2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1397 of 2339
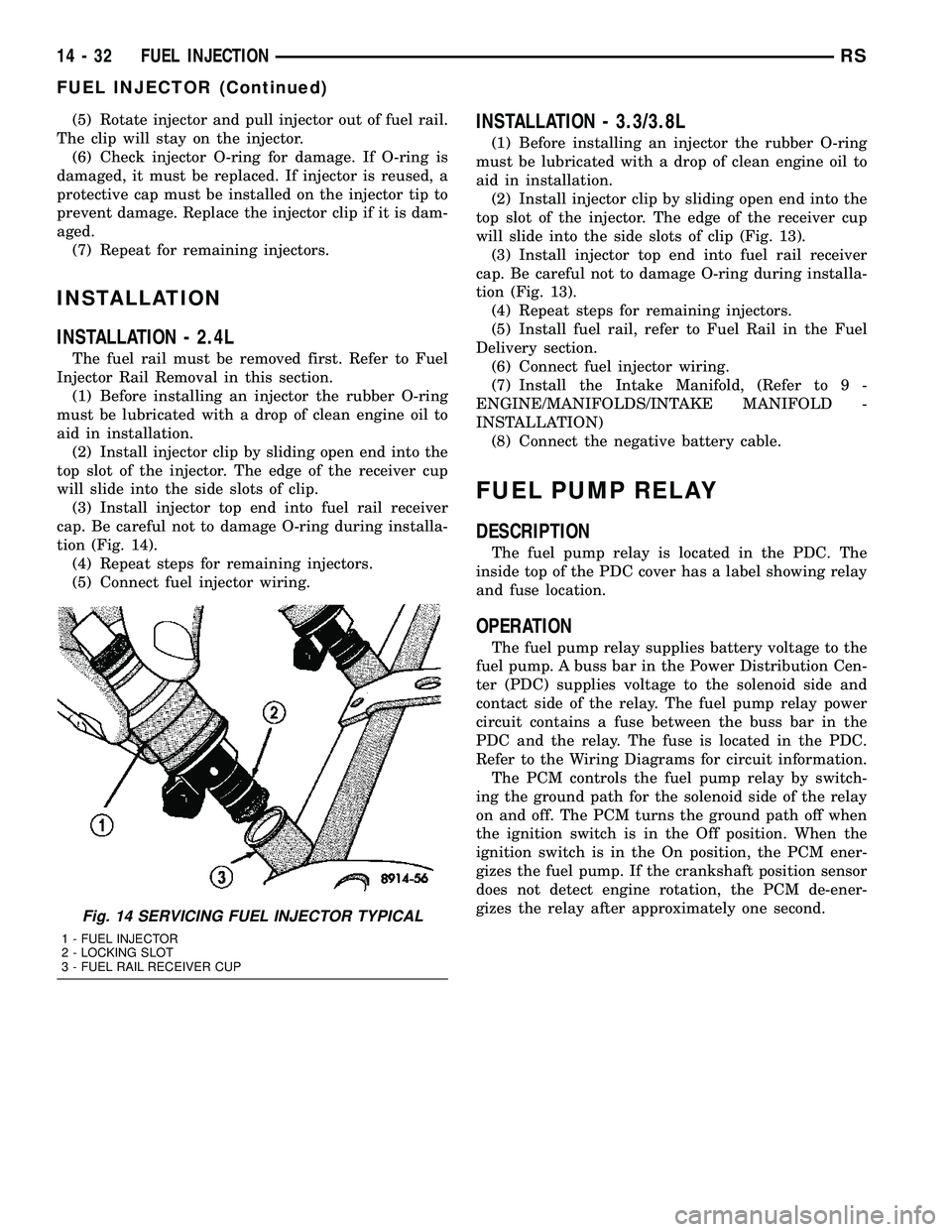
(5) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector.
(6) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is dam-
aged.
(7) Repeat for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The fuel rail must be removed first. Refer to Fuel
Injector Rail Removal in this section.
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip.
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 14).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Connect fuel injector wiring.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 13).
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 13).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install fuel rail, refer to Fuel Rail in the Fuel
Delivery section.
(6) Connect fuel injector wiring.
(7) Install the Intake Manifold, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
OPERATION
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. A buss bar in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) supplies voltage to the solenoid side and
contact side of the relay. The fuel pump relay power
circuit contains a fuse between the buss bar in the
PDC and the relay. The fuse is located in the PDC.
