ONON
Positive diode open ONOFF
Negative diode open ONOFF
Phase voltage sensing ONON
cable open circuit
Power transistor
shorted ON
ON
W arnign lamp driver
O/C OFF
OFF
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2171 of 6020

SECTION 6E
TABLE OF CONTENTS
C24SE ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ABBREVIATIONS CHARTS ......................... 6E-6
ECM Circuit Diagram (1/2) ............................ 6E-11
ECM Circuit Diagram (2/2) ............................ 6E-12
GROUND POINT CHART - LHD G.EXP (1/4) 6E-13
GROUND POINT CHART - RHD G.EXP (1/4) 6E-17
LOCATION ................................................... 6E-21
CABLE HARNESS & CONNECTOR LOCATION .............................................. 6E-23
CABLE HARNESS & CONNECTOR LOCATION - LHD ................................... 6E-24
CABLE HARNESS & CONNECTOR LOCATION - RHD ................................... 6E-25
CONNECTOR LIST ...................................... 6E-28
RELAY AND FUSE ....................................... 6E-30
RELAY AND FUSE BOX LOCATION (LHD & RHD) ........................................... 6E-30
FUSE AND RELAY LOCATION (LHD & RHD) 6E-32
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1/9) ..................... 6E-33
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (2/9) ..................... 6E-34
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (3/9) ..................... 6E-35
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (4/9) ..................... 6E-36
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (5/9) ..................... 6E-37
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (6/9) ..................... 6E-38
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (7/9) ..................... 6E-39
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (8/9) ..................... 6E-40
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (9/9) ..................... 6E-41
ECM CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENT & OUTPUT SIGNAL .................................... 6E-42
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ECM AND SENSORS ............................................... 6E-48
Engine Control Module (ECM) ................... 6E-48
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E-48
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) .................. 6E-49
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve ....................... 6E-49
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor ............ 6E-50
Knock Sensor (KS) .................................... 6E-50
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E-50
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor ........ 6E-51
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) .................... 6E-51
