2004 NISSAN TERRANO sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 626 of 1833
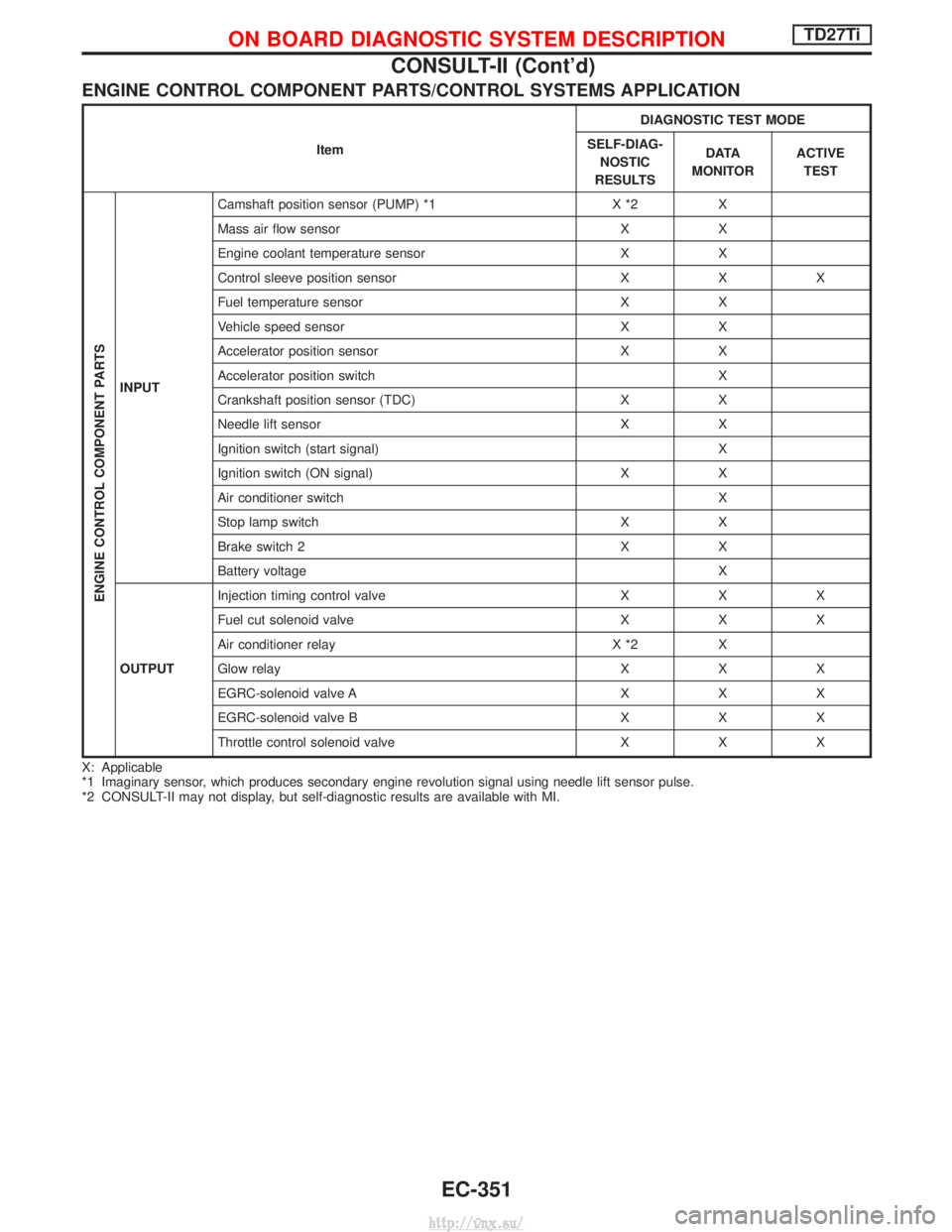
ENGINE CONTROL COMPONENT PARTS/CONTROL SYSTEMS APPLICATION
ItemDIAGNOSTIC TEST MODE
SELF-DIAG- NOSTIC
RESULTS D ATA
MONITOR ACTIVE
TEST
ENGINE CONTROL COMPONENT PARTS
INPUT Camshaft position sensor (PUMP) *1 X *2 X
Mass air flow sensor X X
Engine coolant temperature sensor X X
Control sleeve position sensor X X X
Fuel temperature sensor X X
Vehicle speed sensor X X
Accelerator position sensor X X
Accelerator position switch X
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) X X
Needle lift sensor X X
Ignition switch (start signal) X
Ignition switch (ON signal) X X
Air conditioner switch X
Stop lamp switch X X
Brake switch 2 X X
Battery voltage X
OUTPUT Injection timing control valve X X X
Fuel cut solenoid valve X X X
Air conditioner relay X *2 X
Glow relay X X X
EGRC-solenoid valve A X X X
EGRC-solenoid valve B X X X
Throttle control solenoid valve X X X
X: Applicable
*1 Imaginary sensor, which produces secondary engine revolution signal using needle lift sensor pulse.