Refer to the Wiring Diagrams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-
gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
Fig. 14 SERVICING FUEL INJECTOR TYPICAL
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - LOCKING SLOT
3 - FUEL RAIL RECEIVER CUP
14 - 32 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1398 of 2339
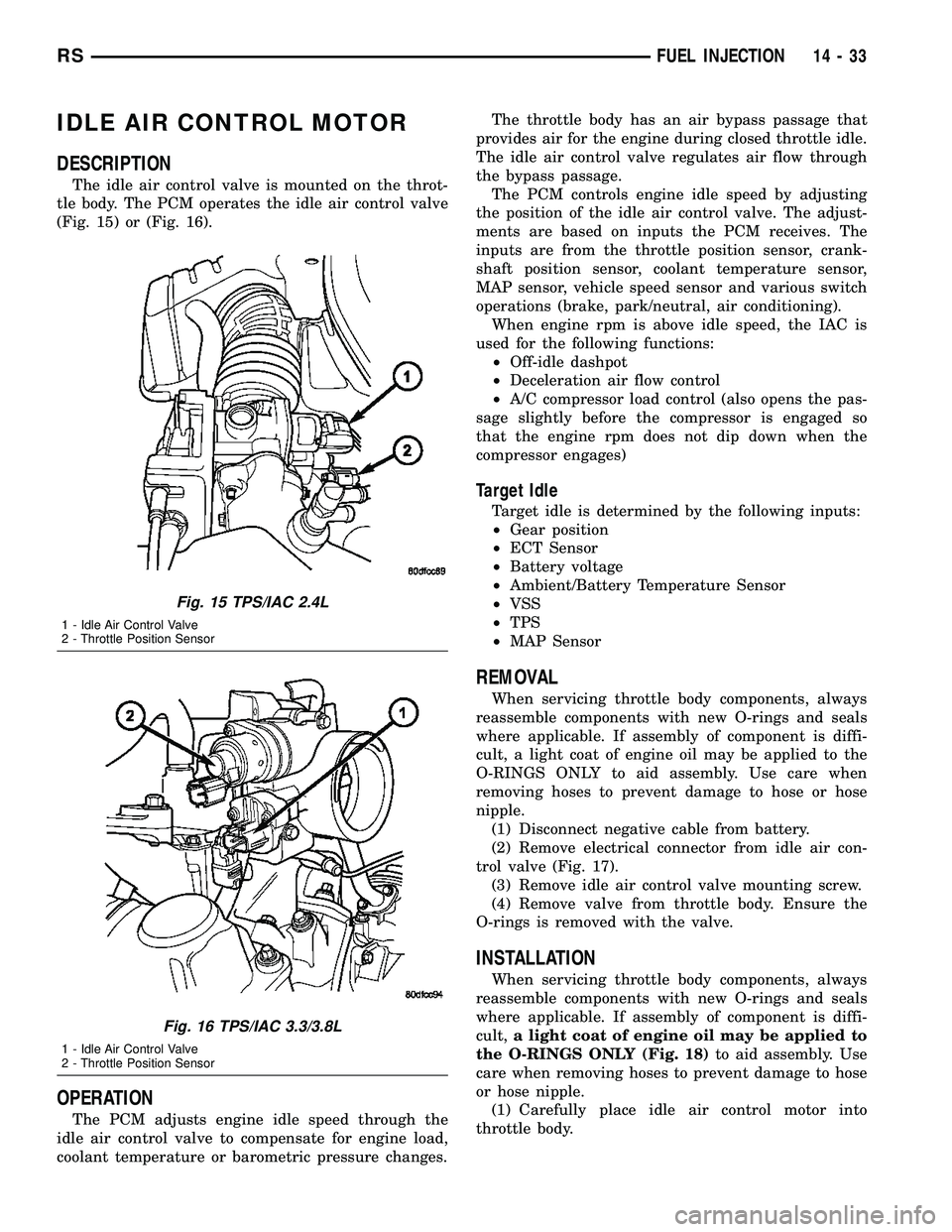
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The idle air control valve is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control valve
(Fig. 15) or (Fig. 16).
OPERATION
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control valve to compensate for engine load,
coolant temperature or barometric pressure changes.The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine during closed throttle idle.
