2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN transmission oil
[x] Cancel search: transmission oilPage 1118 of 2339
CONNECTOR NAME/NUMBER COLOR LOCATION FIG.
Engine Coolant Temp Sensor
(Gas)BK On Cylinder Block N/S
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
(Diesel)BK Rear of Engine 16
Engine Coolant Temp Sensor
(Diesel)BL On Cylinder Block 15
Engine Oil Pressure Switch (Gas) LTGN On Cylinder Block 12, 18
Engine Starter Motor At Starter Motor 13, 15, 18
EVAP/Purge Solenoid (Gas) BK Right Motor Mount 10, 17
Evaporator Temperature Sensor BK Right Side of HVAC N/S
Floor Console Lamp BK At Lamp N/S
Floor Console Power Outlet RD At Front Console N/S
Front Blower Module C1 (ATC) BK On HVAC N/S
Front Blower Module C2 (ATC) BK On HVAC N/S
Front Cigar Lighter RD/NAT Rear of Lighter 20, 23, 25
Front Control Module BK In Integrated Power Module N/S
Front Intrusion Sensor (United
Kingdom)BK At Sensor N/S
Front Reading Lamps/Switch BK At Switch N/S
Fuel Heater (Diesel) BK Left Rear Engine Compartment N/S
Fuel Injector No.1 (2.4L/3.3L/
3.8L)BK At Fuel Injector N/S
Fuel Injector No.1 (Diesel) BK At Fuel Injector 15
Fuel Injector No.2 (2.4L/3.3L/
3.8L)BK At Fuel Injector N/S
Fuel Injector No.2 (Diesel) BK At Fuel Injector 15
Fuel Injector No.3 (2.4L/3.3L/
3.8L)BK At Fuel Injector N/S
Fuel Injector No.3 (Diesel) BK At Fuel Injector 15
Fuel Injector No.4 (2.4L/3.3L/
3.8L)BK At Fuel Injector N/S
Fuel Injector No.4 (Diesel) BK At Fuel Injector 15
Fuel Injector No.5 (3.3L/3.8L) BK At Fuel Injector N/S
Fuel Injector No.6 (3.3L/3.8L) BK At Fuel Injector N/S
Fuel Pressure Sensor (Diesel) BK Top Left of Engine 15
Fuel Pressure Solenoid (Diesel) Right Front Engine 15
Fuel Pump Module LTGY Side of Fuel Tank 34
Generator BK Rear of Generator 11, 15, 17, 18
Glow Plug No.1 (Diesel) Top of Engine N/S
Glow Plug No.2 (Diesel) Top of Engine 15
Glow Plug No.3 (Diesel) Top of Engine 15
Glow Plug No.4 (Diesel) Top of Engine 15
Glow Plug Relay (Diesel) BK Near Transmission 15, 16
Hands Free Module C1 Instrument Panel N/S
RS8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION8W-91-5
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1119 of 2339
CONNECTOR NAME/NUMBER COLOR LOCATION FIG.
