2006 SUZUKI SX4 Can
[x] Cancel search: CanPage 421 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-7
1) Set parking brake and place automatic transaxle in
PARK (NEUTRAL on manual transaxle). Turn off
ignition, turn off lights and all other electrical loads.
2) Check electrolyte level. If it is below low level line,
add distilled water.
3) Attach end of one jumper cable to positive terminal
of booster battery and the other end of the same
cable to positive terminal of discharged battery. (Use
12-volt battery only to jump start engine).
4) Attach one end of the remaining negative cable to
negative terminal of booster battery, and the other
end to a solid engine ground (such as exhaust
manifold) at least 45 cm (18 in.) away from battery of
vehicle being started.
5) Start engine of vehicle with booster battery and turn
off electrical accessories. Then start engine of the
vehicle with discharged battery.
6) Disconnect jumper cables in the exact reverse order.
With Charging Equipment
CAUTION!
When jump starting engine with charging
equipment, be sure equipment used is 12-
volt and negative ground. Do not use 24-volt
charging equipment. Using such equipment
can cause serious damage to electrical
system or electronic parts.
Battery Dismounting and RemountingS6RW0D1A06002
Dismounting
1) Disconnect negative cable (3).
2) Disconnect positive cable (2).
3) Remove retainer (4).
4) Remove battery (1).
Handling
When handling battery, the following safety precautions
should be followed:
• Hydrogen gas is produced by battery. A flame or
spark near battery may cause the gas to ignite.
• Battery fluid is highly acidic. Avoid spilling on clothing
or other fabric. Any spilled electrolyte should be
flushed with large quantity of water and cleaned
immediately.Remounting
1) Reverse removal procedure.
2) Tighten battery cables securely.
NOTE
Check to be sure that ground cable has
enough clearance to hood panel by terminal.
Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension
Inspection and Adjustment
S6RW0D1A06006
WARNING!
• Disconnect negative cable at battery
before checking and adjusting belt
tension.
• To help avoid danger of being burned, do
not remove radiator cap while engine and
radiator are still hot. Scalding fluid and
steam can be blown out under pressure if
cap is taken off too soon.
1) Inspect belt for cracks, cuts, deformation, wear and
cleanliness. If it is necessary to replace belt, refer to
“Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Removal and
Installation”.
2) Check belt for tension. Belt is in proper tension when
it deflects the following specification under thumb
pressure (about 10kg or 22 lb.).
If belt tension is out of specification, go to next steps.
Water pump / generator drive belt tension
“a”
Existing belt: 4.5 – 5.5 mm (0.18 – 0.22 in.) as
deflection / 10 kg (22 lbs)
New belt: 4.0 – 4.5mm (0.16 – 0.18 in.) as
deflection / 10 kg (22 lbs)
1. Battery 4. Retainer
2. Positive cable 5. Nut
3. Negative cable
21
4
3
5I7RW011A0005-01
Page 439 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-2
Front Wheel Alignment ConstructionS6RW0D2201002
Among factors for front wheel alignment, only toe setting
can be adjusted. Camber and caster are not adjustable.
Therefore, should camber or caster be out of
specification due to the damage caused by hazardous
road conditions or collision, whether the damage is in
body or in suspension should be determined and
damaged body should be repaired or damaged
suspension should be replaced.
Preliminary Checks Prior to Adjustment Front Wheel
Alignment
Steering and vibration complaints are not always the
result of improper wheel alignment. An additional item to
be checked is the possibility of tire lead due to worn or
improperly manufactured tires. “Lead” is the vehicle
deviation from a straight path on a level road without
hand pressure on the steering wheel. Refer to “Radial
Tire Lead / Pull Description in Section 2D” in order to
determine if the vehicle has a tire lead problem. Before
making any adjustment affecting wheel alignment, the
following checks and inspections should be made to
ensure correctness of alignment readings and alignment
adjustments:• Check all tires for proper inflation pressures and
approximately the same tread wear.
