2006 SUZUKI SX4 check engine light
[x] Cancel search: check engine lightPage 1000 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-60 Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type
DTC B1504: Sunload Sensor Circuit MalfunctionS6RW0D7224012
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
NOTE
When DTC B1502, B1503, B1511 and B1512 are indicated together, it is possible that sensor ground
circuit is open.
3Evaporator temperature sensor reference voltage check
1) Connect connector to HVAC control module with ignition
switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
3) Measure voltage between signal terminal and ground
terminal of evaporator temperature sensor connector.
Is voltage 4.5 – 5.5 V?Go to Step 4. Substitute a known-
good HVAC control
module and recheck.
4Evaporator temperature sensor check
1) Check evaporator temperature sensor for performance
referring to “Evaporator Temperature Sensor
Inspection”.
Is it in good condition?Substitute a known-
good HVAC control
module and recheck.Replace evaporator
temperature sensor. Step Action Yes No
G20
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 24 23 22 25 26 27 28 29 30
PNK
ORNORN
G20-25
G20-24
2
[S]
[G]15V
3
I7RW01722006-01
[S]: Sunload sensor signal circuit 1. HVAC control module 3. To other sensors
[G]: Sunload sensor ground circuit 2. Sunload sensor
DTC Detecting Condition Trouble Area
• Sunload sensor signal voltage is higher than or lower than specified value
for specified time continuously.
• Without sunlight• Sunload sensor circuit
• Sunload sensor
• HVAC control module
Page 1016 of 1556
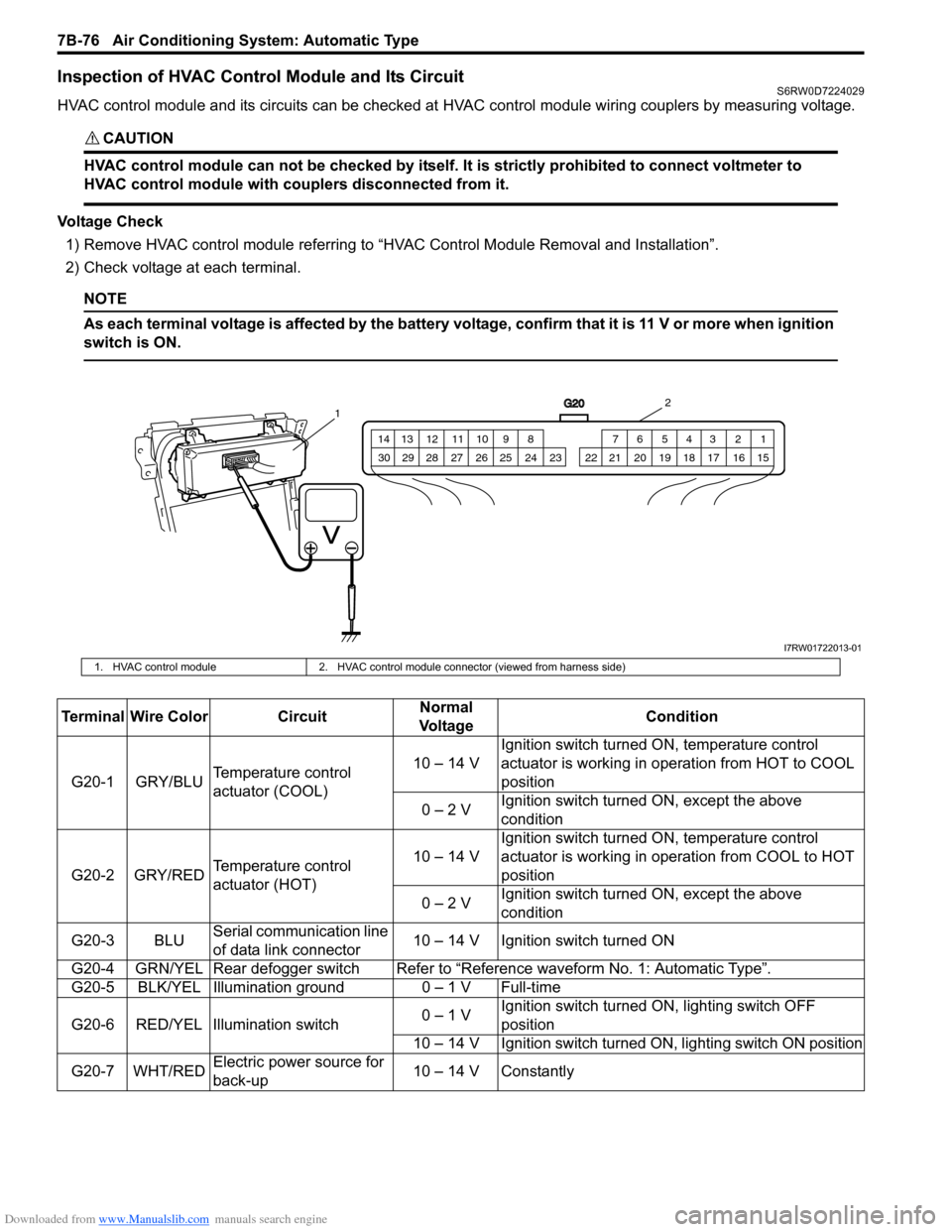
