2005 SUZUKI SWIFT Cord inspection
[x] Cancel search: Cord inspectionPage 588 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-14 Electronic Stability Program:
Step 2: Driving Test
Test the vehicle at 40 km/h for more than a minute including left and right turns and check if any trouble symptom
(such as ESP ® warning lamp and/or ABS warning lamp) exists.
If the malfunction DTC is confirmed at ignition switch ON, proceed to Step 3.
If the malfunction DTC is not confirmed at ignition switch ON, proceed to Step 6.
Step 3: DTC Check
Recheck DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Step 4: ESP ® Check
According to ESP ® Check for the DTC confirmation in Step 3, locate the cause of the trouble, namely in a sensor,
switch, wire harness, connector, actuator assembly or other part and repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 5: Brakes Diagnosis
Check the parts or system suspected as a possible cause referring to “Brakes Symptom Diagnosis in Section 4A” and
based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle (symptom obtain ed through Steps 1 and 2 and repair or replace faulty
parts, if any).
Step 6: Intermittent Problem Check
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection in Section 00” and related circuit of trouble code recorded in Step 1 to 3.
Step 7: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the ESP ® is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has been
repaired is related to the malfunction DTC, clear the DTC once referrin g to “DTC Clearance” and perform test driving
and confirm that no DTC is indicated.
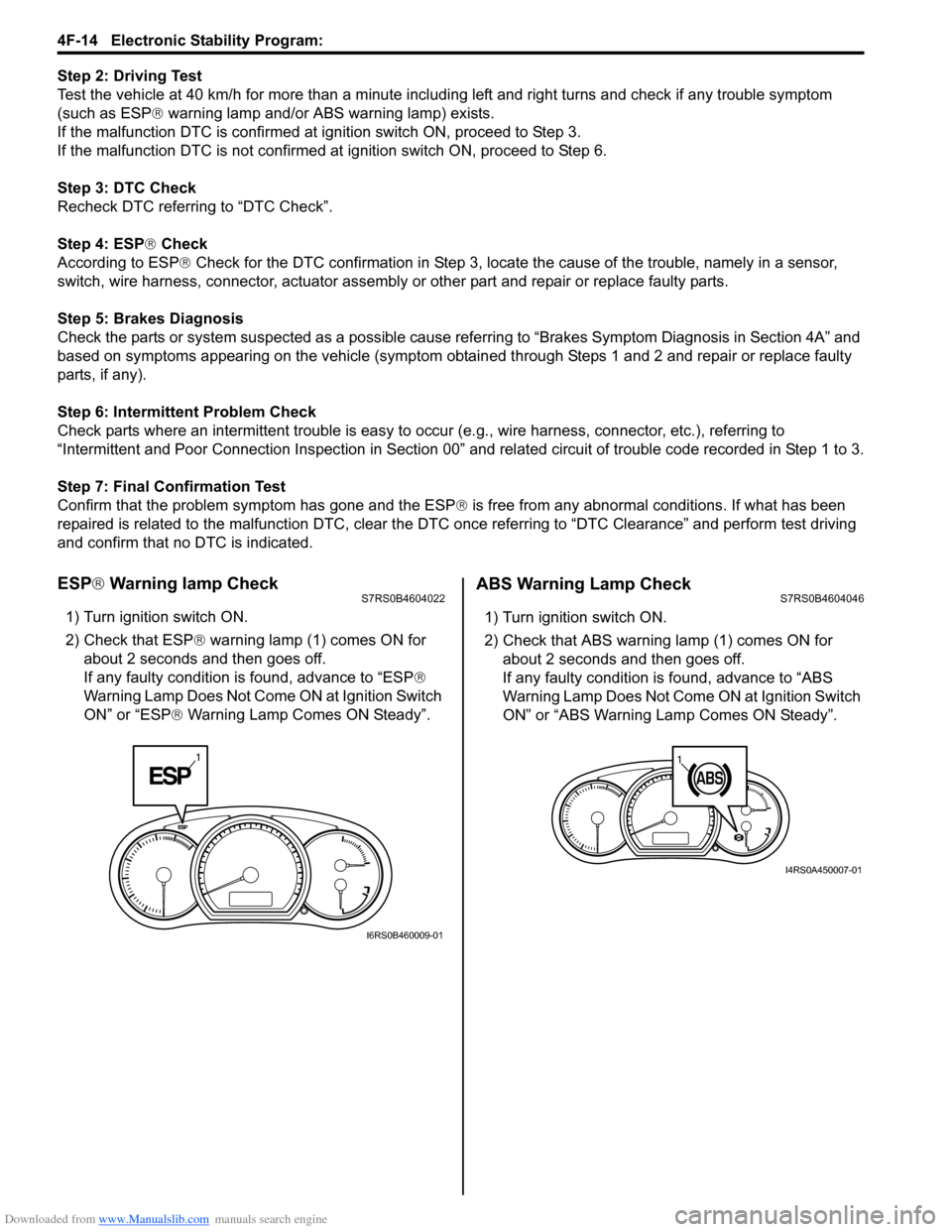
ESP ® Warning lamp CheckS7RS0B4604022
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check that ESP ® warning lamp (1) comes ON for
about 2 seconds and then goes off.