• Check for loose of ball joints. Check tie-rod ends; if
excessive looseness is noted, it must be corrected
before adjusting.
• Check for run-out of wheels and tires.
• Check vehicle trim heights; if it is out of limit and a
correction is needed, it must be done before adjusting
toe.
• Check for loose of suspension control arms.
• Check for loose or missing stabilizer bar attachments.
• Consideration must be given to excess loads, such as
tool boxes. If this excess load is normally carried in
vehicle, it should remain in vehicle during alignment
checks.
• Consider condition of equipment being used to check
alignment and follow manufacturer’s instructions.
• Regardless of equipment used to check alignment,
vehicle must be placed on a level surface.
NOTE
To prevent possible incorrect reading of toe,
camber or caster, vehicle front and rear end
must be moved up and down a few times
before inspection.
Repair Instructions
Front Wheel Alignment Inspection and
Adjustment
S6RW0D2206001
Toe Inspection and Adjustment
Preparation for toe inspection and adjustment.
• Place vehicle in unloaded state on level surface.
• Set steering wheel in straight state.
• Check that inflation pressure of each tire is adjusted
properly and wheel is free from deflection.
• Check that each suspension part is free from bend,
dent, wear or damage in any other form.
• Check that ground clearance at the right and left is
just about the same.Inspection
Measure toe with toe-in gauge (1).
Toe should be within following specifications.
If toe is out of the specification, adjust toe properly.
To e
IN 1.0 ± 1.0 mm (0.0394 ± 0.0394 in.)
I2RH01220062-01
Page 445 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-8
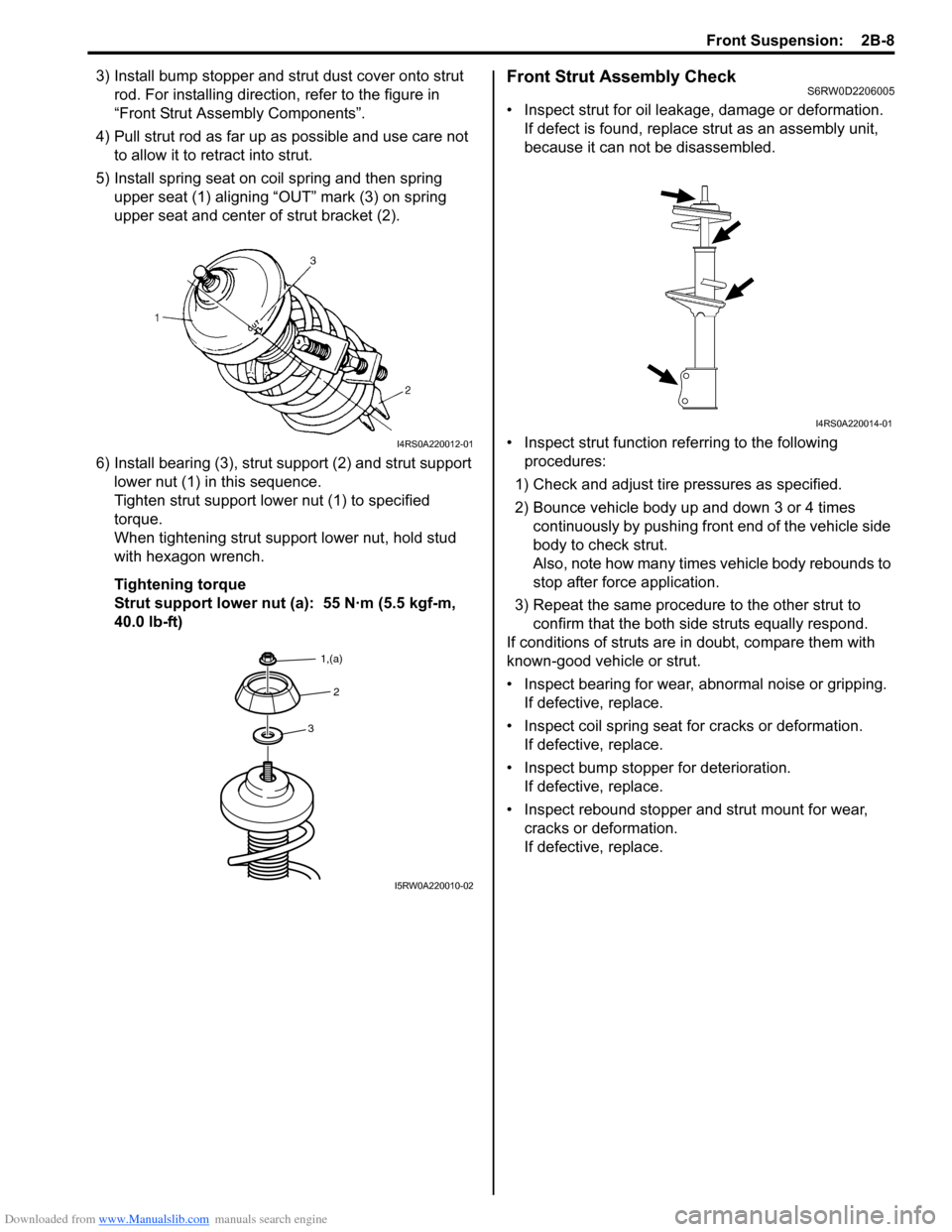
3) Install bump stopper and strut dust cover onto strut
rod. For installing direction, refer to the figure in
“Front Strut Assembly Components”.
4) Pull strut rod as far up as possible and use care not
to allow it to retract into strut.
5) Install spring seat on coil spring and then spring
upper seat (1) aligning “OUT” mark (3) on spring
upper seat and center of strut bracket (2).