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-76 Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type
Inspection of HVAC Control Module and Its CircuitS6RW0D7224029
HVAC control module and its circuits can be checked at HVAC control module wiring couplers by measuring voltage.
CAUTION!
HVAC control module can not be checked by itself. It is strictly prohibited to connect voltmeter to
HVAC control module with couplers disconnected from it.
Voltage Check
1) Remove HVAC control module referring to “HVAC Control Module Removal and Installation”.
2) Check voltage at each terminal.
NOTE
As each terminal voltage is affected by the battery voltage, confirm that it is 11 V or more when ignition
switch is ON.
G20
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 24 23 22 25 26 27 28 29 30
12
I7RW01722013-01
1. HVAC control module 2. HVAC control module connector (viewed from harness side)
Terminal Wire Color CircuitNormal
Vo l ta g eCondition
G20-1 GRY/BLUTemperature control
actuator (COOL)10 – 14 VIgnition switch turned ON, temperature control
actuator is working in operation from HOT to COOL
position
0 – 2 VIgnition switch turned ON, except the above
condition
G20-2 GRY/REDTemperature control
actuator (HOT)10 – 14 VIgnition switch turned ON, temperature control
actuator is working in operation from COOL to HOT
position
0 – 2 VIgnition switch turned ON, except the above
condition
G20-3 BLUSerial communication line
of data link connector10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON
G20-4 GRN/YEL Rear defogger switchRefer to “Reference waveform No. 1: Automatic Type”.