If any faulty condition is found, advance to “ESP ®
Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch
ON” or “ESP ® Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady”.
ABS Warning Lamp CheckS7RS0B4604046
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check that ABS warning lamp (1) comes ON for
about 2 seconds and then goes off.
If any faulty condition is found, advance to “ABS
Warning Lamp Does Not Come ON at Ignition Switch
ON” or “ABS Warning Lamp Comes ON Steady”.
1
I6RS0B460009-01
11
I4RS0A450007-01
Page 652 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-8 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
Brake Interlock System ConstructionS7RS0B5101004
Shift Lock Solenoid Control
This system consists of shift lock solenoid control
system and interlock cable control system.
The shift lock solenoid cont rol system is so designed
that the select lever can not be shifted from “P” range
position unless ignition switch is turned to “ON” or “ACC”
position and the brake pedal is depressed.
And interlock cable control system is so designed that
select lever cannot be shifted from “P” range position
unless ignition switch is turned to “ACC” or “ON”
position. Also, ignition key cannot be pulled out of key
slot unless select le ver is in “P” range.
Shift Lock Solenoid Manual Release
When push down shift lock solenoid valve release button
(1), select lever can be moved from “P” range position to
another range even without depressing the brake pedal.
(To shift select lever from “P” range to any other position,
turn ignition switch to ACC or ON position.)
A/T Diagnosis General DescriptionS7RS0B5101005
This vehicle is equipped with an electronic transaxle
control system, which controls the automatic shift up and
shift down timing, TCC operation, etc. suitably to vehicle
driving conditions.
TCM has an On-Board Diagnosis System which detects
a malfunction in this system.
When diagnosing a trouble in transaxle including this
system, be sure to have full understanding of the outline
of “On-Board Diagnostic System Description” and each
item in “Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute
diagnosis according to “A/T System Check” to obtain
correct result smoothly.
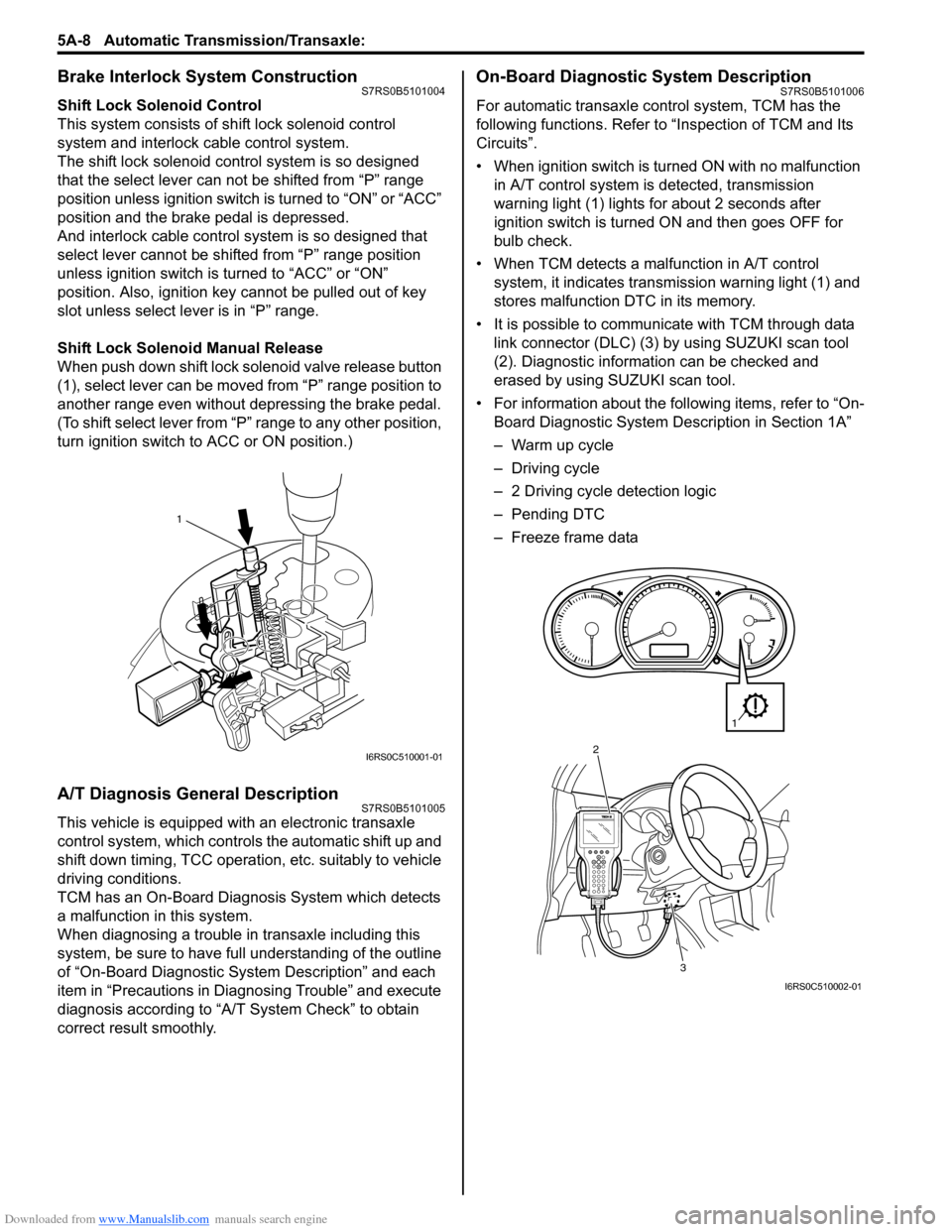
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B5101006
For automatic transaxle co ntrol system, TCM has the
following functions. Refer to “Inspection of TCM and Its
Circuits”.
• When ignition switch is turned ON with no malfunction in A/T control system is detected, transmission
warning light (1) lights for about 2 seconds after
ignition switch is turned ON and then goes OFF for
bulb check.
• When TCM detects a malfunction in A/T control system, it indicates transmission warning light (1) and
stores malfunction DTC in its memory.
• It is possible to communicate with TCM through data link connector (DLC) (3) by using SUZUKI scan tool
(2). Diagnostic information can be checked and
erased by using SUZUKI scan tool.
• For information about the following items, refer to “On- Board Diagnostic System De scription in Section 1A”
– Warm up cycle
– Driving cycle
– 2 Driving cycle detection logic
– Pending DTC
– Freeze frame data
1
I6RS0C510001-01
3
2
1
I6RS0C510002-01
Page 659 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-15
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
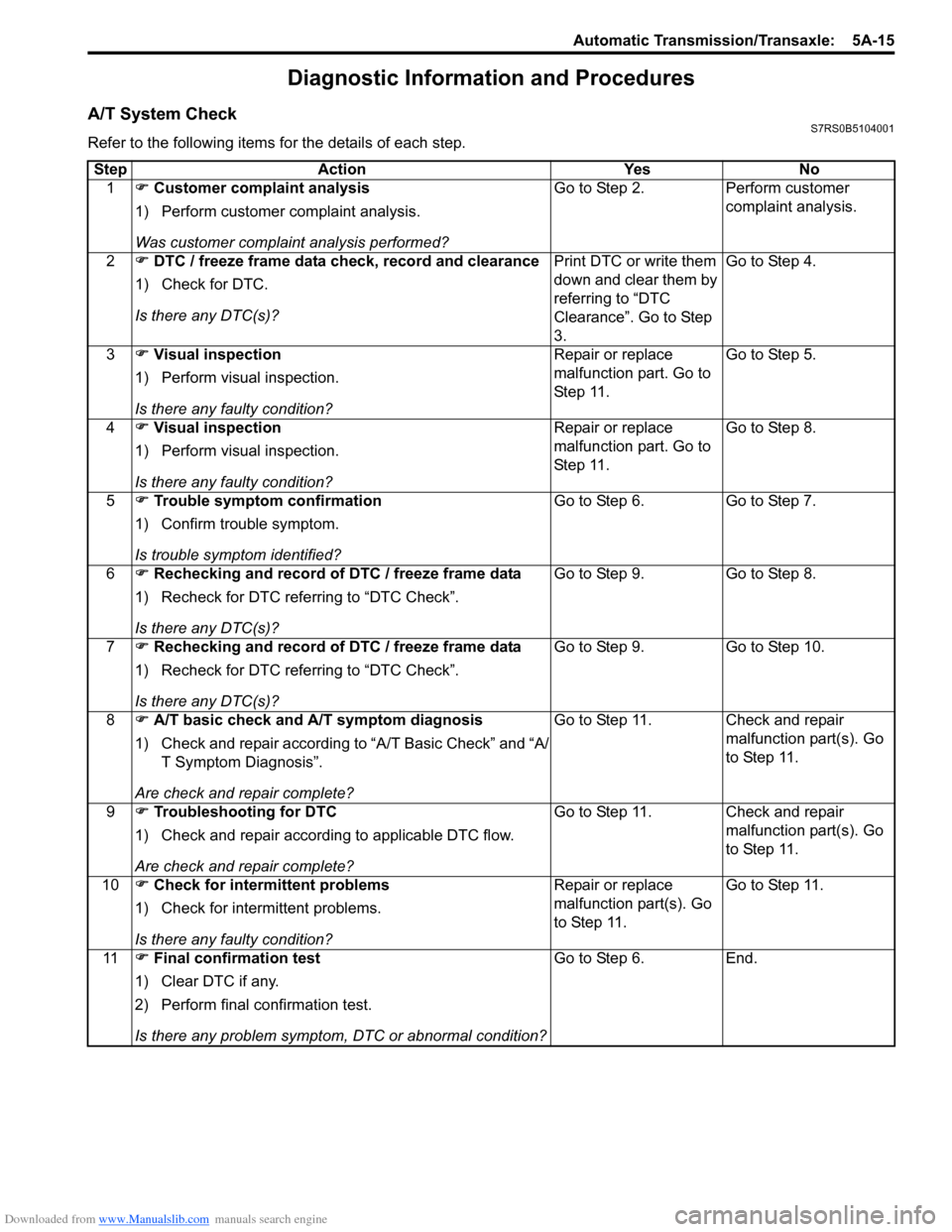
A/T System CheckS7RS0B5104001
Refer to the following items for the details of each step.Step Action Yes No 1 �) Customer complaint analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis.
Was customer complaint analysis performed? Go to Step 2. Perform customer
complaint analysis.
2 �) DTC / freeze frame data check, record and clearance
1) Check for DTC.
Is there any DTC(s)? Print DTC or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC
Clearance”. Go to Step
3.Go to Step 4.
3 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part. Go to
St ep 11 .
Go to Step 5.
4 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part. Go to
St ep 11 .
Go to Step 8.
5 �) Trouble symptom confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom.
Is trouble symptom identified? Go to Step 6.
Go to Step 7.
6 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 8.
