2007 ISUZU KB P190 air bleeding
[x] Cancel search: air bleedingPage 968 of 6020

6C – 4 FUEL SYSTEM
FUEL FILTER AND WATER SEPARATOR
As the inside of the injection pump is lubricated by the fuel which it is pumping, the fuel must be perfectly clean. The
fuel filter and the water separator remove water particles and other foreign material from the fuel before it reaches
the injection pump.
The water separator has an internal float. W hen the float reaches the specified level, a warning light comes on to
remind you to drain the water from the water separator.
A diaphragm type priming pump is installed at the top of the fuel filter. It is used during the air bleeding procedures.
(Except EURO III model)
RTW 36CLF000701
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1137 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-103
DTC P0216 (Symptom Code A, B) (Flash Code 54)
Description
The engine control module (ECM) calculates the
desired fuel injection quantity and timing using data sent
from various sensors. These desired data are sent to
the fuel injection pump control unit (PCU) via a
controller area network (CAN) communication bus. The
PCU also receives signals from the internal inputs:
pump camshaft position (CMP) sensor that is located
inside the fuel injection pump to determine the cam ring
rotation angle and the fuel injection pump speed. The
fuel temperature (FT) sensor is internal the PCU. These
values are used to compare the desired values sent
from the ECM then PCU determines the injection time
r
piston position and fuel injection quantity, and actuates
timing control valve (TCV) & fuel injection solenoid
valve based on control maps in the PCU.
The timing device changes the optimum injection
timing against various engine conditions. The
pressure of the fuel fed from the feed pump is
adjusted and it acts to the timing plunger by TCV
controlled fuel pressure. (
The TCV is installed to the
fuel injection pump rear side and it is controlled by dut
y
ratio cycle from the PCU.) The timing plunger is
connected to the cam ring by a ball pin. Axial
movement of the timing plunger is transferred to the
cam ring in the form of rotational movement.
Movement to the right of the timing plunge
r
advances injection timing.
If the PCU detects an
excessive difference between actual and desired fuel
injection timing, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
Symptom Code A
• The engine speed is higher than 700 RPM.
• The fuel injection quantity is higher than 4 mg/strk.
Symptom Code B
• The engine speed is higher than 2014 RPM.
Condition for Setting the DTC
Symptom Code A
• The PCU monitored actual fuel injection timing is
advanced more than desired by 3°CA for longe
r
than 12 seconds or retarded more than desired by
6°CA for longer than 12 seconds.
Symptom Code B
• The PCU monitored actual fuel injection timing is
oscillated higher than desired by 5.2°CA.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Notice:
• The fuel injection pump installation with incorrect
mechanical timing may set this DTC.
• This DTC most likely indicate loss fuel pressure by
restricted fuel line. Inspect the fuel line restriction
between the fuel injection pump and fuel tank.
• The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel
injection pump is under a slight vacuum with the
engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel
system if these connections are not tight or if there
is a crack in one of the fuel hoses. Air in the fuel
system will cause fuel injection pump internal
pressure fluctuations especially at high engine
speed and load, which may set this DTC.
• Improper fuel will cause this DTC to set. Inspect
fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect
fuel type used in winter season or water intrusion
in the fuel system.
• Contaminated fuel will cause this DTC to set.
Inspect the pipe connector fixing bolt (eye bolt) on
the fuel injection pump suction side.
Important:
If the fuel tank is empty or near empty, air might be
allowed to go into the fuel system. W ith air in the fuel
system, smooth flow of fuel into the fuel injection pump
is interrupted and this DTC may set. Perform bleeding
of fuel system after refilling. Refer to air bleeding
procedure in fuel system section.