G20-5 BLK/YEL Illumination ground 0 – 1 V Full-time
G20-6 RED/YEL Illumination switch0 – 1 VIgnition switch turned ON, lighting switch OFF
position
10 – 14 V Ignition switch turned ON, lighting switch ON position
G20-7 WHT/REDElectric power source for
back-up10 – 14 V Constantly
Page 1025 of 1556
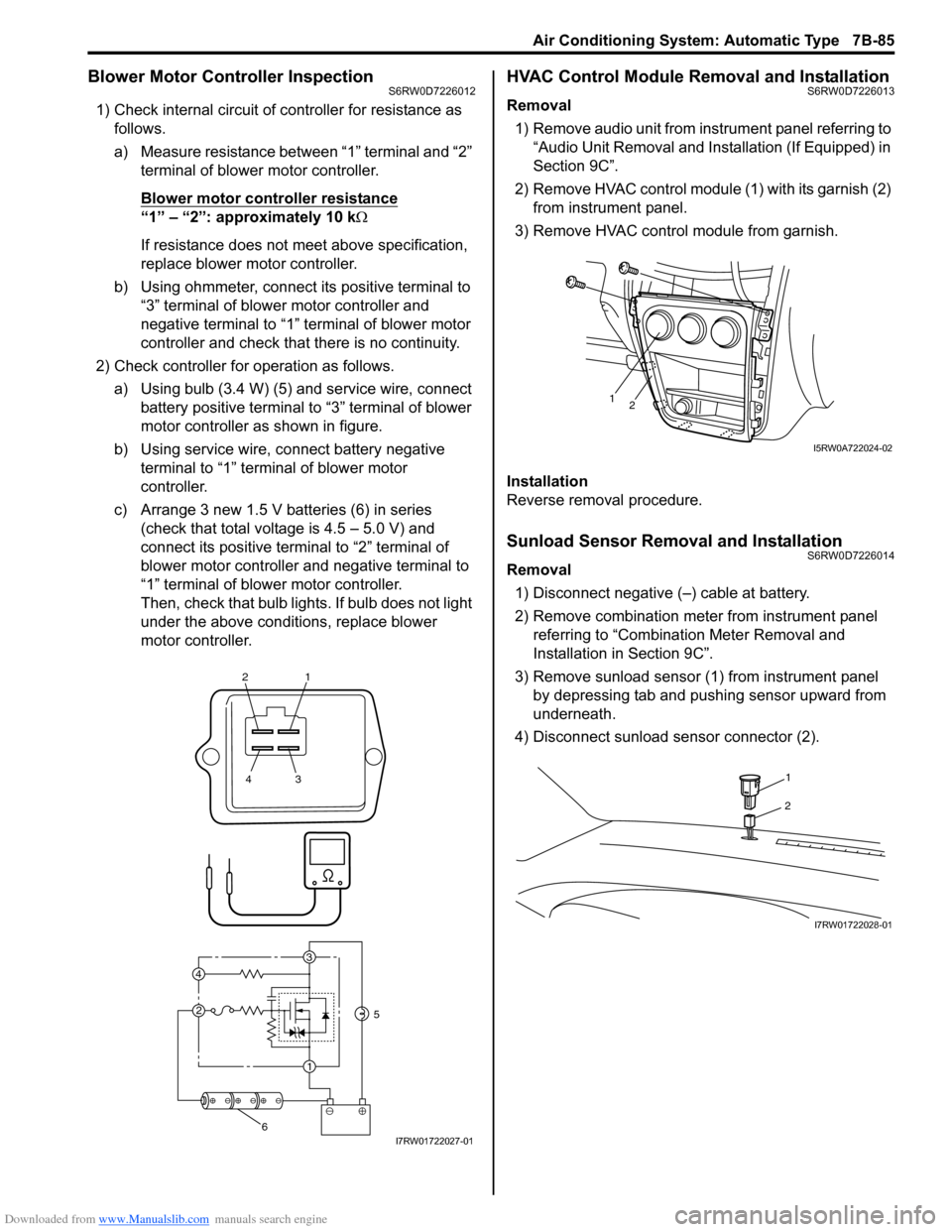
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type 7B-85
Blower Motor Controller InspectionS6RW0D7226012
1) Check internal circuit of controller for resistance as
follows.
a) Measure resistance between “1” terminal and “2”
terminal of blower motor controller.
Blower motor controller resistance
“1” – “2”: approximately 10 kΩ
If resistance does not meet above specification,
replace blower motor controller.
b) Using ohmmeter, connect its positive terminal to
“3” terminal of blower motor controller and
negative terminal to “1” terminal of blower motor
controller and check that there is no continuity.
2) Check controller for operation as follows.
a) Using bulb (3.4 W) (5) and service wire, connect
battery positive terminal to “3” terminal of blower
motor controller as shown in figure.
b) Using service wire, connect battery negative
terminal to “1” terminal of blower motor
controller.
c) Arrange 3 new 1.5 V batteries (6) in series
(check that total voltage is 4.5 – 5.0 V) and
connect its positive terminal to “2” terminal of
blower motor controller and negative terminal to
“1” terminal of blower motor controller.