Hands Free Module C2 BK Instrument Panel N/S
Hands Free Module C3 Instrument Panel N/S
Headlamp Switch BK Rear of Switch 20, 21, 30
Headlamp Washer Pump Motor
(Export)BK At Motor 3
High Note Horn BK Left Frame Rail 5
Hood Ajar Switch (Export) BK Left Fender 6
Idle Air Control Motor (Gas) BK On Throttle Body 10, 11 17
Ignition Coil (2.4L) BK Top of Valve Cover 10, 11
Ignition Coil (3.3L/ 3.8L) DKGY Top of Engine 17, 18
Ignition Switch BK Rear of Switch at Steering Column 20, 21, 22, 23, 31
Inlet Air Temperature Sensor BK Top Left of Engine 9, 10, 11, 17
Input Speed Sensor GY Front of Transmission 14, 19
Instrument Cluster BK Rear of Cluster 20, 21, 28
Instrument Panel Switch Bank
(Heated Seats)BK Right Center of Instrument Panel 20, 23, 25
Instrument Panel Switch Bank
(Except Heated Seats)Right Center of Instrument Panel 20, 23, 25
Integrated Power Module C1 Left Fender Shield 7
Integrated Power Module C2 GN/BL Left Fender Shield 7
Integrated Power Module C3 Left Fender Shield 7, 11
Integrated Power Module C4 BL Left Fender Shield 7, 11
Integrated Power Module C5 BK Left Fender Shield 7
Integrated Power Module C6 NAT Left Fender Shield 7
Integrated Power Module C7 Left Fender Shield 7
Integrated Power Module C8 OR Left Fender Shield 7
Integrated Power Module C9 BK Left Fender Shield 7
Knock Sensor (Except Export) BK At Engine Block 11
Left B Pillar Switch (Power
Sliding Door)GY Left B Pillar 40
Left Cinch/Release Motor (Power
Sliding Door)GY Left Sliding Door N/S
Left Curtain Airbag Squib Rear of Left Roof Rail 47
Left Cylinder Lock Switch BK At Switch 43
Left Door Speaker BK At Speaker 43
Left Fog Lamp BK At Lamp 5
Left Front Door Ajar Switch
(Base)BK At Switch N/S
Left Front Door Lock Motor/Ajar
Switch (Except Base)BK Left Door 43
Left Front Impact Sensor BK Near T/O for C101 5
Left Front Park/Turn Signal Lamp
(Except Export)DKGY At Lamp 1
Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor GY Left Fender Side Shield 5, 11
8W - 91 - 6 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONRS
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1186 of 2339

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-9
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1188 of 2339

(11) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
(13) Start engine and check for any leaks.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN IIis used to seal
components exposed to engine oil. This material is a
specially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTVis a specifically designed
black silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and
sealing properties to seal components exposed to
automatic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKERis an anaerobic type
gasket material. The material cures in the absence of
air when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It
will not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The
anaerobic material is for use between two machined
surfaces. Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtBED PLATE SEALANTis a unique
(green-in-color) anaerobic type gasket material that
is specially made to seal the area between the bed
plate and cylinder block without disturbing the bear-
ing clearance or alignment of these components. The
material cures slowly in the absence of air when
torqued between two metallic surfaces, and will rap-
idly cure when heat is applied.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANTis a slow drying,
permanently soft sealer. This material is recom-
mended for sealing threaded fittings and gasketsagainst leakage of oil and coolant. Can be used on
threaded and machined parts under all tempera-
tures. This material is used on engines with multi-
layer steel (MLS) cylinder head gaskets. This
material also will prevent corrosion. MopartGasket
Sealant is available in a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16
oz. can w/applicator.
SEALER APPLICATION
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE GASKET
SURFACE PREPARATION
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
Neveruse the following to clean gasket surfaces:
²Metal scraper
²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 3)
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 3)
RSENGINE 2.4L9-11
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1190 of 2339
(9) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug cooler
lines and fittings to prevent debris from entering
transaxle or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be
installed upon reassembly.
(10) Disconnect transmission shift linkage and
electrical connectors.
(11) Disconnect throttle body linkage.
(12) Disconnect engine wiring harness.
