2007 ISUZU KB P190 low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 3872 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–86
Step Action Yes No
14 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 On Tech 2 select: Automatic Transmission / Data Display / Transmission Data.
4 Operate the vehicle under the following conditions:
• Drive the vehicle in D4, with the TCC on, and a throttle
position at 20%.
• On Tech 2 ensure the TCC Slip Speed is -20 to +50 RPM
for at least 7 seconds.
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P0894 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 15
15 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
4.27 DTC P0961 – Line Pressure Control
Solenoid System Performance
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0961 Line Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid System Performance.
Circuit Description
The pressure control (PC) solenoid valve is an electronic device that regulates transmission line pressure based on the
current flow through its coil winding. The magnetic field produced by the coil moves the solenoid's internal valve, which
varies pressure to the pressure regulator valve. The transmission control module (TCM) controls the PC solenoid valve
by applying a varying amount of current to the solenoid. The applied current can vary from 0.1 – 1.1 A. Low current,
0.1 A, indicates high line pressure. High current, 1.1 A, indicates low line pressure. The duty cycle of the PC solenoid
valve is expressed as a percentage of energised on time. Zero percent indicates zero on time, non-energised, or no
current flow. Approximately 60 percent at idle indicates maximum on time, energised, or high current flow. The TCM
determines the appropriate line pressure for a given load by comparing the throttle position, the engine speed and other
inputs.
W hen the TCM detects a continuous open or short to ground in the PC solenoid valve circuit, then DTC P0961 sets.
DTC P0961 is a type C DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PC solenoid valve duty cycle reaches its high limit, approximately 95 percent, or low limit, approximately 2 percent.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM does not request the engine control module (ECM) to illuminate the MIL.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3894 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–108
Step Action Yes No
13 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
4.33 DTC P2763 – Torque Converter Clutch
Pressure Control Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2763 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PW M) solenoid valve controls the fluid acting on the converter
clutch valve. The converter clutch valve controls the TCC application and release. The solenoid attaches to the control
valve body within the transmission. The solenoid receives voltage through ignition voltage circuit. The transmission
control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing a ground path on the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit.
Current flows through the solenoid coil according to the duty cycle, percentage of on and off time. The TCC PWM
solenoid valve provides a smooth engagement of the TCC by operating during a duty cycle percent of on time.
When the TCM detects a continuous short to voltage in the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit, then DTC P2763
sets. DTC P2763 is a type A DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2763 sets if the TCM commands the solenoid on and the voltage feedback remains high, battery voltage.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for
setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC engagement.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P2763 in TCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for setting
the DTC are met.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the fourth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3897 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–111
4.34 DTC P2764 – Torque Converter Clutch
Pressure Control Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2764 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PW M) solenoid valve controls the fluid acting on the converter
clutch valve. The converter clutch valve controls the TCC application and release. The solenoid attaches to the control
valve body within the transmission. The solenoid receives voltage through ignition voltage circuit. The transmission
control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing a ground path on the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit.
Current flows through the solenoid coil according to the duty cycle, percentage of on and off time. The TCC PWM
solenoid valve provides a smooth engagement of the TCC by operating during a duty cycle percent of on time.
W hen the TCM detects a continuous open or short to ground in the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit, then
DTC P2764 sets. DTC P2764 is a type A DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2764 sets when either of the following conditions occurs for 5 seconds:
• The TCM detects an open in the TCC PWM shift solenoid valve circuit when the TCC PW M is commanded on.
• The TCM detects a short to ground in the TCC PWM shift solenoid valve circuit when the TCC PWM is
commanded on.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the Conditions for
Setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC engagement.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P2764 in TCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for setting
the DTC are met.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the fourth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
• Tech 2 can clear the DTC.
• The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without a non-emission
related diagnostic fault occurring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3919 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–6
6 Lift the locking lever (1) on the transmission fluid
indicator, then remove the indicator from the filler
tube (2) and check the fluid colour, condition and level.
Do not overfill the transmission. Overfilling
can cause aeration resulting in fluid loss,
shift complaints and possible damage to the
transmission.
7 If the transmission fluid level is low, add only enough of the recommended fluid until
its level shows onto the
crosshatch hot area (3) of the fluid indicator.