The idle air control valve regulates air flow through
the bypass passage.
The PCM controls engine idle speed by adjusting
the position of the idle air control valve. The adjust-
ments are based on inputs the PCM receives. The
inputs are from the throttle position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor, coolant temperature sensor,
MAP sensor, vehicle speed sensor and various switch
operations (brake, park/neutral, air conditioning).
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following functions:
²Off-idle dashpot
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
Target Idle
Target idle is determined by the following inputs:
²Gear position
²ECT Sensor
²Battery voltage
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensor
²VSS
²TPS
²MAP Sensor
REMOVAL
When servicing throttle body components, always
reassemble components with new O-rings and seals
where applicable. If assembly of component is diffi-
cult, a light coat of engine oil may be applied to the
O-RINGS ONLY to aid assembly. Use care when
removing hoses to prevent damage to hose or hose
nipple.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove electrical connector from idle air con-
trol valve (Fig. 17).
(3) Remove idle air control valve mounting screw.
(4) Remove valve from throttle body. Ensure the
O-rings is removed with the valve.
INSTALLATION
When servicing throttle body components, always
reassemble components with new O-rings and seals
where applicable. If assembly of component is diffi-
cult,a light coat of engine oil may be applied to
the O-RINGS ONLY (Fig. 18)to aid assembly. Use
care when removing hoses to prevent damage to hose
or hose nipple.
(1) Carefully place idle air control motor into
throttle body.
Fig. 15 TPS/IAC 2.4L
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
Fig. 16 TPS/IAC 3.3/3.8L
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
RSFUEL INJECTION14-33
Page 1433 of 2339

GEAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS.............26
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD GEAR.................26
REMOVAL - RHD GEAR................29INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LHD GEAR.............31
INSTALLATION - RHD GEAR.............33
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............34
OUTER TIE ROD
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................35
GEAR
DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with a rack and pinion
power steering gear (Fig. 1). It is mounted to the
underside of the front suspension cradle/crossmem-
ber.
The steering column is attached to the gear
through the use of an intermediate shaft and cou-
plers. The outer ends of the power steering gear's
outer tie rods connect to the steering knuckles.
NOTE: The power steering gear should NOT be ser-
viced or adjusted unless DaimlerChrysler Corpora-
tion authorizes. If a malfunction or oil leak occurs,
the complete steering gear should be replaced.
Only the outer tie rods may be replaced separately
from the rest of the gear.
OPERATION
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear (side-to-side) travel through the meshing of the
helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth in the steer-
ing gear. This travel pushes and pulls the tie rods to
change the direction of the vehicle's front wheels.
Power assist steering provided by the power steer-
ing pump is controlled by an open center, rotary type
control valve which directs oil from the pump to
either side of the integral rack piston upon demand.
Road feel is controlled by the diameter of a torsion
bar which initially steers the vehicle. As required
steering effort increases, as in a turn, the torsion bar
twists, causing relative rotary motion between the
rotary valve body and the valve spool. This move-
ment directs oil behind the integral rack piston
which, in turn, builds hydraulic pressure and assists
in the turning effort.Manual steering control of the vehicle can be main-
tained if power steering assist is lost. However,
under this condition, steering effort is significantly
increased.
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD GEAR
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much fluid as
possible from the power steering fluid reservoir.Use
care not to damage the filter mesh below the
fluid surface.
19 - 26 GEARRS
Page 1453 of 2339

HOSE - POWER STEERING
PRESSURE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L ENGINE
NOTE: Before proceeding, review all WARNINGS
and CAUTIONS. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP -
WARNING)(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - CAU-
TION)
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from power steering fluid
reservoir.
(3) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(4) Remove front emissions vapor canister. (Refer
to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS/VAPOR CANISTER - REMOVAL)
(5) Place an oil drain pan under vehicle to catch
power steering fluid.
(6) Back out pressure hose tube nut at power
steering pump pressure fitting and remove hose from
pump (Fig. 20).
(7) Remove bolt attaching right routing clamp to
front suspension cradle crossmember (Fig. 20).
Remove pressure hose from clamp.
(8) Back out pressure hose tube nut at power
steering gear and remove hose from gear (Fig. 20).
(9) Remove power steering fluid pressure hose
from vehicle.
