2005 CHRYSLER VOYAGER accumulator
[x] Cancel search: accumulatorPage 1534 of 2339
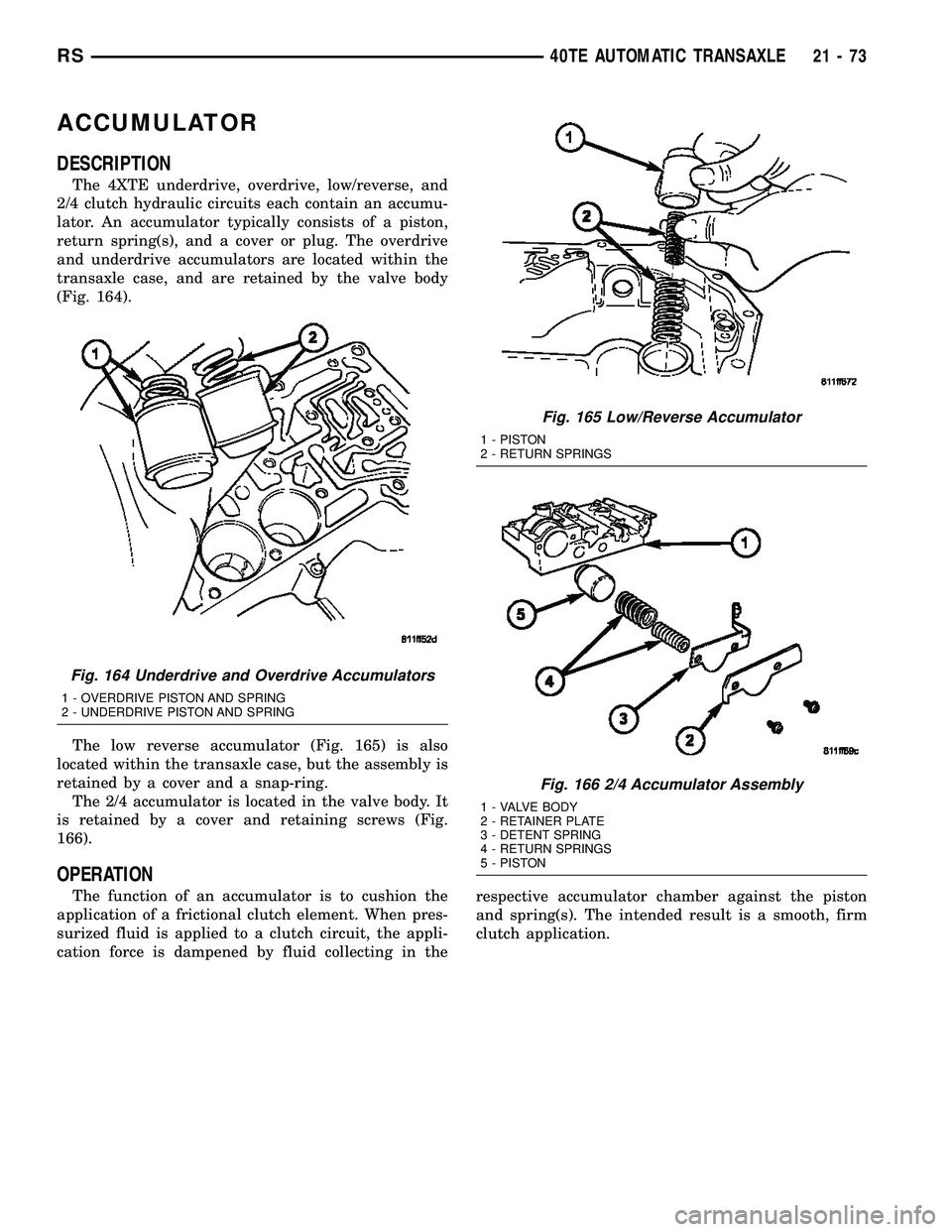
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The 4XTE underdrive, overdrive, low/reverse, and
2/4 clutch hydraulic circuits each contain an accumu-
lator. An accumulator typically consists of a piston,
return spring(s), and a cover or plug. The overdrive
and underdrive accumulators are located within the
transaxle case, and are retained by the valve body
(Fig. 164).
