2005 CHRYSLER VOYAGER Bcm
[x] Cancel search: BcmPage 556 of 2339

OPERATION
When rear wiper operation is required, the BCM
will provide ignition ON voltage to the rear wiper
motor. When the wiper switch is turned OFF, the
BCM provides circuit ground to operate the motor
until the wipe cycle is complete and the wiper arm
returns to the base of the rear window.
The rear wiper/washer switch only offers an inter-
mittent rear wiper mode. The wiper motor will cycle
every 7 seconds. The intermittent delay time is also
adjusted based upon vehicle speed. With the vehicle
traveling greater than 50 mph, the cycle changes to
every 5 seconds.
When rear washer is requested by depressing and
holding down the switch, the BCM then provides a
ground for the rear washer motor. Until the switch is
released, the motor will be in a continuous wipe
mode, then return to an intermittent wipe mode.
WASHER FLUID LEVEL
SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on hoist or jack
stands.
(3) If necessary, remove the right front wheel and
tire assembly (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Disconnect the right front wheelhouse splash
shield and move aside (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/WHEELHOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL).
(5) Drain washer fluid from the reservoir and into
a suitable clean container. This can be done by dis-connecting the windshield washer hose from the
front (outboard) washer pump port allowing the
washer fluid to drain into a container through a tem-
porary jumper hose connected to the front washer
pump.
(6) Disconnect the electrical body harness connec-
tor to the the fluid level sensor. Slide the red lock on
the connector to the release position, then, depress
the black tab and pull the connector off the sensor.
(7) Remove the sensor from reservoir by using a
side foot to gently pry the sensor from the body of
the reservoir. Do not damage the reservoir/sensor
sealing surface or puncture reservoir during removal.
CAUTION: To avoid damage to the sensor, assure
the reservoir is in an upright position before remov-
ing the sensor from the reservoir. Do not rotate the
sensor during removal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Use a new grommet when installing a new sen-
sor assembly.
(2) Assure that the flat of the sensor is aligned
under the ridge of the reservoir and that the sensor
connector is facing down in the fully seated position.
This will allow for proper operation of the sensor
float switch.
(3) Connect the electrical body harness connectors
to the fluid level sensor. Slide the red lock on the
connector to the closed or locked position.
(4) Assure that washer hose is properly routed to
prevent pinching and possible inoperative washers.
(5) Connect the left right front wheelhouse splash
shield and move aside (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/WHEELHOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLA-
TION).
(6) Install the right front wheel and tire assembly
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - INSTALLATION).
(7) lower vehicle from hoist or jack stands.
(8) Connect the battery negative cable.
(9) Verify system operation.
WASHER HOSES
REMOVAL
(1) Remove washer reservoir from vehicle (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WASHER
RESERVOIR - REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect washer hose front the reservoir cav-
ity.
(3) Disconnect the washer hose from the reservoir
pump.
(4) Remove parts as necessary to replace washer
hose (engine compartment, interior components, etc.).
Fig. 4 REAR WIPER/WASHER SWITCH LOCATION
1 - REAR WIPER/WASHER SWITCH
2 - HVAC CONTROL UNIT
RSWIPERS/WASHERS8R-11
REAR WIPER/WASHER SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1390 of 2339
opposite preset limit or switch point. The process
then repeats itself in the opposite direction.
Short term fuel correction will keep increasing or
decreasing injector pulse-width based upon the
upstream O2 Sensor input. The maximum range of
authority for short term memory is 25% (+/-) of base
pulse-width. Short term is violated and is lost when
ignition is turned OFF.
Long Term
The second fuel correction program is the long
term adaptive memory. In order to maintain correct
emission throughout all operating ranges of the
engine, a cell structure based on engine rpm and load
(MAP) is used.
