2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 1270 of 2339
(49) Install the radiator upper support crossmem-
ber (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPEN-
ING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION).
(50) Install the wiper module (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
INSTALLATION).
(51) Connect the fuel line to fuel rail (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(52) Install the air cleaner and hoses.
(53) Install new oil filter. Fill engine crankcase
with proper oil to correct level.
(54) Connect negative cable to battery.
(55) Fill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(56) Start engine and run until operating temper-
ature is reached.
(57) Adjust transmission linkage, if necessary.
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Engine Type 60É V-6 Engine
Number of
Cylinders6
Displacement
3.3L3.3Liters 201 cu.in.
Displacement
3.8L3.8 Liters 231 cu. in.
Bore 3.3L 93.0 mm 201 cu.in.
Bore 3.8L 96.0 mm 3.779 cu.in.
Stroke 3.3L 81 mm 3.188 in.
Stroke 87 mm 3.425 in.
Compression
Ratio 3.3L- 9.35:1
Compression
Ratio 3.8L- 9.6:1
Firing Order - 1-2-3-4-5-6
Compression
Pressure-
Minimum689.5 kPa 100 psi.
Cylinder
Compression
(Max. Difference
Between
Cylinders- 25%
CYLINDER BLOCK
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Cylinder Bore
Diameter
(Standard) 3.3L92.993-93.007
mm3.661-3.6617 in.
Cylinder Bore
Diameter
(Standard) 3.8L95.993-96.007
mm3.7792-3.780 in.
Out of Round
(Service Limits)0.076 mm 0.003 in.
Taper (Service
Limits)0.051 mm 0.002 in.
Lifter Bore
Diameter22.980-23.010
mm0.905-0.906 in.
Deck Surface
Flatness (Max.)0.1 mm 0.004 in.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Connecting Rod
Journal
Diameter57.979-58.005
mm2.2827-2.2837
in.
Main Bearing
Journal
Diameter63.993-64.013
mm2.5194-2.5202
in.
Journal
Out-of-Round
(Max.)0.025 mm 0.001 in.
Journal Taper
(Max.)0.025 mm 0.001 in
End Play 0.09-0.24 mm 0.0036-0.0095
in.
Wear Limit 0.381 mm 0.015 in.
Main Bearing
Diametrical
Clearance
1-2-3-40.011-0.055
mm0.0005-0.0022
in.
Wear Limit 0.076 mm 0.003 in.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-93
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1292 of 2339
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the valve springs. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the valve stem seal (Fig. 44).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the valve stem seal squarely over the
valve guide, using the valve stem as a guide (Fig.
44). Do not force the seal against top of the valve
guide.
(2) Install the valve spring. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - INSTALLA-
TION)
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder block is made of cast iron and is a
deep skirt design.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
(1) Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone,
recommended tool C-823 or equivalent, equipped
with 220 grit stones, is the best tool for this honing
procedure. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring or scratches. Usually a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, recommended tool
C-3501 or equivalent, equipped with 280 grit stones,
if the cylinder bore is straight and round. 20±60
strokes depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Use a light
honing oil.Do not use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.Inspect cylinder walls
after each 20 strokes.