The low reverse accumulator (Fig. 165) is also
located within the transaxle case, but the assembly is
retained by a cover and a snap-ring.
The 2/4 accumulator is located in the valve body. It
is retained by a cover and retaining screws (Fig.
166).
OPERATION
The function of an accumulator is to cushion the
application of a frictional clutch element. When pres-
surized fluid is applied to a clutch circuit, the appli-
cation force is dampened by fluid collecting in therespective accumulator chamber against the piston
and spring(s). The intended result is a smooth, firm
clutch application.
Fig. 164 Underdrive and Overdrive Accumulators
1 - OVERDRIVE PISTON AND SPRING
2 - UNDERDRIVE PISTON AND SPRING
Fig. 165 Low/Reverse Accumulator
1 - PISTON
2 - RETURN SPRINGS
Fig. 166 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - RETURN SPRINGS
5 - PISTON
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-73
Page 1543 of 2339

FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature 82É C
(180É F), the fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT
region on the oil level indicator (Fig. 187). The fluid
level should be within the COLD region of the dip-
stick at 27É C (80É F) fluid temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 188).
(6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart.
(7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
stick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed red so it
can be identified from other fluids used in the vehicle
such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red color is not
permanent and is not an indicator of fluid condition.
As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin to look
darker in color and may eventually become brown.
This is normal.ATF+4 also has a unique odor that
may change with age. Consequently,odor and color