6) Install bearing (3), strut support (2) and strut support
lower nut (1) in this sequence.
Tighten strut support lower nut (1) to specified
torque.
When tightening strut support lower nut, hold stud
with hexagon wrench.
Tightening torque
Strut support lower nut (a): 55 N·m (5.5 kgf-m,
40.0 lb-ft)Front Strut Assembly CheckS6RW0D2206005
• Inspect strut for oil leakage, damage or deformation.
If defect is found, replace strut as an assembly unit,
because it can not be disassembled.
• Inspect strut function referring to the following
procedures:
1) Check and adjust tire pressures as specified.
2) Bounce vehicle body up and down 3 or 4 times
continuously by pushing front end of the vehicle side
body to check strut.
Also, note how many times vehicle body rebounds to
stop after force application.
3) Repeat the same procedure to the other strut to
confirm that the both side struts equally respond.
If conditions of struts are in doubt, compare them with
known-good vehicle or strut.
• Inspect bearing for wear, abnormal noise or gripping.
If defective, replace.
• Inspect coil spring seat for cracks or deformation.
If defective, replace.
• Inspect bump stopper for deterioration.
If defective, replace.
• Inspect rebound stopper and strut mount for wear,
cracks or deformation.
If defective, replace.
I4RS0A220012-01
3
2
1,(a)
I5RW0A220010-02
I4RS0A220014-01
Page 453 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-16
Assembly
1) Front bushing
Press-fit front bushing (1) by using special tools and
press (2).
Special tool
(A): 09943–76310
(B): 09913–75821
CAUTION!
Be sure to use new bushing.
NOTE
• Before installing bushing, apply soap
water on its circumference to facilitate
bushing installation.
2) Press-fit bushing (1) so that dimensions “A” and “B”
in figure become equal.
Suspension Control Arm / Steering Knuckle
Check
S6RW0D2206011
Inspect for cracks, deformation or damage.
If defective, replace.
Suspension Control Arm Bushing CheckS6RW0D2206012
Inspect for damage, wear or deterioration.
If defective, replace.
Suspension Control Arm Joint CheckS6RW0D2206013
• Check smooth rotation of ball stud.