7 �) Rechecking and record of DTC / freeze frame data
1) Recheck for DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 10.
8 �) A/T basic check and A/T symptom diagnosis
1) Check and repair according to “A/T Basic Check” and “A/
T Symptom Diagnosis”.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s). Go
to Step 11.
9 �) Troubleshooting for DTC
1) Check and repair according to applicable DTC flow.
Are check and repair complete? Go to Step 11. Check and repair
malfunction part(s). Go
to Step 11.
10 �) Check for intermittent problems
1) Check for interm ittent problems.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part(s). Go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 11.
11 �) Final confirmation test
1) Clear DTC if any.
2) Perform final confirmation test.
Is there any problem symptom, DTC or abnormal condition? Go to Step 6.
End.
Page 660 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-16 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
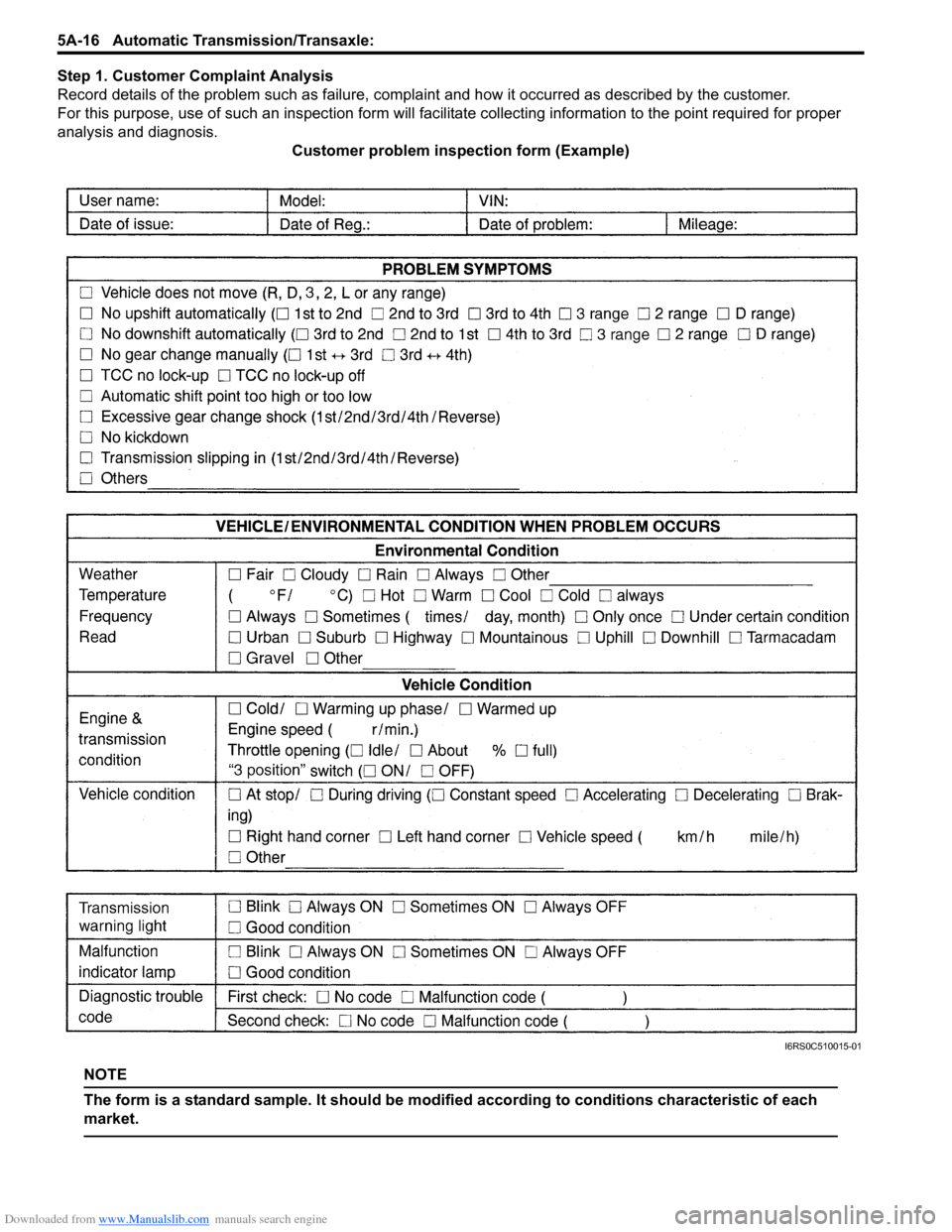
Step 1. Customer Complaint Analysis
Record details of the problem such as failure, complaint and how it occurred as described by the customer.
For this purpose, use of such an inspec tion form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for proper
analysis and diagnosis. Customer problem inspection form (Example)
NOTE
The form is a standard sample. It should be modified according to conditions characteristic of each
market.
I6RS0C510015-01
Page 661 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-17
Step 2. DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and Clearance
First, referring to “DTC Check”, check DTC and pending DTC. If DTC exists, print or write down DTC and freeze frame
data and then clear malfunction DTC(s) by referring to “DTC Clearance”. Malfunction DTC indicates malfunction in the
system but it is not possible to know from it whether the malfunction is occurring now or it occurred in the past and
normal condition has been restored. In order to know that, check symptom in question according to Step 5 and then
recheck DTC according to Step 6.