cannot be used to indicate the fluid condition
or the need for a fluid change.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
Fig. 187 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21 - 82 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1593 of 2339
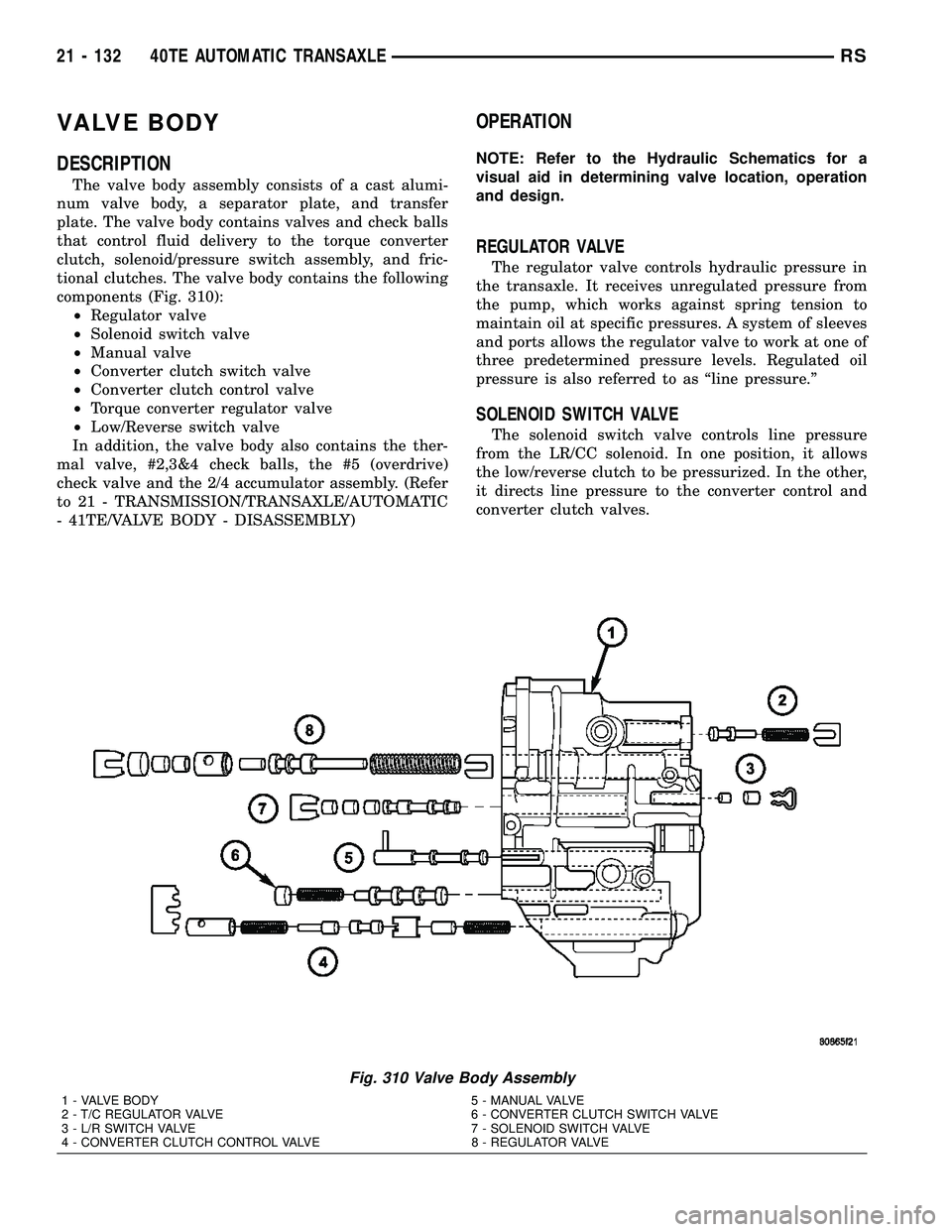
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body assembly consists of a cast alumi-
num valve body, a separator plate, and transfer
plate. The valve body contains valves and check balls
that control fluid delivery to the torque converter
clutch, solenoid/pressure switch assembly, and fric-
tional clutches. The valve body contains the following
components (Fig. 310):
²Regulator valve
²Solenoid switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch switch valve
²Converter clutch control valve
²Torque converter regulator valve
²Low/Reverse switch valve
In addition, the valve body also contains the ther-
mal valve, #2,3&4 check balls, the #5 (overdrive)
check valve and the 2/4 accumulator assembly. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/VALVE BODY - DISASSEMBLY)
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
REGULATOR VALVE
The regulator valve controls hydraulic pressure in
the transaxle. It receives unregulated pressure from
the pump, which works against spring tension to
maintain oil at specific pressures. A system of sleeves
and ports allows the regulator valve to work at one of
three predetermined pressure levels. Regulated oil
pressure is also referred to as ªline pressure.º
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The solenoid switch valve controls line pressure
from the LR/CC solenoid. In one position, it allows
the low/reverse clutch to be pressurized. In the other,
it directs line pressure to the converter control and
converter clutch valves.