Then, check that bulb lights. If bulb does not light
under the above conditions, replace blower
motor controller.
HVAC Control Module Removal and InstallationS6RW0D7226013
Removal
1) Remove audio unit from instrument panel referring to
“Audio Unit Removal and Installation (If Equipped) in
Section 9C”.
2) Remove HVAC control module (1) with its garnish (2)
from instrument panel.
3) Remove HVAC control module from garnish.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure.
Sunload Sensor Removal and InstallationS6RW0D7226014
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove combination meter from instrument panel
referring to “Combination Meter Removal and
Installation in Section 9C”.
3) Remove sunload sensor (1) from instrument panel
by depressing tab and pushing sensor upward from
underneath.
4) Disconnect sunload sensor connector (2).
21
43
3
1 2 4
5
6I7RW01722027-01
12
I5RW0A722024-02
1
2
I7RW01722028-01
Page 1026 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7B-86 Air Conditioning System: Automatic Type
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following
instructions.
• Install sunload sensor (1) to instrument panel fitting
tab (2) of sunload sensor into the groove (3) of
instrument panel as shown in figure.
Sunload Sensor InspectionS6RW0D7226015
1) Light over sunload sensor vertically with an
incandescent light of approximately 100 W. The
distance between sunload sensor and light should
be approximately 100 mm (3.94 in.).
2) Measure voltage between terminals “a” and “b” of
sunload sensor as shown in figure.
If check result is not satisfactory, replace sunload
sensor with new one.
Sunload sensor voltage specification
“a” – “b”: Approx. 0.38 – 0.42 V
Outside Air Temperature Sensor Removal and
Installation
S6RW0D7226016
Refer to “Outside Air Temperature Sensor Removal and
Installation (If Equipped) in Section 9C”.
Outside Air Temperature Sensor InspectionS6RW0D7226017
Refer to “Outside Air Temperature Sensor Inspection (If
Equipped) in Section 9C”.
Inside Air Temperature Sensor Removal and
Installation
S6RW0D7226018
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove audio unit from instrument panel referring to
“Audio Unit Removal and Installation (If Equipped) in
Section 9C”.
3) Remove combination meter from instrument panel
referring to “Combination Meter Removal and
Installation in Section 9C”.
4) Remove connector (3) and aspirator hose (1) from
inside air temperature sensor (2).
5) Remove inside air temperature sensor (2) from
instrument panel by removing screw (4).
Installation
Reverse removal procedure.
Inside Air Temperature Sensor InspectionS6RW0D7226019
Measure resistance between each connector terminal
with an ohmmeter.
If resistance is incorrect, replace inside air temperature
sensor with new one.