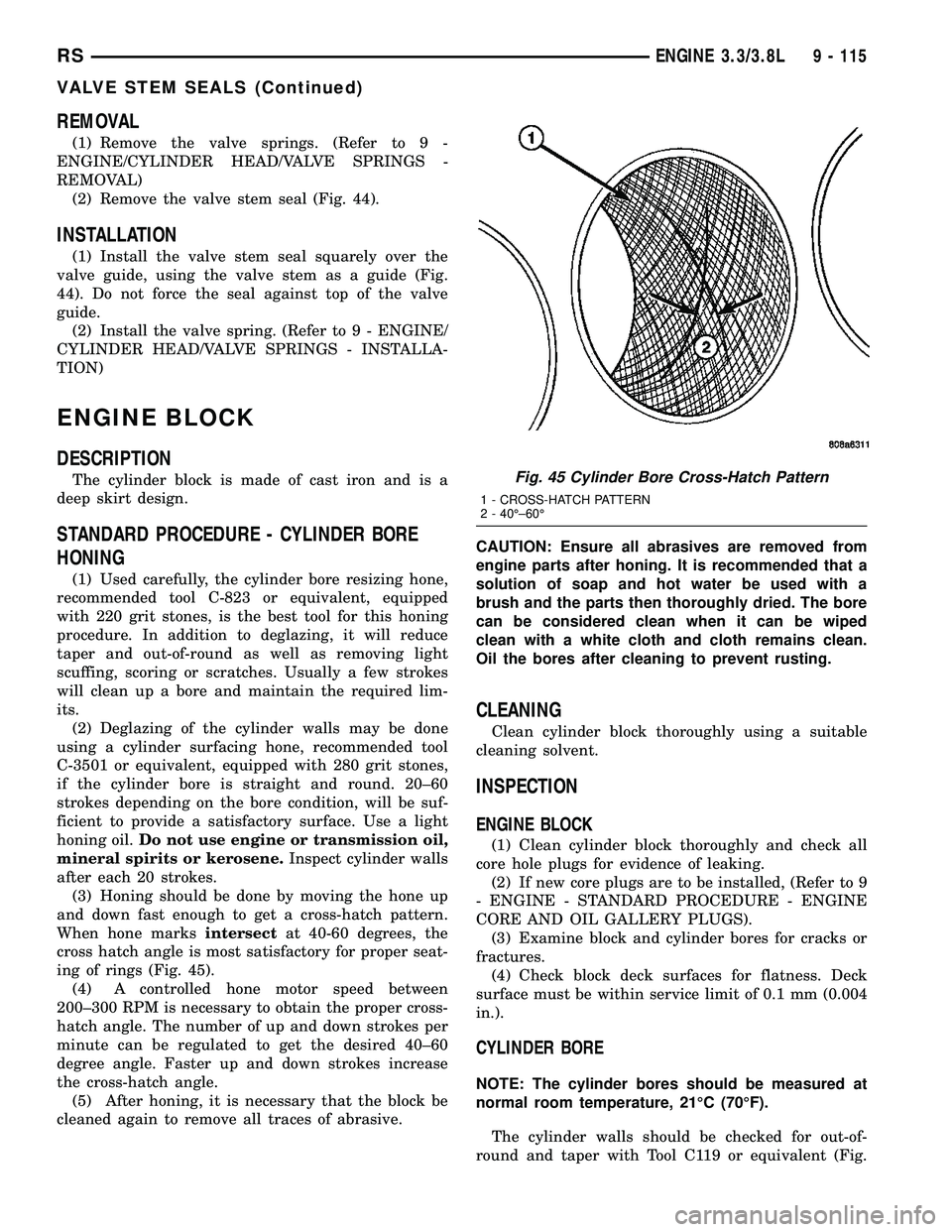
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 40-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 45).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly using a suitable
cleaning solvent.
INSPECTION
ENGINE BLOCK
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
(2) If new core plugs are to be installed, (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
CORE AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS).
(3) Examine block and cylinder bores for cracks or
fractures.
(4) Check block deck surfaces for flatness. Deck
surface must be within service limit of 0.1 mm (0.004
in.).
CYLINDER BORE
NOTE: The cylinder bores should be measured at
normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C119 or equivalent (Fig.
Fig. 45 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
1 - CROSS-HATCH PATTERN
2 - 40ɱ60É
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 115
VALVE STEM SEALS (Continued)
Page 1377 of 2339

INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surface.
(6) Install the Upper Intake Manifold, refer to
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more information.
(7) Install fuel hose quick connector fitting to chas-
sis tubes.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Push the
fitting onto the chassis tube until it clicks into place.
Pull on the fitting to ensure complete insertion.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module. The tank is made
from High density Polyethylene (HDPE) material.If
equipped with ORVR (Onboard Refueling Vapor
Recovery) it has been added to the fuel tank to con-
trol refueling vapor emissions.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with either one or two
check valves mounted into the top of the fuel tank (or
pump module).
An evaporation control system is connected to the
check valve(s)/control valve(Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/
ORVR - OPERATION) to reduce emissions of fuel
vapors into the atmosphere, when the tank is vented
due to vapor expansion in the tank. When fuel evap-
orates from the fuel tank, vapors pass through vent
hoses or tubes to a charcoal canister where they are
temporarily held. When the engine is running, the
vapors are drawn into the intake manifold. In addi-
tion, fuel vapors produced during vehicle refueling
are allowed to pass through the vent hoses/tubes to
the charcoal canister(s) for temporary storage (priorto being drawn into the intake manifold). All models
are equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) or Natural Vacuum
Leak Detection (NVLD). Refer to the Emission Con-
trol System for additional information.