*2 CONSULT-II may not display, but self-diagnostic results are available with MI.
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
CONSULT-II (Cont'd)
EC-351
http://vnx.su/
Page 627 of 1833
![NISSAN TERRANO 2004 Service Repair Manual SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
Regarding items detected in ªSELF-DIAG RESULTSº mode, refer to ªTROUBLE DIAGNOSIS Ð INDEXº,
EC-313.
DATA MONITOR MODE
Monitored item
[Unit]ECM
input
signals Main
signals Desc NISSAN TERRANO 2004 Service Repair Manual SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
Regarding items detected in ªSELF-DIAG RESULTSº mode, refer to ªTROUBLE DIAGNOSIS Ð INDEXº,
EC-313.
DATA MONITOR MODE
Monitored item
[Unit]ECM
input
signals Main
signals Desc](/manual-img/5/57394/w960_57394-626.png)
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
Regarding items detected in ªSELF-DIAG RESULTSº mode, refer to ªTROUBLE DIAGNOSIS Ð INDEXº,
EC-313.
DATA MONITOR MODE
Monitored item
[Unit]ECM
input
signals Main
signals Description
Remarks
CKPS×RPM
(TDC) [rpm]
qq
I The engine speed computed from the
crankshaft position sensor (TDC) signal
is displayed.
CMPS×RPM -
PUMP [rpm]
qqI The engine speed computed from the
needle lift sensor signal is displayed.
COOLAN TEMP/S
[ÉC] or [ÉF]
qq
I The engine coolant temperature (deter-
mined by the signal voltage of the engine
coolant temperature sensor) is displayed. I
When the engine coolant temperature
sensor is open or short-circuited, ECM
enters fail-safe mode. The same data as
the fuel temperature is displayed.
VHCL SPEED SE
[km/h] or [mph]
qqI The vehicle speed computed from the
vehicle speed sensor signal is displayed.
FUEL TEMP SEN
[ÉC] or [ÉF]
qq
I The fuel temperature (determined by the
signal voltage of the fuel temperature
sensor) is displayed.
ACCEL POS SEN [V]
qqI The accelerator position sensor signal
voltage is displayed.
OFF ACCEL POS
[ON/OFF]
qqI Indicates [ON/OFF] condition from the
accelerator position switch signal. I
Signal at approximately 9É opened.
C/SLEEV POS/S [V]
qqI The control sleeve position sensor signal
voltage is displayed.
BATTERY VOLT [V]
qqI The power supply voltage of ECM is dis-
played.
START SIGNAL
[ON/OFF]
qqI Indicates [ON/OFF] condition from the
starter signal. I
After starting the engine, [OFF] is dis-
played regardless of the starter signal.
AIR COND SIG
[ON/OFF]
qq
I Indicates [ON/OFF] condition of the air
conditioner switch as determined by the
air conditioner signal.
BRAKE SW
[ON/OFF]
qI Indicates [ON/OFF] condition of the stop
lamp switch.
BRAKE SW2
[ON/OFF]
qI Indicates [ON/OFF] condition of the
brake switch 2.
IGN SW
[ON/OFF]
qqI Indicates [ON/OFF] condition from igni-
tion switch.
MAS AIR/FL SE [V]
qqI The signal voltage of the mass air flow
sensor is displayed. I
When the engine is stopped, a certain
value is indicated.
ACT INJ TIMG [É]
q
I The actual injection timing angle deter-
mined by the ECM (an approximate aver-
age angle between injection start and
end from TDC) is displayed.
TARGET F/INJ
[mm
3/stroke]qI The target fuel injection quantity (deter-
mined by the ECM according to the input
signal) is indicated.
NOTE:
Any monitored item that does not match the vehicle being diagnosed is deleted from the display automatically.
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
CONSULT-II (Cont'd)
EC-352
http://vnx.su/
Page 629 of 1833

ACTIVE TEST MODE
TEST ITEMCONDITION JUDGEMENTCHECK ITEM (REMEDY)
TARGET F/INJ I
Engine: Return to the original
trouble condition.
I Fix the target injection quantity
using CONSULT-II. If trouble symptom disappears, see
CHECK ITEM
I
Control sleeve position sensor.
FUEL CUT SOL/V I
Ignition switch: ON
I Turn solenoid valve ªONº and
ªOFFº with the CONSULT-II and
listen to operating sound. Solenoid valve makes an operating
sound.