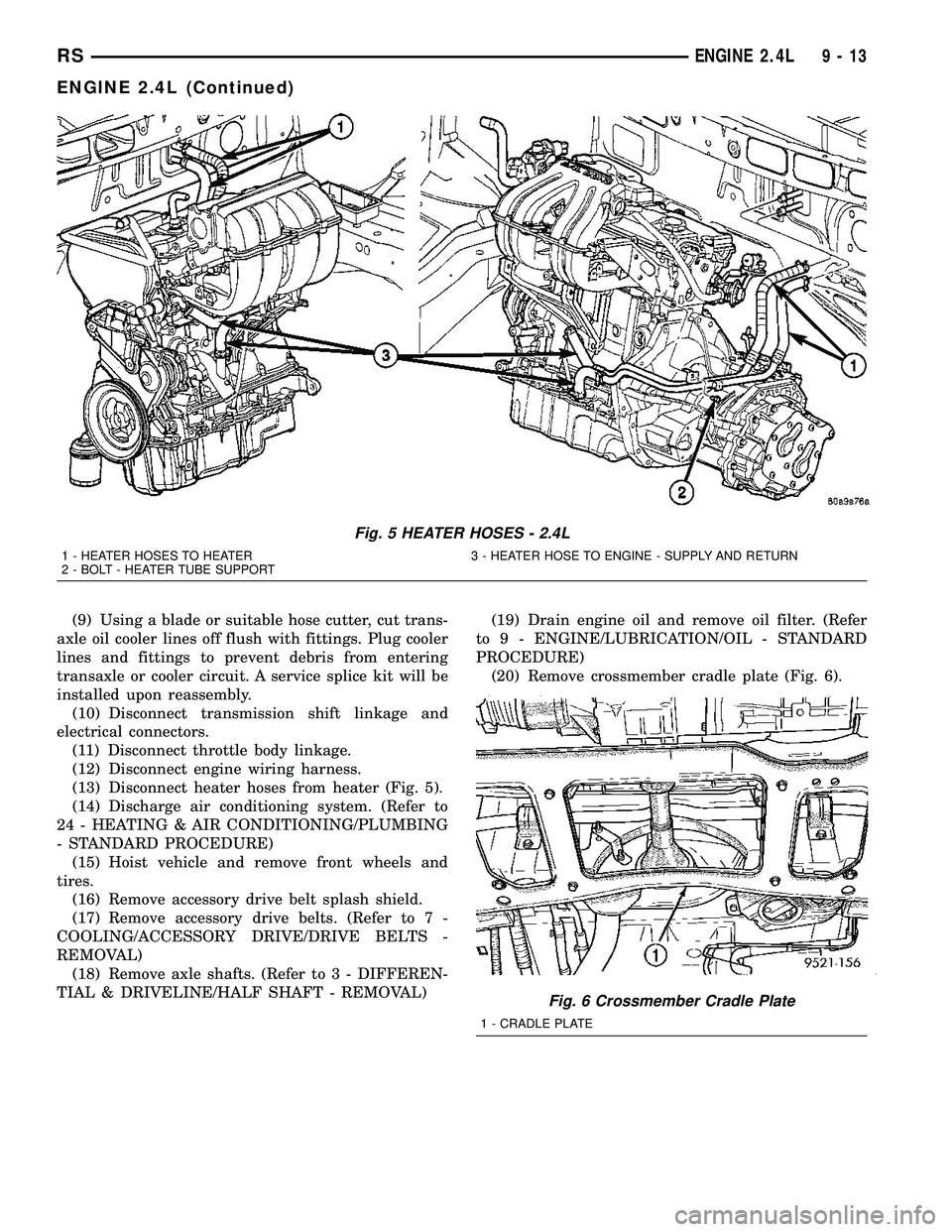
(13) Disconnect heater hoses from heater (Fig. 5).
(14) Discharge air conditioning system. (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(15) Hoist vehicle and remove front wheels and
tires.
(16) Remove accessory drive belt splash shield.
(17) Remove accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL)
(18) Remove axle shafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - REMOVAL)(19) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(20) Remove crossmember cradle plate (Fig. 6).
Fig. 5 HEATER HOSES - 2.4L
1 - HEATER HOSES TO HEATER 3 - HEATER HOSE TO ENGINE - SUPPLY AND RETURN
2 - BOLT - HEATER TUBE SUPPORT
Fig. 6 Crossmember Cradle Plate
1 - CRADLE PLATE
RSENGINE 2.4L9-13
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1191 of 2339
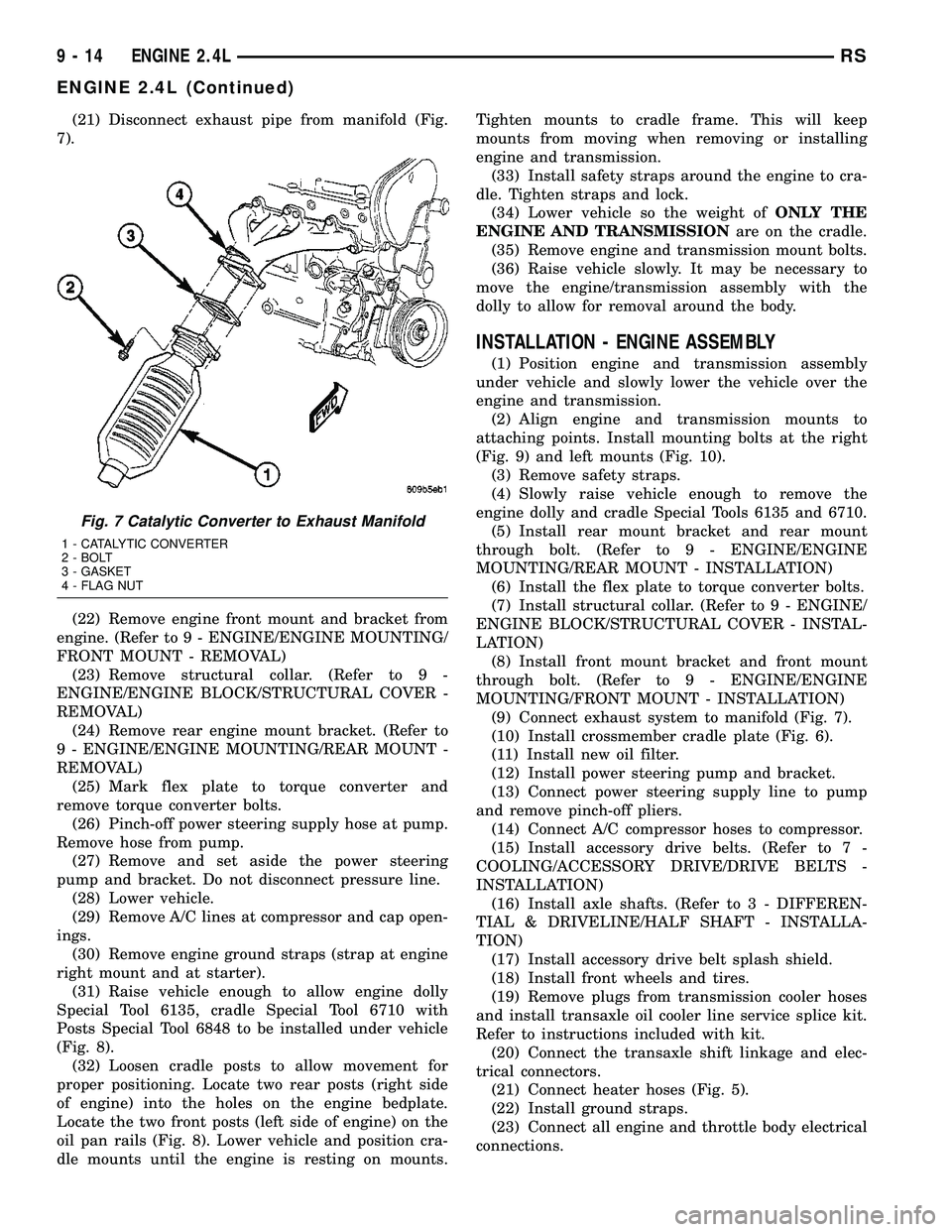
(21) Disconnect exhaust pipe from manifold (Fig.
7).
(22) Remove engine front mount and bracket from
engine. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/
FRONT MOUNT - REMOVAL)
(23) Remove structural collar. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER -
REMOVAL)
(24) Remove rear engine mount bracket. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/REAR MOUNT -
REMOVAL)
(25) Mark flex plate to torque converter and
remove torque converter bolts.
(26) Pinch-off power steering supply hose at pump.
Remove hose from pump.
(27) Remove and set aside the power steering
pump and bracket. Do not disconnect pressure line.
(28) Lower vehicle.
(29) Remove A/C lines at compressor and cap open-
ings.
(30) Remove engine ground straps (strap at engine
right mount and at starter).
(31) Raise vehicle enough to allow engine dolly
Special Tool 6135, cradle Special Tool 6710 with
Posts Special Tool 6848 to be installed under vehicle
(Fig. 8).
(32) Loosen cradle posts to allow movement for
proper positioning. Locate two rear posts (right side
of engine) into the holes on the engine bedplate.
Locate the two front posts (left side of engine) on the
oil pan rails (Fig. 8). Lower vehicle and position cra-
dle mounts until the engine is resting on mounts.Tighten mounts to cradle frame. This will keep
mounts from moving when removing or installing
engine and transmission.
