2007 ISUZU KB P190 heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 2215 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–45
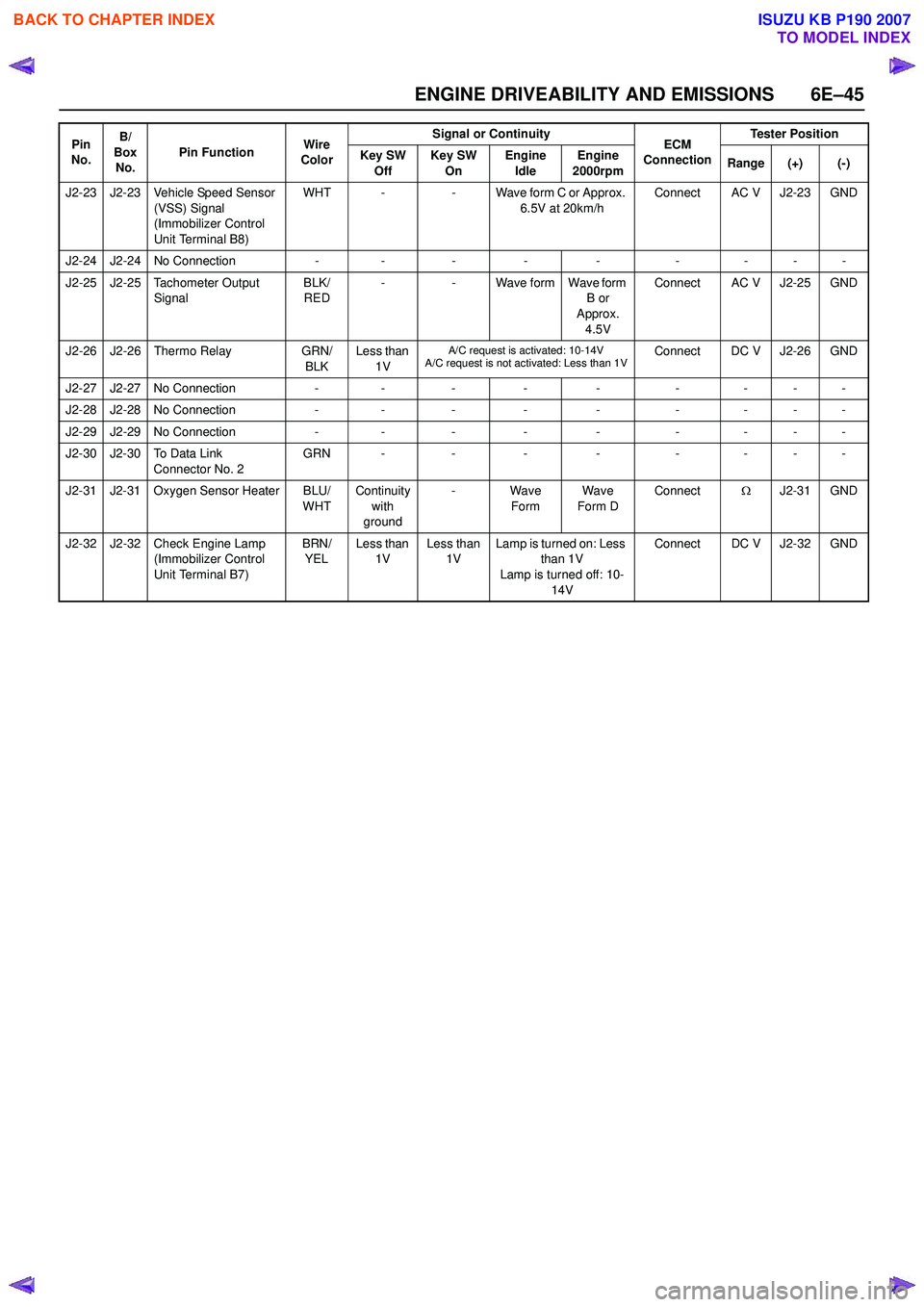
J2-23 J2-23 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Signal
(Immobilizer Control
Unit Terminal B8) WHT -
- Wave form C or Approx.
6.5V at 20km/h Connect AC V J2-23 GND
J2-24 J2-24 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-25 J2-25 Tachometer Output Signal BLK/
RED -
- Wave form Wave form
B or
Approx.