Inside air temperature sensor resistance
2.2 ± 0.07 kΩ at 25 °C (77 °F)
F: Vehicle forward
2
F
1
3
I7RW01722029-01
“b” “a”I5JB0A720053-01
1
23 4
I7RW01722031-01
I7RW01722030-01
Page 1029 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Table of Contents 8- i
8
Section 8
CONTENTS
Restraint
Precautions ................................................. 8-1
Precautions............................................................. 8-1
Precautions on Restraint ....................................... 8-1
Seat Belts ................................................. 8A-1
Precautions........................................................... 8A-1
Precautions on Service and Diagnosis of Seat
Belt .................................................................... 8A-1
General Description ............................................. 8A-2
Seat Belt Construction ........................................ 8A-2
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............ 8A-3
Repair and Inspection Required after
Accident ............................................................ 8A-3
Repair Instructions .............................................. 8A-4
Front Seat Belt Components ............................... 8A-4
Front Seat Belt Removal and Installation ............ 8A-5
Front Seat Belt Inspection................................... 8A-6
Rear Seat Belt Components ............................... 8A-7
Rear Seat Belt Removal and Installation ............ 8A-8
Rear Seat Belt Inspection ................................... 8A-8
Specifications....................................................... 8A-8
Tightening Torque Specifications ........................ 8A-8
Air Bag System ........................................ 8B-1
Precautions........................................................... 8B-1
Precautions on Service and Diagnosis of Air
Bag System....................................................... 8B-1
Precautions on Handling and Storage of Air
Bag System Components ................................. 8B-1
Precautions on Disposal of Air Bag and Seat
Belt Pretensioner .............................................. 8B-5
General Description ............................................. 8B-5
Air Bag System Construction .............................. 8B-5
Air Bag System Block Diagram ........................... 8B-6
Air Bag System Input / Output Table .................. 8B-7
Schematic and Routing Diagram ........................ 8B-8
Air Bag System Wiring Circuit Diagram .............. 8B-8
Component Location ......................................... 8B-11
Air Bag System Components, Wiring and
Connectors Location ....................................... 8B-11
Diagnostic Information and Procedures .......... 8B-12
Air Bag Diagnostic System Check .................... 8B-12
Air Bag Diagnostic System Check Flow ............ 8B-13
DTC Table ......................................................... 8B-14DTC Check........................................................ 8B-18
DTC Clearance ................................................. 8B-18
Scan Tool Data ................................................. 8B-18
“AIR BAG” Warning Light Comes ON Steady ... 8B-19
“AIR BAG” Warning Light Does Not Come ON .. 8B-22
Serial Data Link Circuit Check .......................... 8B-23
DTC B1013: SDM Internal Failure .................... 8B-25
DTC B1014: “AIR BAG” Warning Light Circuit .. 8B-26
DTC B1016: Power Supply Voltage too High.... 8B-26
DTC B1017: Power Supply Voltage too Low .... 8B-27
DTC B1021: Front Air Bag Deployment
Record............................................................. 8B-28
DTC B1024 / B1025: Side Air-Bag
Deployment Record ........................................ 8B-29
DTC B1026: Seat Belt Pretensioner
Activation Record ............................................ 8B-29
DTC B1027: Number of Deployment Times
Exceeded Limit................................................ 8B-30
DTC B1031: Driver Air Bag Circuit High
Resistance ...................................................... 8B-31
DTC B1032: Driver Air Bag Circuit Low
Resistance ...................................................... 8B-33
DTC B1033: Driver Air Bag Circuit Shorted to
Ground ............................................................ 8B-35
DTC B1034: Driver Air Bag Circuit Shorted to
Power Supply .................................................. 8B-37
DTC B1041: Passenger Air Bag Circuit High
Resistance ...................................................... 8B-40
DTC B1042: Passenger Air Bag Circuit Low
Resistance ...................................................... 8B-43
DTC B1043: Passenger Air Bag Circuit
Shorted to Ground........................................... 8B-45
DTC B1044: Passenger Air Bag Circuit
Shorted to Power Supply ................................ 8B-46
DTC B1051 / B1055: Seat Belt Pretensioner
Circuit High Resistance ................................... 8B-48
DTC B1052 / B1056: Seat Belt Pretensioner
Circuit Low Resistance.................................... 8B-51
DTC B1053 / B1057: Seat Belt Pretensioner
Shorted to Ground........................................... 8B-52
DTC B1054 / B1058: Seat Belt Pretensioner
Circuit Shorted to Power Supply ..................... 8B-54
DTC B1061 / B1065: Side-Air Bag Circuit
High Resistance .............................................. 8B-55
Page 1034 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 8A-3 Seat Belts:
Seat Belt with ELR
The seat belt with emergency locking retractor (ELR) is
designed so that it locks immediately (to prevent the
webbing from being pulled out of the retractor any
further) when any of the following items is detected as
exceeding each set value;
• Speed at which the webbing is pulled out of the
retractor.
• Acceleration or deceleration of the vehicle speed.