Figure 7C4 – 1
2.2 Reverse Flush and Flow Rate Test
It is essential to perform a reverse flush and oil cooler flow rate test after any of the following:
• the transmission is repaired or replaced,
• fluid contamination is suspected, or
• whenever the oil pump and/or torque converter is replaced.
NOTE
The reverse flush must be completed prior to
conducting a flow rate test.
Reverse Flush
1 Disconnect both cooler hose/line assemblies at the transmission and at the radiator cooler, refer to 3.17 Transmission Cooler Line/Hose Assemblies.
2 Check the cooler hose/line to radiator cooler fittings for damage, replace as required.
To avoid personal injury, wear safety glasses
when using compressed air.
3 Carefully check the radiator cooler lower fitting to see if any foreign material is evident at this point. If foreign material is found, remove it with a suitable tool and/or compressed air at a reduced pressure of approximately
345 kPa blown in the reverse direction through the cooler.
4 Using compressed air at a reduced pressure of approximately 345 kPa blown in a reverse direction, clean the cooler hose/line assemblies.
5 Reconnect the cooler outlet line to the transmission and both cooler hose/line assemblies to the radiator cooler fittings, refer to 3.17 Transmission Cooler Line/Hose Assemblies.
NOTE
Do not reconnect the cooler inlet line at the
transmission end. This line needs to be left
disconnected to perform the flow rate test.
6 Perform the flow rate test, refer to Flow Rate Test in this Section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3938 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–25
3.11 Shift Solenoid Locations
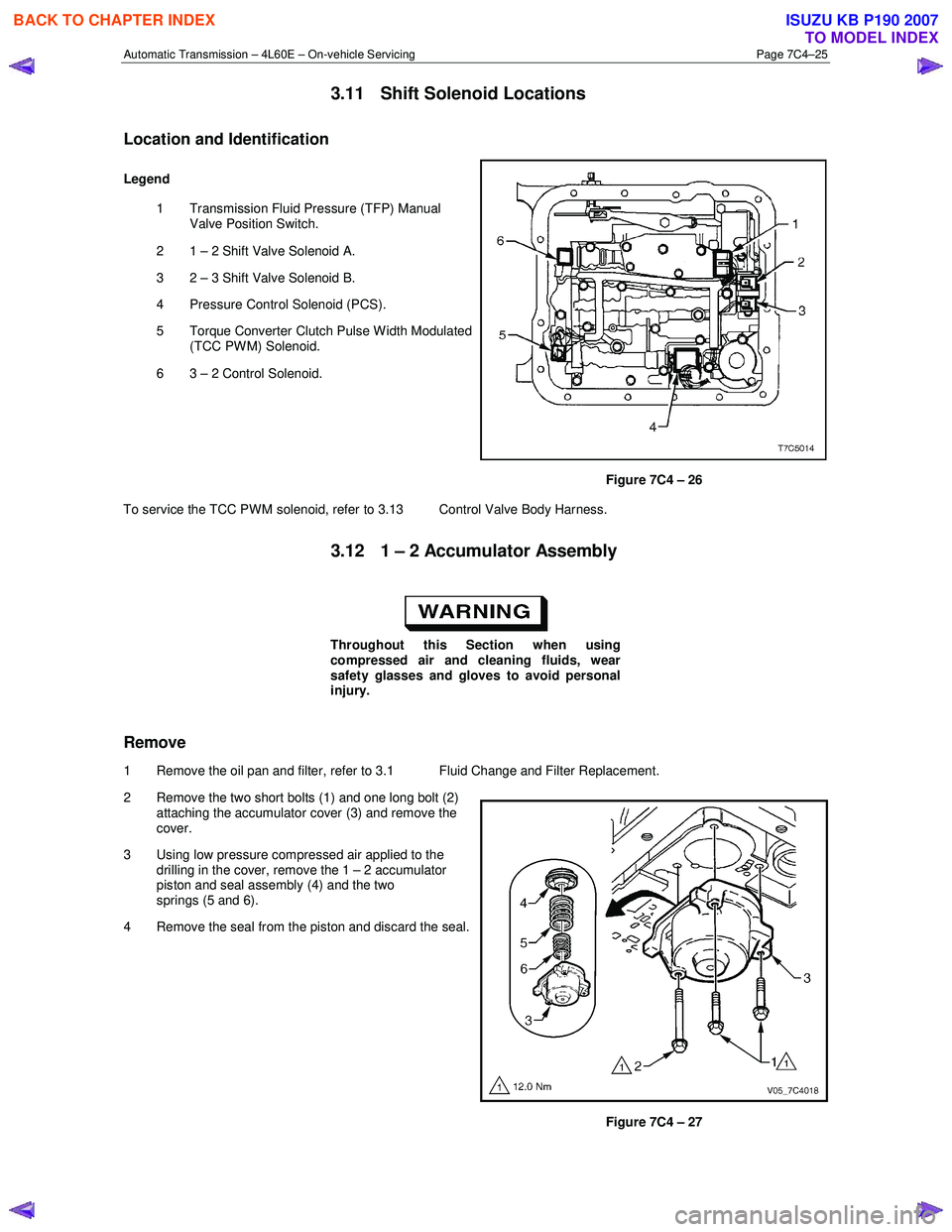
Location and Identification
Legend
1 Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Manual Valve Position Switch.