DTC P0216 (Symptom Code A, B) (Flash Code 54)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1325 of 6020
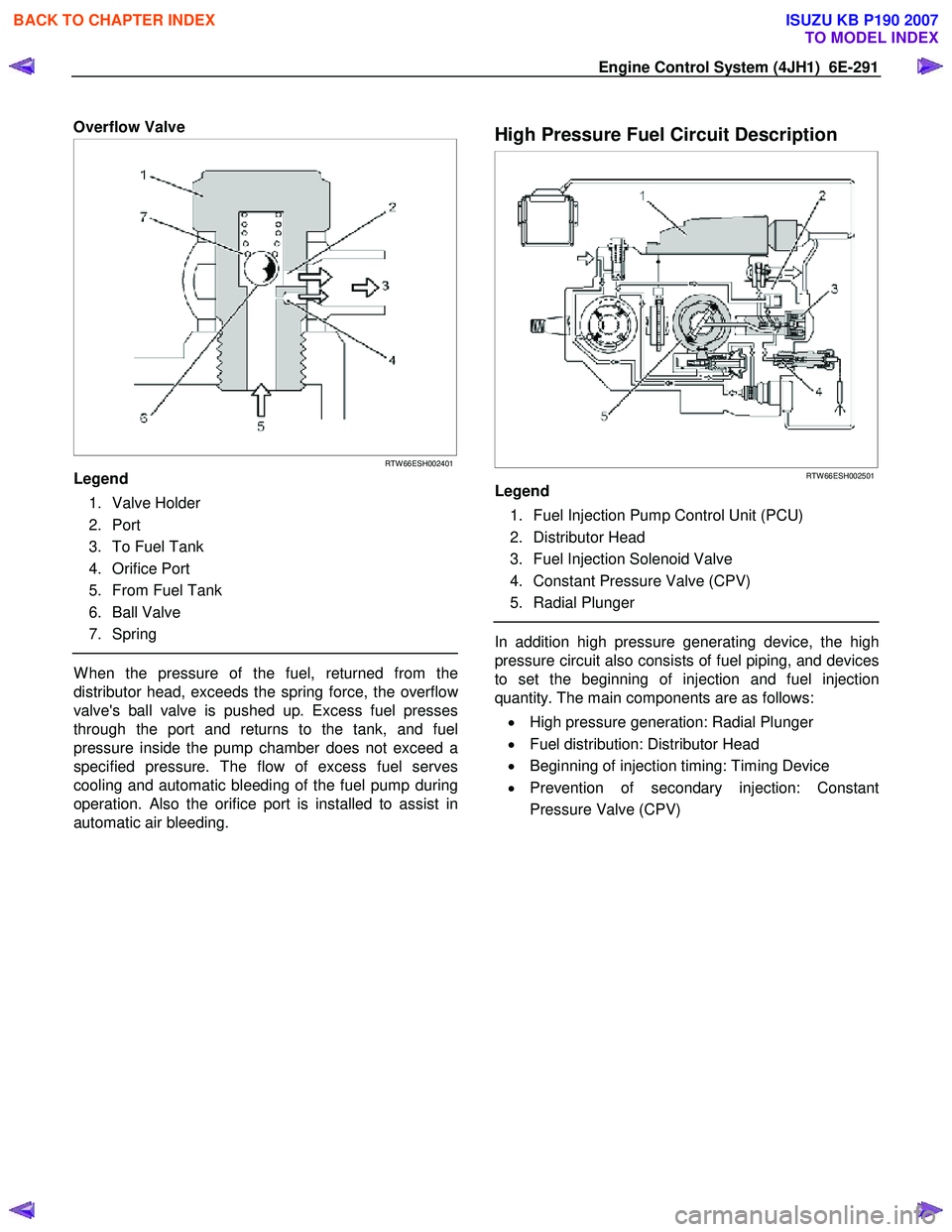
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-291
Overflow Valve
RTW 66ESH002401
Legend
1. Valve Holder
2. Port
3. To Fuel Tank
4. Orifice Port
5. From Fuel Tank
6. Ball Valve
7. Spring
W hen the pressure of the fuel, returned from the
distributor head, exceeds the spring force, the overflo
w
valve's ball valve is pushed up. Excess fuel presses
through the port and returns to the tank, and fuel
pressure inside the pump chamber does not exceed a
specified pressure. The flow of excess fuel serves
cooling and automatic bleeding of the fuel pump during
operation. Also the orifice port is installed to assist in
automatic air bleeding.