Fig. 310 Valve Body Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY 5 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - T/C REGULATOR VALVE 6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
3 - L/R SWITCH VALVE 7 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
4 - CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE 8 - REGULATOR VALVE
21 - 132 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1596 of 2339
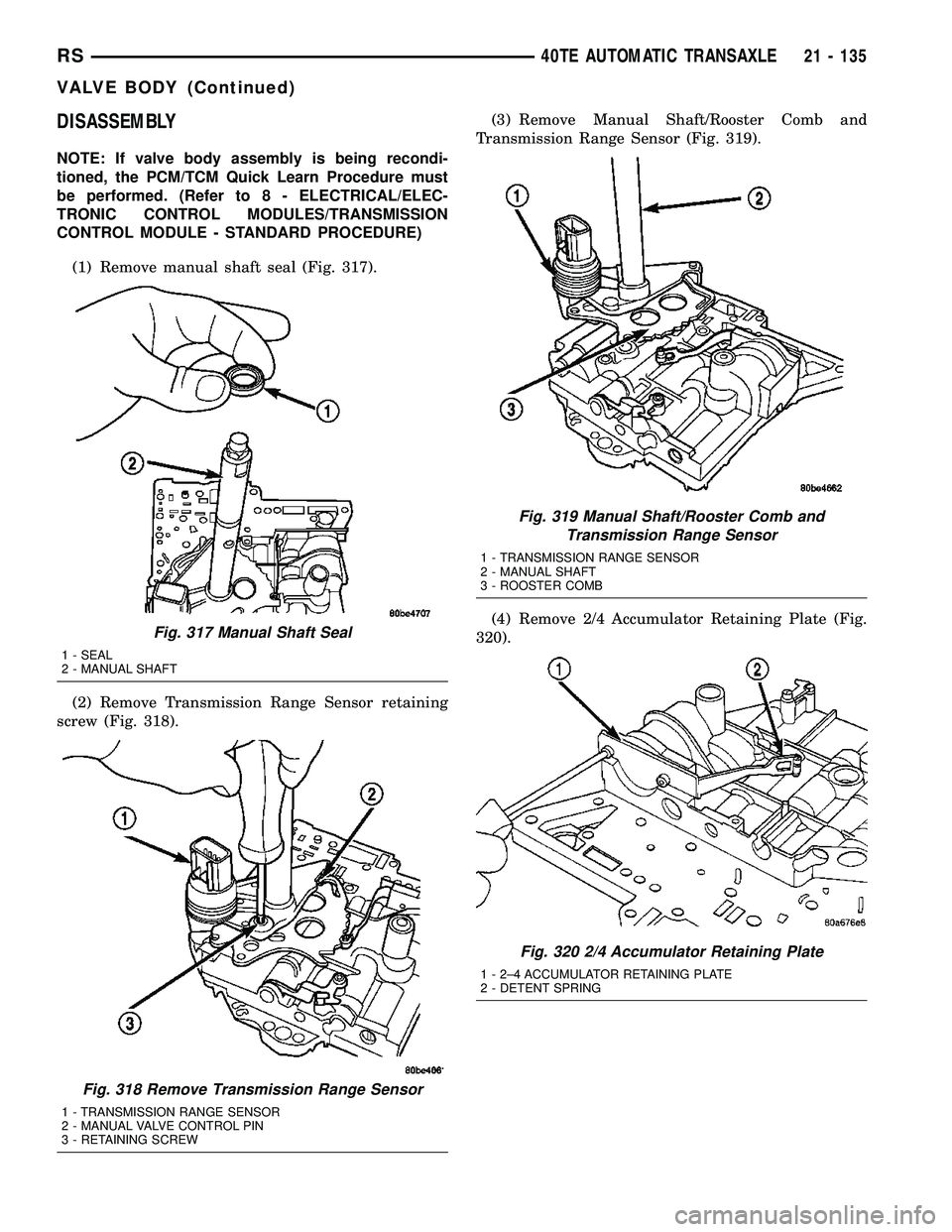
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: If valve body assembly is being recondi-
tioned, the PCM/TCM Quick Learn Procedure must
be performed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Remove manual shaft seal (Fig. 317).
(2) Remove Transmission Range Sensor retaining
screw (Fig. 318).(3) Remove Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor (Fig. 319).
(4) Remove 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate (Fig.
320).