INLET CHECK VALVE
All vehicles have an inlet check valve on the inside
of the fuel tank at the filler inlet
The valve prevents fuel from splashing back on
customer during vehicle refueling. The valve is a
non-serviceable item.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure (Fig. 18).
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(6) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(7) Lower tank slightly.
(8) Disconnect the fuel filler vent tube. Squeeze
tabs and pull apart (Fig. 19).
Fig. 18 Fuel Tank
1 - ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL FILLER INLET
3 - ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
14 - 12 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1380 of 2339
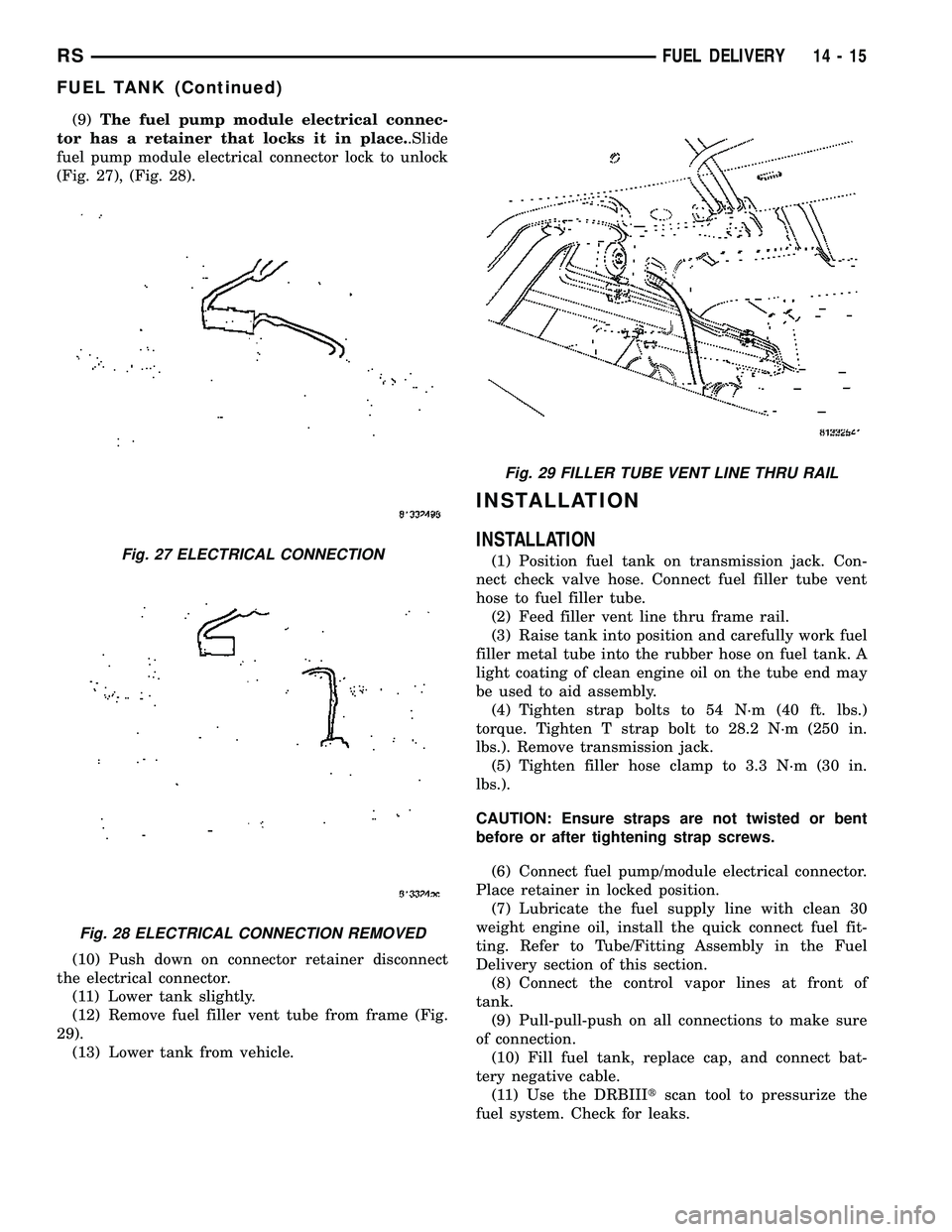
(9)The fuel pump module electrical connec-
tor has a retainer that locks it in place..Slide
fuel pump module electrical connector lock to unlock
(Fig. 27), (Fig. 28).
(10) Push down on connector retainer disconnect
the electrical connector.
(11) Lower tank slightly.