Ther number of cells varies upon the driving con-
ditions. Two cells are used only during idle, based
upon TPS and Park/Neutral switch inputs. There
may be two other cells used for deceleration, based
on TPS, engine rpm, and vehicle speed. The other
twelve cells represent a manifold pressure and an
rpm range. Six of the cells are high rpm and the
other six are low rpm. Each of these cells has a spe-
cific MAP voltage range Typical Adaptive Memory
Fuel Cells.As the engine enters one of these cells the PCM
looks at the amount of short term correction being
used. Because the goal is to keep short term at 0 (O2
Sensor switching at 0.5 volt), long term will update
in the same direction as short term correction was
moving to bring the short term back to 0. Once short
term is back at 0, this long term correction factor is
stored in memory.
The values stored in long term adaptive memory
are used for all operating conditions, including open
loop and cold starting. However, the updating of the
long term memory occurs after the engine has
exceeded approximately 170É-190É F, with fuel control
in closed loop and two minutes of engine run time.
This is done to prevent any transitional temperature
or start-up compensations from corrupting long term
fuel correction.
Long term adaptive memory can change the pulse-
width by as much as 25%, which means it can correct
for all of short term. It is possible to have a problem
that would drive long term to 25% and short term to
another 25% for a total change of 50% away from
base pulse-width calculation.
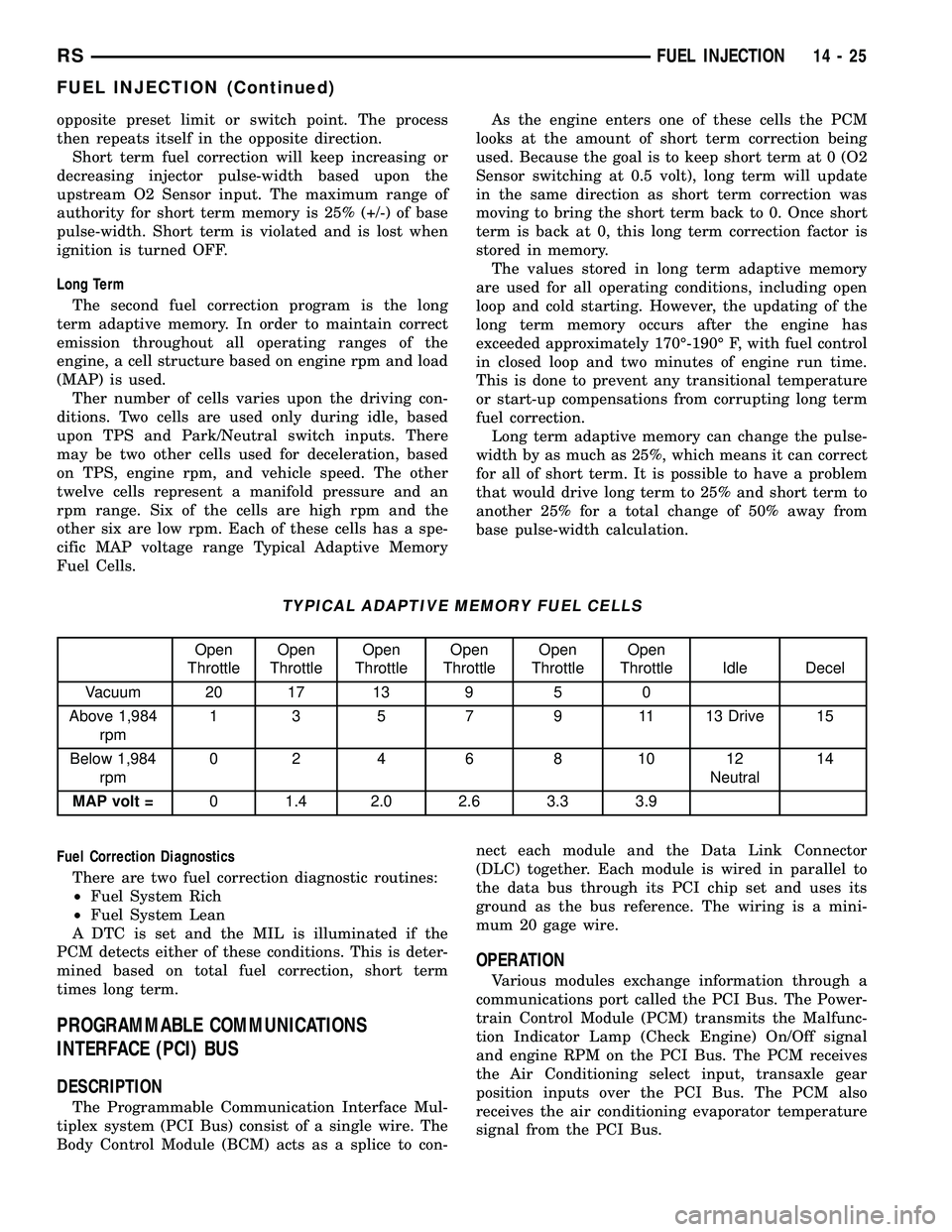
TYPICAL ADAPTIVE MEMORY FUEL CELLS
Open
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
Throttle Idle Decel
Vacuum 20 17 13 9 5 0
Above 1,984
rpm1 3 5 7 9 11 13 Drive 15
Below 1,984