4.5V Connect AC V J2-25 GND
J2-26 J2-26 Thermo Relay GRN/
BLK Less than
1V
A/C request is activated: 10-14V
A/C request is not activated: Less than 1VConnect DC V J2-26 GND
J2-27 J2-27 No Connection - - - - - - - - -
J2-28 J2-28 No Connection - - - - - - - - -
J2-29 J2-29 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-30 J2-30 To Data Link Connector No. 2 GRN -
-- - -- - -
J2-31 J2-31 Oxygen Sensor Heater BLU/ WHTContinuity
with
ground - Wave
Form Wave
Form D Connect
ΩJ2-31 GND
J2-32 J2-32 Check Engine Lamp (Immobilizer Control
Unit Terminal B7) BRN/
YEL Less than
1V Less than
1V Lamp is turned on: Less
than 1V
Lamp is turned off: 10-
14V Connect DC V J2-32 GND
Pin
No. B/
Box No. Pin Function
Wire
Color Signal or Continuity
ECM
Connection Tester Position
Key SW Off Key SW
On Engine
Idle Engine
2000rpm Range (+) (-)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2221 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–51
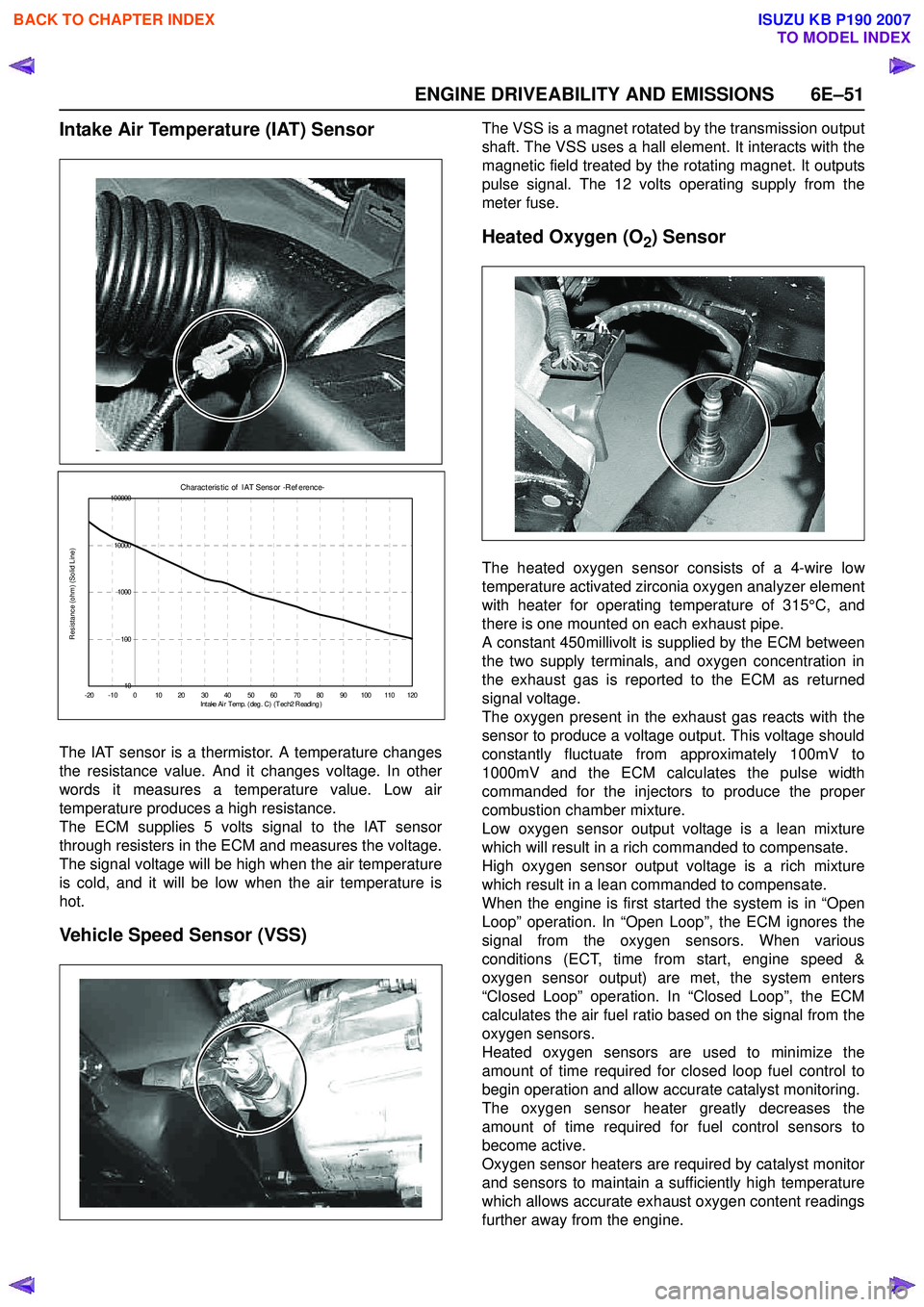
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The IAT sensor is a thermistor. A temperature changes
the resistance value. And it changes voltage. In other
words it measures a temperature value. Low air
temperature produces a high resistance.
The ECM supplies 5 volts signal to the IAT sensor
through resisters in the ECM and measures the voltage.
The signal voltage will be high when the air temperature
is cold, and it will be low when the air temperature is
hot.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The VSS is a magnet rotated by the transmission output
shaft. The VSS uses a hall element. It interacts with the
magnetic field treated by the rotating magnet. It outputs
pulse signal. The 12 volts operating supply from the
meter fuse.
Heated Oxygen (O2) Sensor
The heated oxygen sensor consists of a 4-wire low
temperature activated zirconia oxygen analyzer element
with heater for operating temperature of 315°C, and
there is one mounted on each exhaust pipe.
A constant 450millivolt is supplied by the ECM between
the two supply terminals, and oxygen concentration in
the exhaust gas is reported to the ECM as returned
signal voltage.