High Pressure Fuel Circuit Description
RTW 66ESH002501
Legend
1. Fuel Injection Pump Control Unit (PCU)
2. Distributor Head
3. Fuel Injection Solenoid Valve
4. Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
5. Radial Plunger
In addition high pressure generating device, the high
pressure circuit also consists of fuel piping, and devices
to set the beginning of injection and fuel injection
quantity. The main components are as follows:
• High pressure generation: Radial Plunger
• Fuel distribution: Distributor Head
• Beginning of injection timing: Timing Device
• Prevention of secondary injection: Constant
Pressure Valve (CPV)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1547 of 6020
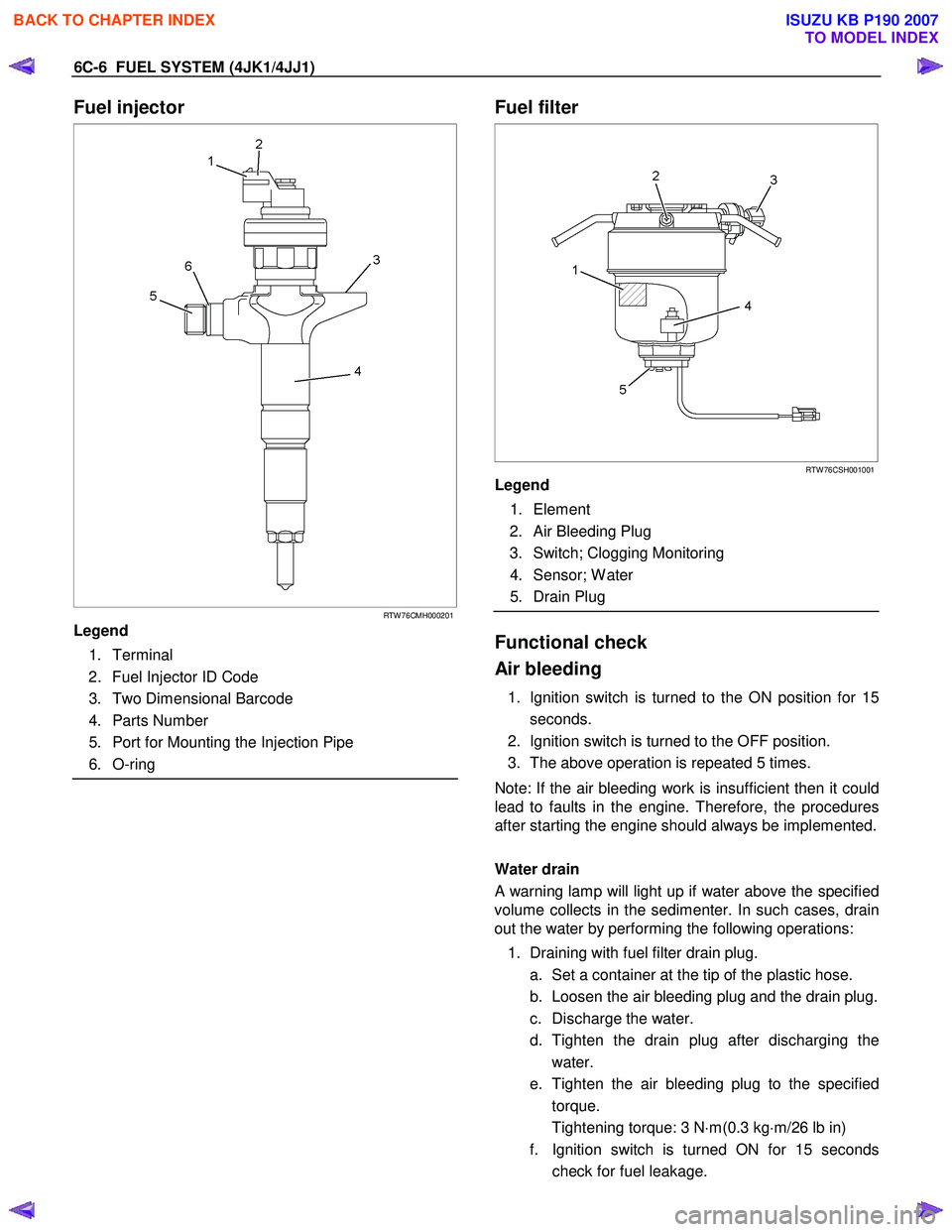
6C-6 FUEL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Fuel injector
RTW 76CMH000201
Legend
1. Terminal
2. Fuel Injector ID Code
3. Two Dimensional Barcode
4. Parts Number
5. Port for Mounting the Injection Pipe
6. O-ring
Fuel filter
RTW 76CSH001001
Legend
1. Element
2. Air Bleeding Plug
3. Switch; Clogging Monitoring
4. Sensor; W ater
5. Drain Plug
Functional check
Air bleeding
1. Ignition switch is turned to the ON position for 15 seconds.
2. Ignition switch is turned to the OFF position.
3. The above operation is repeated 5 times.
Note: If the air bleeding work is insufficient then it could
lead to faults in the engine. Therefore, the procedures
after starting the engine should always be implemented.
Water drain
A warning lamp will light up if water above the specified
volume collects in the sedimenter. In such cases, drain
out the water by performing the following operations:
1. Draining with fuel filter drain plug. a. Set a container at the tip of the plastic hose.
b. Loosen the air bleeding plug and the drain plug.
c. Discharge the water.
d. Tighten the drain plug after discharging the water.
e. Tighten the air bleeding plug to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 3 N ⋅m(0.3 kg ⋅m/26 lb in)
f. Ignition switch is turned ON for 15 seconds check for fuel leakage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1551 of 6020
6C-10 FUEL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Fuel System Check
Description
Conforms to a fuel leak. Engine acceleration raises fuel
pressure and which increases the leak.
Leak could be in the following pipes and locations.
• Between injectors and fuel rail.
• Between fuel rail and fuel supply pump.
• Between fuel supply pump and fuel filter.
• Between fuel filter and fuel tank.
• Between pressure limiter and fuel cooler.
• Between fuel cooler and fuel tank.
