2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 1278 of 2339
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Unsnap 2 clips.
(2) Lift cover and pull toward the engine and
remove cover tabs from air box.
(3) Lift cover and remove the element (Fig. 15).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the air filter element into air box (Fig.
15).
(2) Move cover so that the tabs insert into the air
box.
(3) Push cover down and snap the 2 clips.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
Combustion Leak Tester C-3685-A
Pressure Transducer CH7059
Compression Test Adapter 8116
DRB IIITwith PEP Module OT-CH6010A
Fig. 15 AIR BOX COVER
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 101
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1279 of 2339
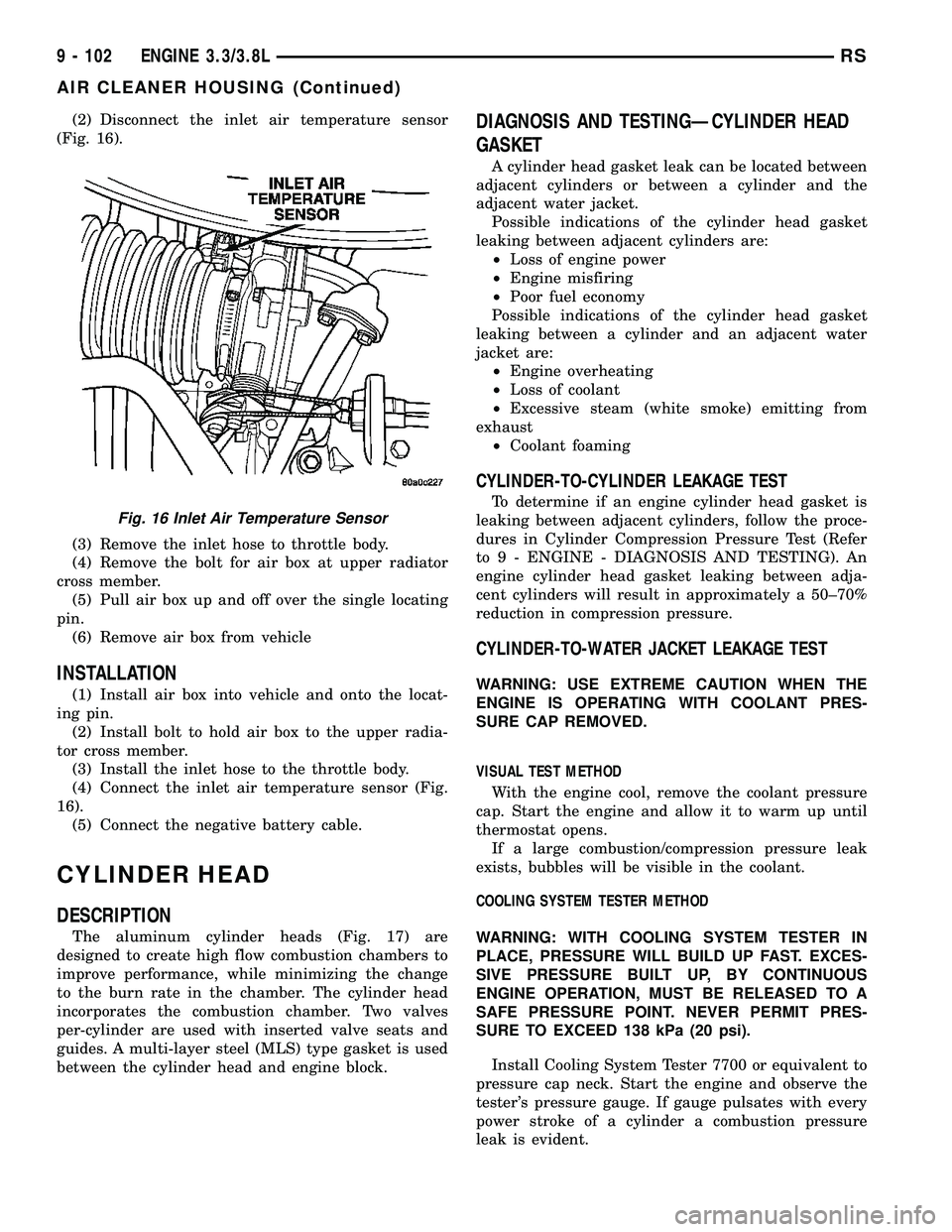
(2) Disconnect the inlet air temperature sensor
(Fig. 16).
(3) Remove the inlet hose to throttle body.
(4) Remove the bolt for air box at upper radiator
cross member.
(5) Pull air box up and off over the single locating
pin.
(6) Remove air box from vehicle
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air box into vehicle and onto the locat-
ing pin.
(2) Install bolt to hold air box to the upper radia-
tor cross member.
