2007 ISUZU KB P190 technical data
[x] Cancel search: technical dataPage 2074 of 6020
6A-60 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
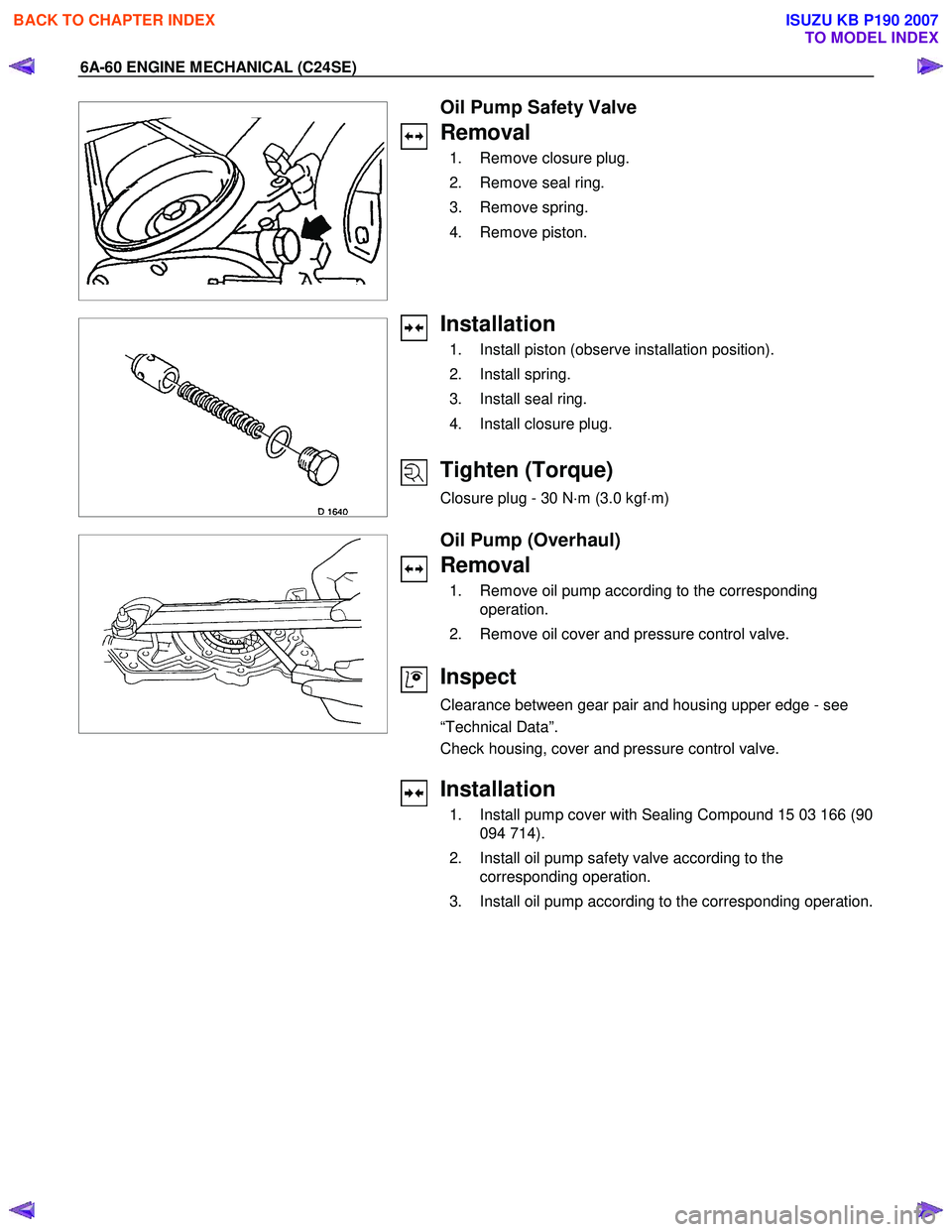
Oil Pump Safety Valve
Removal
1. Remove closure plug.
2. Remove seal ring.
3. Remove spring.
4. Remove piston.
Installation
1. Install piston (observe installation position).
2. Install spring.
3. Install seal ring.
4. Install closure plug.
Tighten (Torque)
Closure plug - 30 N ⋅m (3.0 kgf ⋅m)
Oil Pump (Overhaul)
Removal
1. Remove oil pump according to the corresponding operation.
2. Remove oil cover and pressure control valve.
Inspect
Clearance between gear pair and housing upper edge - see
“Technical Data”.
Check housing, cover and pressure control valve.
Installation
1. Install pump cover with Sealing Compound 15 03 166 (90 094 714).
2. Install oil pump safety valve according to the corresponding operation.
3. Install oil pump according to the corresponding operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2091 of 6020
ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE) 6A-77
TECHNICAL DATA
SOHC Gasoline Engine C24SE
Engine Oil Viscosity
The following engine oils can be used:
A = single-grade oils
B = multigrade oils
C = easy run oils
depending on the outside temperature.