The oxygen present in the exhaust gas reacts with the
sensor to produce a voltage output. This voltage should
constantly fluctuate from approximately 100mV to
1000mV and the ECM calculates the pulse width
commanded for the injectors to produce the proper
combustion chamber mixture.
Low oxygen sensor output voltage is a lean mixture
which will result in a rich commanded to compensate.
High oxygen sensor output voltage is a rich mixture
which result in a lean commanded to compensate.
When the engine is first started the system is in “Open
Loop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the oxygen sensors. When various
conditions (ECT, time from start, engine speed &
oxygen sensor output) are met, the system enters
“Closed Loop” operation. In “Closed Loop”, the ECM
calculates the air fuel ratio based on the signal from the
oxygen sensors.
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for closed loop fuel control to
begin operation and allow accurate catalyst monitoring.
The oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the
amount of time required for fuel control sensors to
become active.
Oxygen sensor heaters are required by catalyst monitor
and sensors to maintain a sufficiently high temperature
which allows accurate exhaust oxygen content readings
further away from the engine.
Charac t eris t ic of I AT Sens or -R ef erenc e-
10
100
1000
10000
100000
- 20 - 10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Intake Ai r T emp. ( deg . C ) ( T ec h2 R eadi ng )
Resistance (ohm) (Solid Line)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2286 of 6020
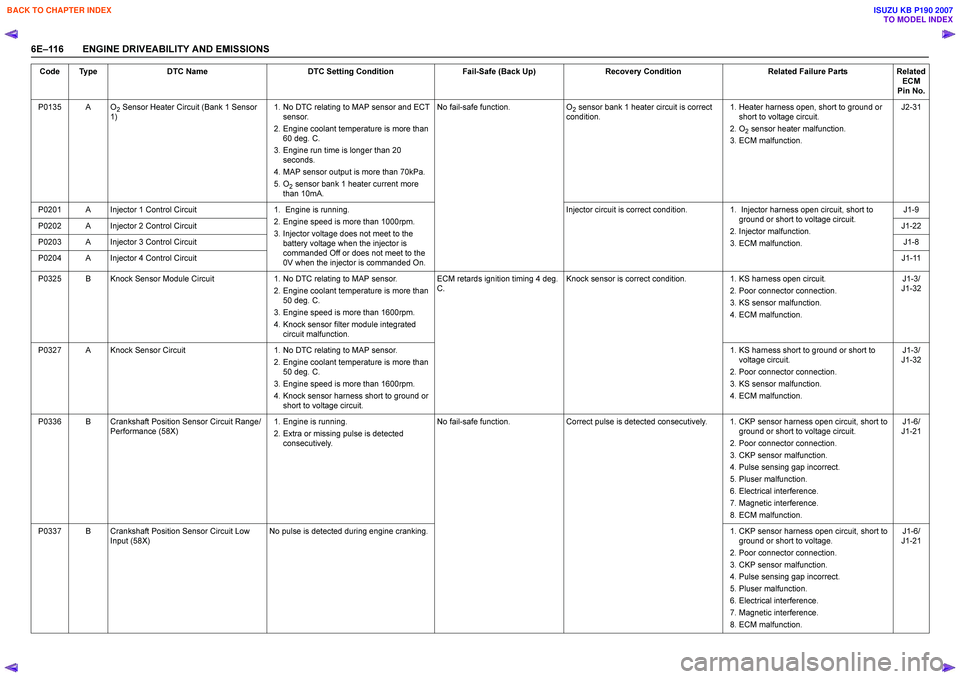
6E–116 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONSP0135 A O
2 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor
1) 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor and ECT
sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 60 deg. C.
3. Engine run time is longer than 20 seconds.
4. MAP sensor output is more than 70kPa.
5. O
2 sensor bank 1 heater current more
than 10mA. No fail-safe function.
O
2 sensor bank 1 heater circuit is correct
condition. 1. Heater harness open, short to ground or
short to voltage circuit.
2. O
2 sensor heater malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction. J2-31
P0201 A Injector 1 Control Circuit 1. Engine is running. 2. Engine speed is more than 1000rpm.
3. Injector voltage does not meet to the battery voltage when the injector is
commanded Off or does not meet to the
0V when the injector is commanded On. Injector circuit is correct condition.
1. Injector harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.
2. Injector malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction. J1-9
P0202 A Injector 2 Control Circuit J1-22
P0203 A Injector 3 Control Circuit J1-8
P0204 A Injector 4 Control Circuit J1-11
P0325 B Knock Sensor Module Circuit 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 50 deg. C.
3. Engine speed is more than 1600rpm.
4. Knock sensor filter module integrated circuit malfunction. ECM retards ignition timing 4 deg.
C . Knock sensor is correct condition.
1. KS harness open circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. KS sensor malfunction.
4. ECM malfunction. J1-3/
J1-32
P0327 A Knock Sensor Circuit 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 50 deg. C.
3. Engine speed is more than 1600rpm.
4. Knock sensor harness short to ground or short to voltage circuit. 1. KS harness short to ground or short to
voltage circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. KS sensor malfunction.
4. ECM malfunction. J1-3/
J1-32
P0336 B Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Range/ Performance (58X) 1. Engine is running.