REMOVAL - 3.3L/3.8L ENGINE
NOTE: Before proceeding, review all WARNINGS
and CAUTIONS. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP -
WARNING)(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - CAU-
TION)
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from power steering fluid
reservoir.(3) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(4) Remove front emissions vapor canister. (Refer
to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS/VAPOR CANISTER - REMOVAL)
(5) Remove two bolts securing pressure hose rout-
ing clamps to suspension cradle crossmember and
steel reinforcement (Fig. 21).
(6) Place an oil drain pan under vehicle to catch
draining power steering fluid.
(7) Disconnect pressure hose at power steering
gear (Fig. 21).
Fig. 20 PRESSURE AND RETURN HOSES - 2.4L
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP
2 - RETURN HOSE (HEAT SLEEVE COVERED)
3 - ROUTING CLAMPS
4 - PRESSURE HOSE TUBE NUT
5 - RETURN HOSE TUBE NUT
6 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER
7 - POWER STEERING GEAR
8 - PRESSURE HOSE
19 - 46 PUMPRS
Page 1456 of 2339

(3) Install new O-rings on ends of power steering
fluid pressure hose. Lubricate O-rings using clean
power steering fluid.
CAUTION: Use care not to bend tube ends of the
power steering hoses when installing. Leaks and
restrictions may occur.
CAUTION: Power steering fluid hoses must remain
away from the exhaust system and must not come
in contact with any unfriendly surfaces on the vehi-
cle.
(4) Route hose up behind engine toward pump
avoiding tight bends or kinking.
(5) Install power steering pressure hose end into
pump pressure outlet fitting (Fig. 22). Thread tube
nut into outlet fitting, but do not tighten at this time.
(6) Attach pressure hose routing bracket to engine
(Fig. 22). Tighten bolt to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(7) Tighten hose tube nut at pump outlet fitting to
31 N´m (275 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Route hose behind cradle crossmember and
start hose end into gear port. Do not tighten hose
tube nut at this time.
(9) Attach hose to suspension cradle crossmember
and steel reinforcement using two routing clamps
and bolts (Fig. 21). Tighten clamp bolt at steel rein-
forcement to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten
clamp bolt at cradle crossmember to 23 N´m (200 in.
lbs.) torque.
(10) Tighten hose tube nut at power steering gear
port to 31 N´m (275 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Install front emissions vapor canister. (Refer
to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS/VAPOR CANISTER - INSTALLATION)
(12) Lower vehicle.
(13) Fill and bleed the power steering system
using the Power Steering Pump Initial Operation
Procedure. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
(14) Inspect system for leaks.
HOSE - POWER STEERING
RETURN
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L ENGINE
NOTE: Before proceeding, review all WARNINGS
and CAUTIONS. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP -
WARNING)(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - CAU-
TION)(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from power steering fluid
reservoir.
(3) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(4) Remove front emissions vapor canister. (Refer
to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS/VAPOR CANISTER - REMOVAL)
(5) Place an oil drain pan under vehicle to catch
power steering fluid.
(6) Cut tie-strap securing insulating heat sleeve to
power steering fluid return hose near power steering
pump. Pull back heat sleeve to expose hose clamp.
(7) Remove clamp, then return hose from power
steering pump (Fig. 20).
(8) Remove 2 bolts attaching power steering cooler
to cradle crossmember reinforcement (Fig. 24).
(9) Remove bolts attaching routing clamps to front
suspension cradle crossmember (Fig. 20). Remove
return hose from clamps.
(10) Back out return hose tube nut at power steer-
ing gear and remove hose (Fig. 20).
REMOVAL - 3.3L/3.8L ENGINE
NOTE: Before proceeding, review all WARNINGS
and CAUTIONS. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP -
WARNING)(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - CAU-
TION)
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from power steering fluid
reservoir.
(3) Place an oil drain pan under vehicle to catch
any draining power steering fluid.
(4) Remove clamp attaching return hose to power
steering fluid reservoir. Disconnect hose from reser-
voir (Fig. 22).
(5) Follow return hose downward and open
retainer at ABS bracket (Fig. 21). Remove hose tube
from retainer.
(6) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(7) Remove front emissions vapor canister. (Refer
to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS/VAPOR CANISTER - REMOVAL)
(8) Remove bolt securing return hose routing
clamp to suspension cradle crossmember (Fig. 21).