(12) Remove fuel filler vent tube from frame (Fig.
29).
(13) Lower tank from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fuel tank on transmission jack. Con-
nect check valve hose. Connect fuel filler tube vent
hose to fuel filler tube.
(2) Feed filler vent line thru frame rail.
(3) Raise tank into position and carefully work fuel
filler metal tube into the rubber hose on fuel tank. A
light coating of clean engine oil on the tube end may
be used to aid assembly.
(4) Tighten strap bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
torque. Tighten T strap bolt to 28.2 N´m (250 in.
lbs.). Remove transmission jack.
(5) Tighten filler hose clamp to 3.3 N´m (30 in.
lbs.).
CAUTION: Ensure straps are not twisted or bent
before or after tightening strap screws.
(6) Connect fuel pump/module electrical connector.
Place retainer in locked position.
(7) Lubricate the fuel supply line with clean 30
weight engine oil, install the quick connect fuel fit-
ting. Refer to Tube/Fitting Assembly in the Fuel
Delivery section of this section.
(8) Connect the control vapor lines at front of
tank.
(9) Pull-pull-push on all connections to make sure
of connection.
(10) Fill fuel tank, replace cap, and connect bat-
tery negative cable.
(11) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.Fig. 27 ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
Fig. 28 ELECTRICAL CONNECTION REMOVED
Fig. 29 FILLER TUBE VENT LINE THRU RAIL
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-15
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1462 of 2339

TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE..............141TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE............146
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTE
TRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS........5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST....5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS.....................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS.....................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE....9
REMOVAL.............................9
DISASSEMBLY.........................12
ASSEMBLY............................29
INSTALLATION.........................51
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
4XTE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC
SCHEMATICS........................54
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE.......66
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................68
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................73
OPERATION...........................73
DRIVING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION.........................74
OPERATION...........................74
FINAL DRIVE
DESCRIPTION.........................74
OPERATION...........................75
DISASSEMBLY.........................75
ASSEMBLY............................78
ADJUSTMENTS
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD
MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT......79FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK....82
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER SERVICE......................82
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL.............................84
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION.........................86
OPERATION...........................86
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY.........................86
ASSEMBLY............................95
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................110
OPERATION..........................110
DISASSEMBLY........................110
ASSEMBLY...........................112
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................112
OPERATION..........................112
SEAL - OIL PUMP
REMOVAL............................113
INSTALLATION........................113
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................113
OPERATION..........................114
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID..........................115
REMOVAL............................115
INSTALLATION........................116
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY
DESCRIPTION........................117
OPERATION..........................118
REMOVAL............................118
INSTALLATION........................119
RSTRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE21-1
Page 1463 of 2339

SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION........................120
OPERATION..........................120
REMOVAL............................121
INSTALLATION........................121
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION........................122
OPERATION..........................122
REMOVAL............................123
INSTALLATION........................123
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................124
OPERATION..........................128
REMOVAL............................129
INSTALLATION........................129TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................130
OPERATION..........................130
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................130
OPERATION..........................131
REMOVAL............................131
INSTALLATION........................131
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................132
OPERATION..........................132
REMOVAL............................133
DISASSEMBLY........................135
ASSEMBLY...........................139
INSTALLATION........................144
40TE AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION
The 40TE (Fig. 1) is a four-speed transaxle that is
a conventional hydraulic/mechanical assembly with
an integral differential, and is controlled with adap-
tive electronic controls and monitors. The hydraulic
system of the transaxle consists of the transaxle
fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic valves, and various
line pressure control components. An input clutch
assembly which houses the underdrive, overdrive,
and reverse clutches is used. It also utilizes separate
holding clutches: 2nd/4th gear and Low/Reverse. The
primary mechanical components of the transaxle con-
sist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Two multiple disc holding clutches
²Four hydraulic accumulators
²Two planetary gear sets
²Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body²Solenoid/Pressure switch assembly
²Integral differential assembly
Control of the transaxle is accomplished by fully
adaptive electronics. Optimum shift scheduling is
accomplished through continuous real-time sensor
feedback information provided to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) or Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
The PCM/TCM is the heart of the electronic control
system and relies on information from various direct
and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.) to deter-
mine driver demand and vehicle operating condi-
tions. With this information, the PCM/TCM can
calculate and perform timely and quality shifts
through various output or control devices (solenoid
pack, transmission control relay, etc.).