2. Extra or missing pulse is detected consecutively. No fail-safe function.
Correct pulse is detected consecutively. 1. CKP sensor harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. CKP sensor malfunction.
4. Pulse sensing gap incorrect.
5. Pluser malfunction.
6. Electrical interference.
7. Magnetic interference.
8. ECM malfunction. J1-6/
J1-21
P0337 B Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low Input (58X) No pulse is detected during engine cranking.
1. CKP sensor harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. CKP sensor malfunction.
4. Pulse sensing gap incorrect.
5. Pluser malfunction.
6. Electrical interference.
7. Magnetic interference.
8. ECM malfunction. J1-6/
J1-21
Code Type
DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)Recovery Condition Related Failure PartsRelated
ECM
Pin No.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2322 of 6020
6E–152 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
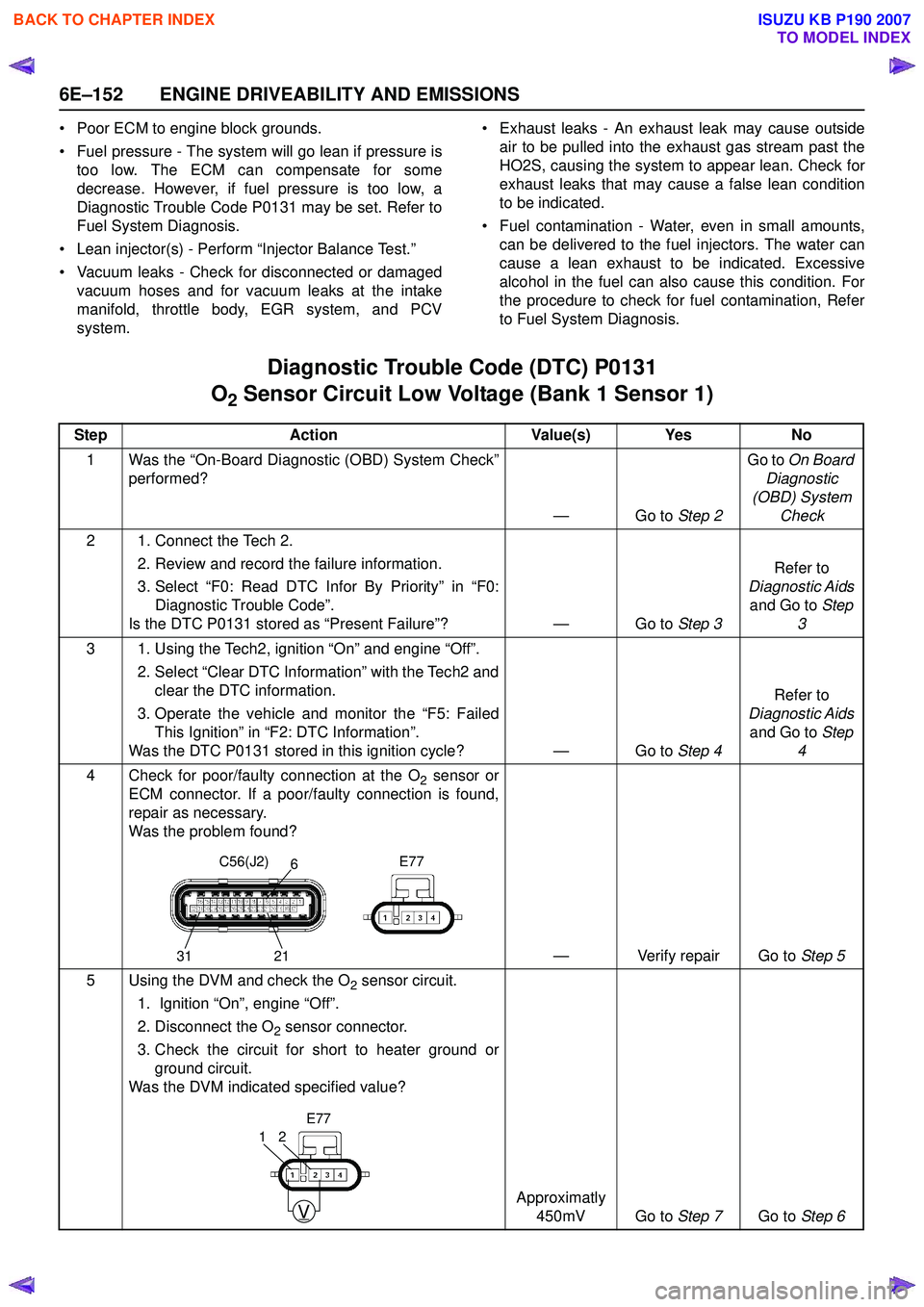
• Poor ECM to engine block grounds.
• Fuel pressure - The system will go lean if pressure is too low. The ECM can compensate for some
decrease. However, if fuel pressure is too low, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0131 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis.
• Lean injector(s) - Perform “Injector Balance Test.”
• Vacuum leaks - Check for disconnected or damaged vacuum hoses and for vacuum leaks at the intake
manifold, throttle body, EGR system, and PCV
system. • Exhaust leaks - An exhaust leak may cause outside
air to be pulled into the exhaust gas stream past the
HO2S, causing the system to appear lean. Check for
exhaust leaks that may cause a false lean condition
to be indicated.