RSPUMP19-49
HOSE - POWER STEERING PRESSURE (Continued)
Page 1458 of 2339

(4) Route hose (with cooler attached) up toward
reservoir avoiding tight bends or kinking.
(5) Start steering gear end of hose into gear port.
Do not tighten hose tube nut at this time.
(6) Attach return hose tubes to suspension cradle
crossmember using routing clamp and bolt (Fig. 21).
Tighten clamp bolt to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the power steering fluid cooler on the
cradle crossmember reinforcement (Fig. 24). Install
the mounting bolts and tighten to 11 N´m (100 in.
lbs.). When installing mounting bolts, include pres-
sure hose routing clamp.
(8) Tighten hose tube nut at power steering gear
port to 31 N´m (275 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install front emissions vapor canister. (Refer to
25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMIS-
SIONS/VAPOR CANISTER - INSTALLATION)
(10) Lower vehicle.
(11) Install return hose tube into retainer on ABS
bracket (Fig. 21). Close the bracket.
(12) Install return hose onto reservoir (Fig. 22).
Slide the hose clamp into position on fluid reservoir
and attach it.Be sure hose clamp in installed
past bead on fluid reservoir fitting.
(13) Fill and bleed power steering system using
the Power Steering Pump Initial Operation Proce-
dure. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(14) Inspect system for leaks.
HOSE - POWER STEERING
SUPPLY
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L ENGINE
(1) Remove filler cap from power steering fluid res-
ervoir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(3) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(4) Remove hose clamp securing supply hose to
power steering pump, then remove supply hose from
pump fitting.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Remove hose clamp attaching power steering
fluid supply hose to power steering fluid reservoir,
then remove supply hose.
(7) Remove the power steering fluid supply hose
from the vehicle.
REMOVAL - 3.3L/3.8L ENGINE
NOTE: Before proceeding, review all WARNINGS
and CAUTIONS. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP -
WARNING)(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - CAU-
TION)
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from power steering fluid
reservoir.
(3) Place an oil drain pan under vehicle to catch
any draining power steering fluid.
(4) Remove clamp attaching supply hose to power
steering fluid reservoir. Disconnect hose from reser-
voir (Fig. 22).
(5) Pull upward on hose routing clip releasing it
from bracket on cylinder head cover (Fig. 22).
NOTE: It may be necessary to remove air cleaner
housing to gain greater access to supply hose at
power steering pump. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove clamp attaching supply hose to power
steering pump. Disconnect hose from pump and
remove from vehicle (Fig. 22).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L ENGINE
(1) Install and correctly route power steering fluid
supply hose from remote fluid reservoir to power
steering pump.
(2) Install fluid supply hose onto power steering
fluid reservoir. Install hose clamp.Be sure hose
clamp is installed past bead on fluid reservoir
fitting.
(3) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(4) Install power steering fluid supply hose on
power steering pump supply fitting. Install hose
clamp.Be sure hose clamp is installed past bead
on pump fitting.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Fill and bleed power steering system using
Power Steering Pump Initial Operation Procedure.
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE)
(7) Inspect system for leaks.