• Inclination.
Seat Belt with A-ELR
The automatic and emergency locking retractor (A-ELR)
works as an Emergency Locking Retractor (ELR) till its
webbing is pulled all the way out and then on as an
Automatic Locking Retractor (ALR) till it is retracted fully.
ALR: Automatically locks when the webbing is pulled out
from the retractor and allowed to retract even a little.
Then the webbing can not be pulled out any further,
unless it is wound all the way back into the retractor,
which releases the lock and allows the webbing to be
pulled out.
Seat Belt with ELR and Pretensioner
The seat belt with ELR and a pretensioner has a
pretensioner mechanism which operates in linkage with
the air bag in addition to the described ELR.The pretensioner is incorporated in retractor and
controlled by SDM as one of air bag system
components. It will be activated at the same time as the
driver and passenger air bag module when an impact at
the front of vehicle exceeds the specified value.
When servicing seat belt (retractor) with pretensioner, be
sure to observe all WARNINGS and CAUTIONS and
“Precautions on Service and Diagnosis of Air Bag
System in Section 8B”.
CAUTION!
Do not reuse the seat belt pretensioner
(retractor) that has activated. Replace it with
a new seat belt and buckle together as a set.
For checking procedure of its activation,
refer to “Repair and Inspection Required after
Accident in Section 8B”.
Seat Belt Remainder
When driver’s seat belt is unfastened (under the
following conditions), seat belt reminder light inform that
driver’s seat belt is unfastened. Seat belt reminder light
located in combination meter located inside BCM
operate as follows:
• Seat belt reminder light comes on when driver’s seat
belt is unfastened while ignition key switch is at ON
position.
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Repair and Inspection Required after AccidentS6RW0D8104001
After an accident, whether the seat belt pretensioner has been activated or not, be sure to perform checks and repairs
described on “Repair and Inspection Required after Accident in Section 8B”.
Page 1040 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 8B-1 Air Bag System:
Restraint
Air Bag System
Precautions
Precautions on Service and Diagnosis of Air
Bag System
S6RW0D8200004
WARNING!
• If the air bag system and another vehicle
system both need repair, SUZUKI
recommends that the air bag system be
repaired first, to help avoid unintended air
bag system activation.
• Do not modify the steering wheel,
dashboard, both front seat or any other on
or around air bag system components.
Modifications can adversely affect air bag
system performance and lead to injury.
• Be sure to follow the procedures described
in this section. Failure to follow
procedures could result in possible air bag
system activation, personal injury or
unneeded air bag system repairs.
• WARNING / CAUTION labels are attached on each
part of air bag system components (SDM, air bag
(inflator) modules and seat belt pretensioners). Be
sure to follow the instructions.
• Many of service procedures require disconnection of
“A/B” fuse and air bag (inflator) module(s) (driver
module, passenger module, side modules and curtain
modules) from initiator circuit to avoid an accidental
deployment.
• Do not apply power to the air bag system unless all
components are connected or a diagnostic flow
requests it, as this will set a DTC.
• The “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check” must be the
starting point of any air bag diagnostics. The “Air Bag
Diagnostic System Check” will verify proper “AIR
BAG” warning light operation and will lead you to the
correct flow to diagnose any air bag malfunctions.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis, and incorrect
parts replacements.
• Never use air bag component parts from another
vehicle.
• If the vehicle will be exposed to temperatures over 93
°C (200 °F) (for example, during a paint baking
process), remove the air bag system components
beforehand to avoid component damage or
unintended system activation.• When handling the air bag (inflator) modules (driver
module, passenger module, side modules and curtain
modules), seat belt pretensioners (driver module and
passenger module), SDM, forward impact-sensor or
side impact-sensor be careful not to drop it or apply
an impact to it. If an excessive impact was applied
(e.g., SDM, forward impact-sensor are dropped, air
bag (inflator) module is dropped from a height of 90
cm (3 ft) or more, seat belt pretensioner (retractor
assembly) is dropped from a height of 30 cm (1 ft) or
more), never attempt disassembly or repair but
replace it with a new one.