• Fuel contamination - Water, even in small amounts, can be delivered to the fuel injectors. The water can
cause a lean exhaust to be indicated. Excessive
alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition. For
the procedure to check for fuel contamination, Refer
to Fuel System Diagnosis.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0131
O
2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0131 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0131 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 Check for poor/faulty connection at the O
2 sensor or
ECM connector. If a poor/faulty connection is found,
repair as necessary.
Was the problem found?
— Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Using the DVM and check the O
2 sensor circuit.
1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the O
2 sensor connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to heater ground or ground circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
Approximatly 450mV Go to Step 7Go to Step 6
C56(J2) E77
31 216
V
21
E77
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2323 of 6020
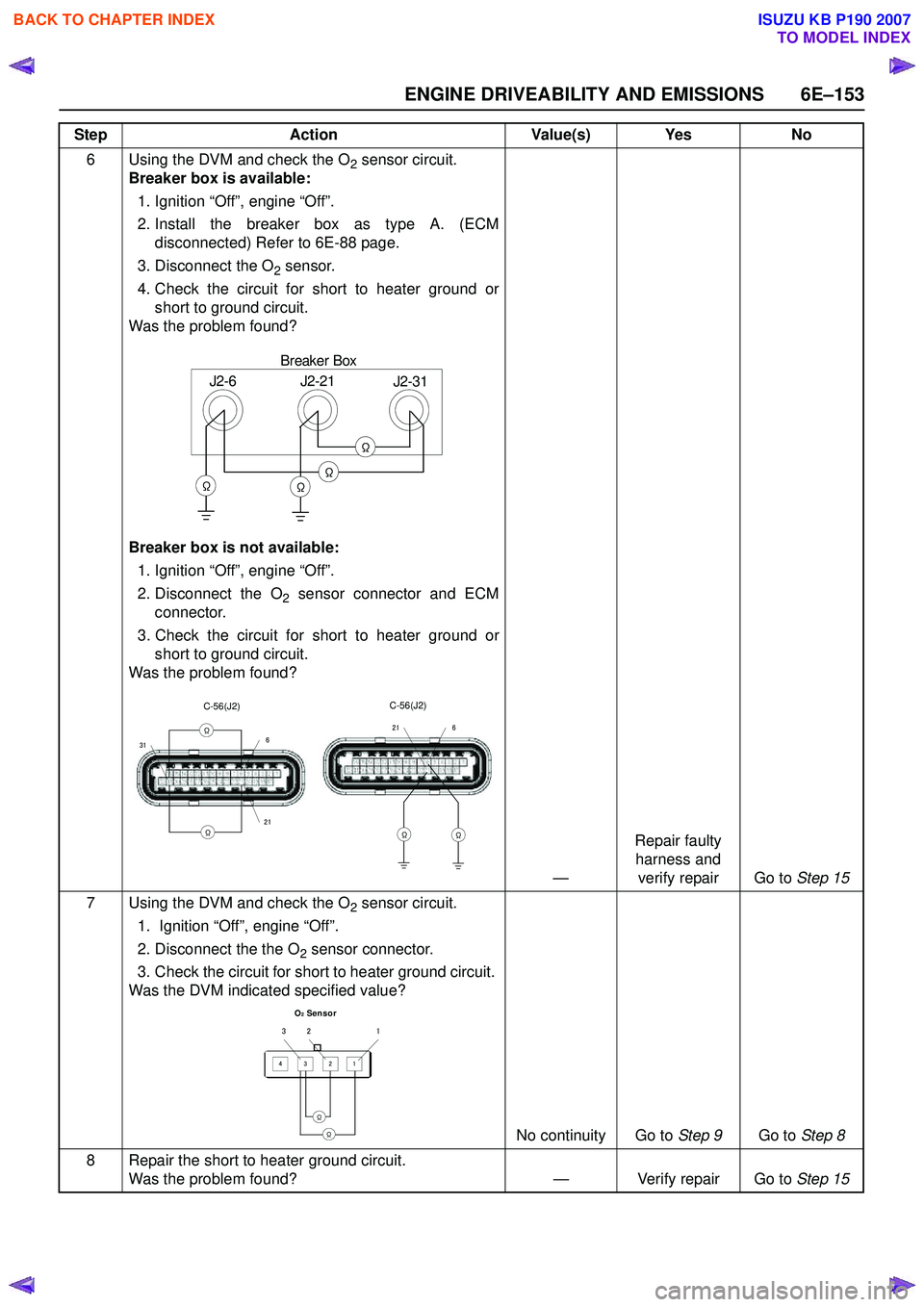
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–153
6 Using the DVM and check the O2 sensor circuit.
Breaker box is available:
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Install the breaker box as type A. (ECM disconnected) Refer to 6E-88 page.
3. Disconnect the O
2 sensor.
4. Check the circuit for short to heater ground or short to ground circuit.
Was the problem found?
Breaker box is not available: 1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the O
2 sensor connector and ECM
connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to heater ground or short to ground circuit.