RSPUMP19-51
HOSE - POWER STEERING RETURN (Continued)
Page 1470 of 2339
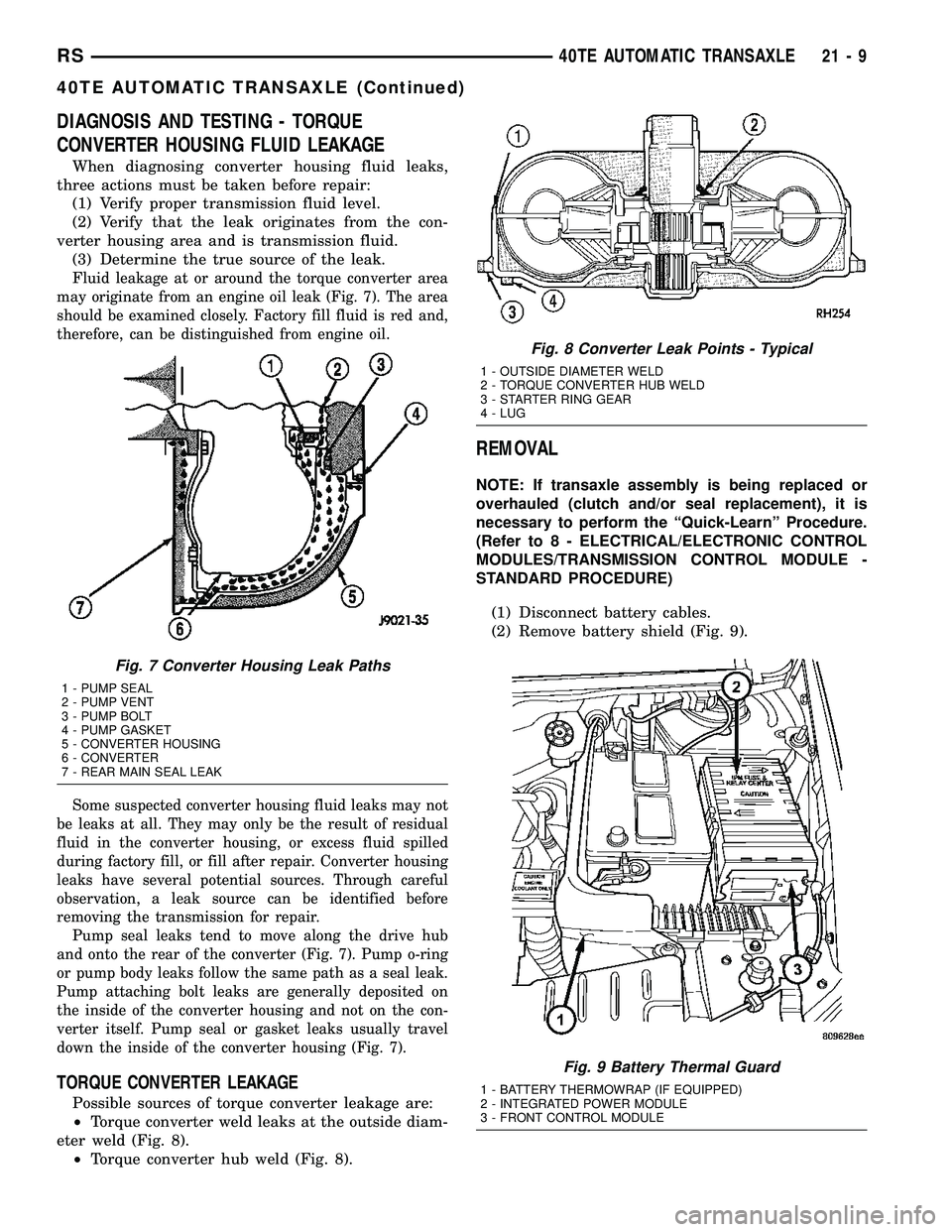
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
F
luid leakage at or around the torque converter area
may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 7). The area
should be examined closely. Factory fill fluid is red and,
therefore, can be distinguished from engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may not
be leaks at all. They may only be the result of residual
fluid in the converter housing, or excess fluid spilled
during factory fill, or fill after repair. Converter housing
leaks have several potential sources. Through careful
observation, a leak source can be identified before
removing the transmission for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 7). Pump o-ring
or pump body leaks follow the same path as a seal leak.
Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally deposited on
the inside of the converter housing and not on the con-
verter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaks usually travel
down the inside of the converter housing (Fig. 7).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 8).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transaxle assembly is being replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perform the ªQuick-Learnº Procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield (Fig. 9).