• When using electric welding, be sure to disconnect air
bag (inflator) module connectors (driver module,
passenger module, side modules and curtain
modules) and seat belt pretensioner connectors
(driver module and passenger module) respectively.
• When applying paint around the air bag system
related parts, use care so that the harness or
connector will not be exposed to the paint mist.
• Never expose air bag system component parts
directly to hot air (drying or baking the vehicle after
painting) or flames.
WARNING!
When performing service on or around air
bag system components or air bag wiring,
follow the procedures listed in “Disabling Air
Bag System” to temporarily disable the air
bag system.
Failure to follow procedures could result in
possible air bag system activation, personal
injury or unneeded air bag system repairs.
Precautions on Handling and Storage of Air Bag
System Components
S6RW0D8200002
SDM
WARNING!
Never power up air bag system when SDM is
not rigidly attached to the vehicle. Otherwise,
personal injury may result.
CAUTION!
After detecting one time of such collision as
to meet deployment conditions, SDM must
not be used. Refer to “Air Bag Diagnostic
System Check” when checking SDM.
Page 1051 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Air Bag System: 8B-12
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Air Bag Diagnostic System CheckS6RW0D8204001
WARNING!
To avoid deployment when troubleshooting
the air bag system, do not use electrical test
equipment such as a battery powered or AC
powered voltmeter, ohmmeter, etc., or any
type of electrical equipment other than that
specified in this manual. Do not use a non-
powered probe type tester.
Instructions in this manual must be followed
carefully, otherwise personal injury may
result.
CAUTION!
• The order in which DTCs are diagnosed is
very important. Failure to diagnose the
DTCs in the order specified may result in
extended diagnostic time, incorrect
diagnosis and incorrect parts replacement.
• When measurement of resistance or
voltage is required in the flow, use a tester
along with a correct terminal adapter from
special tool (Connector test adapter kit).
• When a check for proper connection is
required, refer to “Inspection of
Intermittent and Poor Connections”.
• If an open circuit in the air bag wire
harness damaged, connector or terminal is
found, replace the wire harness,
connectors and terminals as an assembly.
The diagnostic procedures used are designed to find
and repair air bag system malfunctions.
To get the best results, it is important to use the
diagnostic flow and follow the sequence in the following.
1) Perform the “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check
Flow”.
(The “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check Flow” must
be the starting point of any air bag system diagnosis.
The “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check Flow” checks
for proper “AIR BAG” warning light operation through
“AIR BAG” warning light and whether air bag DTCs
exist.)
2) Refer to the proper diagnostic flow as directed by the
“Air Bag Diagnostic System Check Flow”.
(The “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check Flow” will
lead you to the correct flow to diagnose any air bag
system malfunctions. Bypassing these procedures
may result in extended diagnostic time, incorrect
diagnosis and incorrect parts replacement.)
3) Repeat the “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check Flow”
after any repair or diagnostic procedures have been
performed.
(Performing the “Air Bag Diagnostic System Check
Flow” after all repair or diagnostic procedures will
ensure that the repair has been made correctly and
that no other malfunctions exist.)