• Check damages of ball stud.
• Check damages of dust cover.
NOTE
Suspension control arm and arm joint cannot
be separated.
If there is any damage to either parts, control arm must
be replaced as a complete unit.
12
(A) (B)
I4RS0B220021-01
I4RS0A220033-01
I4RS0B220022-01
I4RS0B220023-01
Page 457 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-20
12) Install exhaust No.1, No.2 and center pipe referring
to “Exhaust System Components in Section 1K”.
13) Install wheel and tighten nut to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
14) Install air cleaner assembly referring to “Air Cleaner
Assembly Removal and Installation in Section 1D”.
15) Install hood referring to “Hood Removal and
Installation in Section 9J”.
16) Lower hoist and vehicle in unloaded condition,
tighten suspension control arm bolts to specified
torque.
Tightening torque
Suspension control arm bolt: 95 N·m (9.5 kgf-m,
69.0 lb-ft)
17) Connect negative (–) cable at battery.
18) Confirm front wheel alignment referring to “Front
Wheel Alignment Inspection and Adjustment”.
Front Suspension Frame CheckS6RW0D2206017
Inspect for cracks, deformation or damage.
If defective, replace.
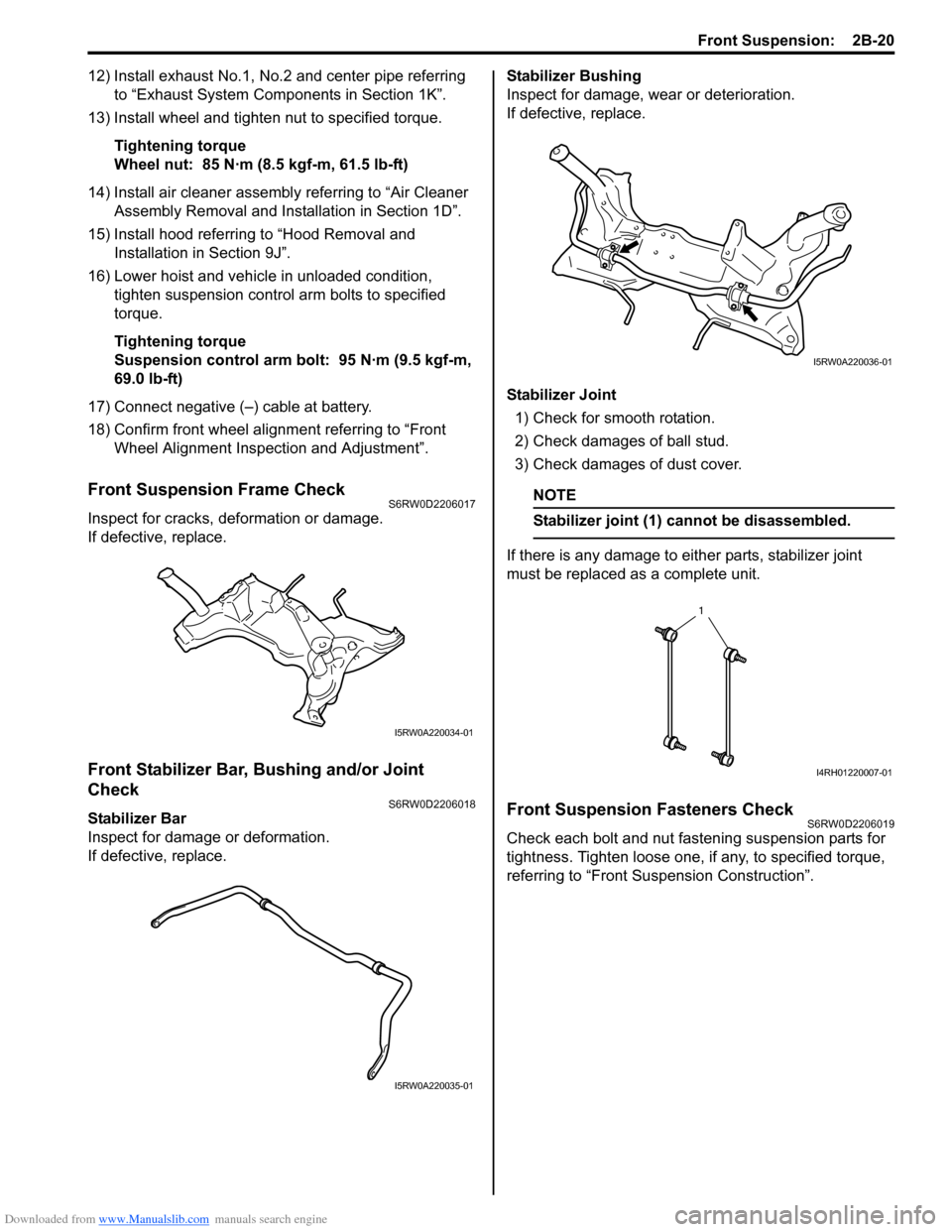
Front Stabilizer Bar, Bushing and/or Joint
Check
S6RW0D2206018
Stabilizer Bar
Inspect for damage or deformation.