I
Harness and connector
I Solenoid valve
EGRC SOL/V A I
Ignition switch: ON
I Turn solenoid valve ªONº and
ªOFFº with the CONSULT-II and
listen to operating sound. Solenoid valve makes an operating
sound.
I
Harness and connector
I Solenoid valve
EGRC SOL/V B I
Ignition switch: ON
I Turn solenoid valve ªONº and
ªOFFº with the CONSULT-II and
listen to operating sound. Solenoid valve makes an operating
sound.
I
Harness and connector
I Solenoid valve
THROT CONT
SOL/V I
Ignition switch: ON
I Turn solenoid valve ªONº and
ªOFFº with the CONSULT-II and
listen to operating sound. Solenoid valve makes an operating
sound.
I
Harness and connector
I Solenoid valve
GLOW RLY I
Ignition switch: ON (Engine
stopped)
I Turn the glow relay ªONº and
ªOFFº using CONSULT-II and
listen to operating sound. Glow relay makes the operating
sound.
I
Harness and connector
I Glow relay
INJ TIMING I
Engine: Return to the original
trouble condition
I Retard the injection timing using
CONSULT-II. If trouble symptom disappears, see
CHECK ITEM.
I
Adjust initial injection timing
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
CONSULT-II (Cont'd)
EC-354
http://vnx.su/
Page 632 of 1833

Introduction
The engine has an ECM to control major systems such as fuel
injection control, fuel injection timing control, glow control system,
etc. The ECM accepts input signals from sensors and instantly
drives electronic fuel injection pump. It is essential that both input
and output signals are correct and stable. It is also important that
there are no problems such as vacuum leaks, with the engine.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a problem that occurs intermit-
tently rather than continuously. Most intermittent problems are
caused by poor electric connections or faulty wiring. In this case,
careful checking of suspected circuits may help prevent the unnec-
essary replacement of good parts.
A visual check may not be sufficient to determine the cause of the
problems. An active road test with CONSULT-II or a circuit tester
connected should be performed. Follow the ªWork Flowº on the
next page.
Before undertaking actual checks, take a few minutes to talk with
a customer who approaches with a driveability complaint. The cus-
tomer can supply important information about such problems,
especially intermittent ones. Find out what symptoms are present
and under what conditions they occur. A ªDiagnostic Worksheetº
like the example on the next page should be used.
Start your diagnosis by looking for ªconventionalº problems first.
This will help troubleshoot driveability problems on a vehicle with
an electronically controlled engine.
SEF858S
SEF233G
SEF234G
TROUBLE DIAGNOSESTD27Ti
EC-357
http://vnx.su/
Page 635 of 1833

Description for Work Flow
STEPDESCRIPTION
STEP I Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident/symptom occurred using the
ªDIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEETº as shown on the next page.
STEP II Before confirming the concern, check and write down (print out using CONSULT-II) the Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC), then erase the code. (Refer to EC-344). The DTC can be used when duplicating the incident at STEP III &
IV.
Study the relationship between the cause, specified by DTC, and the symptom described by the customer. (The
ªSymptom Matrix Chartº will be useful. Refer to EC-363.)
STEP III Try to confirm the symptom and under what conditions the incident occurs.
The ªDIAGNOSTIC WORK SHEETº is useful to verify the incident. Connect CONSULT-II to the vehicle in DATA
MONITOR (AUTO TRIG) mode and check real time diagnosis results.
If the malfunction code is detected, skip STEP IV and perform STEP V.
STEP IV Try to detect the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) by driving in (or performing) the ªDTC CONFIRMATION PROCE-
DUREº. Check and read the DTC by using CONSULT-II.
During the DTC verification, be sure to connect CONSULT-II to the vehicle in DATA MONITOR (AUTO TRIG) mode
and check real time diagnosis results.
In case the ªDTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDUREº is not available, perform the ªOVERALL FUNCTION CHECKº
instead. The DTC cannot be displayed by this check, however, this simplified ªcheckº is an effective alternative.
The ªNGº result of the ªOVERALL FUNCTION CHECKº is the same as the DTC detection.
STEP V Take the appropriate action based on the results of STEP I through IV.
If the malfunction code is indicated, proceed to TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR DTC.
If the normal code is indicated, proceed to the BASIC INSPECTION. Refer to EC-361. Then perform inspections
according to the Symptom Matrix Chart. Refer to EC-363.
STEP VI Identify where to begin diagnosis based on the relationship study between symptom and possible causes. Inspect
the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage using (tracing) ªHarness Layoutsº.