Was the problem found?
—Repair faulty
harness and verify repair Go to Step 15
7 Using the DVM and check the O
2 sensor circuit.
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the the O
2 sensor connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to heater ground circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
No continuity Go to Step 9Go to Step 8
8 Repair the short to heater ground circuit. Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
J2-6J2-21
Breaker BoxJ2-31
ΩΩΩ
Ω
C-56(J2)
2
16
ΩΩ
C-56(J2)
2 1
631Ω
Ω
O2 Sensor
423
2
Ω
3
1
Ω
1
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2327 of 6020
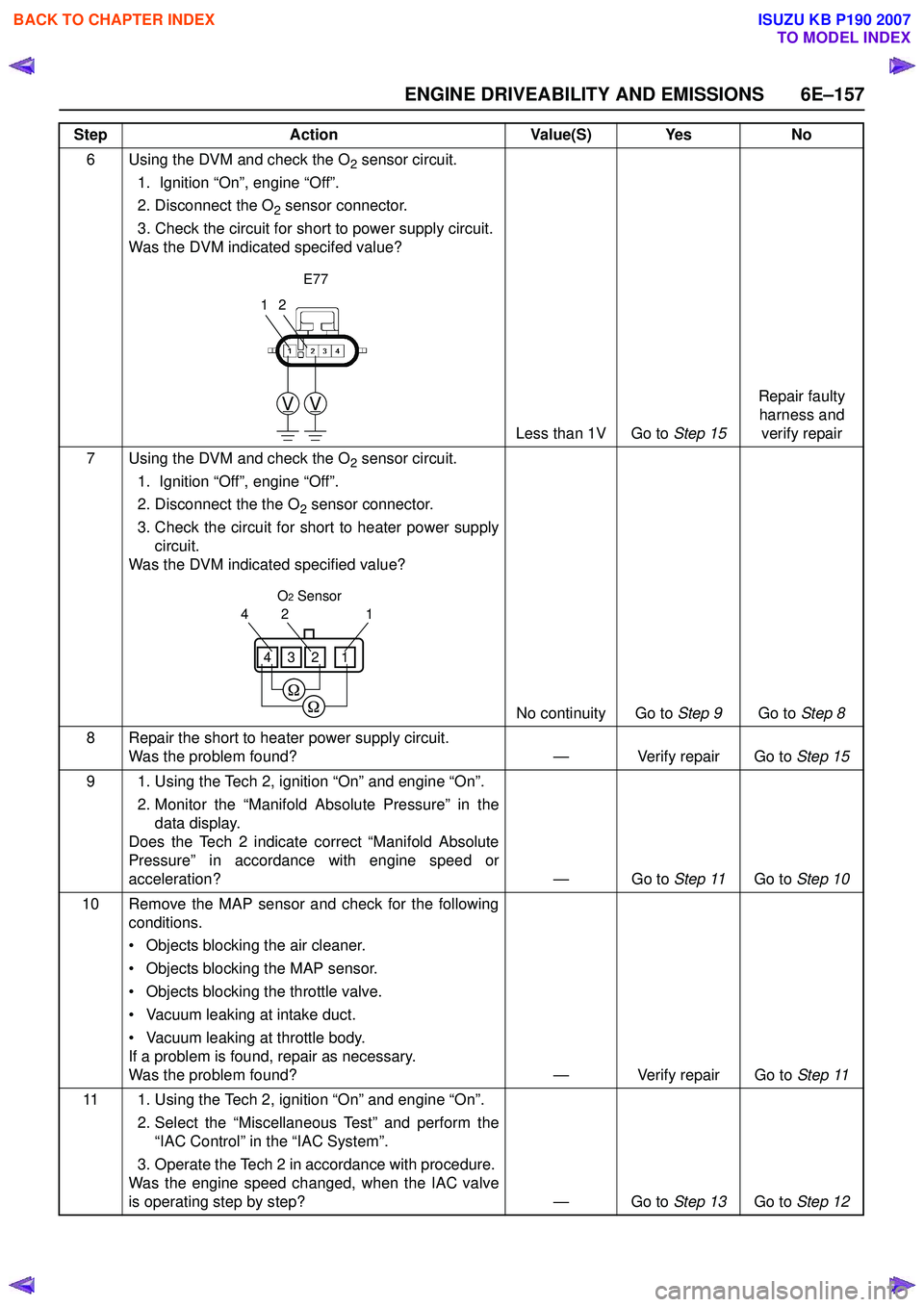
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–157
6 Using the DVM and check the O2 sensor circuit.
1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the O
2 sensor connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to power supply circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specifed value?
Less than 1V Go to Step 15Repair faulty
harness and verify repair
7 Using the DVM and check the O
2 sensor circuit.
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the the O
2 sensor connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to heater power supply circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
No continuity Go to Step 9Go to Step 8
8 Repair the short to heater power supply circuit. Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
9 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Monitor the “Manifold Absolute Pressure” in thedata display.
Does the Tech 2 indicate correct “Manifold Absolute
Pressure” in accordance with engine speed or
acceleration? — Go to Step 11Go to Step 10
10 Remove the MAP sensor and check for the following conditions.
• Objects blocking the air cleaner.