Diagnosing a trouble based on the DTC in this step only or fa ilure to clear the DTC in this step may result in an faulty
diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit or difficulty in troubleshooting which is otherwise unnecessary.
Step 3 and 4. Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of the items that support proper function of the engine and
automatic transaxle referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5. Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Check trouble symptoms based on information obtained in “Step 1. Customer Complaint Analysis: ” and “Step 2. DTC
/ Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and Clearance: ”.
Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC Confirmation Procedure” described in each DTC flow.
Step 6 and 7. Rechecking and Record of DTC and Freeze Frame Data
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8. A/T Basic Check and A/T Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic check of A/T according to “A/T Basic Check” first. When the end of the flow has been reached, check
the parts of the system suspected as a possible cause referring to “A/T Symptom Diagnosis” and based on symptoms
appearing on the vehicle (symptoms obtained through step s of customer complaint analysis, trouble symptom
confirmation and/or A/T basic check) and re pair or replace faulty parts, if any.
Step 9. Troubleshooting for DTC
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 / 7 and referring to “a pplicable DTC flow”, locate the cause of the trouble,
namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness, connector, actuator, TCM or other part and repair or replace faulty parts.
Step 10. Check for Intermittent Problem
Check parts where an intermittent trouble is easy to occur (e.g . wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection Inspection in Section 00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
Step 11. Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the vehicl e is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has been
repaired is related to the malfunction DTC, clear the DTC once and check to ensure that no malfunction DTC is
indicated.