• Between injector over flow and leak off pipe.
Diagnostic Aids
Check the following items.
• Air in the fuel line
• Clogged fuel filter
• Fuel pipe malfunction (Crushing, breakage,
clogging, disconnection, etc.)
• Fuel cooler malfunction (Crushing, breakage,
clogging, disconnection, etc.)
• Fuel tank malfunction
• Injector malfunction
• Fuel supply pump malfunction
• Pressure limiter malfunction
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for poor connections or a
damaged harness.
Inspect the ECM harness and connector for imprope
r
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection, and
damaged harness.
ECU may set a DTC, if there is adequate air in fuel line.
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Check the fuel quantity. W as a problem found?
Go to Step 2 Add fuel and
Go to Step 2
2 Check the fuel quality.
1. Discharge the fuel from fuel tank
2. Replenish the tank with specified fuel
3. Bleed the air from the fuel system
4. Start the engine
Could the engine be started?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 3
3 Bleed the air from fuel system. Refer to Fuel
System Air Bleeding in this section.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 4
4 Check the main fuel filter for clogging.
Clean, repair, or replace as required.
Notice: Replacement of a fuel filter is checking
to a dealer.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 5
5 Check the fuel line and fuel cooler for damage
and leakage.
Clean, repair, or replace as required.
• Crushed areas
• Breakage
• Cracks
• Loose connections
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1552 of 6020
FUEL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6C-11
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
6 Check the fuel tank.
If a problem is found, clean, repair, or replace
as necessary.
• Foreign material (Clogged suction port)
• Bent or cracked suction pipe
• Fuel tank distortion
• Fuel tank improper installation
• Fuel pump and sender malfunction
• Clogged fuel cap hole
• Water
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 7
7 Bleed the air from the fuel pipe again. Refer to
Fuel System Air Bleeding in this section.
Is the action complete?
Verify repair
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1691 of 6020

6E-74 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
DTC P0087 (Flash Code 225)
Description
The common rail fuel system is comprised of two fuel
pressure sections: a suction side between the fuel tank
and the fuel supply pump and a high-pressure side
between the fuel supply pump and the fuel injectors.