Engine Oil Quality
It is important that the following API and CCMC classes are
used:
Engines Single and multigrade oils Easy run oils
Petrol API-SF/CC, SF/CD, SG/CC,
SG/CD, CCMC/G4 API-SF/CC, SF/CD, SG/CD
CCMC-G5/PD2
Important!
CD engine oils designed by manufacturers specially for diesel
engines are not suitable for petrol engines, unless a sufficient
performance class for petrol engines (e.g. API-SF/CCMC-G4)
is also indicated.
Disposal.
Observe the relevant national regulations when disposing of
used oil.
Engine Oil Filling Quantities
Engine Model Initial filling
(litres) Filling quantity
with filter change* (litres) MIN to MAX
(litres)
2.4L 4.80 4.25 1.00
*Up to mark "MAX" on oil dipstick
Oil Pump
Backlash 0.1 to 0.2mm
Gaps in gears opposite housing 0.03 to 0.1mm
Oil pressure at idle speed Engine at operating temperature (>70°C oil and
approx. 80 °C coolant)
450 - 500 kpa
Oil drain plug M14 × 1.5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2149 of 6020

SECTION 6D3
STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
Starting System .............................................................................................................. 6D3- 2
General Description ....................................................................................................... 6D3- 2
Service Precaution ......................................................................................................... 6D3- 2
Diagnosis ........................................................................................................................ 6D3- 2
Starter .............................................................................................................................. 6D3- 3
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6D3- 3
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6D3- 3
Disassembled View ................................................................................................... 6D3- 4
Inspection and Repair ............................................................................................... 6D3- 5
Characteristic Test .................................................................................................... 6D3- 6
Charging System ............................................................................................................ 6D3- 7
General Description ....................................................................................................... 6D3- 7
General On-Vehicle Inspection ..................................................................................... 6D3- 8
Generator ........................................................................................................................ 6D3- 8
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6D3- 8
Inspection ................................................................................................................... 6D3- 8
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6D3- 9
Diagnosis ........................................................................................................................ 6D3-12
Disassembly ............................................................................................................... 6D3- 13
Clean .......................................................................................................................... . 6D3-14
Inspection ................................................................................................................... 6 D3-14
Reassembly ................................................................................................................ 6D3- 18
Inspection ................................................................................................................... 6 D3-19
Technical Data ................................................................................................................ 6D3-21
S
TA RT ING A ND CHA RGING S YSTE M 6D3-1
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2169 of 6020
STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-21
Technical Data
(mm)
Brush wear - Minimum Length 3.8
Sliprings - Minimum Diameter 26.7
Sliprings - Trueness <0.06
Pole claws - Trueness <0.05(93.25 ±0.05)
Torque N.m(kgf⋅m)
Pulley retaining nut 54-68(5.5-6.9)
Capacitor retaining screw 2.7-3.8(0.3-0.4)
Capacitor whiz nut 1.5-2.2(0.1-0.2)
B+ terminal nut M8 7.5-8.5(0.8-0.9)
B+ terminal rectifier nut 6.0-7.5(0.6-0.8)
Regulator retaining screw 1.6-2.3(0.1-0.2)
Rectifier retaining screw 1.6-2.3(0.1-0.2)
Bearing retaining plate screw 2.1-3.0(0.2-0.3)
Through bolt 3.8-5.5(0.4-0.6)
W inding resistance(between phases) (Ω )
Stator Rotor
70 Amp generator 0.086+10% 2.6 ±0.13
85 Amp generator 0.058+10% 2.6 ±0.13
90 Amp generator 0.056+10% 2.6 ±0.13
W arning lamp fault indication
Fault running Generator not
running Ignition ON Generator
Iginiton ON
Generator out cable
O/C ON
ON
Battery "S" cable O/C ONON
Battery overcharged ONON
Positive diode short OFFON
Negative diode short ONON
Positive diode open ONOFF
Negative diode open ONOFF
Phase voltage sensing ONON
cable open circuit
Power transistor
shorted ON
ON
W arnign lamp driver
O/C OFF
OFF
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2232 of 6020

6E–62 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Thought Process
As you follow a diagnostic plan, every box on the
Strategy Based Diagnostics chart requires you to use
the diagnostic thought process. This method of thinking
optimizes your diagnosis in the following ways:
• Improves your understanding and definition of the customer complaint
• Saves time by avoiding testing and/or replacing good parts
• Allows you to look at the problem from different perspectives
• Guides you to determine what level of understanding about system operation is needed:
– Owner’s manual level
– Service manual level
– In-depth (engineering) level – Owner’s manual level
– Service manual level
– In-depth (engineering) level
1. Verify the Complaint
What you should do
To verify the customer complaint, you need to know the
correct (normal) operating behavior of the system and
verify that the customer complaint is a valid failure of the
system.