rpm02 4 6 8 1012
Neutral14
MAP volt =0 1.4 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9
Fuel Correction Diagnostics
There are two fuel correction diagnostic routines:
²Fuel System Rich
²Fuel System Lean
A DTC is set and the MIL is illuminated if the
PCM detects either of these conditions. This is deter-
mined based on total fuel correction, short term
times long term.
PROGRAMMABLE COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (PCI) BUS
DESCRIPTION
The Programmable Communication Interface Mul-
tiplex system (PCI Bus) consist of a single wire. The
Body Control Module (BCM) acts as a splice to con-nect each module and the Data Link Connector
(DLC) together. Each module is wired in parallel to
the data bus through its PCI chip set and uses its
ground as the bus reference. The wiring is a mini-
mum 20 gage wire.
OPERATION
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the PCI Bus. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) transmits the Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp (Check Engine) On/Off signal
and engine RPM on the PCI Bus. The PCM receives
the Air Conditioning select input, transaxle gear
position inputs over the PCI Bus. The PCM also
receives the air conditioning evaporator temperature
signal from the PCI Bus.
RSFUEL INJECTION14-25
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1584 of 2339
VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
The vehicle speed signal is taken from the Output
Speed Sensor. The PCM converts this signal into a
pulse per mile signal and sends the vehicle speed
message across the communication bus to the BCM.
The BCM sends this signal to the Instrument Cluster
to display vehicle speed to the driver. The vehicle
speed signal pulse is roughly 8000 pulses per mile.