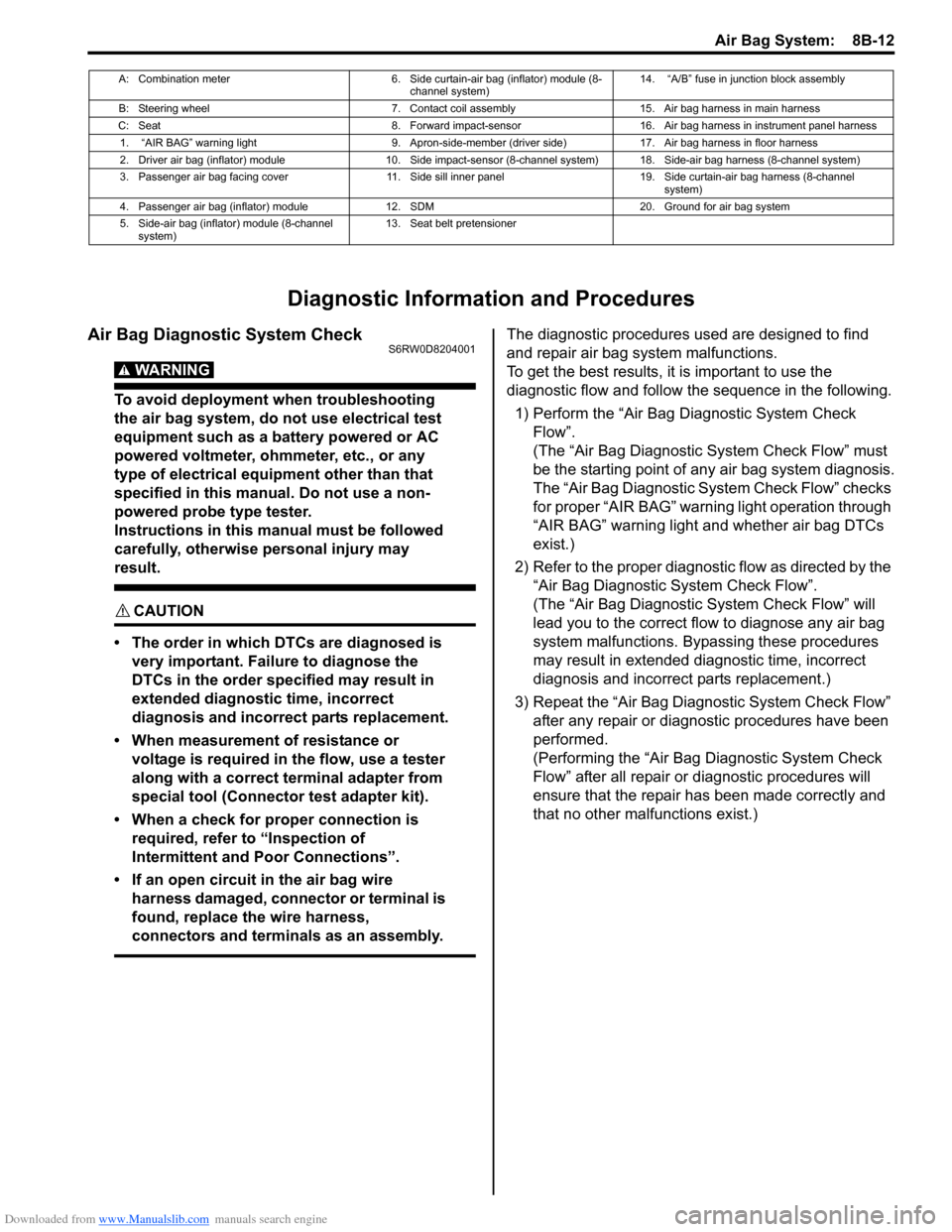
A: Combination meter 6. Side curtain-air bag (inflator) module (8-
channel system)14. “A/B” fuse in junction block assembly
B: Steering wheel 7. Contact coil assembly 15. Air bag harness in main harness
C: Seat 8. Forward impact-sensor 16. Air bag harness in instrument panel harness
1. “AIR BAG” warning light 9. Apron-side-member (driver side) 17. Air bag harness in floor harness
2. Driver air bag (inflator) module 10. Side impact-sensor (8-channel system) 18. Side-air bag harness (8-channel system)
3. Passenger air bag facing cover 11. Side sill inner panel 19. Side curtain-air bag harness (8-channel
system)
4. Passenger air bag (inflator) module 12. SDM 20. Ground for air bag system
5. Side-air bag (inflator) module (8-channel
system)13. Seat belt pretensioner