2 1 – 2 Shift Valve Solenoid A.
3 2 – 3 Shift Valve Solenoid B.
4 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS).
5 Torque Converter Clutch Pulse W idth Modulated (TCC PWM) Solenoid.
6 3 – 2 Control Solenoid.
Figure 7C4 – 26
To service the TCC PWM solenoid, refer to 3.13 Control Valve Body Harness.
3.12 1 – 2 Accumulator Assembly
Throughout this Section when using
compressed air and cleaning fluids, wear
safety glasses and gloves to avoid personal
injury.
Remove
1 Remove the oil pan and filter, refer to 3.1 Fluid Change and Filter Replacement.
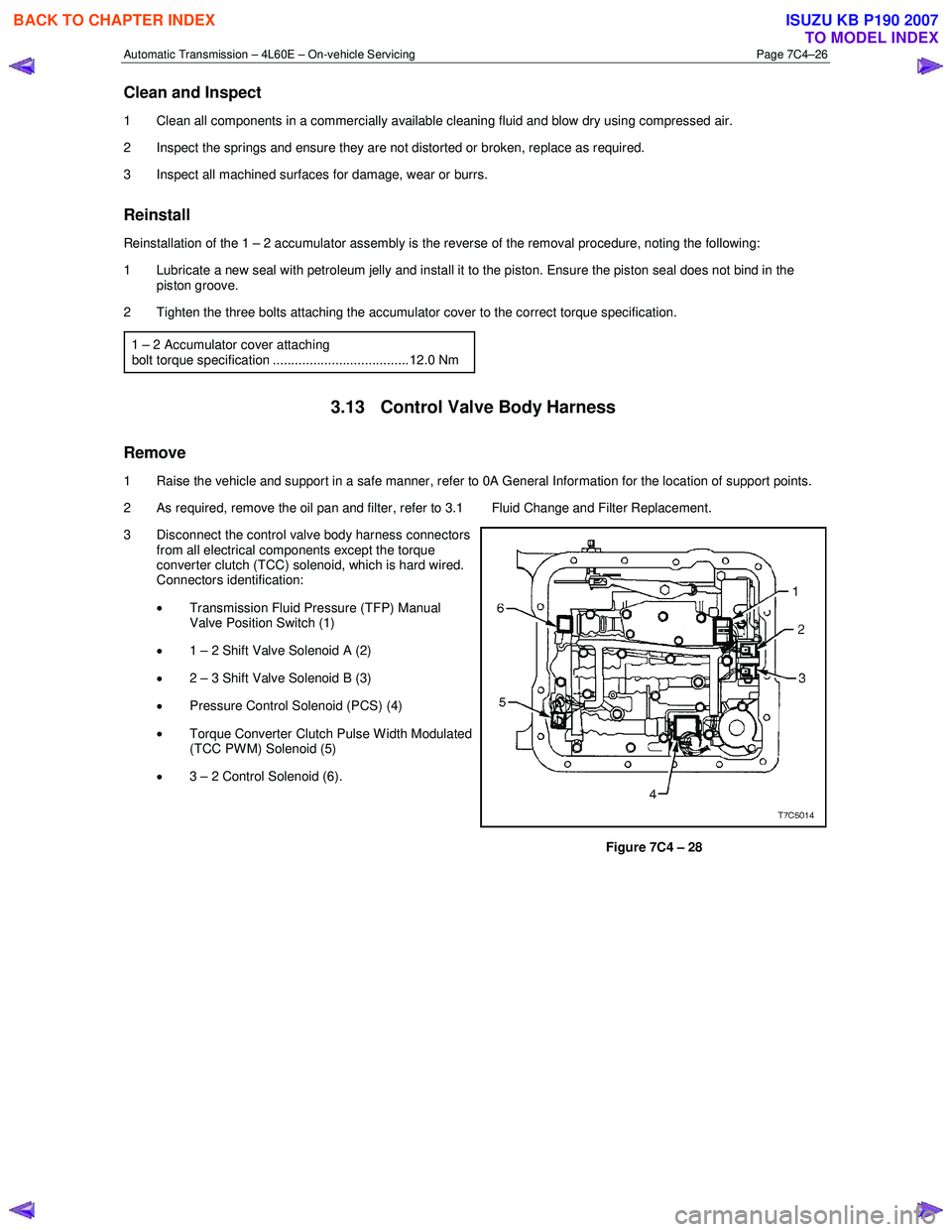
2 Remove the two short bolts (1) and one long bolt (2) attaching the accumulator cover (3) and remove the
cover.