Heated Oxygen (O
2) Sensor ..................... 6E-51
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR FUEL METERING .............................................. 6E-52 Battery Voltage Correction Mode ............... 6E-52
Clear Flood Mode ...................................... 6E-52
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) Mode .... 6E-52
Engine Speed/ Vehicle Speed/ Fuel Disable Mode ........................................................ 6E-52
Acceleration Mode ..................................... 6E-52
Fuel Cutoff Mode ....................................... 6E-52
Starting Mode ............................................ 6E-52
Run Mode .................................................. 6E-52
Fuel Metering System Components .......... 6E-53
Fuel Injector ............................................... 6E-53
Fuel Pressure Regulator ............................ 6E-53
Fuel Rail ..................................................... 6E-53
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit ....................... 6E-53
Thottle Body Unit ....................................... 6E-53
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ELECTRIC IGNITION SYSTEM ................................. 6E-54
Spark Plug ................................................. 6E-54
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM ............................... 6E-57
EVAP Emission Control System Purpose .. 6E-57
EVAP Emission Control System Operation 6E-57
System Fault Detection .............................. 6E-57
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV) SYSTEM .................................................. 6E-59
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose .... 6E-59
A/C CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS ........................ 6E-60
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation ...................... 6E-60
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose ........................ 6E-60
A/C Request Signal ................................... 6E-60
ISUZU STRATEGY BASED DIAGNOSTICS 6E-61
Overview .................................................... 6E-61
STRATEGY BASED DIAGNOSTICS CHART 6E-61 Diagnostic Thought Process ...................... 6E-62
1. Verify the Complaint .............................. 6E-62
2. Perform Preliminary Checks .................. 6E-62
3. Check Bulletins and Troubleshooting Hints 6E-63
4. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Checks 6E-63
5a and 5b. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Procedures .............................................. 6E-63
5c. Technician Self Diagnoses .................. 6E-63
5d. Intermittent Diagnosis .......................... 6E-64
6 E –1