(3) Install the inlet hose to the throttle body.
(4) Connect the inlet air temperature sensor (Fig.
16).
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
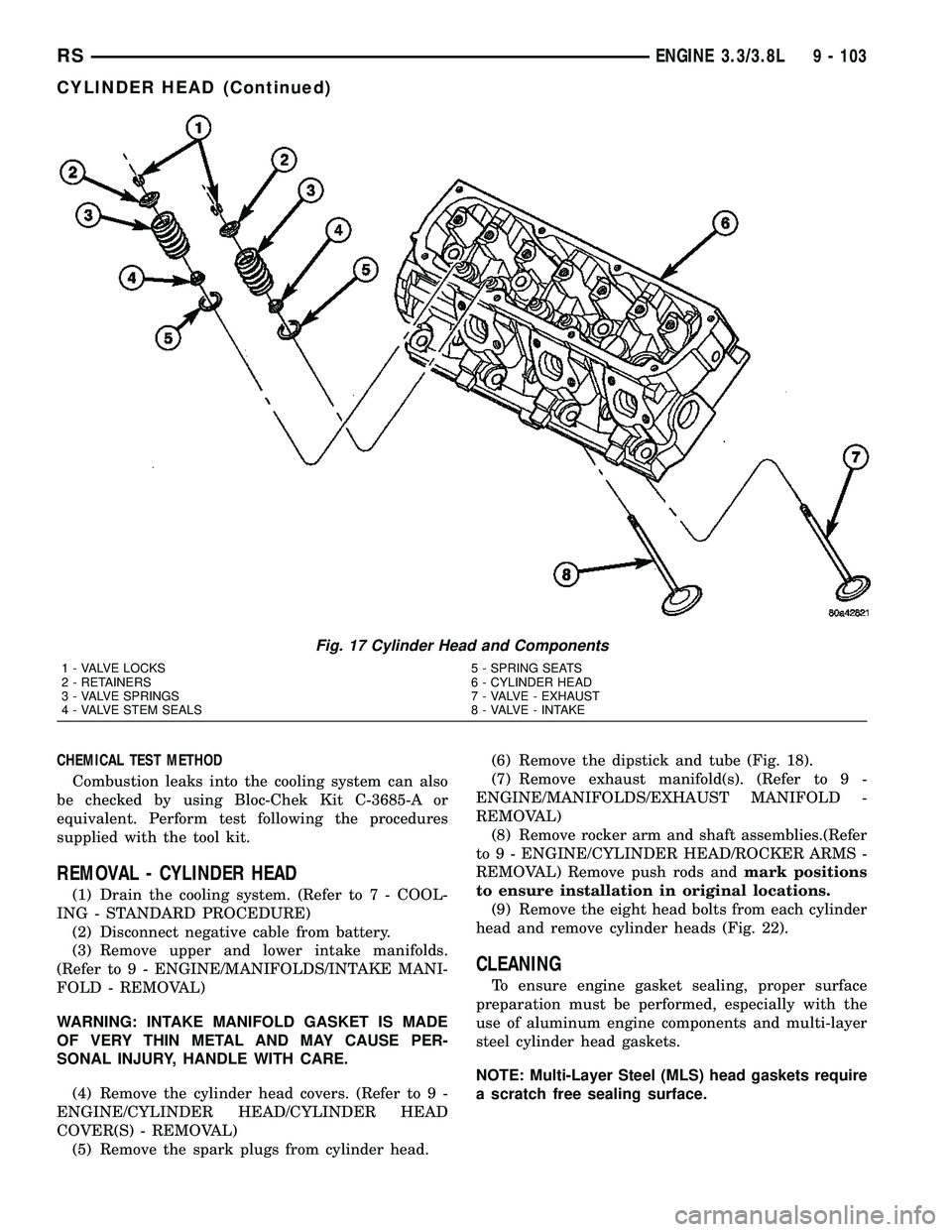
The aluminum cylinder heads (Fig. 17) are
designed to create high flow combustion chambers to
improve performance, while minimizing the change
to the burn rate in the chamber. The cylinder head
incorporates the combustion chamber. Two valves
per-cylinder are used with inserted valve seats and
guides. A multi-layer steel (MLS) type gasket is used
between the cylinder head and engine block.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
Fig. 16 Inlet Air Temperature Sensor
9 - 102 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
AIR CLEANER HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1280 of 2339
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper and lower intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - REMOVAL)
WARNING: INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET IS MADE
OF VERY THIN METAL AND MAY CAUSE PER-
SONAL INJURY, HANDLE WITH CARE.
(4) Remove the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(5) Remove the spark plugs from cylinder head.(6) Remove the dipstick and tube (Fig. 18).