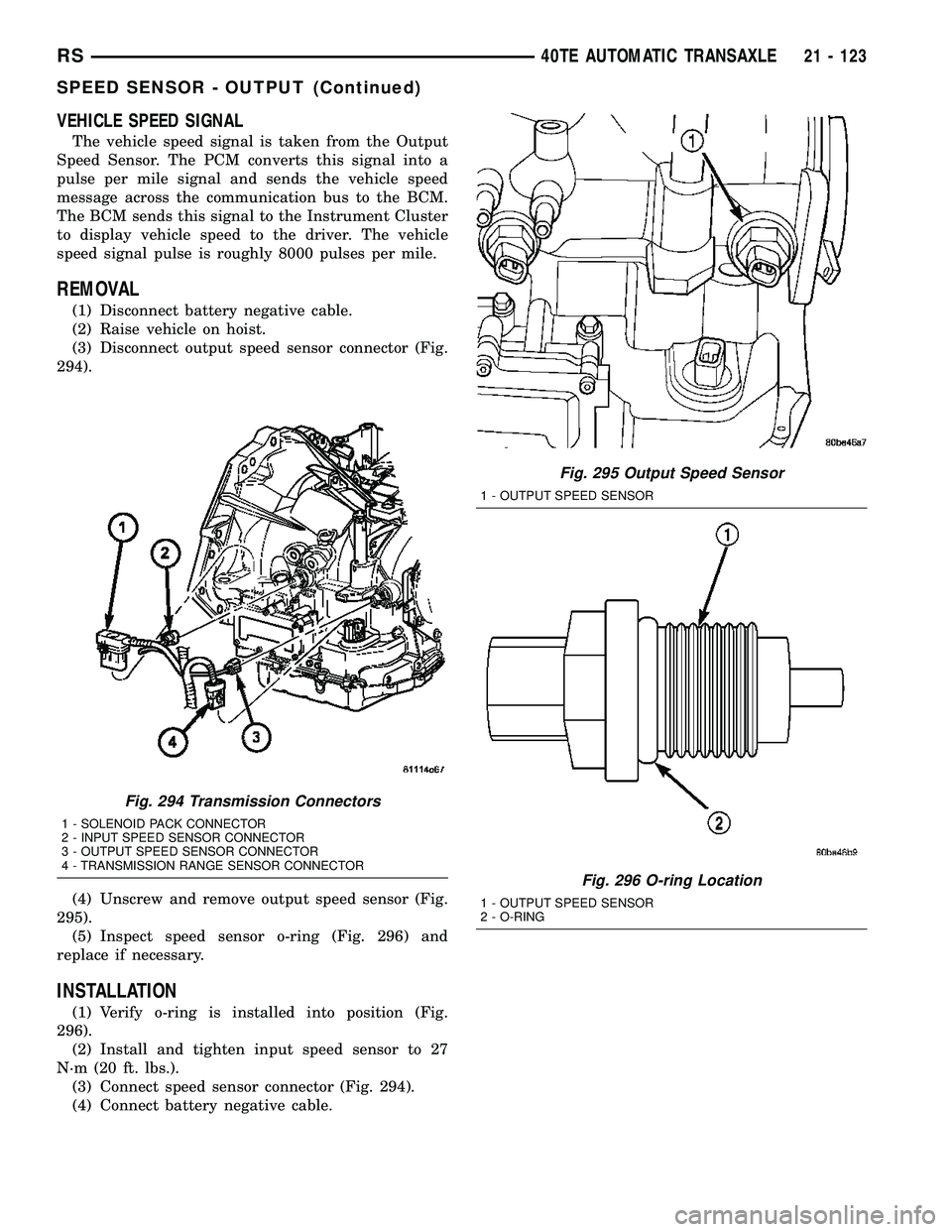
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect output speed sensor connector (Fig.
294).
(4) Unscrew and remove output speed sensor (Fig.
295).
(5) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 296) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
296).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 294).