E N GINE DRIV EABILITY AND E M IS SIONS
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2199 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–29
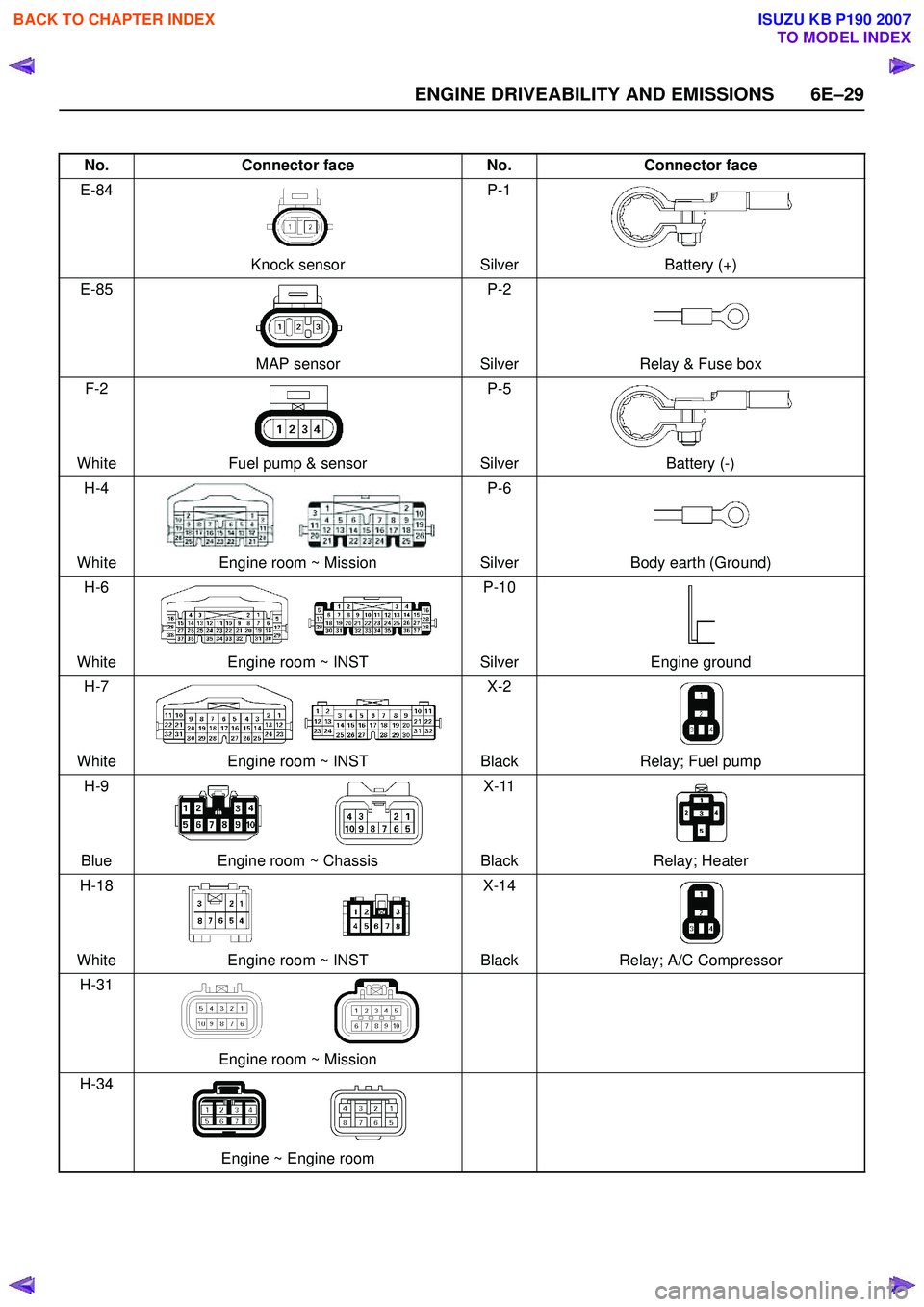
No.Connector face No.Connector face
E-84
Knock sensor P-1
Silver Battery (+)
E-85
MAP sensor P-2
Silver Relay & Fuse box
F-2
White Fuel pump & sensor P-5
Silver Battery (-)
H-4
White Engine room ~ Mission P-6
Silver Body earth (Ground)
H-6
White Engine room ~ INST P-10
Silver Engine ground
H-7
White Engine room ~ INST X-2
Black Relay; Fuel pump
H-9
Blue Engine room ~ Chassis X-11
Black Relay; Heater
H-18
White Engine room ~ INST X-14
Black Relay; A/C Compressor
H-31
Engine room ~ Mission
H-34
Engine ~ Engine room
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2214 of 6020
6E–44 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
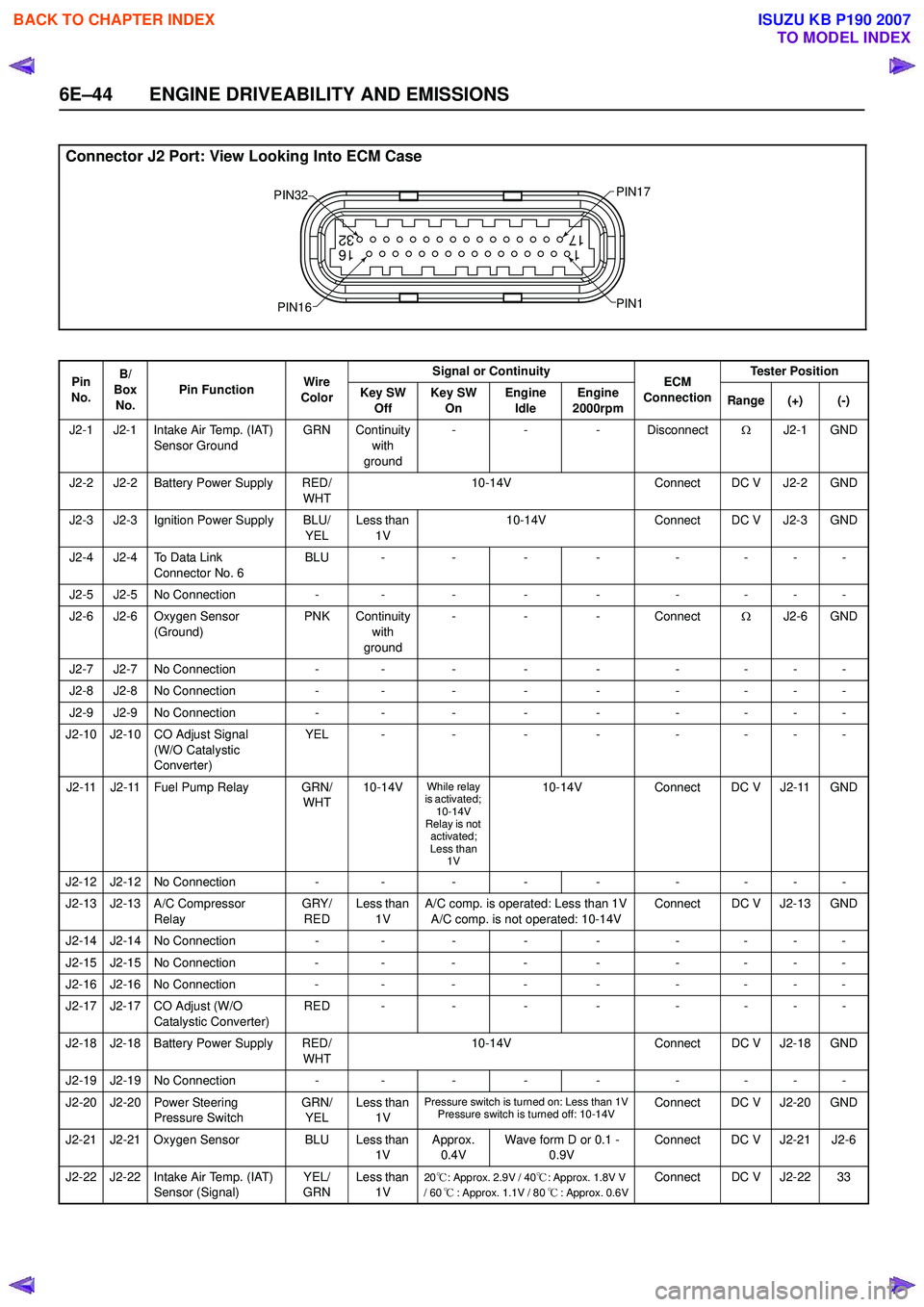
Connector J2 Port: View Looking Into ECM Case
1
17 16
32
PIN32
PIN1
PIN17
PIN16
Pin
No. B/
Box No. Pin Function
Wire
Color Signal or Continuity
ECM
Connection Tester Position
Key SW Off Key SW
On Engine
Idle Engine
2000rpm Range (+) (-)
J2-1 J2-1 Intake Air Temp. (IAT) Sensor Ground GRN Continuity
with
ground -
- - Disconnect ΩJ2-1 GND
J2-2 J2-2 Battery Power Supply RED/ WHT10-14V
Connect DC V J2-2 GND
J2-3 J2-3 Ignition Power Supply BLU/ YELLess than
1V 10-14V
Connect DC V J2-3 GND
J2-4 J2-4 To Data Link Connector No. 6 BLU -
-- - -- - -
J2-5 J2-5 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-6 J2-6 Oxygen Sensor (Ground) PNK Continuity
with
ground -
- - Connect ΩJ2-6 GND
J2-7 J2-7 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-8 J2-8 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-9 J2-9 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-10 J2-10 CO Adjust Signal (W/O Catalystic
Converter) YEL -
-- - -- - -
J2-11 J2-11 Fuel Pump Relay GRN/ WHT10-14V
While relay
is activated; 10-14V
Relay is not
activated;
Less than 1V10-14V Connect DC V J2-11 GND
J2-12 J2-12 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-13 J2-13 A/C Compressor Relay GRY/
RED Less than
1V A/C comp. is operated: Less than 1V
A/C comp. is not operated: 10-14V Connect DC V J2-13 GND
J2-14 J2-14 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-15 J2-15 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-16 J2-16 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-17 J2-17 CO Adjust (W/O Catalystic Converter) RED -
-- - -- - -
J2-18 J2-18 Battery Power Supply RED/ WHT10-14V
Connect DC V J2-18 GND
J2-19 J2-19 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-20 J2-20 Power Steering Pressure Switch GRN/
YEL Less than
1V
Pressure switch is turned on: Less than 1VPressure switch is turned off: 10-14VConnect DC V J2-20 GND
J2-21 J2-21 Oxygen Sensor BLU Less than 1VApprox.