3 Using low pressure compressed air applied to the drilling in the cover, remove the 1 – 2 accumulator
piston and seal assembly (4) and the two
springs (5 and 6).
4 Remove the seal from the piston and discard the seal.
Figure 7C4 – 27
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3939 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–26
Clean and Inspect
1 Clean all components in a commercially available cleaning fluid and blow dry using compressed air.
2 Inspect the springs and ensure they are not distorted or broken, replace as required.
3 Inspect all machined surfaces for damage, wear or burrs.
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the 1 – 2 accumulator assembly is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 Lubricate a new seal with petroleum jelly and install it to the piston. Ensure the piston seal does not bind in the piston groove.
2 Tighten the three bolts attaching the accumulator cover to the correct torque specification.
1 – 2 Accumulator cover attaching
bolt torque specification ..................................... 12.0 Nm
3.13 Control Valve Body Harness
Remove
1 Raise the vehicle and support in a safe manner, refer to 0A General Information for the location of support points.
2 As required, remove the oil pan and filter, refer to 3.1 Fluid Change and Filter Replacement.
3 Disconnect the control valve body harness connectors from all electrical components except the torque
converter clutch (TCC) solenoid, which is hard wired.
Connectors identification:
• Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Manual
Valve Position Switch (1)
• 1 – 2 Shift Valve Solenoid A (2)
• 2 – 3 Shift Valve Solenoid B (3)
• Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (4)
• Torque Converter Clutch Pulse W idth Modulated
(TCC PWM) Solenoid (5)
• 3 – 2 Control Solenoid (6).
Figure 7C4 – 28
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3942 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–29
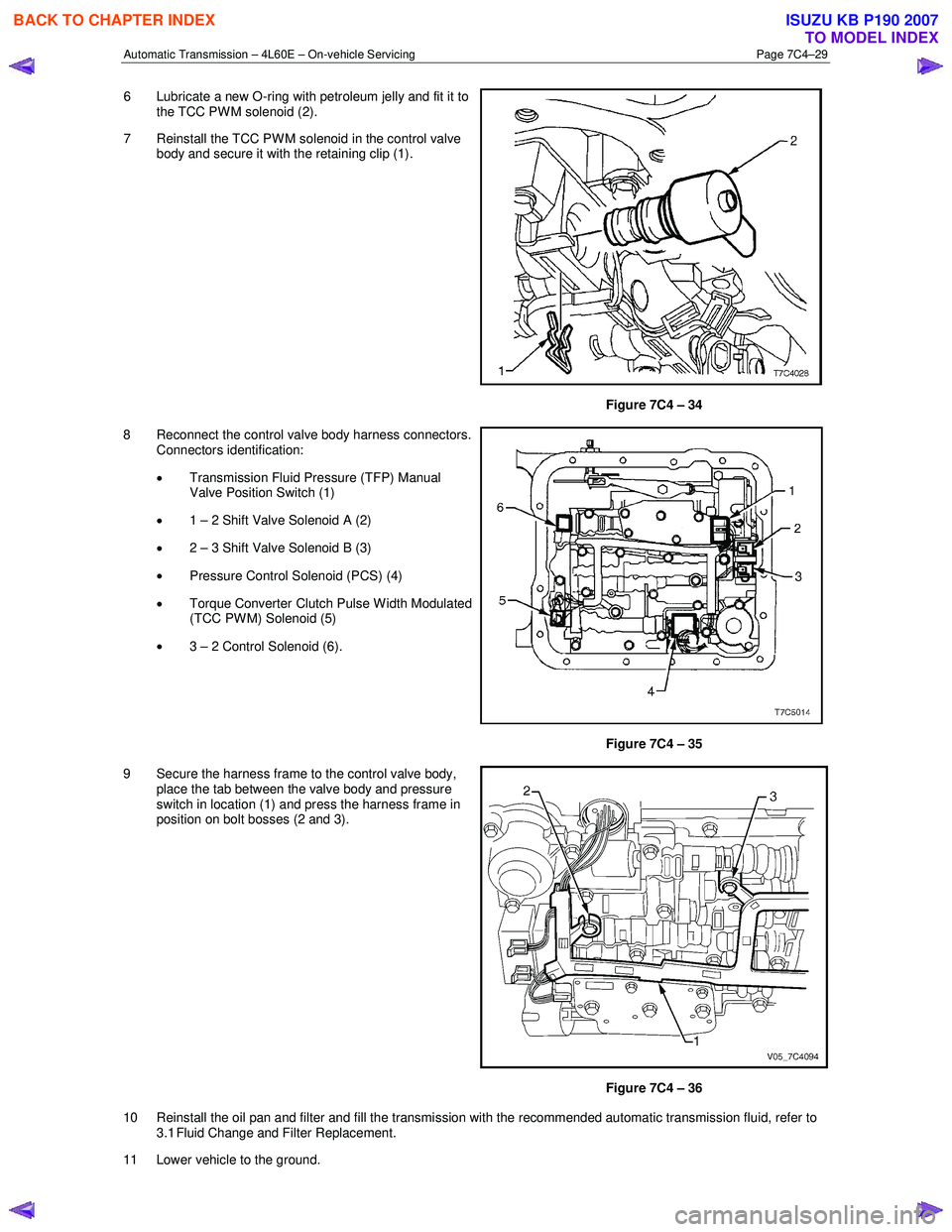
6 Lubricate a new O-ring with petroleum jelly and fit it to