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 294 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 295 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 296 O-ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 123
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT (Continued)
Page 1734 of 2339
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
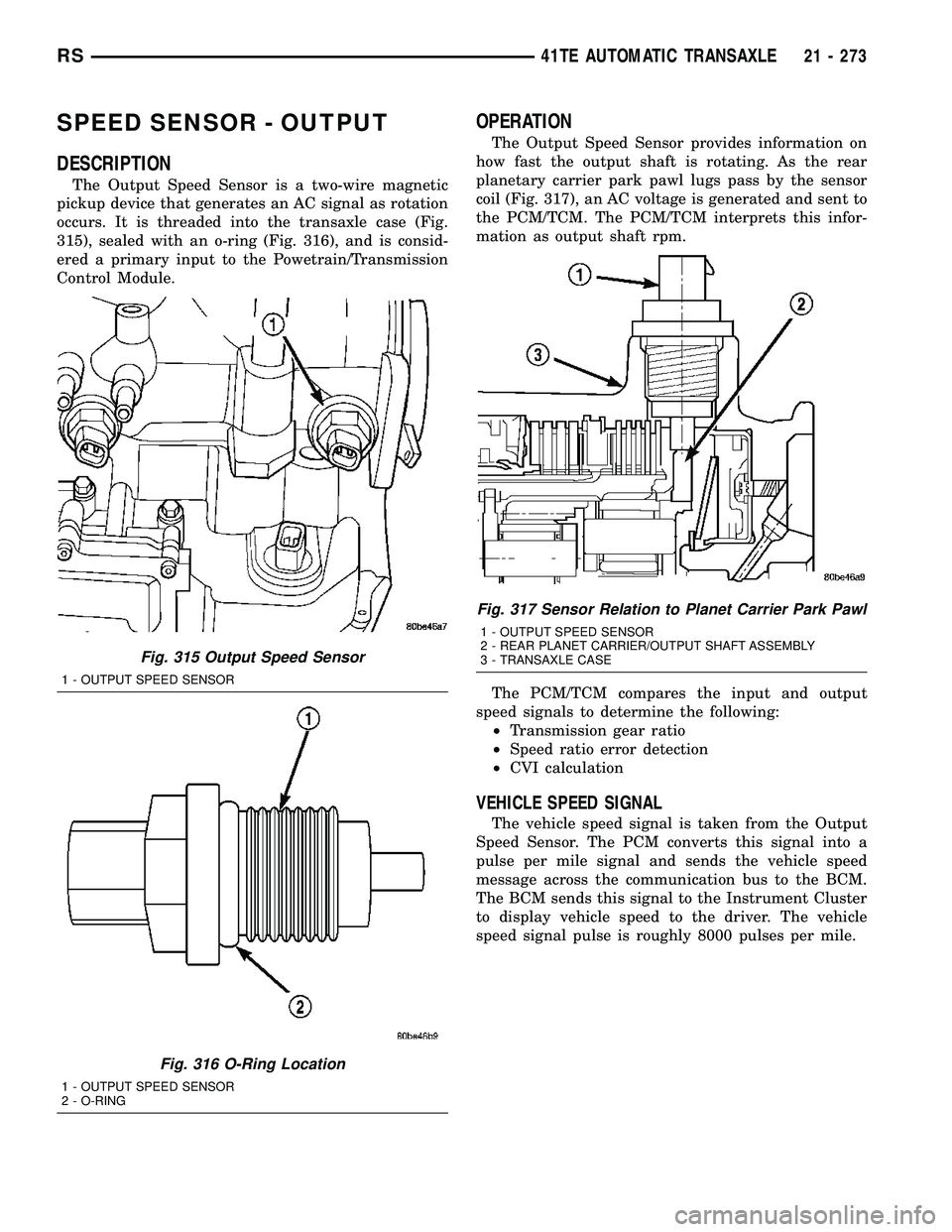
DESCRIPTION
The Output Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates an AC signal as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
315), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 316), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powetrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Output Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the output shaft is rotating. As the rear
planetary carrier park pawl lugs pass by the sensor
coil (Fig. 317), an AC voltage is generated and sent to
the PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this infor-
mation as output shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input and output
speed signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
The vehicle speed signal is taken from the Output
Speed Sensor. The PCM converts this signal into a
pulse per mile signal and sends the vehicle speed
message across the communication bus to the BCM.
The BCM sends this signal to the Instrument Cluster
to display vehicle speed to the driver. The vehicle
speed signal pulse is roughly 8000 pulses per mile.
Fig. 315 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 316 O-Ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 317 Sensor Relation to Planet Carrier Park Pawl
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - REAR PLANET CARRIER/OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - TRANSAXLE CASE
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 273
Page 2154 of 2339

²a rotary adjustment knob for temperature.
²a rotary adjustment for fan speed control.
AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL
Two different automatic temperature control (ATC)
heating-A/C systems are available for this model
depending on the market.
The Dual-Zone ATC system allows the driver and
front occupants to each select individual comfort tem-
peratures.