0.4V Wave form D or 0.1 -
0.9V Connect DC V J2-21 J2-6
J2-22 J2-22 Intake Air Temp. (IAT) Sensor (Signal) YEL/
GRN Less than
1V
20℃: Approx. 2.9V / 40 ℃: Approx. 1.8V V
/ 60 ℃: Approx. 1.1V / 80 ℃: Approx. 0.6VConnect DC V J2-22 33
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2218 of 6020
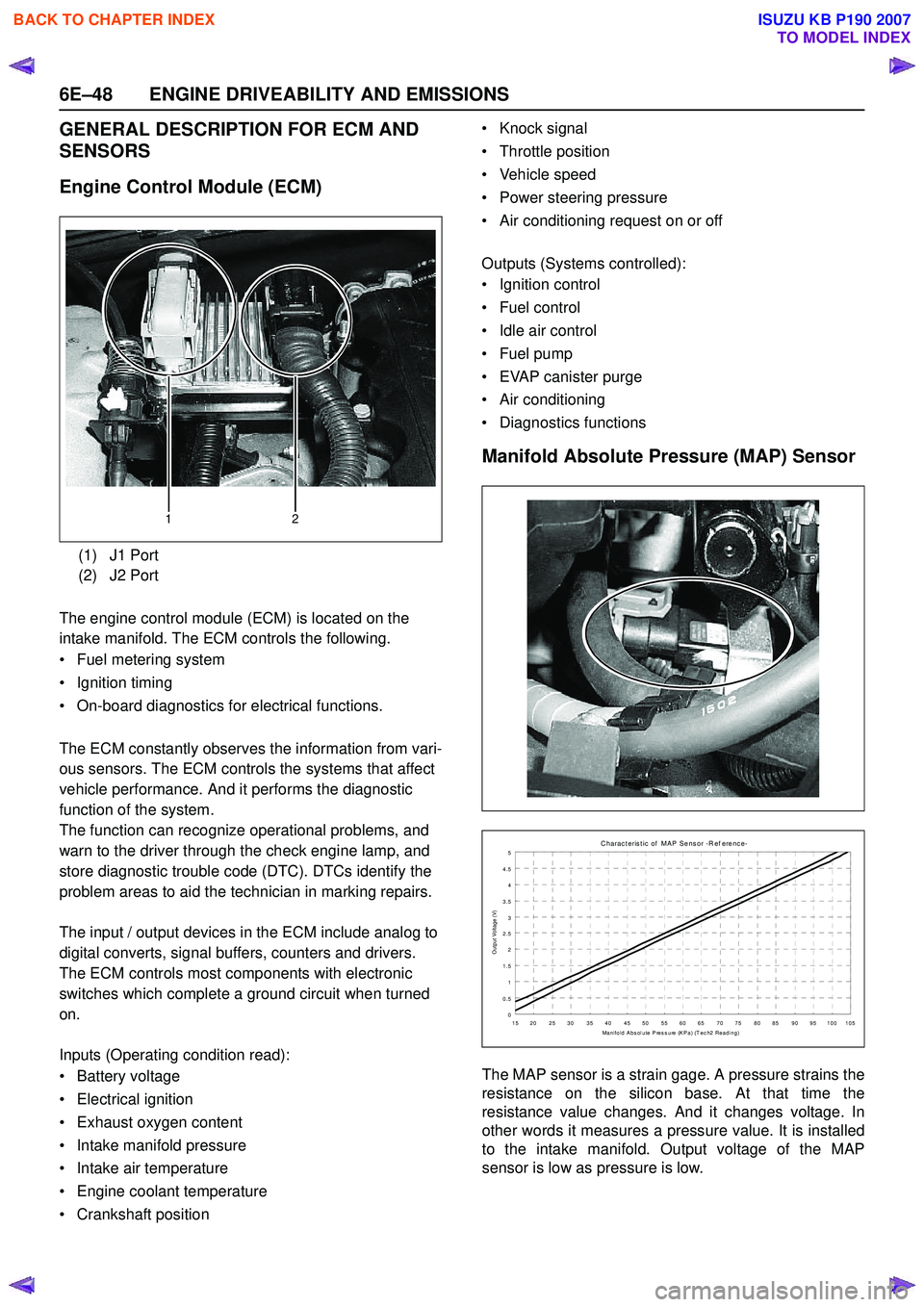
6E–48 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ECM AND
SENSORS
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located on the
intake manifold. The ECM controls the following.