(33) Install safety straps around the engine to cra-
dle. Tighten straps and lock.
(34) Lower vehicle so the weight ofONLY THE
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSIONare on the cradle.
(35) Remove engine and transmission mount bolts.
(36) Raise vehicle slowly. It may be necessary to
move the engine/transmission assembly with the
dolly to allow for removal around the body.
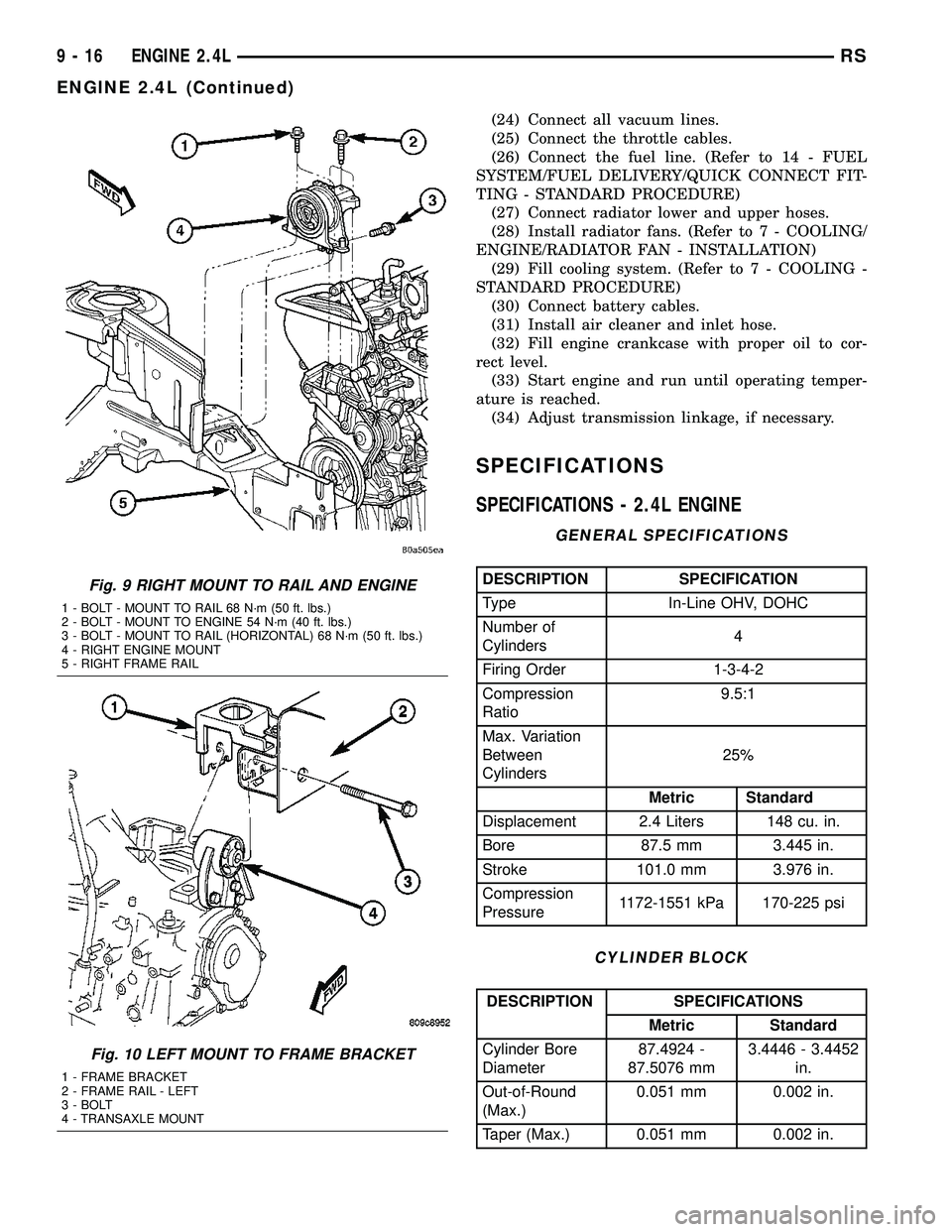
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ASSEMBLY
(1) Position engine and transmission assembly
under vehicle and slowly lower the vehicle over the
engine and transmission.