The Three-Zone ATC system allows both the driver
and front occupants and the rear intermediate occu-
pants to select individual comfort temperatures.
NOTE: Individual comfort temperatures are the per-
ceived temperature level at the individual seating
areas, NOT the actual passenger compartment air
temperature.
The ATC system includes a particulate air filter.
The filter element is the same size as the A/C evap-
orator to ensure ample capacity. A door at the base of
the HVAC housing below the glove box provides easy
access to the filter element.
The ATC computer utilizes integrated circuitry and
information carried on the programmable communi-
cations interface (PCI) data bus network to monitor
many sensors and switch inputs throughout the vehi-
cle. In response to those inputs, the internal circuitry
and programming of the ATC computer allow it to
control electronic functions and features of the ATC
system. The inputs to the ATC computer are:
²Vehicle Speed/Engine RPM± The ATC com-
puter monitors engine rpm, vehicle speed and mani-
fold absolute pressure information from the
powertrain control module (PCM).
²Coolant Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors coolant temperature received from the PCM and
converts it to degrees Fahrenheit.
²Ambient Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors ambient temperature from the compass mini trip
computer (CMTC) and converts it to degrees Fahren-
heit.
²Engine Miscellaneous Sensor Status±ATC
computer monitors A/C disable information from the
PCM.
²Refrigerant Pressure± ATC computer moni-
tors barometric pressure, intake air temperature,
high side pressure and methanol content as broad-
cast by the PCM.
²Door Ajar Status± The ATC computer moni-
tors driver front door, passenger front door, left rear
door, right rear door and liftgate ajar information, as
identified by the body control module (BCM), to
determine if all in-car temperatures should be main-
tained.²Dimming± The ATC computer monitors dim-
ming status from the BCM to determine the required
level of brightness and will dim accordingly.
²Vehicle Odometer± The ATC computer moni-
tors the vehicle odometer information from the BCM
to prevent flashing the vacuum-flourescent (VF) dig-
ital display icons if the manual motor calibration or
manual cool down tests have failed. Flashing of the
display icons will cease when the vehicle odometer is
greater than 3 miles.
²English/Metric± The ATC computer monitors
the English/Metric information broadcast by the
CMTC. The set temp displays for both the front and
rear control heads will be set accordingly.
²Vehicle Identification Number± The ATC
computer monitors the last eight characters of the
VIN broadcast by the PCM and compares it to the
information stored in EEPROM. If it is different, the
new number will be stored over the old one and a
motor calibration shall be initiated.
²A/C System Information± The ATC computer
will send a message for evaporator temperature too
low, fan blower relay status, evaporator sensor fail-
ure, rear window defogger relay and A/C select.
FRONT CONTROL PANEL
The front A/C-heater control and integral computer
is mounted in the instrument panel and contains:
²a power button which allows the system to be
completely turned off. The display is blank when the
system is off.
²a rocker switch that selects a cool-down rate.
LO-AUTO or HI-AUTO are displayed when the sys-
tem is in automatic operation.
²three rocker switches that select comfort temper-
atures from 15É to 30É C (59É to 85É F), which are
shown in the VF digital display. If the set temp is 15É
C (59É F) and the down button is pressed, the set
temp value will become 13É C (55É F) but the display
will show LO. If the set temp is 29É C (85É F) and the
up button is pressed, the set temp value will become
32É C (90É F) but the display will show HIGH. Tem-
peratures can be displayed in either metric or Fahr-
enheit, which is controlled from the overhead console.
²an air conditioning button that allows the com-
pressor to be turned off. A Snowflake symbol is illu-
minated when air conditioning is on, whether under
manual or automatic control.
²an air recirculation button. A Recirculation sym-
bol appears in the display when the button is
pressed, or when the system exceeds 80 percent recir-
culated air under automatic control due to high air
conditioning demand.
²a rear window defogger on/off switch. A graphic
symbol shows when the defroster is on.
RSHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24-3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)