• Fuel metering system
• Ignition timing
• On-board diagnostics for electrical functions.
The ECM constantly observes the information from vari-
ous sensors. The ECM controls the systems that affect
vehicle performance. And it performs the diagnostic
function of the system.
The function can recognize operational problems, and
warn to the driver through the check engine lamp, and
store diagnostic trouble code (DTC). DTCs identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in marking repairs.
The input / output devices in the ECM include analog to
digital converts, signal buffers, counters and drivers.
The ECM controls most components with electronic
switches which complete a ground circuit when turned
on.
Inputs (Operating condition read):
• Battery voltage
• Electrical ignition
• Exhaust oxygen content
• Intake manifold pressure
• Intake air temperature
• Engine coolant temperature
• Crankshaft position • Knock signal
• Throttle position
• Vehicle speed
• Power steering pressure
• Air conditioning request on or off
Outputs (Systems controlled):
• Ignition control
• Fuel control
• Idle air control
• Fuel pump
• EVAP canister purge
• Air conditioning
• Diagnostics functions
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The MAP sensor is a strain gage. A pressure strains the
resistance on the silicon base. At that time the
resistance value changes. And it changes voltage. In
other words it measures a pressure value. It is installed
to the intake manifold. Output voltage of the MAP
sensor is low as pressure is low.
(1) J1 Port
(2) J2 Port
12
C harac t eris t ic of MAP Sens or -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5 1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 Manifold Abs olute Press ure (KPa) (T ec h2 Reading)
Output Voltage (V)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2219 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–49
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS is a potentiometer connected to throttle shaft
on the throttle body.
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the voltage
on the signal line and calculates throttle position. As the
throttle valve angle is changed when accelerator pedal
moved. The TPS signal also changed at a moved
throttle valve. As the throttle valve opens, the output
increases so that the output voltage should be high.
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of the air delivered to the engine.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The idle air control valve (IAC) valve is two directional
and gives 2-way control. With power supply to the coils
controlled steps by the engine control module (ECM),
the IAC valve's pintle is moved to adjust idle speed,
raising it for fast idle when cold or there is extra load
from the air conditioning or power steering.
By moving the pintle in (to decrease air flow) or out (to
increase air flow), a controlled amount of the air can
move around the throttle plate. If the engine speed is
too low, the engine control module (ECM) will retract the
IAC pintle, resulting in more air moving past the throttle
plate to increase the engine speed.
If the engine speed is too high, the engine control
module (ECM) will extend the IAC pintle, allowing less
air to move past the throttle plate, decreasing the
engine speed.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small step called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the engine control module (ECM) based
on battery voltage, coolant temperature, engine load,
and engine speed.
If the engine speed drops below a specified value, and
the throttle plate is closed, the engine control module
(ECM) senses a near-stall condition. The engine control
module (ECM) will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve
position to prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with
the engine running, the idle speed will be wrong. In this
case, the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the
key is cycled “On” then “Off”. When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “Off”.
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-
up and the idle characteristic of the vehicle.
If the IAC pintle is fully open, too much air will be
allowed into the manifold. This results in high idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and lean air/
fuel ratio.
(1) Throttle Position Sensor
(2) Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
1
2
C harac teris t ic of TPS -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5
1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
0 10 2030 405060 7080 90100 Throt t le Angle (% ) (Tec h2 R eading)
Output Voltage (V)
StepCoilAB CDCoil A H igh
(ECM J1-28) On On
Coil A Low
(ECM J1-30) On On
Coil B H igh
(ECM J1-13) On On
Coil B Low
(ECM J1-29) On On
(IAC Valve Close Direction)
(IAC Valve Open Direction)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007