The PCM/TCM also performs certain self-diagnos-
tic functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
21 - 2 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1470 of 2339
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
F
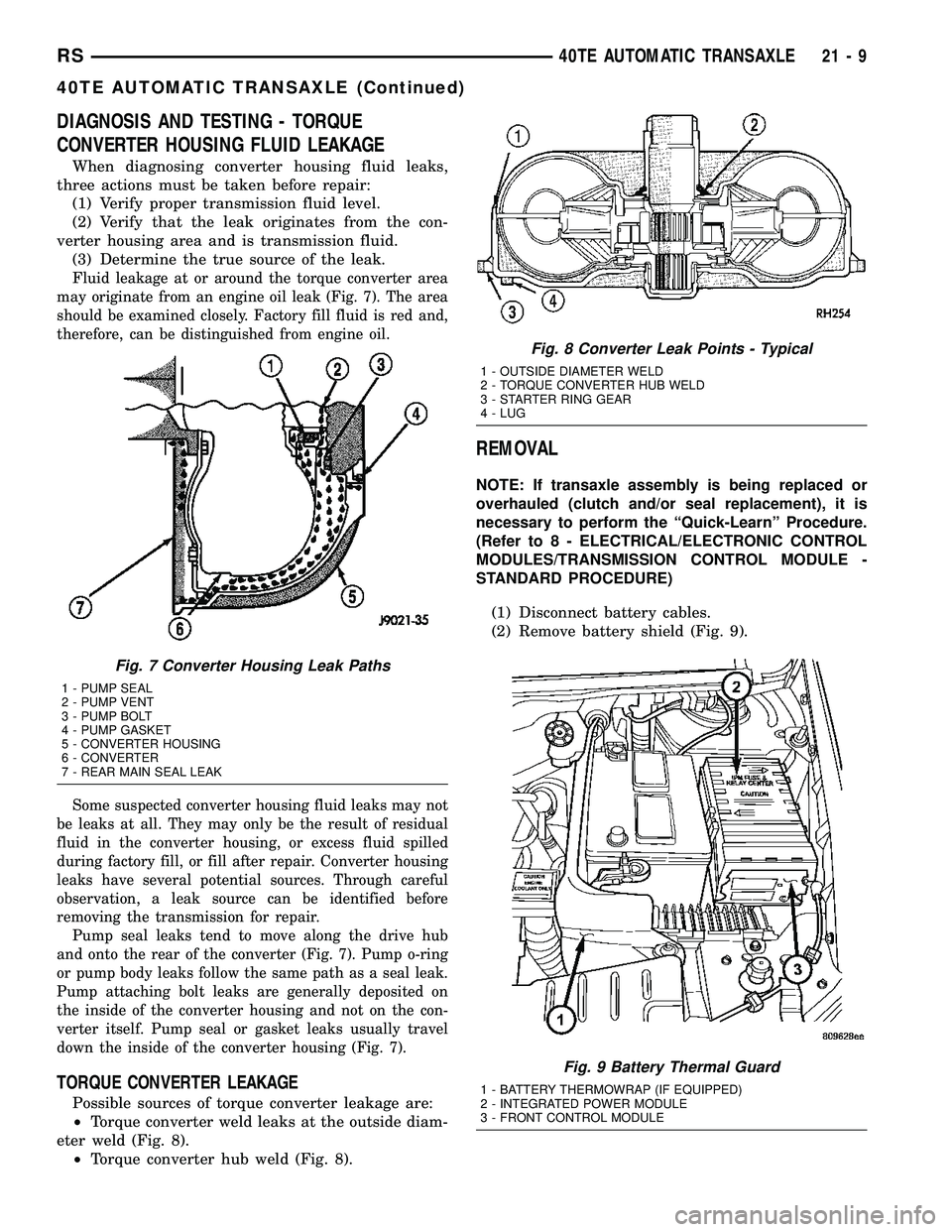
luid leakage at or around the torque converter area
may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 7). The area
should be examined closely. Factory fill fluid is red and,
therefore, can be distinguished from engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may not
be leaks at all. They may only be the result of residual
fluid in the converter housing, or excess fluid spilled
during factory fill, or fill after repair. Converter housing
leaks have several potential sources. Through careful
observation, a leak source can be identified before
removing the transmission for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 7). Pump o-ring
or pump body leaks follow the same path as a seal leak.
Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally deposited on
the inside of the converter housing and not on the con-
verter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaks usually travel
down the inside of the converter housing (Fig. 7).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 8).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transaxle assembly is being replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perform the ªQuick-Learnº Procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield (Fig. 9).