Page 741 of 1496
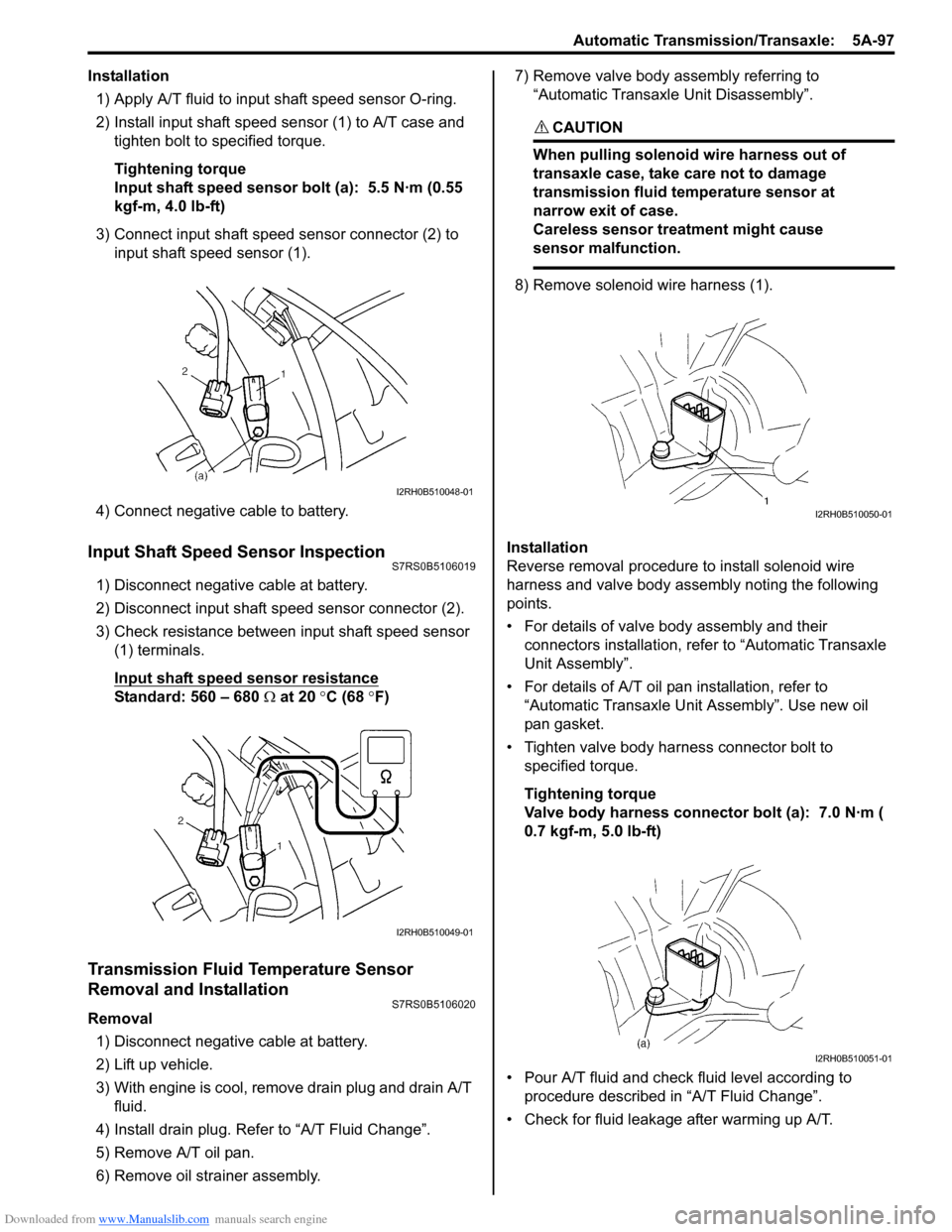
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-97
Installation1) Apply A/T fluid to input shaft speed sensor O-ring.
2) Install input shaft speed se nsor (1) to A/T case and
tighten bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Input shaft speed sensor bolt (a): 5.5 N·m (0.55
kgf-m, 4.0 lb-ft)
3) Connect input shaft speed sensor connector (2) to input shaft speed sensor (1).
4) Connect negative cable to battery.
Input Shaft Speed Sensor InspectionS7RS0B5106019
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Disconnect input shaft speed sensor connector (2).
3) Check resistance between input shaft speed sensor (1) terminals.
Input shaft speed sensor resistance
Standard: 560 – 680 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
Removal and Installation
S7RS0B5106020
Removal
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Lift up vehicle.
3) With engine is cool, remove drain plug and drain A/T fluid.
4) Install drain plug. Refer to “A/T Fluid Change”.
