2007 ISUZU KB P190 keyless entry
[x] Cancel search: keyless entryPage 5547 of 6020
ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS 8A-609
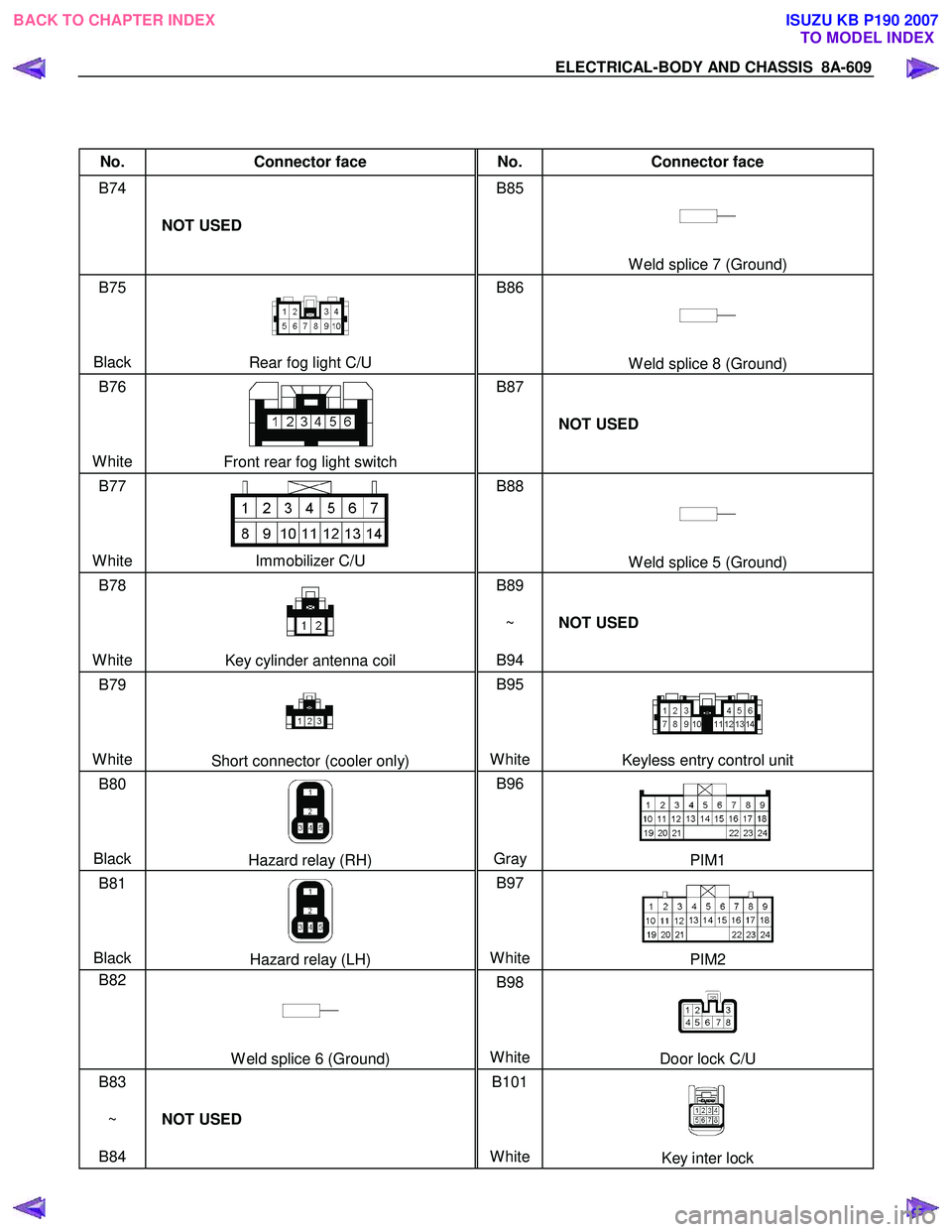
No. Connector face No. Connector face
B74
NOT USED B85
W eld splice 7 (Ground)
B75
Black
Rear fog light C/U B86
W eld splice 8 (Ground)
B76
White
Front rear fog light switch B87
NOT USED
B77
White
Immobilizer C/U B88
W eld splice 5 (Ground)
B78
White
Key cylinder antenna coil B89
~
B94 NOT USED
B79
White
Short connector (cooler only) B95
White
Keyless entry control unit
B80
Black
Hazard relay (RH) B96
Gray PIM1
B81
Black
Hazard relay (LH) B97
WhitePIM2
B82
W eld splice 6 (Ground) B98
WhiteDoor lock C/U
B83
~
B84 NOT USED B101
White
Key inter lock
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5925 of 6020

IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM (C24SE, 4JA1-T) 11A-27
Diagnostic procedure
• Once the cause of DTC is repaired or gone,
engine can be operated normally, and present
DTC becomes history code.