the TCC PW M solenoid (2).
7 Reinstall the TCC PWM solenoid in the control valve body and secure it with the retaining clip (1).
Figure 7C4 – 34
8 Reconnect the control valve body harness connectors. Connectors identification:
• Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Manual
Valve Position Switch (1)
• 1 – 2 Shift Valve Solenoid A (2)
• 2 – 3 Shift Valve Solenoid B (3)
• Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (4)
• Torque Converter Clutch Pulse W idth Modulated
(TCC PWM) Solenoid (5)
• 3 – 2 Control Solenoid (6).
Figure 7C4 – 35
9 Secure the harness frame to the control valve body, place the tab between the valve body and pressure
switch in location (1) and press the harness frame in
position on bolt bosses (2 and 3).
Figure 7C4 – 36
10 Reinstall the oil pan and filter and fill the transmission with the recommended automatic transmission fluid, refer to 3.1 Fluid Change and Filter Replacement.
11 Lower vehicle to the ground.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3943 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing Page 7C4–30
12 Road test until the transmission has reached operating temperature. Re-check the fluid level and for any fluid leaks
from the oil pan area, refer to 2.1 Transmission Fluid.
3.14 Control Valve Body
Remove
1 Partially remove the control valve body harness until it hangs from the pass-thru connector, refer to
3.13 Control Valve Body Harness.
2 Remove the three long bolts (1) and the two short bolts (2) attaching the transmission fluid pressure
(TFP) manual valve position switch assembly (3),
remove the switch and discard the shield (4).
3 Remove the attaching bolt (5) and the manual detent spring (6).
Figure 7C4 – 37
In the following procedure support the
control valve body before removing the last
bolt.
NOTE
The removal may be more manageable by
removing the bolts in a spiral pattern starting
from the outside, removing the centre bolt last.
4 Remove the fourteen remaining bolts (1) attaching the control valve body.
Figure 7C4 – 38
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007