Fig. 317 Manual Shaft Seal
1 - SEAL
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
Fig. 318 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
Fig. 319 Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
3 - ROOSTER COMB
Fig. 320 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate
1 - 2±4 ACCUMULATOR RETAINING PLATE
2 - DETENT SPRING
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 135
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1597 of 2339
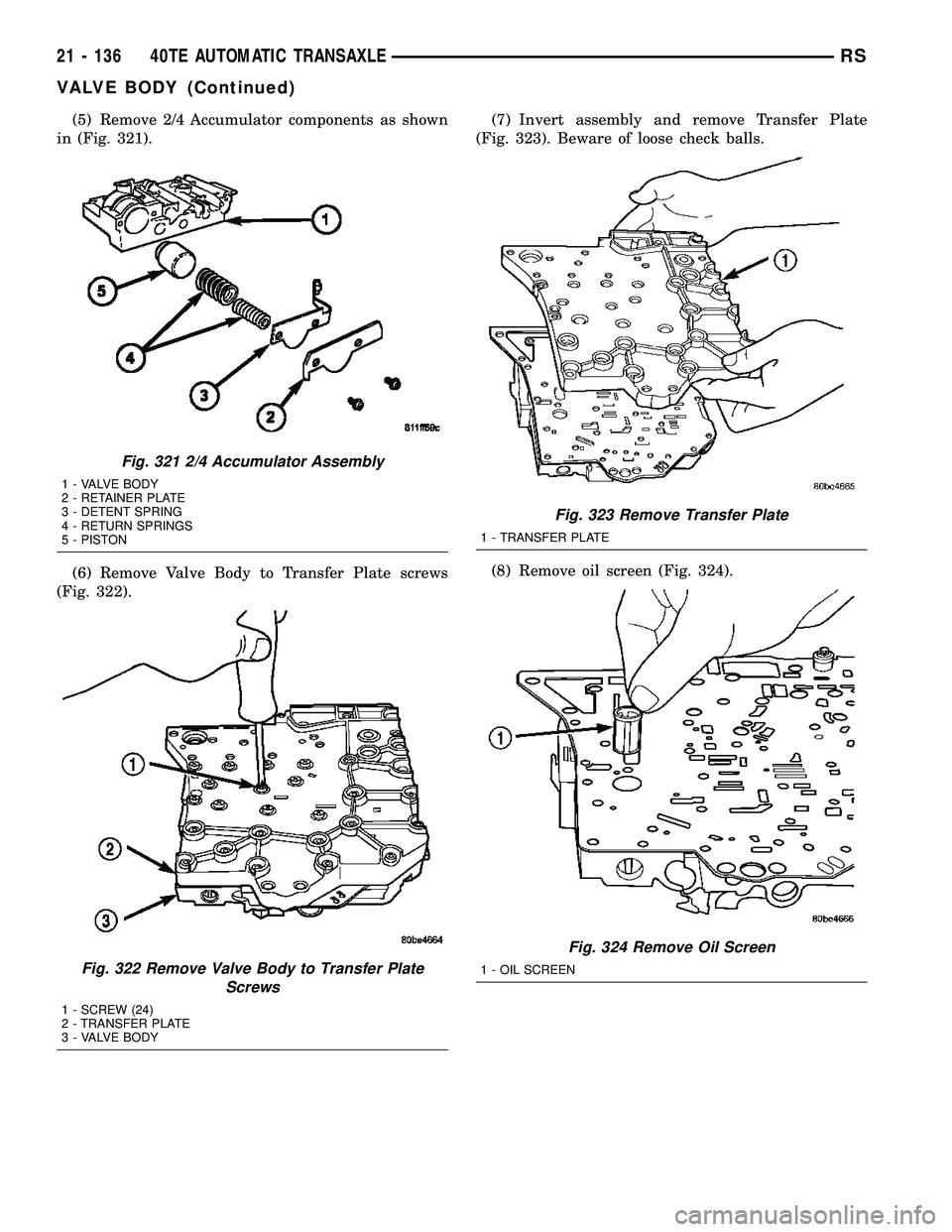
(5) Remove 2/4 Accumulator components as shown
in (Fig. 321).
(6) Remove Valve Body to Transfer Plate screws
(Fig. 322).(7) Invert assembly and remove Transfer Plate
(Fig. 323). Beware of loose check balls.
(8) Remove oil screen (Fig. 324).