The following information will help you verify the
complaint:
• WHAT the vehicle model/options are
• WHAT aftermarket and dealer-installed accessories exist
• WHAT related system(s) operate properly
• WHEN the problem occurs
• WHERE the problem occurs
• HOW the problem occurs
• HOW LONG the condition has existed (and if the system ever worked correctly)
• HOW OFTEN the problem occurs
• Whether the severity of the problem has increased, decreased or stayed the same
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to assist you in verifying the complaint:
• Service manual Theory or Circuit Description sections
• Service manual “System Performance Check”
• Owner manual operational description
• Technician experience
• Identical vehicle for comparison • Circuit testing tools
• Vehicle road tests
• Complaint check sheet
• Contact with the customer
2. Perform Preliminary Checks
NOTE: An estimated 10 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with this step!
What you should do
You perform preliminary checks for several reasons:
• To detect if the cause of the complaint is VISUALLY OBVIOUS
• To identify parts of the system that work correctly
• To accumulate enough data to correctly and accurately search for a ISUZU Service Bulletin on
ISUZU Web site.
The initial checks may vary depending on the
complexity of the system and may include the following
actions:
• Operate the suspect system
• Make a visual inspection of harness routing and accessible/visible power and ground circuits
• Check for blown fuses
• Make a visual inspection for separated connectors
• Make a visual inspection of connectors (includes checking terminals for damage and tightness)
• Check for any DTCs stored by the on-board computers
• Sense unusual noises, smells, vibrations or movements
• Investigate the vehicle service history (call other dealerships, if appropriate)
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources for assistance in performing preliminary
checks:
• Tech II or other technical equipment for viewing DTCs
• Service manual information: – Component locations
– Harness routing
– Wiring schematics
– Procedures for viewing DTCs
• Dealership service history file
• Vehicle road test
• Identical vehicle or system for comparison
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2233 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–63
3. Check Bulletins and Troubleshooting Hints
NOTE: As estimated 30 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with this step!
What you should do
You should have enough information gained from
preliminary checks to accurately search for a bulletin
and other related service information. Some service
manual sections provide troubleshooting hints that
match symptoms with specific complaints.
What resources you should use
You should use the following resources for assistance in
checking for bulletins and troubleshooting hints:
• Printed bulletins
• Access ISUZU Bulletin Web site.
• Videotapes
• Service manual
4. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Checks
What you should do
The “System Checks” in most service manual sections
and in most cells of section 8A (electrical) provide you
with:
• A systematic approach to narrowing down the possible causes of a system fault
• Direction to specific diagnostic procedures in the service manual
• Assistance to identify what systems work correctly
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to perform service manual checks:
• Service manual
• Technical equipment (for viewing DTCs and analyzing data)
• Digital multimeter and circuit testing tools
• Other tools as needed
5a and 5b. Perform Service Manual Diagnostic Procedures
NOTE: An estimated 40 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with these steps!
What you should do
When directed by service manual diagnostic checks,
you must then carefully and accurately perform the
steps of diagnostic procedures to locate the fault related to the customer complaint.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to perform service manual diagnostic
procedures:
• Service manual
• Technical equipment (for analyzing diagnostic data)
• Digital multimeter and circuit testing tools
• Essential and special tools
5c. Technician Self Diagnoses
When there is no DTC stored and no matching
symptom for the condition identified in the service
manual, you must begin with a thorough understanding
of how the system(s) operates. Efficient use of the
service manual combined with you experience and a
good process of elimination will result in accurate
diagnosis of the condition.
What you should do
Step 1: Identify and understand the suspect
circuit(s)
Having completed steps 1 through 4 of the Strategy
Based Diagnostics chart, you should have enough
information to identify the system(s) or sub-system(s)
involved. Using the service manual, you should
determine and investigate the following circuit
characteristics:
• Electrical: – How is the circuit powered (power distributioncharts and/or fuse block details)?
– How is the circuit grounded (ground distribution charts)?
– How is the circuit controlled or sensed (theory of operation):
– If it is a switched circuit, is it normally open or normally closed?
– Is the power switched or is the ground switched?
– Is it a variable resistance circuit (ECT sensor or TP sensor, for example)?
– Is it a signal generating device (MAF sensor of VSS, for example)?
– Does it rely on some mechanical/vacuum device to operate?
•Physical:
– Where are the circuit components (componentlocators and wire harness routing diagrams):
– Are there areas where wires could be chafed or pinched (brackets or frames)?