(7) Remove exhaust manifold(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(8) Remove rocker arm and shaft assemblies.(Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
REMOVAL) Remove push rods andmark positions
to ensure installation in original locations.
(9) Remove the eight head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads (Fig. 22).
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Fig. 17 Cylinder Head and Components
1 - VALVE LOCKS 5 - SPRING SEATS
2 - RETAINERS 6 - CYLINDER HEAD
3 - VALVE SPRINGS 7 - VALVE - EXHAUST
4 - VALVE STEM SEALS 8 - VALVE - INTAKE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 103
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1282 of 2339
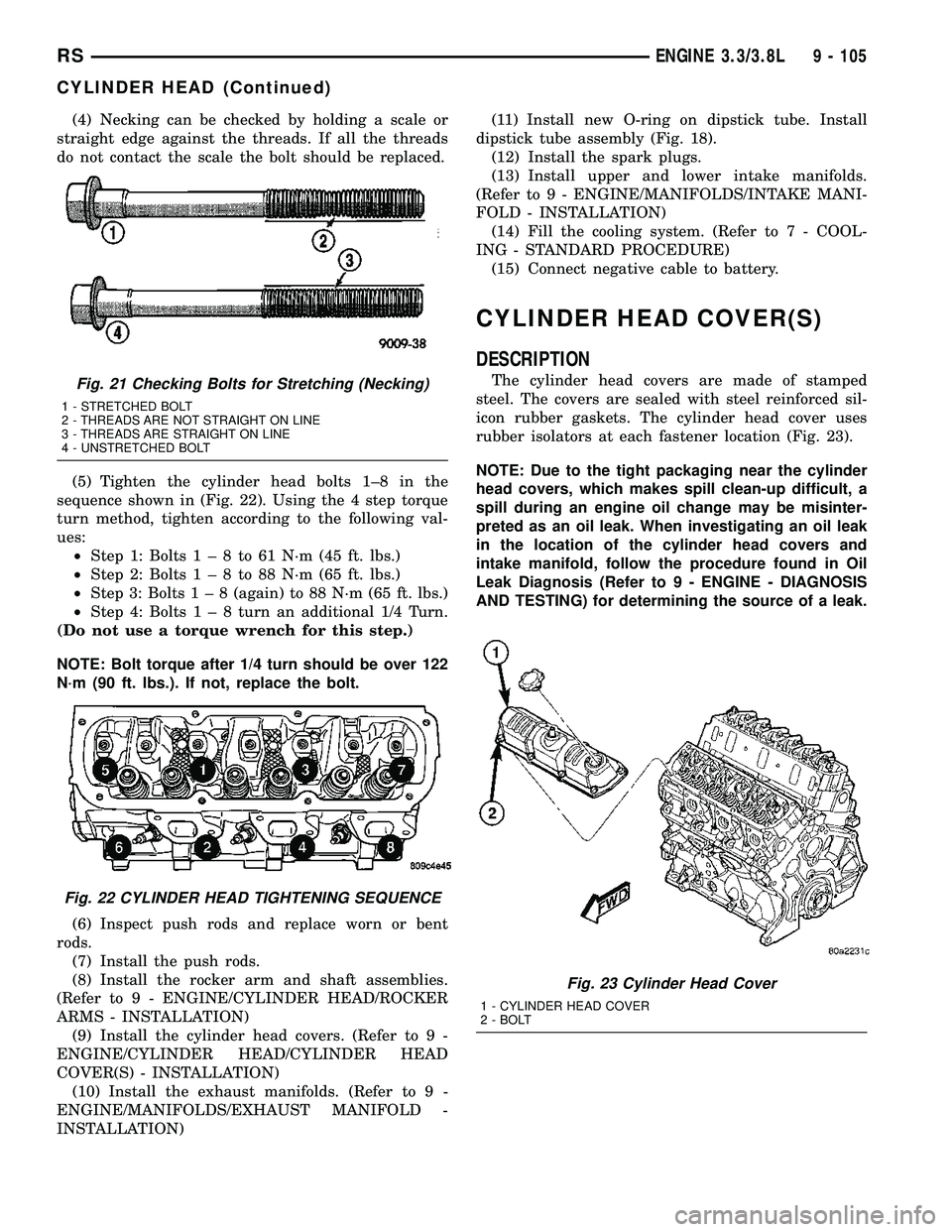
(4) Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale the bolt should be replaced.
(5) Tighten the cylinder head bolts 1±8 in the
sequence shown in (Fig. 22). Using the 4 step torque
turn method, tighten according to the following val-
ues:
²Step 1: Bolts1±8to61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
²Step 2: Bolts1±8to88N´m(65ft.lbs.)
²Step 3: Bolts1±8(again) to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.)
²Step 4: Bolts1±8turn an additional 1/4 Turn.