Fig. 7 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 8 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
Fig. 9 Battery Thermal Guard
1 - BATTERY THERMOWRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-9
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1472 of 2339
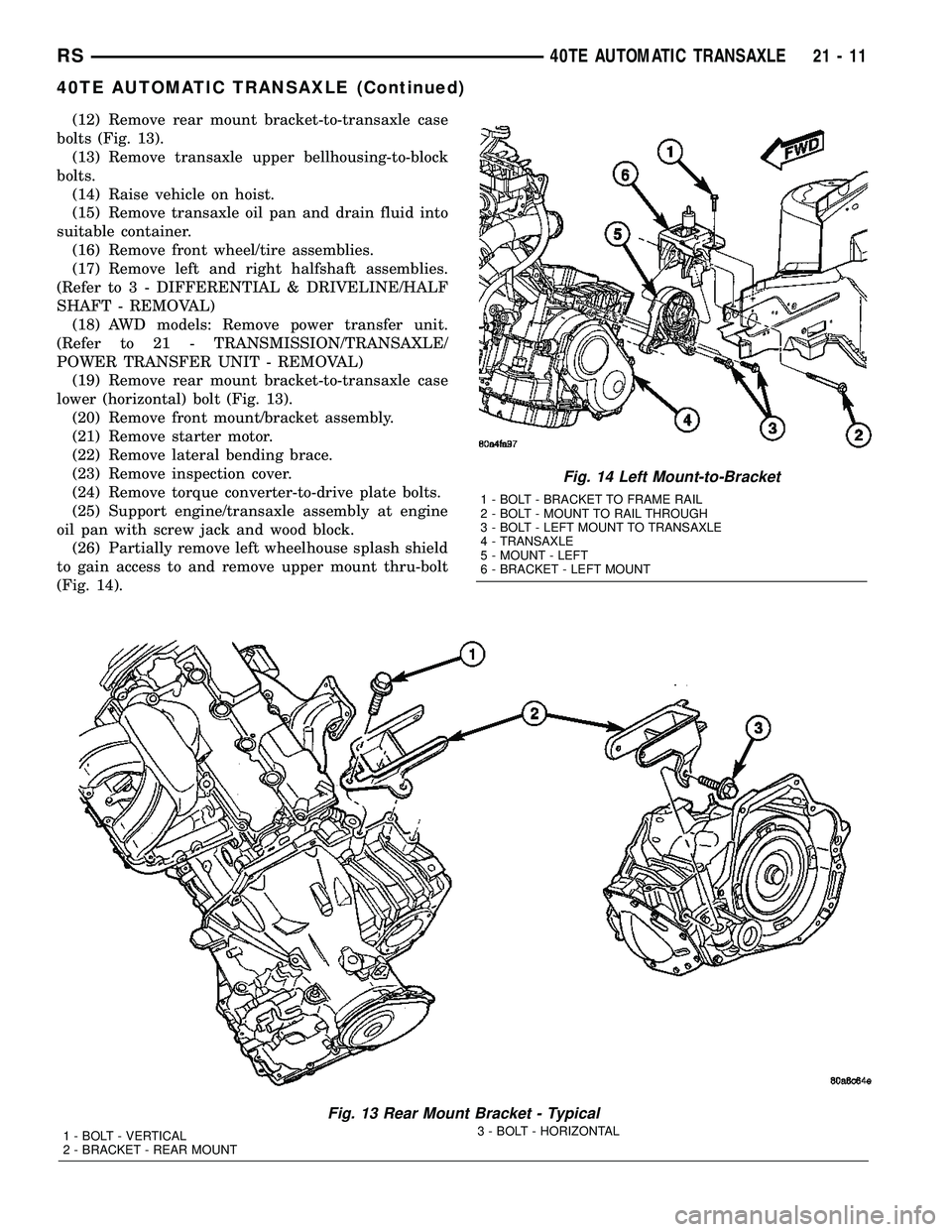
(12) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 13).
(13) Remove transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts.
(14) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(15) Remove transaxle oil pan and drain fluid into
suitable container.
(16) Remove front wheel/tire assemblies.
(17) Remove left and right halfshaft assemblies.
(Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF
SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(18) AWD models: Remove power transfer unit.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
POWER TRANSFER UNIT - REMOVAL)
(19) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
lower (horizontal) bolt (Fig. 13).
(20) Remove front mount/bracket assembly.
(21) Remove starter motor.
(22) Remove lateral bending brace.
(23) Remove inspection cover.
(24) Remove torque converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(25) Support engine/transaxle assembly at engine
oil pan with screw jack and wood block.
(26) Partially remove left wheelhouse splash shield
to gain access to and remove upper mount thru-bolt
(Fig. 14).
Fig. 13 Rear Mount Bracket - Typical
1 - BOLT - VERTICAL
2 - BRACKET - REAR MOUNT3 - BOLT - HORIZONTAL
Fig. 14 Left Mount-to-Bracket
1 - BOLT - BRACKET TO FRAME RAIL
2 - BOLT - MOUNT TO RAIL THROUGH
3 - BOLT - LEFT MOUNT TO TRANSAXLE
4 - TRANSAXLE
5 - MOUNT - LEFT
6 - BRACKET - LEFT MOUNT
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-11
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)