• Objects blocking the MAP sensor.
• Objects blocking the throttle valve.
• Vacuum leaking at intake duct.
• Vacuum leaking at throttle body.
If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Select the “Miscellaneous Test” and perform the“IAC Control” in the “IAC System”.
3. Operate the Tech 2 in accordance with procedure.
Was the engine speed changed, when the IAC valve
is operating step by step? — Go to Step 13Go to Step 12
Step
Action Value(S) Yes No
12
VV
E77
1
24
1234
O2 Sensor
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2333 of 6020
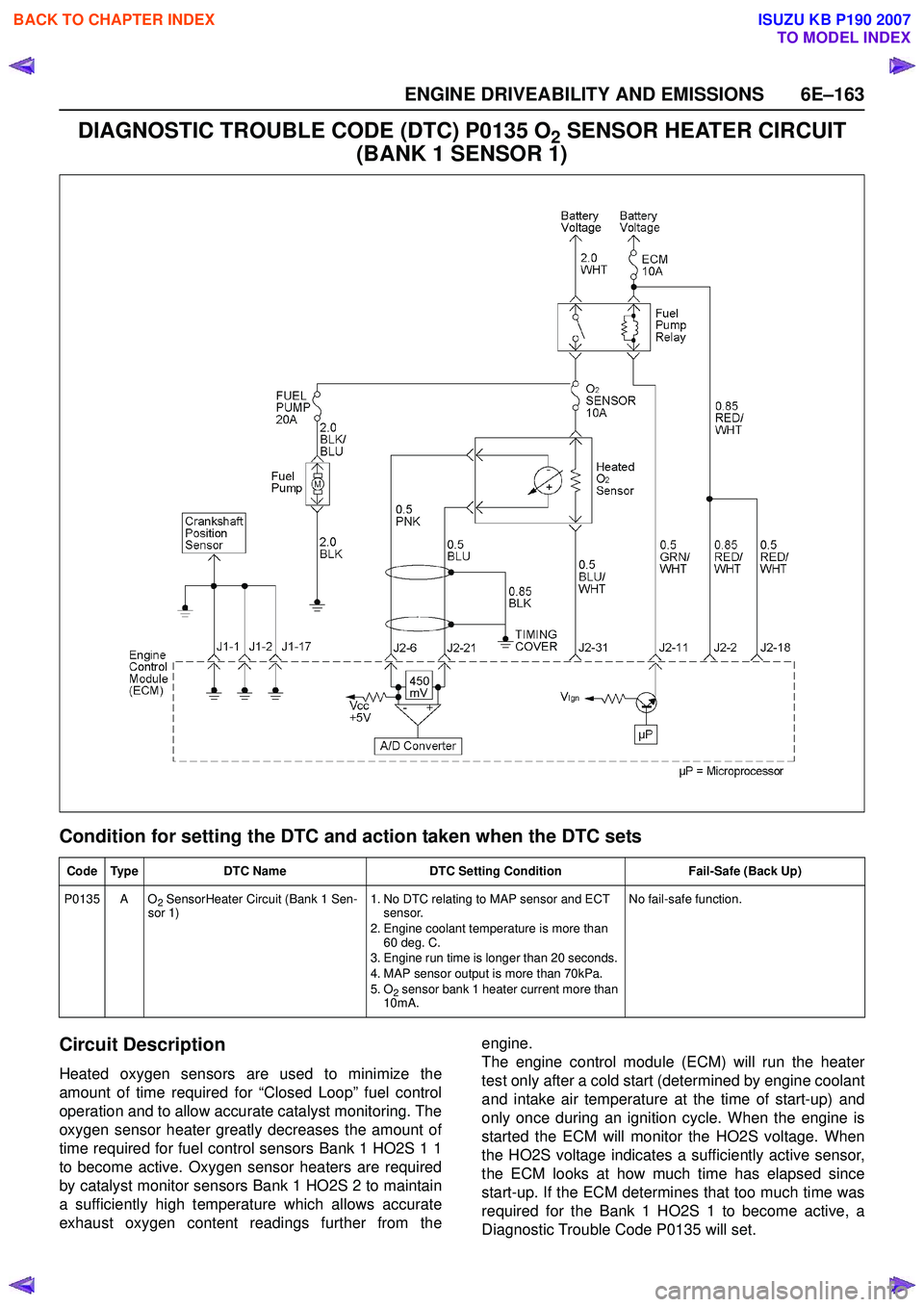
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–163
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0135 O2 SENSOR HEATER CIRCUIT
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for “Closed Loop” fuel control
operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The
oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of
time required for fuel control sensors Bank 1 HO2S 1 1
to become active. Oxygen sensor heaters are required
by catalyst monitor sensors Bank 1 HO2S 2 to maintain
a sufficiently high temperature which allows accurate
exhaust oxygen content readings further from the engine.