5) Remove A/T oil pan.
6) Remove oil stra iner assembly. 7) Remove valve body assembly referring to
“Automatic Transaxl e Unit Disassembly”.
CAUTION!
When pulling solenoid wire harness out of
transaxle case, take care not to damage
transmission fluid temperature sensor at
narrow exit of case.
Careless sensor treatment might cause
sensor malfunction.
8) Remove solenoid wire harness (1).
Installation
Reverse removal procedure to install solenoid wire
harness and valve body assembly noting the following
points.
• For details of valve body assembly and their connectors installation, refer to “Automatic Transaxle
Unit Assembly”.
• For details of A/T oil pa n installation, refer to
“Automatic Transaxle Unit Assembly”. Use new oil
pan gasket.
• Tighten valve body harness connector bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Valve body harness connector bolt (a): 7.0 N·m (
0.7 kgf-m, 5.0 lb-ft)
• Pour A/T fluid and check fluid level according to procedure described in “A/T Fluid Change”.
• Check for fluid leakage after warming up A/T.
I2RH0B510048-01
I2RH0B510049-01
I2RH0B510050-01
I2RH0B510051-01
Page 745 of 1496
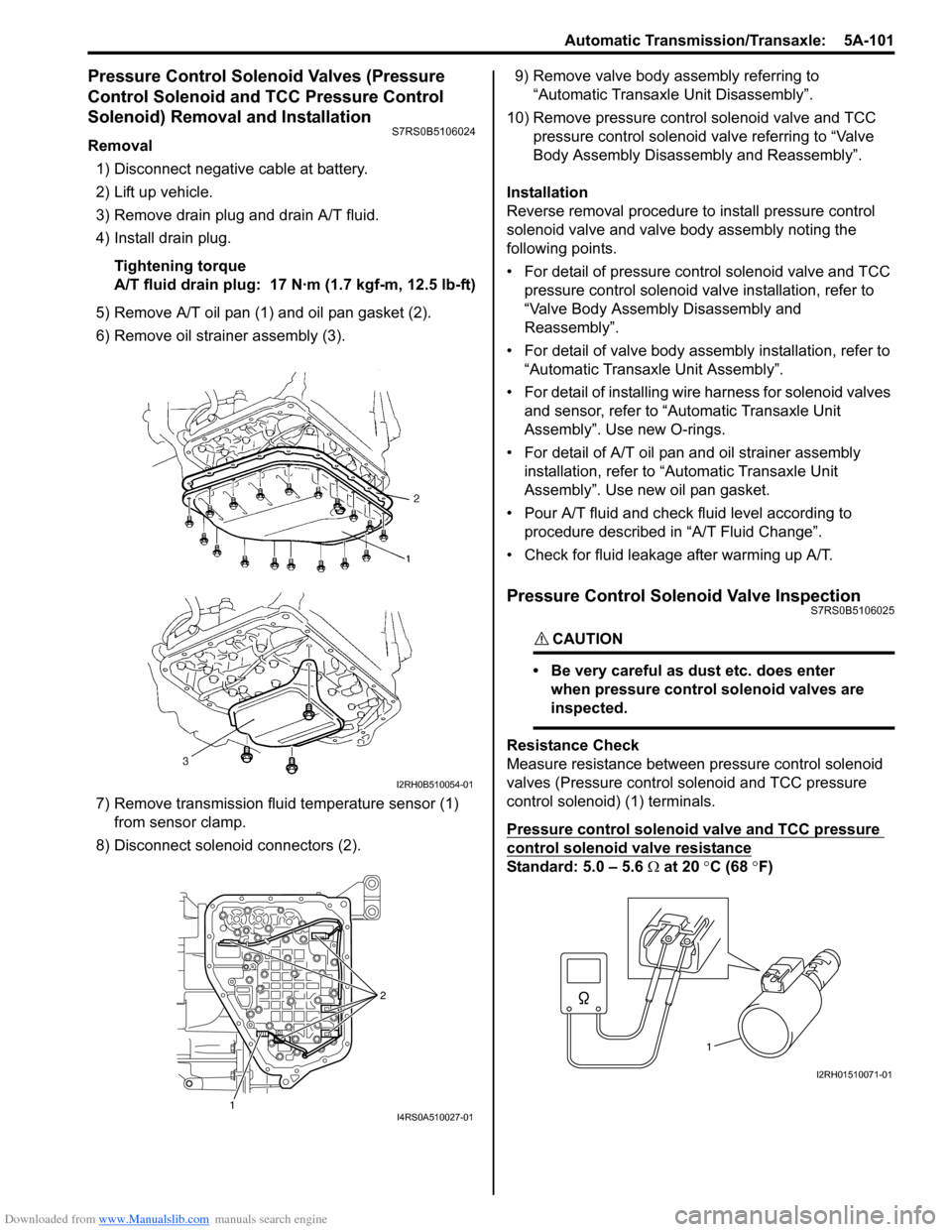
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-101
Pressure Control Solenoid Valves (Pressure
Control Solenoid and TCC Pressure Control
Solenoid) Removal and Installation
S7RS0B5106024
Removal1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Lift up vehicle.