If defective, replace.Stabilizer Bushing
Inspect for damage, wear or deterioration.
If defective, replace.
Stabilizer Joint
1) Check for smooth rotation.
2) Check damages of ball stud.
3) Check damages of dust cover.
NOTE
Stabilizer joint (1) cannot be disassembled.
If there is any damage to either parts, stabilizer joint
must be replaced as a complete unit.
Front Suspension Fasteners CheckS6RW0D2206019
Check each bolt and nut fastening suspension parts for
tightness. Tighten loose one, if any, to specified torque,
referring to “Front Suspension Construction”.
I5RW0A220034-01
I5RW0A220035-01
I5RW0A220036-01
1
I4RH01220007-01
Page 463 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Suspension: 2C-4
Rear Coil Spring Removal and InstallationS6RW0D2306005
CAUTION!
Removal and Installation both coil springs
(right and left) at the same time to avoid rear
axle twisting and other damage.
Removal
1) Hoist vehicle and remove rear wheels.
2) Dismount rear differential (4WD model) referring to
“Rear Differential Dismounting and Remounting in
Section 3B”.
3) Remove rear fender lining (1) and then loosen rear
axle bolt (2) a little.
CAUTION!
Do not reuse rear axle bolt. Otherwise, bolt
may loosen.
4) Support both ends of rear axle (1) by using two floor
jacks (2).5) Detach each lower end (2) of shock absorbers (1)
(right and left) from rear axle.
6) Lower rear axle gradually as far down as the coil
spring can be removed.
CAUTION!
Be careful not to lower rear axle down too
much.
It may cause damage to brake flexible hose,
wheel speed sensor lead wire and parking
brake cable.
7) Remove coil spring (3).
8) Remove spring upper seat (1) from vehicle body and
lower seat (2) from rear axle.
2
1
I5RW0A230008-01
1
2
2
I5RW0A230009-01
1
2
3
I5RW0A230010-01
1
2
I5RW0A230011-01
Page 470 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-1 Wheels and Tires:
Suspension
Wheels and Tires
General Description
Tires DescriptionS6RW0D2401001
The tire is of tubeless type. The tire is designed to
operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load
capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation
pressures.
Correct tire pressures and driving habits have an
important influence on tire life. Heavy cornering,
excessively rapid acceleration, and unnecessary sharp
braking increase tire wear.
Tire Placard
The “Tire Placard” is located on the left or right door lock
pillar and should be referred to tire information.
The placard lists the maximum load, tire size and cold
tire pressure where applicable.
NOTE
Whether rim size and/or maximum load are
listed or not depends on regulations of each
country.
Inflation of Tires
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully
calculated to give a satisfactory ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for 3
hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should be
checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the
specifications on the “Tire Placard” located on the left or
right door lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure to increase when the tires
become hot during driving.