The engine control module (ECM) will run the heater
test only after a cold start (determined by engine coolant
and intake air temperature at the time of start-up) and
only once during an ignition cycle. When the engine is
started the ECM will monitor the HO2S voltage. When
the HO2S voltage indicates a sufficiently active sensor,
the ECM looks at how much time has elapsed since
start-up. If the ECM determines that too much time was
required for the Bank 1 HO2S 1 to become active, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0135 will set.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0135 A O
2 SensorHeater Circuit (Bank 1 Sen-
sor 1) 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor and ECT
sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 60 deg. C.
3. Engine run time is longer than 20 seconds.
4. MAP sensor output is more than 70kPa.
5. O
2 sensor bank 1 heater current more than
10mA. No fail-safe function.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2334 of 6020
6E–164 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
• Poor connection at ECM - Inspect harness connectors for backed-out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal-to-wire connection.
• Damaged harness - Inspect the wiring harness for damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0135
O
2 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0135 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0135 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 Check for poor/faulty connection at the O
2 sensor or
ECM connector. If a poor/faulty connection is found,
repair as necessary.
Was the problem found?
— Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Visually check the O
2 sensor.
Was the problem found? — Go to Step 11Go to Step 6
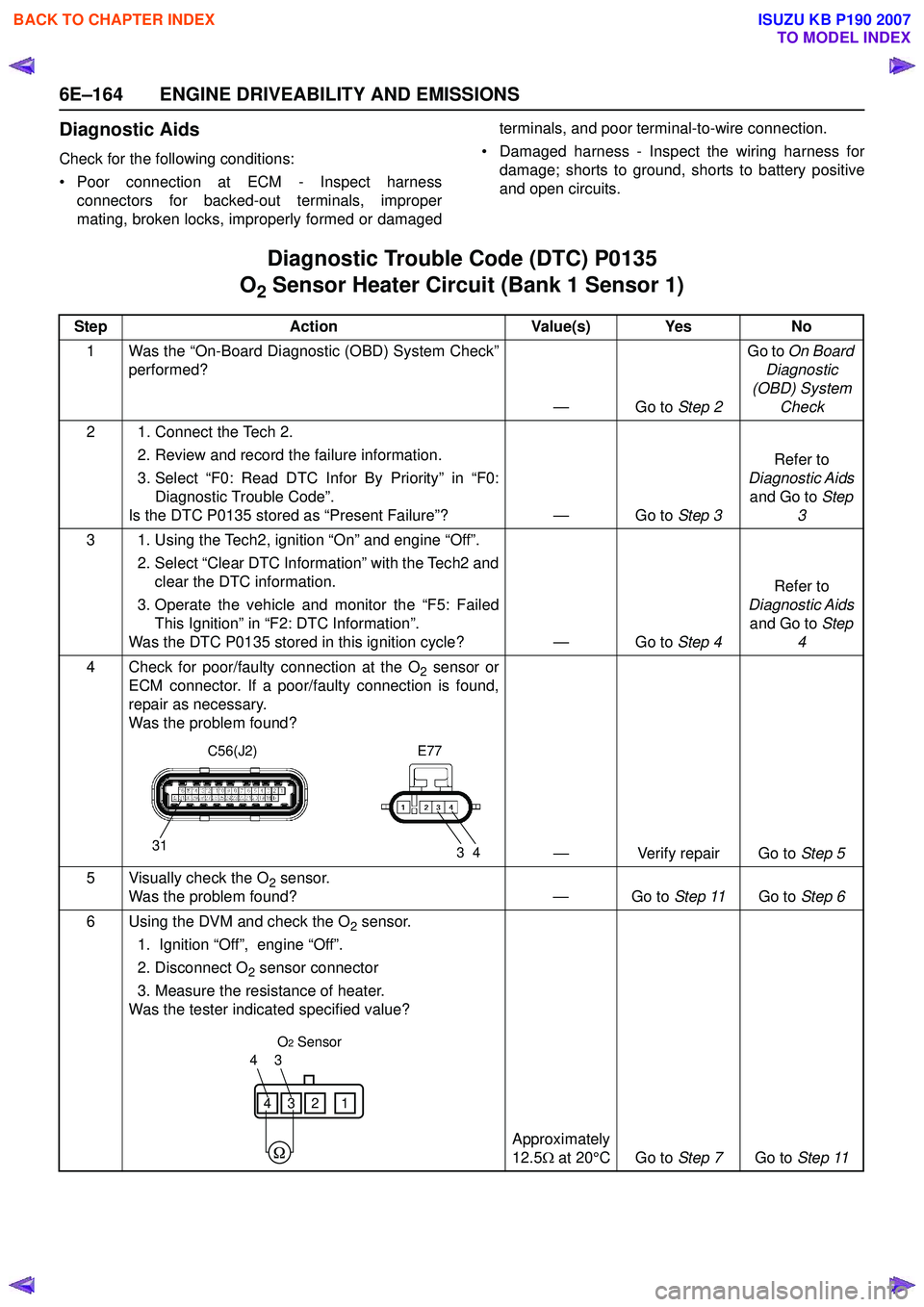
6 Using the DVM and check the O
2 sensor.
1. Ignition “Off”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect O
2 sensor connector
3. Measure the resistance of heater.
Was the tester indicated specified value?
Approximately
12.5 Ω at 20°C Go to Step 7Go to Step 11
3431
C56(J2) E77
34
1234
O2 Sensor
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007