Fig. 321 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - RETURN SPRINGS
5 - PISTON
Fig. 322 Remove Valve Body to Transfer Plate
Screws
1 - SCREW (24)
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
3 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 323 Remove Transfer Plate
1 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 324 Remove Oil Screen
1 - OIL SCREEN
21 - 136 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1604 of 2339
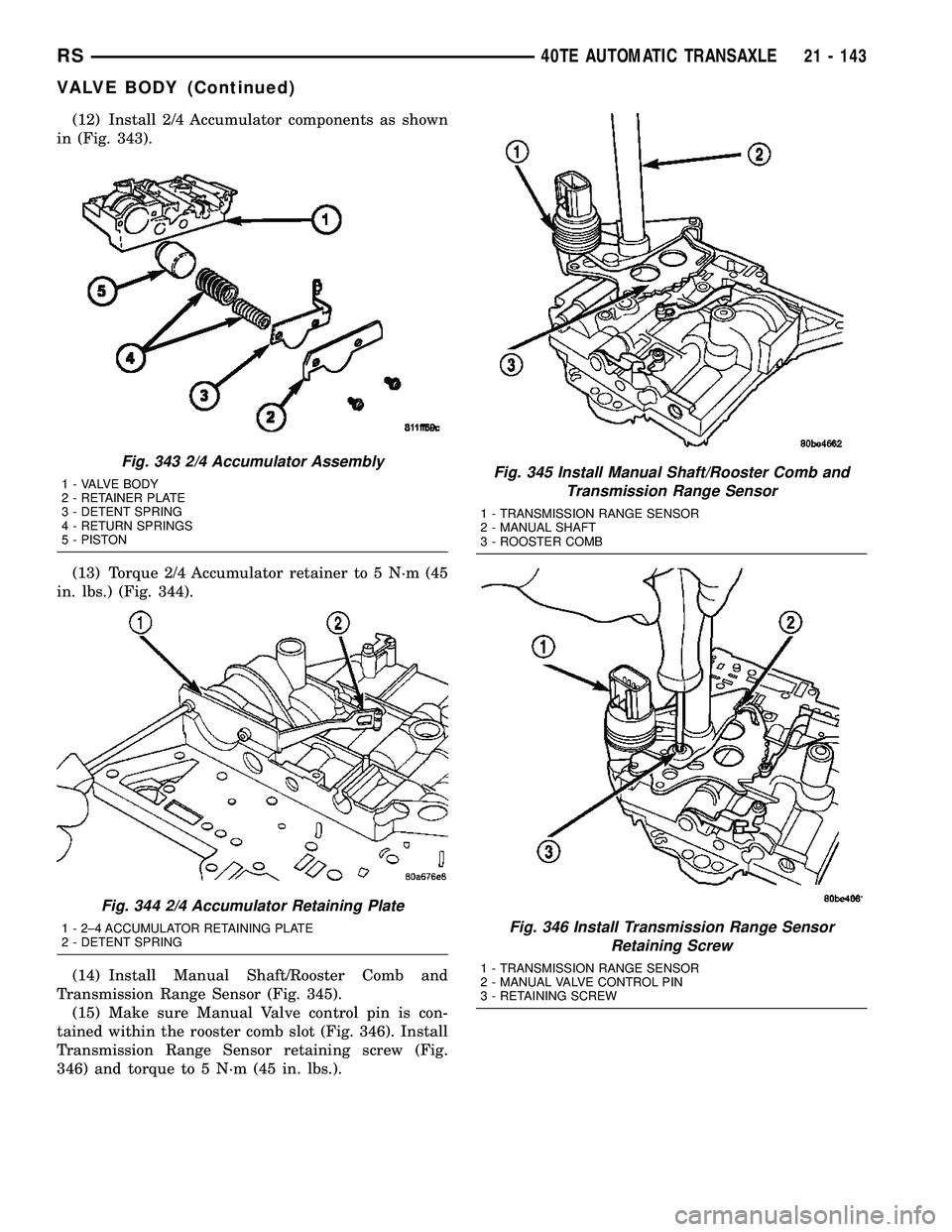
(12) Install 2/4 Accumulator components as shown
in (Fig. 343).