Gently shake the related connectors, components or wiring harness with CONSULT-II set in ªDATA MONITOR
(AUTO TRIG)º mode.
Check the voltage of the related ECM terminals or monitor the output data from the related sensors with CON-
SULT-II. Refer to EC-369.
The ªDIAGNOSTIC PROCEDUREº in EC section contains a description based on open circuit inspection. A short
circuit inspection is also required for the circuit check in the DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE.
Repair or replace the malfunctioning parts.
STEP VII Once you have repaired the circuit or replaced a component, you need to run the engine in the same conditions
and circumstances which resulted in the customer's initial complaint.
Perform the ªDTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDUREº and confirm the normal code (Diagnostic trouble code No. 55)
is detected. If the incident is still detected in the final check, perform STEP VI by using a different method from the
previous one.
Before returning the vehicle to the customer, be sure to erase the unnecessary (already fixed) DTC in ECM. (Refer
to EC-344.)
TROUBLE DIAGNOSESTD27Ti
EC-360
http://vnx.su/
Page 639 of 1833

SYSTEM Ð Engine control system
Malfunction
SYMPTOM
Reference page
Feature of symptom
Check point
HARD/NO START/
RESTART (EXCP. HA) ENGINE STALL HESITATION/SURGING/FLAT SPOT SPARK KNOCK/DETONATION
LACK OF POWER
POOR ACCELERATION
HI IDLE
LOW IDLE
ROUGH IDLE/HUNTING
IDLING VIBRATION
SLOW/NO RETURN TO IDLE
OVERHEAT/HIGH ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
EXCESSIVE FUEL CONSUMPTION
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION ABNORMAL SMOKE COLOR
DEAD BATTERY (UNDER CHARGE) Malfunction indicator lamp illuminates.
Can be detected by CONSULT-II?
Fuel cut NO START (with first firing)
NO START (without first firing)
HARD TO START WHEN ENGINE IS COLD
HARD TO START WHEN ENGINE IS HOT
AT IDLE
DURING DRIVING
WHEN DECELERATINGBLACK SMOKE
WHITE SMOKE
New CT/CS
AAAB AC AD AE AF AG AH AJ AK AL AM AP HA
Mass air flow sensor circuit open, ground short qqq q
EC-379
short qqq
Engine coolant temperature sensor
circuit open, short qqq qqq qq EC-384Compensation according to
engine coolant temperature does
not function.
Vehicle speed sensor circuit open, short qqEC-420
Control sleeve position sensor circuit open, short qqq qqqEC-437
Injection timing control valve circuit open, short qqq
EC-403Injection timing cannot be con-
trolled.
ground short qq
Accelerator switch (F/C) circuit open, short qqq
EC-388
ground short qq
Needle lift sensor circuit open, short qqqEC-450
Fuel cut solenoid valve circuit open, ground short q qqq q
EC-399
short qqqEngine runs on after turning igni-
tion switch OFF.
Fuel temperature sensor circuit open, shortqq qq qq qq q q EC-395Compensation for amount of fuel
injected according to fuel tem-
perature does not function.
Accelerator position sensor circuit open, short qqq qqEC-388
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) cir-
cuit open, short
qq qq
EC-408
noise qqq qq
TROUBLE DIAGNOSESTD27Ti
Symptom Matrix Chart (Cont'd)
EC-364
http://vnx.su/
Page 643 of 1833

Major Sensor Reference Graph in Data Monitor
Mode
The following are the major sensor reference graphs in ªDATA MONITORº mode.
(Select ªHI SPEEDº in ªDATA MONITORº with CONSULT-II.)
ACCEL POS SEN, C/SLEEV POS/S, ACT INJ TIMG
Below is the data for ªACCEL POS SENº, ªC/SLEEV POS/Sº and ªACT INJ TIMGº when revving engine quickly
up to 3,000 rpm under no load after warming up engine sufficiently.
Each value is for reference, the exact value may vary.
NEF766
TROUBLE DIAGNOSESTD27Ti
EC-368
http://vnx.su/
Page 644 of 1833

ECM Terminals and Reference Value
PREPARATION
Perform all voltage measurements with all the connectors con-
nected. Measure ECM terminal voltage at the nearest connector to
the sensors or actuators to be measured as accessing ECM termi-
nals from outside is impossible.
IUse extreme care not to touch 2 pins at the same time.
I Data is for comparison and may not be exact.
I Use care not to enlarge the opening to keep the seal in good
condition.
Be sure ECM unit is properly grounded before checking.
ECM HARNESS CONNECTOR TERMINAL LAYOUT
SGI841
MEC032E
TROUBLE DIAGNOSESTD27Ti
EC-369
http://vnx.su/