(2) Align engine and transmission mounts to
attaching points. Install mounting bolts at the right
(Fig. 9) and left mounts (Fig. 10).
(3) Remove safety straps.
(4) Slowly raise vehicle enough to remove the
engine dolly and cradle Special Tools 6135 and 6710.
(5) Install rear mount bracket and rear mount
through bolt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE
MOUNTING/REAR MOUNT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install the flex plate to torque converter bolts.
(7) Install structural collar. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - INSTAL-
LATION)
(8) Install front mount bracket and front mount
through bolt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE
MOUNTING/FRONT MOUNT - INSTALLATION)
(9) Connect exhaust system to manifold (Fig. 7).
(10) Install crossmember cradle plate (Fig. 6).
(11) Install new oil filter.
(12) Install power steering pump and bracket.
(13) Connect power steering supply line to pump
and remove pinch-off pliers.
(14) Connect A/C compressor hoses to compressor.
(15) Install accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION)
(16) Install axle shafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - INSTALLA-
TION)
(17) Install accessory drive belt splash shield.
(18) Install front wheels and tires.
(19) Remove plugs from transmission cooler hoses
and install transaxle oil cooler line service splice kit.
Refer to instructions included with kit.
(20) Connect the transaxle shift linkage and elec-
trical connectors.
(21) Connect heater hoses (Fig. 5).
(22) Install ground straps.
(23) Connect all engine and throttle body electrical
connections.
Fig. 7 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - BOLT
3 - GASKET
4 - FLAG NUT
9 - 14 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1193 of 2339
(24) Connect all vacuum lines.
(25) Connect the throttle cables.
(26) Connect the fuel line. (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FIT-
TING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(27) Connect radiator lower and upper hoses.
(28) Install radiator fans. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION)
(29) Fill cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(30) Connect battery cables.
(31) Install air cleaner and inlet hose.
(32) Fill engine crankcase with proper oil to cor-
rect level.
(33) Start engine and run until operating temper-
ature is reached.
(34) Adjust transmission linkage, if necessary.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 2.4L ENGINE
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Type In-Line OHV, DOHC
Number of
Cylinders4
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Compression
Ratio9.5:1
Max. Variation
Between
Cylinders25%
Metric Standard
Displacement 2.4 Liters 148 cu. in.
Bore 87.5 mm 3.445 in.
Stroke 101.0 mm 3.976 in.
Compression
Pressure1172-1551 kPa 170-225 psi
CYLINDER BLOCK
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATIONS
Metric Standard
Cylinder Bore
Diameter87.4924 -
87.5076 mm3.4446 - 3.4452
in.
Out-of-Round
(Max.)0.051 mm 0.002 in.
Taper (Max.) 0.051 mm 0.002 in.
Fig. 9 RIGHT MOUNT TO RAIL AND ENGINE
1 - BOLT - MOUNT TO RAIL 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
2 - BOLT - MOUNT TO ENGINE 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
3 - BOLT - MOUNT TO RAIL (HORIZONTAL) 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
4 - RIGHT ENGINE MOUNT
5 - RIGHT FRAME RAIL
Fig. 10 LEFT MOUNT TO FRAME BRACKET
1 - FRAME BRACKET
2 - FRAME RAIL - LEFT
3 - BOLT
4 - TRANSAXLE MOUNT
9 - 16 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1213 of 2339
(4) Install spark plugs.