(13) Torque 2/4 Accumulator retainer to 5 N´m (45
in. lbs.) (Fig. 344).
(14) Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor (Fig. 345).
(15) Make sure Manual Valve control pin is con-
tained within the rooster comb slot (Fig. 346). Install
Transmission Range Sensor retaining screw (Fig.
346) and torque to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
Fig. 343 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - RETURN SPRINGS
5 - PISTON
Fig. 344 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate
1 - 2±4 ACCUMULATOR RETAINING PLATE
2 - DETENT SPRING
Fig. 345 Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
3 - ROOSTER COMB
Fig. 346 Install Transmission Range Sensor
Retaining Screw
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 143
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1607 of 2339

41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION........................147
OPERATION..........................149
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTE
TRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS......149
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST . . 150
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS...................150
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS...................153
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE . . 154
REMOVAL............................154
DISASSEMBLY........................157
ASSEMBLY...........................174
INSTALLATION........................196
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
4XTE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC
SCHEMATICS.......................199
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE......211
SPECIAL TOOLS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.........213
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION........................218
OPERATION..........................218
DRIVING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................219
OPERATION..........................219
FINAL DRIVE
DESCRIPTION........................219
OPERATION..........................220
DISASSEMBLY........................220
ASSEMBLY...........................224
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
PRELOAD..........................228
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK . . . 230
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER SERVICE.....................231
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................233
INSTALLATION........................234
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT.......235
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................236
OPERATION..........................236INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY........................237
ASSEMBLY...........................246
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................261
DISASSEMBLY........................261
ASSEMBLY...........................263
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................263
OPERATION..........................263
SEAL - OIL PUMP
REMOVAL............................264
INSTALLATION........................264
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................264
OPERATION..........................265
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID..........................266
REMOVAL............................266
INSTALLATION........................267
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY
DESCRIPTION........................268
OPERATION..........................268
REMOVAL............................269
INSTALLATION........................270
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION........................271
OPERATION..........................271
REMOVAL............................272
INSTALLATION........................272
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION........................273
OPERATION..........................273
REMOVAL............................274
INSTALLATION........................274
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................275
OPERATION..........................278
REMOVAL............................280
INSTALLATION........................280
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................281
OPERATION..........................281
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................281
OPERATION..........................282
REMOVAL............................282
INSTALLATION........................282
21 - 146 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1608 of 2339

VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................283
OPERATION..........................283
REMOVAL............................284DISASSEMBLY........................286
ASSEMBLY...........................291
INSTALLATION........................295
41TE AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION
The 41TE (Fig. 1) is a four-speed transaxle that is
a conventional hydraulic/mechanical assembly with
an integral differential, and is controlled with adap-
tive electronic controls and monitors. The hydraulic
system of the transaxle consists of the transaxle
fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic valves, and various
line pressure control components. An input clutch
assembly which houses the underdrive, overdrive,
and reverse clutches is used. It also utilizes separate
holding clutches: 2nd/4th gear and Low/Reverse. The
primary mechanical components of the transaxle con-
sist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Two multiple disc holding clutches
²Four hydraulic accumulators
²Two planetary gear sets
²Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body²Solenoid/Pressure switch assembly
²Integral differential assembly
Control of the transaxle is accomplished by fully
adaptive electronics. Optimum shift scheduling is
accomplished through continuous real-time sensor
feedback information provided to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) or Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
The PCM/TCM is the heart of the electronic control
system and relies on information from various direct
and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.) to deter-
mine driver demand and vehicle operating condi-
tions. With this information, the PCM/TCM can
calculate and perform timely and quality shifts
through various output or control devices (solenoid
pack, transmission control relay, etc.).
The PCM/TCM also performs certain self-diagnos-
tic functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 147