• History code is canceled by no repeat failure on 25
consequence ignition key on afterward.
• History code cannot be canceled by batter
y
connector disconnected.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
IMPORTANT: Do not clear DTCs unless directed to do
so by the service information provided for each
diagnostic procedure. W hen DTCs are cleared, the
Failure Record data which may help diagnose an
intermittent fault will also be erased from memory.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with immobilizer system
diagnostic. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records for the DTC
which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the
Fail Records.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the DTC
which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic test
associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on immobilizer systems. Failure to follow these
steps could result in unnecessary repairs.
Diagnostic Aids
Check the condition for system parts.
• Installation condition, poor connection, damage,
system parts malfunction. Harness, Fuse, Relay,
Immobilizer coil (antenna), Key, Meter, Immobilize
r
control unit (ICU), Engine control module (ECM).
NOTE: Breakage of immobilizer fuse does not operate
immobilizer system. Check engine lamp flashes at this
time.
Check the Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI)
• Location of vehicle check
Move the vehicle to a new location and perform
the check again.
• Non-OEM Parts.
Switch is "OFF" or remove the Non-OEM parts and
perform the check again.
• Other
Remove the accessory and another key from key.
Check the other items.
• Battery voltage is low.
• Immobilizer programming functions.
Must be programmed immobilizer system.
• Registration for security code, immobilizer control
unit parts number.
• Key switch operation.
Immobilizer system may detect a history DTC b
y
the timing of ON-OFF of a key switch.
• Active the immobilizer system.
• Keyless entry system is malfunction.
• Anti theft system is malfunction.
Check the operation
Check the operation "Lock / unlock" by using transmitte
r
(key) on the vehicle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5957 of 6020
ANTITHEFT SYSTEM 11B-3
Function of a keyless entry system
W ith a keyless entry system the car can be locked or
unlocked from any position around the car up to a
specified distance, by using the potable radio remote
transmitter inside key (remote key).
Status LED
W hile the system is in delay the alarm system is active
and LED flashes at 0.5Hz with or without activated
interior protection.
Hazard relay
The hazard warning lights will be activated by an
external relay. The output is low active.
Switches
All switches to ground. This makes it possible for failure
analysis to detect a short circuit or a broken wire to
each switch. To use this feature it is necessary to place
a 1.8k Ω resistor in parallel to the required switch.
Receiver
The receiver is integrated into the control unit.
To lower the idle current the receiver is equipped with a
standby mode. The antenna is integrated on the printed
circuit board.
Depending on the mounting position of the control unit
the antenna can be connected externally.
Range of communication
The range of communication between remote key and
receiver is intended to be least 3 m from centre of the
car.
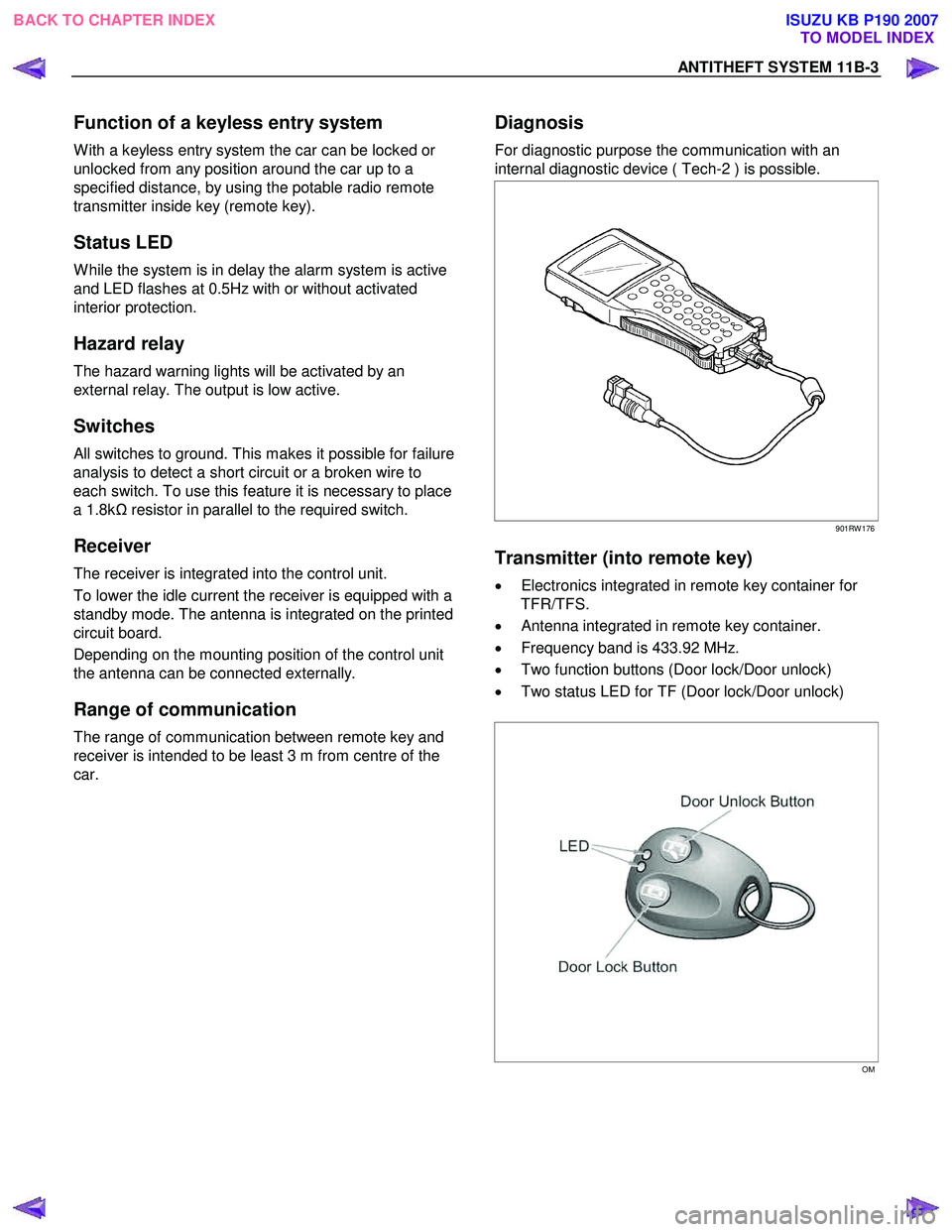
Diagnosis
For diagnostic purpose the communication with an