Do not bleed or reduce tire pressure after driving.
Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure”.
Higher than recommended pressure can cause:
• Hard ride
• Tire bruising or carcass damage
• Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal pressure on same axle can cause:
• Uneven braking
• Steering lead
• Reduced handling
• Swerve on accelerationLower than recommended pressure can cause:
• Tire squeal on turns
• Hard Steering
• Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
• Tire rim bruises and rupture
• Tire cord breakage
• High tire temperature
• Reduced handling
• High fuel consumption
Matched Tires and Wheels (Steel Type)
Tires and wheels are match mounted at the assembly
plant.
This means that the radially stiffest part of the tire, or
“high spot”, is matched to the smallest radius or “low
spot” of the wheel.
This is done to provide the smoothest possible ride.
The “high spot” of the tire is originally marked by paint
dot (1) on the outboard sidewall. This paint dot will
eventually wash off the tire.
The “low spot” of the wheel is originally marked by paint
dot (2) on the wheel rim-flange. Properly assembled, the
wheel rims’ paint dot should be aligned with the tires’
paint dot as shown in figure.
Whenever a tire is dismounted from its wheel, it should
be remounted so that the tire and wheel are matched. If
the tire’s paint dot cannot be located, a line should be
scribed on the tire and wheel before dismounting to
assure that it is remounted in the same position.
I2RH01240001-01
Page 472 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-3 Wheels and Tires:
Irregular and/or Premature Wear DescriptionS6RW0D2401003
Irregular and premature wear has many causes. Some
of them are as follows: incorrect inflation pressures, lack
of tire rotation, driving habits, improper alignment.
If the following conditions are noted, tire rotation is
necessary:
• Front tire wear is different from rear’s.
• Uneven wear exists across tread of any tires.
• Both sides of front tire wears are not even.
• Both sides of rear tire wears are not even.
• There is cupping, flat spotting, etc.
A wheel alignment check is necessary if following
conditions are noted:
• Both sides of front tire wears are not even.
• Wear is uneven across the tread of any front tire.
• Front tire treads have scuffed appearance with
“feather” edges on one side of tread ribs or blocks.
Wear Indicators DescriptionS6RW0D2401004
Original equipment tires have built-in tread wear
indicators (1) to show when they need replacement.
These indicators (1) will appear as 12 mm (0.47 in.) wide
bands when the tire tread depth becomes 1.6 mm (0.063
in.).
When the indicators (1) appear in 3 or more grooves at 6
locations, tire replacement is recommended.
Radial Tire Waddle DescriptionS6RW0D2401005
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear
of the vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being
straight within the tire. It is most noticeable at a low
speed, 8 to 48 kph (5 to 30 mph).
It is possible to locate the faulty tire by road testing the
vehicle. If it is on the rear, the rear end of the vehicle
shakes from side to side or “waddles”. To the driver in
the seat, it feels as though someone is pushing on the
side of vehicle.
If the faulty tire is on the front, waddling is more visual.
The front sheet metal appears to be moving back and
forth and the driver feels as though he is at the pivot
point in vehicle.
Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using Tire Problem
Detector (TPD) and following the equipment
manufacture’s recommendations.
If TPD is not available, an alternative method of
substituting known-good tire / wheel assemblies can be
used as follows, although it takes a longer time.
1) Ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear
waddles.
2) Install tires and wheels that are known to be good
(on similar vehicle) in place of those on waddling end
of vehicle. If waddling end cannot be identified,
substitute rear ones.
3) Road test again. If improvement is noted, reinstall
originals one at a time till waddle causal tire is found.
If no improvement is noted, install known-good tires
in place of all four. Then reinstall originals in the
same manner.
[A]: Hard Cornering, under inflation or lack of tire rotation
[B]: Incorrect wheel alignment, tire construction not uniform or wheel
heavy acceleration
I3RH0A240002-01
I2RH01240005-01
I2RH01240006-01