Fig. 7 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 8 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
Fig. 9 Battery Thermal Guard
1 - BATTERY THERMOWRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-9
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1471 of 2339
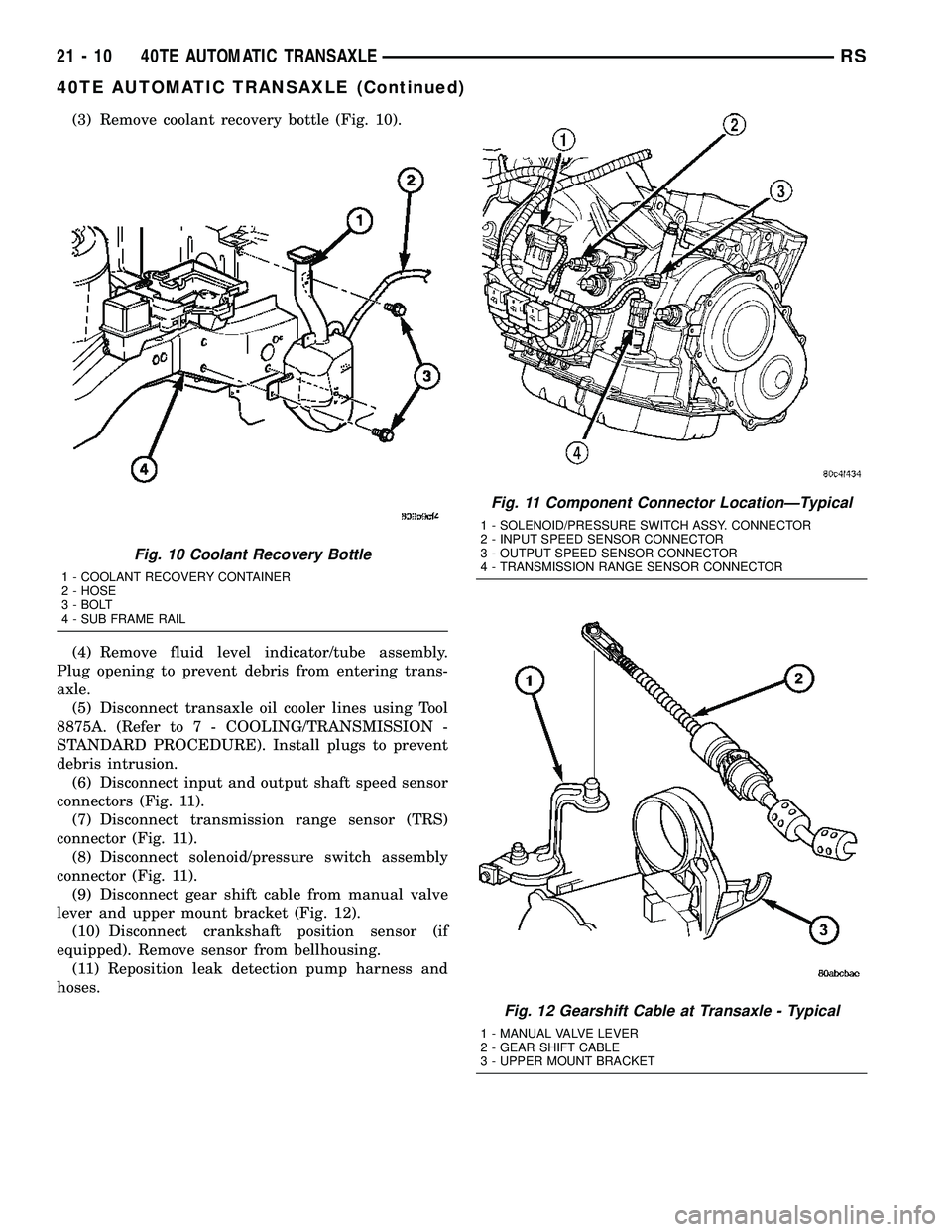
(3) Remove coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle.
(5) Disconnect transaxle oil cooler lines using Tool
8875A. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Install plugs to prevent
debris intrusion.
(6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 11).
(7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 11).
(8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 11).
(9) Disconnect gear shift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 12).
(10) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor (if
equipped). Remove sensor from bellhousing.
(11) Reposition leak detection pump harness and
hoses.
Fig. 10 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
2 - HOSE
3 - BOLT
4 - SUB FRAME RAIL
Fig. 11 Component Connector LocationÐTypical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 12 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
21 - 10 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)