(Do not use a torque wrench for this step.)
NOTE: Bolt torque after 1/4 turn should be over 122
N´m (90 ft. lbs.). If not, replace the bolt.
(6) Inspect push rods and replace worn or bent
rods.
(7) Install the push rods.
(8) Install the rocker arm and shaft assemblies.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
ARMS - INSTALLATION)
(9) Install the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(10) Install the exhaust manifolds. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)(11) Install new O-ring on dipstick tube. Install
dipstick tube assembly (Fig. 18).
(12) Install the spark plugs.
(13) Install upper and lower intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - INSTALLATION)
(14) Fill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(15) Connect negative cable to battery.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of stamped
steel. The covers are sealed with steel reinforced sil-
icon rubber gaskets. The cylinder head cover uses
rubber isolators at each fastener location (Fig. 23).
NOTE: Due to the tight packaging near the cylinder
head covers, which makes spill clean-up difficult, a
spill during an engine oil change may be misinter-
preted as an oil leak. When investigating an oil leak
in the location of the cylinder head covers and
intake manifold, follow the procedure found in Oil
Leak Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for determining the source of a leak.Fig. 21 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 22 CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
Fig. 23 Cylinder Head Cover
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 105
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1283 of 2339
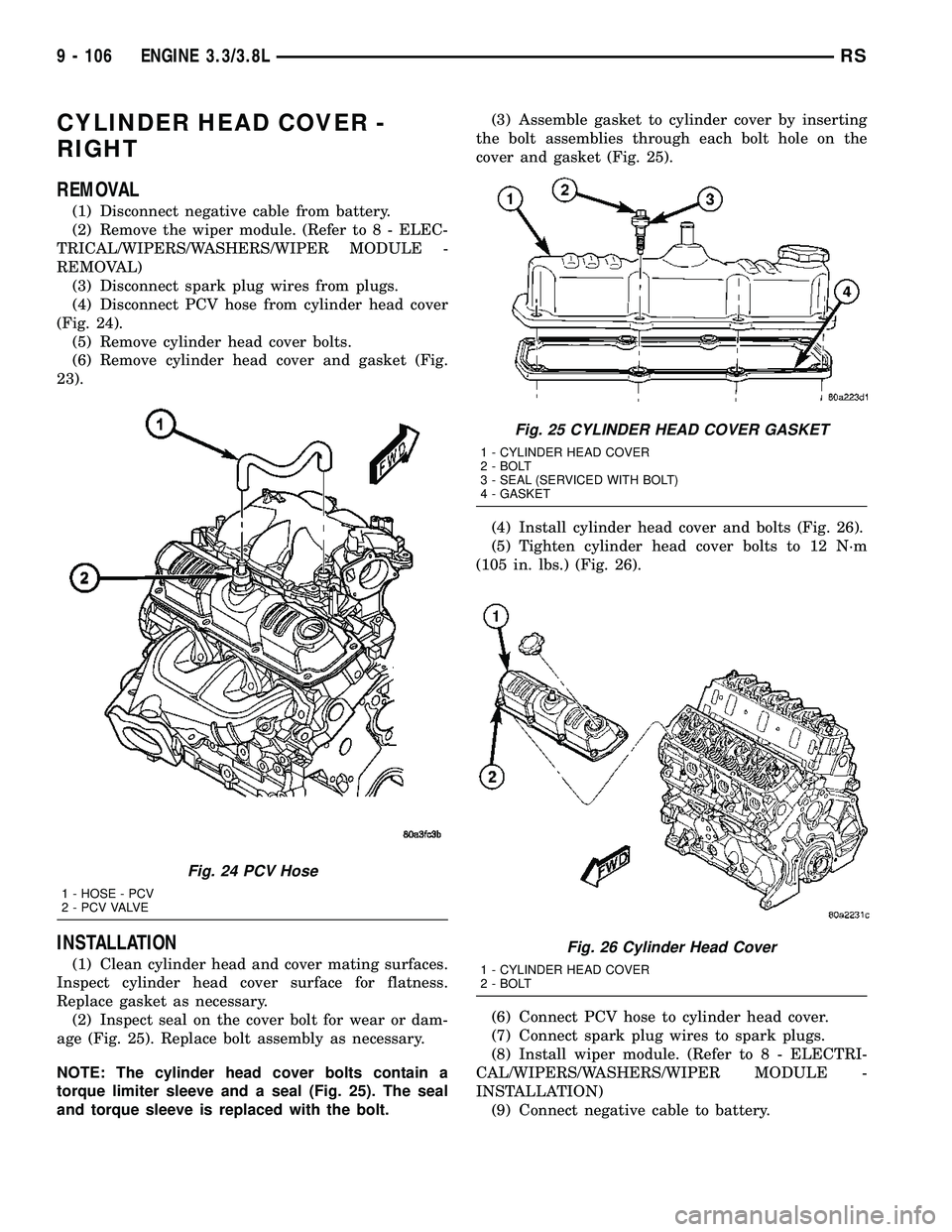
CYLINDER HEAD COVER -
RIGHT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the wiper module. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
REMOVAL)
(3) Disconnect spark plug wires from plugs.