– Are there areas subjected to extreme temperatures?
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2234 of 6020

6E–64 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
– Are there areas subjected to vibration ormovement (engine, transmission or
suspension)?
– Are there areas exposed to moisture, road salt or other corrosives (battery acid, oil or other
fluids)?
– Are there common mounting areas with other systems/components?
– Have previous repairs been performed to wiring, connectors, components or mounting areas
(causing pinched wires between panels and
drivetrain or suspension components without
causing and immediate problem)?
– Does the vehicle have aftermarket or dealer- installed equipment (radios, telephone, etc.)
Step 2: Isolate the problem
At this point, you should have a good idea of what could
cause the present condition, as well as could not cause
the condition. Actions to take include the following:
• Divide (and separate, where possible) the system or circuit into smaller sections
• Confine the problem to a smaller area of the vehicle (start with main harness connections while removing
panels and trim as necessary in order to eliminate
large vehicle sections from further investigation)
• For two or more circuits that do not share a common power or ground, concentrate on areas where
harnesses are routed together or connectors are
shared (refer to the following hints)
Hints
Though the symptoms may vary, basic electrical failures
are generally caused by:
• Loose connections: – Open/high resistance in terminals, splices,connectors or grounds
• Incorrect connector/harness routing (usually in new vehicles or after a repair has been made):
– Open/high resistance in terminals, splices, connectors of grounds
• Corrosion and wire damage:
– Open/high resistance in terminals, splices,connectors of grounds
• Component failure: – Opens/short and high resistance in relays,modules, switches or loads
• Aftermarket equipment affecting normal operation of other systems
You may isolate circuits by:
• Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to separate one part of the circuit from another part
• Operating shared circuits and eliminating those that function normally from the suspect circuit
• If only one component fails to operate, begin testing at the component
• If a number of components do no operate, begin tests at the area of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches or major connectors)
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
• Service manual
• Technical equipment (for data analysis)
• Experience
• Technical Assistance
• Circuit testing tools
5d. Intermittent Diagnosis
By definition, an intermittent problem is one that does
not occur continuously and will occur when certain
conditions are met. All these conditions, however, may
not be obvious or currently known. Generally,
intermittents are caused by:
• Faulty electrical connections and wiring
• Malfunctioning components (such as sticking relays, solenoids, etc.)
• EMI/RFI (Electromagnetic/radio frequency interference)
• Aftermarket equipment
Intermittent diagnosis requires careful analysis of
suspected systems to help prevent replacing good
parts. This may involve using creativity and ingenuity to
interpret customer complaints and simulating all
external and internal system conditions to duplicate the
problem.
What you should do
Step 1: Acquire information
A thorough and comprehensive customer check sheet
is critical to intermittent problem diagnosis. You should
require this, since it will dictate the diagnostic starting
point. The vehicle service history file is another
source for accumulating information about the
complaint.
Step 2: Analyze the intermittent problem
Analyze the customer check sheet and service history
file to determine conditions relevant to the suspect
system(s).
Using service manual information, you must identify,
trace and locate all electrical circuits related to the
malfunctioning system(s). If there is more than one
system failure, you should identify, trace and locate
areas of commonality shared by the suspect circuits.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3735 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–74
12 PIM Security and Programming
12.1 Security and Programming Information
Car Pass Card
W hen performing certain powertrain interface module (PIM) programming functions using Tech 2, you may be prompted
to enter a four digit Security Code (1). This information is found on the car pass card issued with the vehicle when new. If
the card is unavailable, contact the GM Holden Technical Assistance (TAS) centre to obtain the relevant Security Code.
Security Code
The security code is required when performing certain PIM, ICU and ECM programming functions. W hen Tech 2
requests the security code to be entered, and an incorrect code is entered, the PIM will go into a security wait time stage.
This wait time stage will prevent any further attempts to enter the security code until the wait time has elapsed.
Should a second incorrect security code be entered after the initial wait time has elapsed, the PIM will go into a second
wait time stage. The wait time will increase each time an incorrect code is entered. W hen the correct code is entered the
wait time will reset back to its original value of 10 seconds.
NOTE
The ignition switch must be in the ON position
with the battery connected during the wait time
period.
The wait time stages are as follows:
• Stage 1 = 10 seconds.
• Stage 2 = 10 seconds.
• Stage 3 = 10 minutes.
• Stage 4 = 20 minutes.
• Stage 5 = 40 minutes.
• Stage 5 = 80 minutes.
Tech 2 PIM Security Information Data List
The Tech 2 PIM Security Information Data List displays the PIM's current security status.
To view the data list:
1 Connect Tech 2 to the data link connector (DLC) and turn the ignition switch on.
2 On Tech 2 select: Body / Powertrain Interface Module / Security / Security Information .
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007