internal diagnostic device ( Tech-2 ) is possible.
901RW 176
Transmitter (into remote key)
• Electronics integrated in remote key container for
TFR/TFS.
• Antenna integrated in remote key container.
• Frequency band is 433.92 MHz.
• Two function buttons (Door lock/Door unlock)
• Two status LED for TF (Door lock/Door unlock)
OM
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5990 of 6020

11B-36 ANTITHEFT SYSTEM
Diagnosis
Diagnostic procedure
• Once the cause of DTC is repaired or gone,
engine can be operated normally, and present
DTC becomes history code.
• History code is canceled by no repeat failure on 25
consequence ignition key on afterward.
• History code cannot be canceled by batter
y
connector disconnected.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
IMPORTANT: Do not clear DTCs unless directed to do
so by the service information provided for each
diagnostic procedure. W hen DTCs are cleared, the
Failure Record data which may help diagnose an
intermittent fault will also be erased from memory.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with immobilizer system
diagnostic. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records for the DTC which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC (s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail Records.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic test
associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on immobilizer systems. Failure to follow these
steps could result in unnecessary repairs.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by the following:
• Poor connections.
• Miss routed harness.
• Rubbed through wire insulation.
• Broken wire inside the insulation.
Check for the following conditions:
• Poor connection at ACU-Inspect harness
connectors for backed out terminals, imprope
r
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire
connection.
• Damaged harness-Inspect the wiring harness fo
r
damage.
If the harness appears to be OK, observe the data
display on the Tech2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the switch or actuator.
A change in the display will indicate the location of
the fault.
If DTC cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Failure Records data can be useful
in determined vehicle mileage since the DTC was
last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently, performing the DTC Diagnostic
Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
NOTE: Breakage of antitheft fuse does not operate
antitheft system. Check LED lamp flashes at this time.
Check the Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI)
• Location of vehicle check
Move the vehicle to a new location and perform
the check again.
• Non-OEM Parts.
Switch is “OFF” or remove the Non-OEM parts and
perform the check again.
• Other
Remove the accessory and another key from key.
Check the other items.
• Battery voltage is low.
• Antitheft programming functions.
Must be programmed antitheft system.
• Registration for security code, antitheft control unit
parts number.
• Key switch operation.
Antitheft system may detect a history DTC by the
timing of ON-OFF of a key switch.
• Active the antitheft system.
• Keyless entry system is malfunction.
• Immobilizer system is malfunction.
Check the operation
Check the operation "Lock / unlock" by using transmitter
(key) on the vehicle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007