(4) Disconnect PCV hose from cylinder head cover
(Fig. 24).
(5) Remove cylinder head cover bolts.
(6) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket (Fig.
23).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean cylinder head and cover mating surfaces.
Inspect cylinder head cover surface for flatness.
Replace gasket as necessary.
(2) Inspect seal on the cover bolt for wear or dam-
age (Fig. 25). Replace bolt assembly as necessary.
NOTE: The cylinder head cover bolts contain a
torque limiter sleeve and a seal (Fig. 25). The seal
and torque sleeve is replaced with the bolt.(3) Assemble gasket to cylinder cover by inserting
the bolt assemblies through each bolt hole on the
cover and gasket (Fig. 25).
(4) Install cylinder head cover and bolts (Fig. 26).
(5) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 26).
(6) Connect PCV hose to cylinder head cover.
(7) Connect spark plug wires to spark plugs.
(8) Install wiper module. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
INSTALLATION)
(9) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 24 PCV Hose
1 - HOSE - PCV
2 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 25 CYLINDER HEAD COVER GASKET
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT
3 - SEAL (SERVICED WITH BOLT)
4 - GASKET
Fig. 26 Cylinder Head Cover
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT
9 - 106 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
Page 1288 of 2339
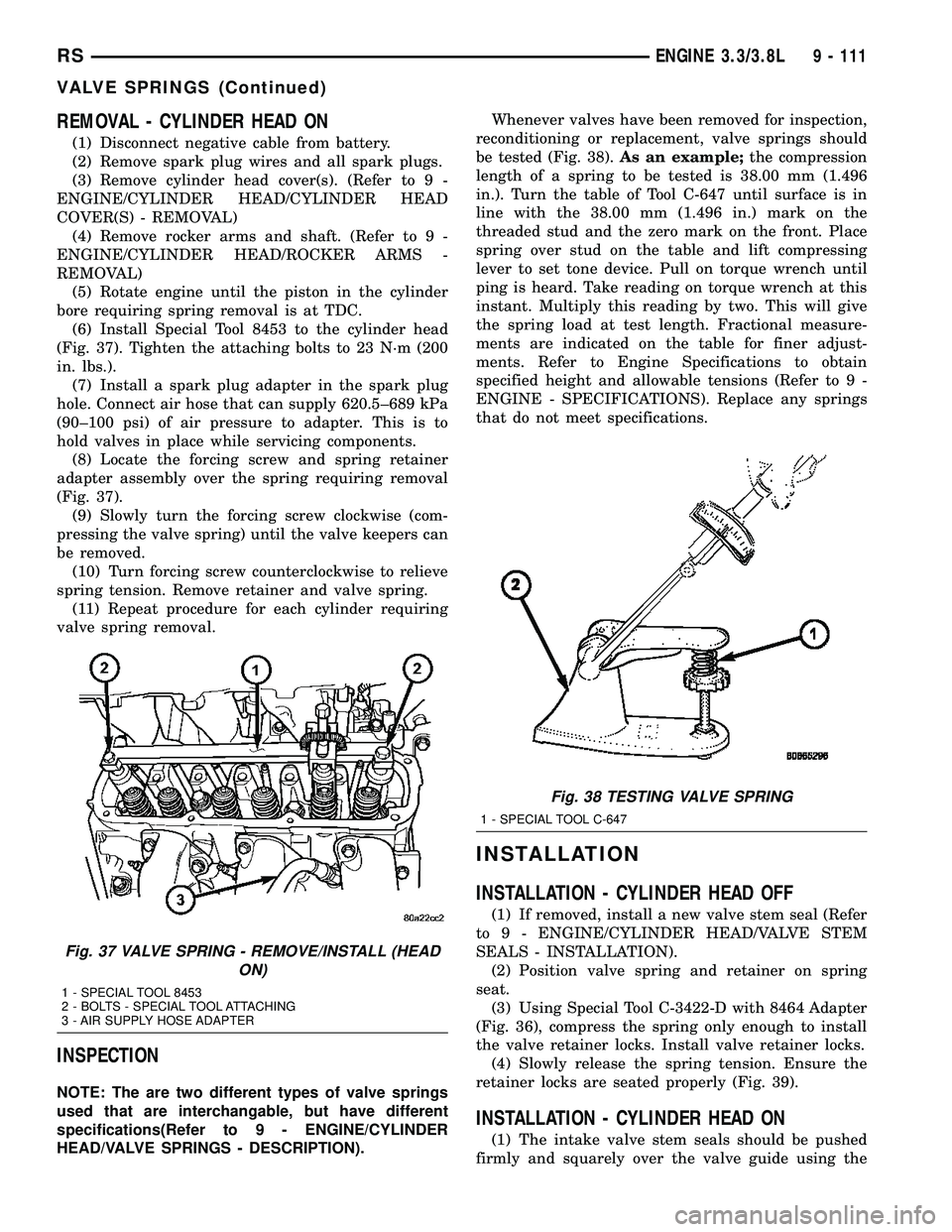
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove spark plug wires and all spark plugs.