3) Remove drain plug and drain A/T fluid.
4) Install drain plug.
Tightening torque
A/T fluid drain plug: 17 N·m (1.7 kgf-m, 12.5 lb-ft)
5) Remove A/T oil pan (1) and oil pan gasket (2).
6) Remove oil strain er assembly (3).
7) Remove transmission fluid temperature sensor (1) from sensor clamp.
8) Disconnect solenoid connectors (2). 9) Remove valve body assembly referring to
“Automatic Transaxl e Unit Disassembly”.
10) Remove pressure control solenoid valve and TCC pressure control solenoid valve referring to “Valve
Body Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly”.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure to install pressure control
solenoid valve and valve body assembly noting the
following points.
• For detail of pressure control solenoid valve and TCC pressure control solenoid va lve installation, refer to
“Valve Body Assembly Disassembly and
Reassembly”.
• For detail of valve body asse mbly installation, refer to
“Automatic Transaxle Unit Assembly”.
• For detail of installing wire harness for solenoid valves and sensor, refer to “Automatic Transaxle Unit
Assembly”. Use new O-rings.
• For detail of A/T oil pan and oil strainer assembly
installation, refer to “A utomatic Transaxle Unit
Assembly”. Use new oil pan gasket.
• Pour A/T fluid and check fluid level according to procedure described in “A/T Fluid Change”.
• Check for fluid leakage after warming up A/T.
Pressure Control Solenoid Valve InspectionS7RS0B5106025
CAUTION!
• Be very careful as dust etc. does enter when pressure control solenoid valves are
inspected.
Resistance Check
Measure resistance between pressure control solenoid
valves (Pressure control solenoid and TCC pressure
control solenoid) (1) terminals.
Pressure control solenoid valve and TCC pressure
control solenoid valve resistance
Standard: 5.0 – 5.6 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
I2RH0B510054-01
1 2I4RS0A510027-01
1
I2RH01510071-01
Page 887 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Assisted Steering System: 6C-5
Terminal Arrangement of P/S Control Module Coupler (Viewed from Harness Side)
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
EPS System CheckS7RS0B6304001
WARNING!
Carry out test drive in light traffic area to prevent an accident.
Refer to the following items for the details of each step.Terminal Circuit Terminal Circuit
E49-1 Main power supply for internal memory
and EPS motor E52-9 Ground for torque sensors
E49-2 Ground for P/S control module E52-10 —
E51-1 Motor output 1 E52-11 Serial communication for data link
connector
E51-2 Motor output 2 E52-12 Engine speed signal
E52-1 Ignition switch signal for P/S control
module E52-13 —
E52-2 — E52-14 P/S operation signal (idle up signal)
E52-3 — E52-15 —
E52-4 Vehicle speed signal E52-16 Torque sensor internal failure signal
E52-5 “EPS” warning light E52-17 —
E52-6 Torque sensor signal (Sub) E52-18 Torque sensor signal (Main)
E52-7 — E52-19 Ground for shield wire
E52-8 Main power supply for torque sensor E52-20 5 V reference power supply for torque
sensor
Step
Action YesNo
1 �) Customer complaint analysis
1) Perform customer complaint analysis referring to “Customer Complaint Analysis”.
Was customer complaint analysis performed? Go to Step 2.
Perform customer
complaint analysis.
2 �) DTC check, record and clearance
1) Check for DTC (including pending DTC) referring to “DTC Check”, Record and Clearance.
Is there any DTC(s)? Print DTC or write them
down and clear them by
referring to “DTC
Clearance” and go to
St ep 3 .Go to Step 4.
3 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 5.
4 �) Visual inspection
1) Perform visual inspection referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Is there any faulty condition? Repair or replace
malfunction part, and go
to Step 11.
Go to Step 8.
5 �) Trouble symptom confirmation
1) Confirm trouble symptom referring to “Trouble Symptom Confirmation”.
Is trouble symptom identified? Go to Step 6.
Go to Step 7.
6 �) Rechecking and record of DTC
1) Recheck for DTC referring to “DTC Check”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to Step 9.
Go to Step 8.