Fuel is drawn from the fuel tank via a feed pump and
then pumped into the fuel rail by two plungers, all of
which are internal to the fuel supply pump. This high
pressure is regulated by the ECM using the fuel rail
pressure (FRP) regulator dependant upon values from
the FRP sensor attached to the fuel rail. In case of fuel
rail overpressure, a pressure limiter valve threaded into
the fuel rail will open to release overpressure and
return fuel back to the fuel tank. If the ECM detects that
the fuel rail pressure went excessively high, then
sharply decreased, this DTC will set indicating high fuel
pressure, which activated the pressure limiter valve.
Condition for Running the DTC • DTCs P0192 and P0193 are not set.
• The battery voltage is more than 9 volts.
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine is running.
Condition for Setting the DTC • The ECM detects that the pressure limiter valve is activated with overpressure (more than 190 MPa
[27,600 psi]) in the fuel rail.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM illuminates the MIL when the diagnostic runs and fails. Refer to DTC Type Definitions for
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type A. • The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM inhibits pilot injection.
• The ECM inhibits cruise control.
Condition for Clearing the DTC • Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Condition for Clearing the MIL/ DTC - Type A.
Diagnostic Aids • An intermittently sticking FRP regulator may have allowed the fuel pressure to become high enough
to open the pressure limiter valve.
• A skewed FRP sensor value can set this DTC. The FRP Sensor on the scan tool should read 0.9 to
1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1
minute.
Notice: • If the fuel tank is empty or near empty, air might be allowed to go into the fuel system. With air in the
fuel system, smooth flow of fuel into the supply
pump is interrupted and this DTC may set. Perform
bleeding of fuel system after refilling.
Schematic Reference: Fuel System Routing Diagram
and Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or ECM Connector End Views
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P0087
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
2 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0088, P0089, P0091, P0092, P0192,
P0193, P0201 - P0204, P1064, P1065, P124B or
P2146 - P2151 set? —
Go to Applicable DTC Go to Step 3
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1707 of 6020

6E-90 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
DTC P0093 (Flash Code 227)
Description
The common rail fuel system is comprised of two fuel
pressure sections: a suction side between the fuel tank
and the fuel supply pump and a high-pressure side
between the fuel supply pump and the fuel injectors.
Fuel is drawn from the fuel tank via a feed pump and
then pumped into the fuel rail by two plungers, all of
which are internal to the fuel supply pump. This high
pressure is regulated by the ECM using the fuel rail
pressure (FRP) regulator dependant upon values from
the FRP sensor attached to the fuel rail. If the ECM
detects that the fuel rail pressure is certain pressure
low as compared with the engine speed, this DTC will
set.
Condition for Running the DTC • DTC P0087, P0091, P0092, P0192, P0193, P0652, P0653, P0201 - P0204, P1064, P1065,
P124B and P2146 - P2151 are not set.
• The battery voltage is more than 9 volts.
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine is running.
Condition for Setting the DTC • The ECM detects that the actual fuel rail pressure is lower than 15 MPa (2,180 psi) for longer than 5
seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM illuminates the MIL when the diagnostic runs and fails. Refer to DTC Type Definitions for
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type A.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM inhibits pilot injection. • The ECM inhibits cruise control.
Condition for Clearing the DTC • Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Condition for Clearing the MIL/ DTC - Type A.
Diagnostic Aids • An intermittently sticking FRP regulator may have allowed the fuel pressure to become low enough to
set this DTC.
• Normal Fuel Rail Pressure readings on the scan tool with the engine running in neutral at idle is
around 27 to 33 MPa (3,900 to 4,800 psi) after
warm up.
• A skewed FRP sensor value can set this DTC. The FRP Sensor on the scan tool should read 0.9 to
1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1
minute.
Notice: • This DTC most likely indicates a loss of fuel pressure by a fuel leak from the high pressure
side. Inspect the high pressure side fuel leakage
between the fuel supply pump and fuel injector
first.
• If the fuel tank is empty or near empty, air might be allowed to go into the fuel system. With air in the
fuel system, smooth flow of fuel into the supply
pump is interrupted and this DTC may set. Perform
bleeding of fuel system after refilling.
Schematic Reference: Fuel System Routing Diagram
and Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or ECM Connector End Views
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P0093
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007