(3) Remove cylinder head cover(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove rocker arms and shaft. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
REMOVAL)
(5) Rotate engine until the piston in the cylinder
bore requiring spring removal is at TDC.
(6) Install Special Tool 8453 to the cylinder head
(Fig. 37). Tighten the attaching bolts to 23 N´m (200
in. lbs.).
(7) Install a spark plug adapter in the spark plug
hole. Connect air hose that can supply 620.5±689 kPa
(90±100 psi) of air pressure to adapter. This is to
hold valves in place while servicing components.
(8) Locate the forcing screw and spring retainer
adapter assembly over the spring requiring removal
(Fig. 37).
(9) Slowly turn the forcing screw clockwise (com-
pressing the valve spring) until the valve keepers can
be removed.
(10) Turn forcing screw counterclockwise to relieve
spring tension. Remove retainer and valve spring.
(11) Repeat procedure for each cylinder requiring
valve spring removal.
INSPECTION
NOTE: The are two different types of valve springs
used that are interchangable, but have different
specifications(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - DESCRIPTION).Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested (Fig. 38).As an example;the compression
length of a spring to be tested is 38.00 mm (1.496
in.). Turn the table of Tool C-647 until surface is in
line with the 38.00 mm (1.496 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by two. This will give
the spring load at test length. Fractional measure-
ments are indicated on the table for finer adjust-
ments. Refer to Engine Specifications to obtain
specified height and allowable tensions (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Replace any springs
that do not meet specifications.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) If removed, install a new valve stem seal (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE STEM
SEALS - INSTALLATION).
(2) Position valve spring and retainer on spring
seat.
(3) Using Special Tool C-3422-D with 8464 Adapter
(Fig. 36), compress the spring only enough to install
the valve retainer locks. Install valve retainer locks.
(4) Slowly release the spring tension. Ensure the
retainer locks are seated properly (Fig. 39).
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) The intake valve stem seals should be pushed
firmly and squarely over the valve guide using the