(5) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The cast iron cylinder block is a two-piece assem-
bly, consisting of the cylinder block and bed plate
(Fig. 40). The bed plate incorporates the main bear-
ing caps and bolts to the cylinder block. This design
offers a much stronger lower end and increased cyl-
inder block rigidity. The rear oil seal retainer is inte-
gral with the block. The bed plate and block are
serviced as an assembly.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
(1) Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone,
recommended tool C-823 or equivalent, equipped
with 220 grit stones, is the best tool for this honing
procedure. In addition to deglazing, it will reducetaper and out-of-round as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring or scratches. Usually a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, recommended tool
C-3501 or equivalent, equipped with 280 grit stones,
if the cylinder bore is straight and round. 20±60
strokes depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Use a light
honing oil.Do not use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.Inspect cylinder walls
after each 20 strokes.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 40-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 41).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
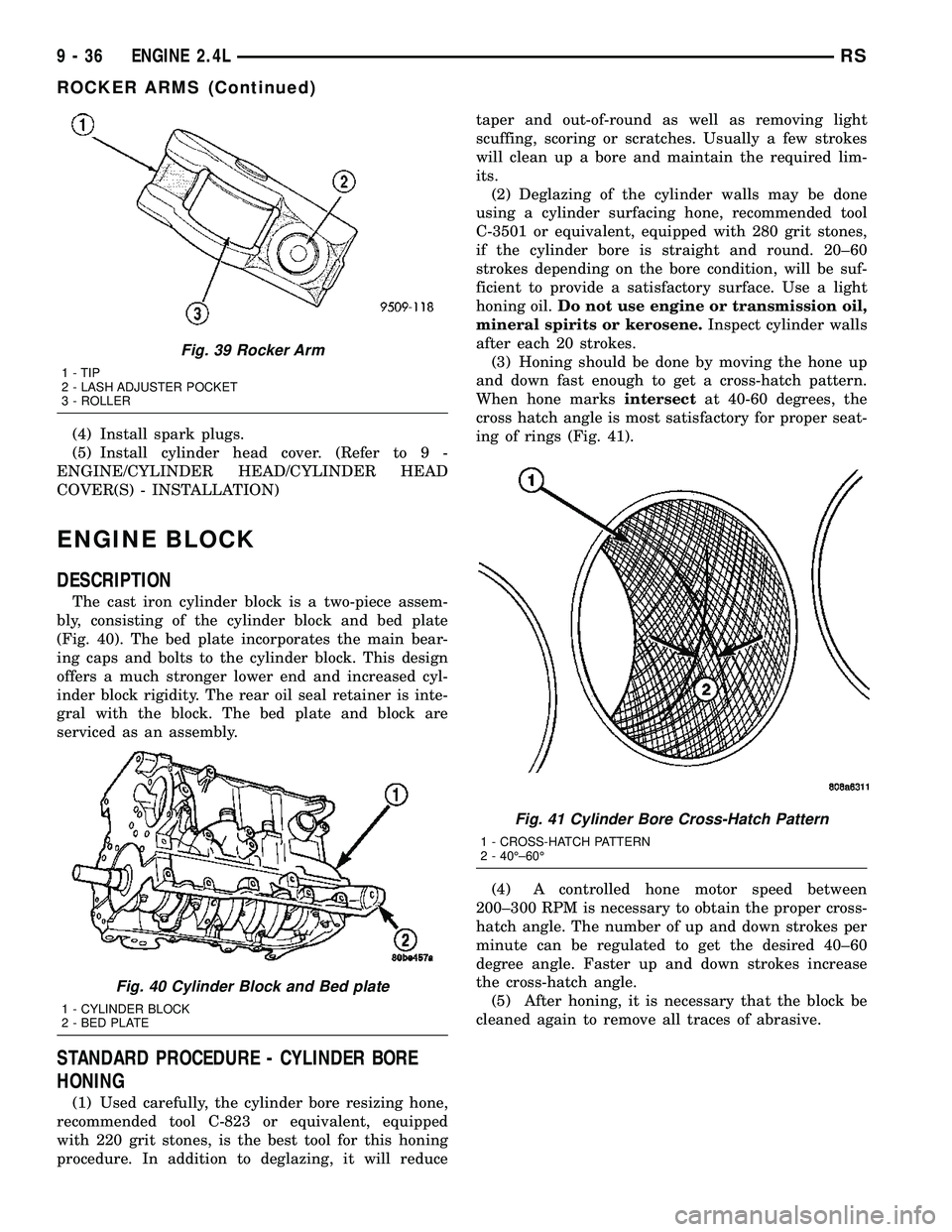
Fig. 39 Rocker Arm
1 - TIP
2 - LASH ADJUSTER POCKET
3 - ROLLER
Fig. 40 Cylinder Block and Bed plate
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - BED PLATE
Fig. 41 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
1 - CROSS-HATCH PATTERN
2 - 40ɱ60É
9 - 36 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ROCKER ARMS (Continued)