Fig. 37 VALVE SPRING - REMOVE/INSTALL (HEAD
ON)
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8453
2 - BOLTS - SPECIAL TOOL ATTACHING
3 - AIR SUPPLY HOSE ADAPTER
Fig. 38 TESTING VALVE SPRING
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-647
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 111
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1289 of 2339
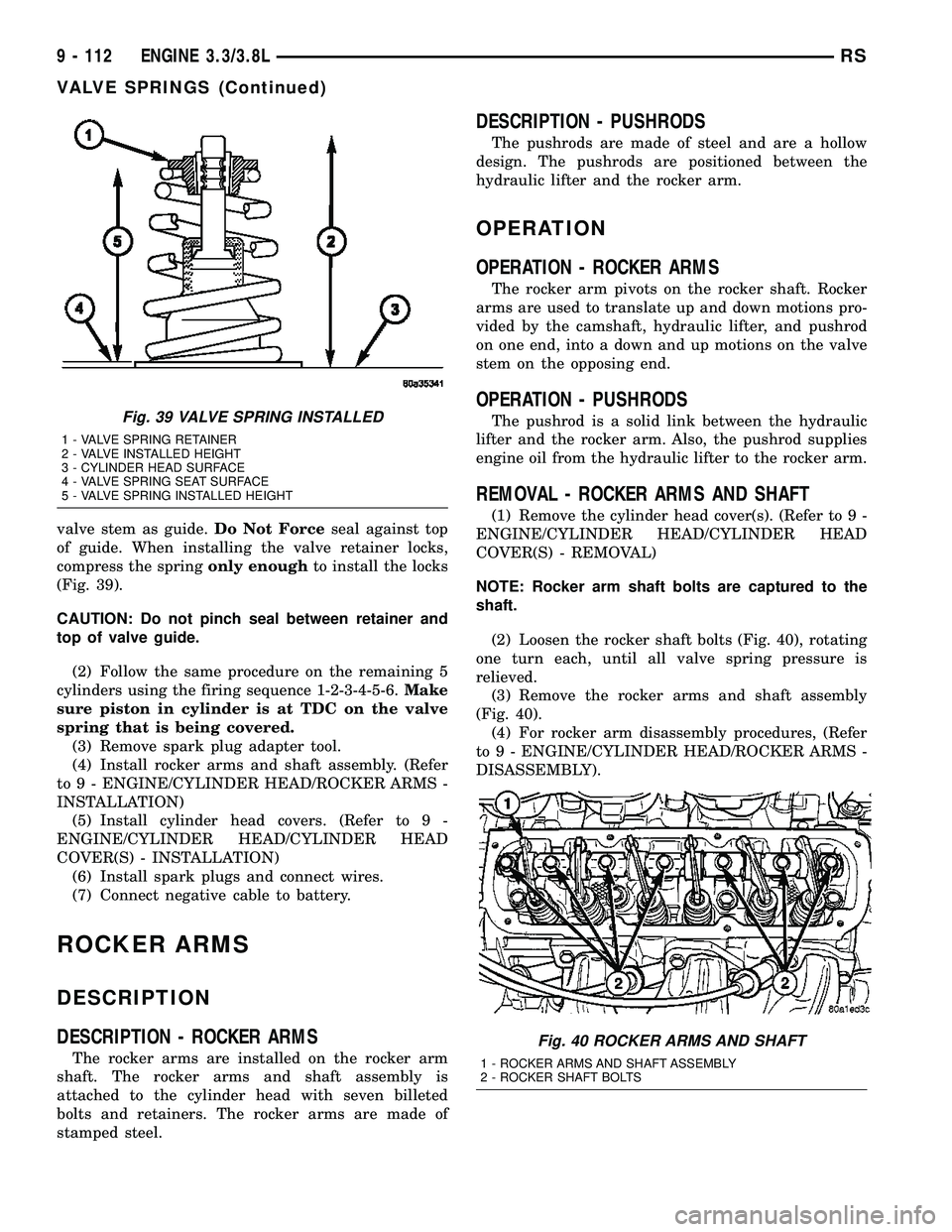
valve stem as guide.Do Not Forceseal against top
of guide. When installing the valve retainer locks,
compress the springonly enoughto install the locks
(Fig. 39).
CAUTION: Do not pinch seal between retainer and
top of valve guide.
(2) Follow the same procedure on the remaining 5
cylinders using the firing sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6.Make
sure piston in cylinder is at TDC on the valve
spring that is being covered.
(3) Remove spark plug adapter tool.
(4) Install rocker arms and shaft assembly. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
INSTALLATION)
(5) Install cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install spark plugs and connect wires.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ROCKER ARMS
The rocker arms are installed on the rocker arm
shaft. The rocker arms and shaft assembly is
attached to the cylinder head with seven billeted
bolts and retainers. The rocker arms are made of
stamped steel.
DESCRIPTION - PUSHRODS
The pushrods are made of steel and are a hollow
design. The pushrods are positioned between the
hydraulic lifter and the rocker arm.
OPERATION
OPERATION - ROCKER ARMS
The rocker arm pivots on the rocker shaft. Rocker
arms are used to translate up and down motions pro-
vided by the camshaft, hydraulic lifter, and pushrod
on one end, into a down and up motions on the valve
stem on the opposing end.
OPERATION - PUSHRODS
The pushrod is a solid link between the hydraulic
lifter and the rocker arm. Also, the pushrod supplies
engine oil from the hydraulic lifter to the rocker arm.
REMOVAL - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
NOTE: Rocker arm shaft bolts are captured to the
shaft.
(2) Loosen the rocker shaft bolts (Fig. 40), rotating
one turn each, until all valve spring pressure is
relieved.
(3) Remove the rocker arms and shaft assembly
(Fig. 40).
(4) For rocker arm disassembly procedures, (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
DISASSEMBLY).
Fig. 39 VALVE SPRING INSTALLED
1 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER
2 - VALVE INSTALLED HEIGHT
3 - CYLINDER HEAD SURFACE
4 - VALVE SPRING SEAT SURFACE
5 - VALVE SPRING INSTALLED HEIGHT
Fig. 40 ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
1 - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT ASSEMBLY
2 - ROCKER SHAFT BOLTS
9 - 112 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1297 of 2339
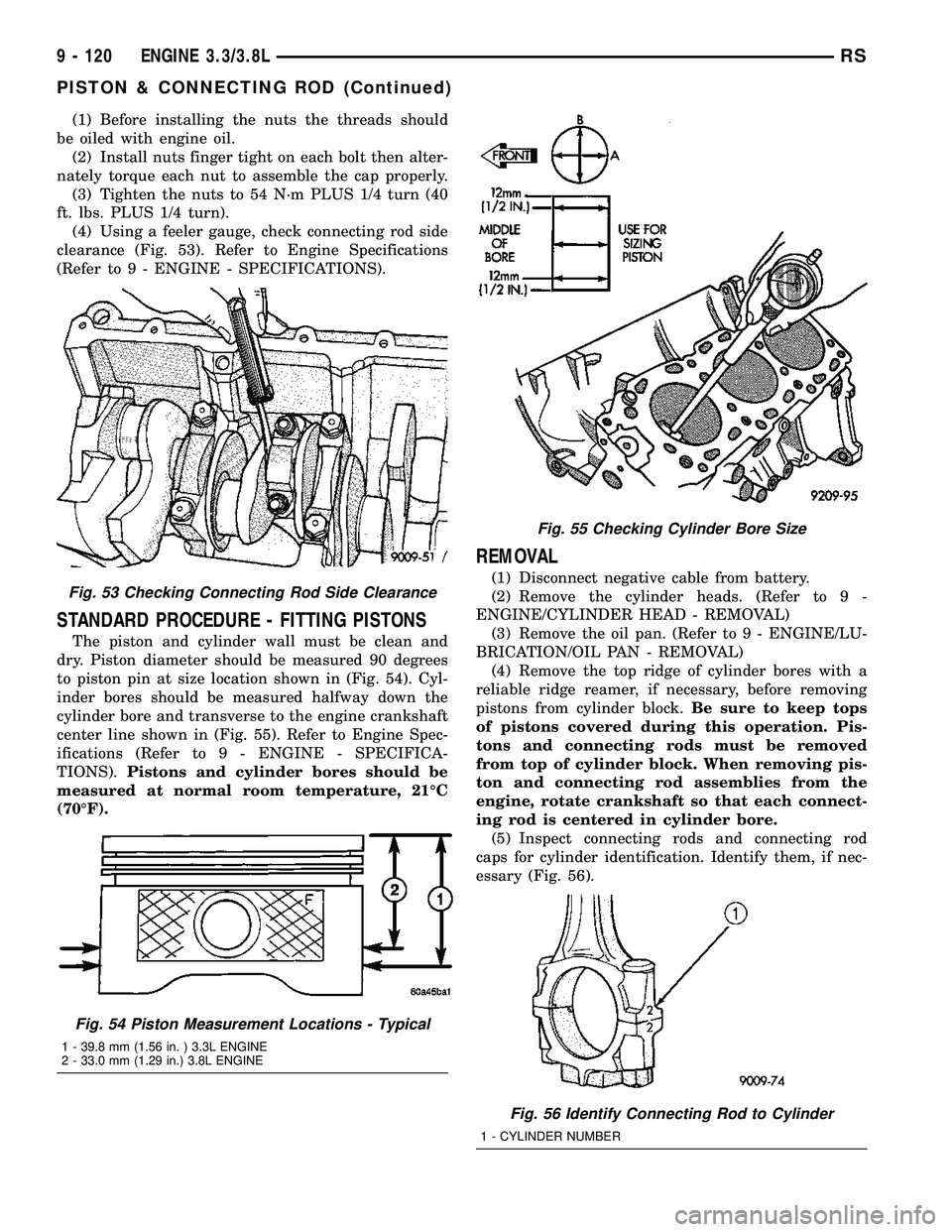
(1) Before installing the nuts the threads should
be oiled with engine oil.
(2) Install nuts finger tight on each bolt then alter-
nately torque each nut to assemble the cap properly.
(3) Tighten the nuts to 54 N´m PLUS 1/4 turn (40
ft. lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn).
(4) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 53). Refer to Engine Specifications
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING PISTONS
The piston and cylinder wall must be clean and
dry. Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees
to piston pin at size location shown in (Fig. 54). Cyl-
inder bores should be measured halfway down the
cylinder bore and transverse to the engine crankshaft
center line shown in (Fig. 55). Refer to Engine Spec-
ifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).Pistons and cylinder bores should be
measured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC
(70ÉF).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the top ridge of cylinder bores with a
reliable ridge reamer, if necessary, before removing
pistons from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops
of pistons covered during this operation. Pis-
tons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. When removing pis-
ton and connecting rod assemblies from the
engine, rotate crankshaft so that each connect-
ing rod is centered in cylinder bore.
(5) Inspect connecting rods and connecting rod
caps for cylinder identification. Identify them, if nec-
essary (Fig. 56).Fig. 53 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance
Fig. 54 Piston Measurement Locations - Typical
1 - 39.8 mm (1.56 in. ) 3.3L ENGINE
2 - 33.0 mm (1.29 in.) 3.8L ENGINE
Fig. 55 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
Fig. 56 Identify Connecting Rod to Cylinder
1 - CYLINDER NUMBER
9 - 120 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)