2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 701 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 455
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0337
58X CRANK POSITION SENSOR NO SIGNAL
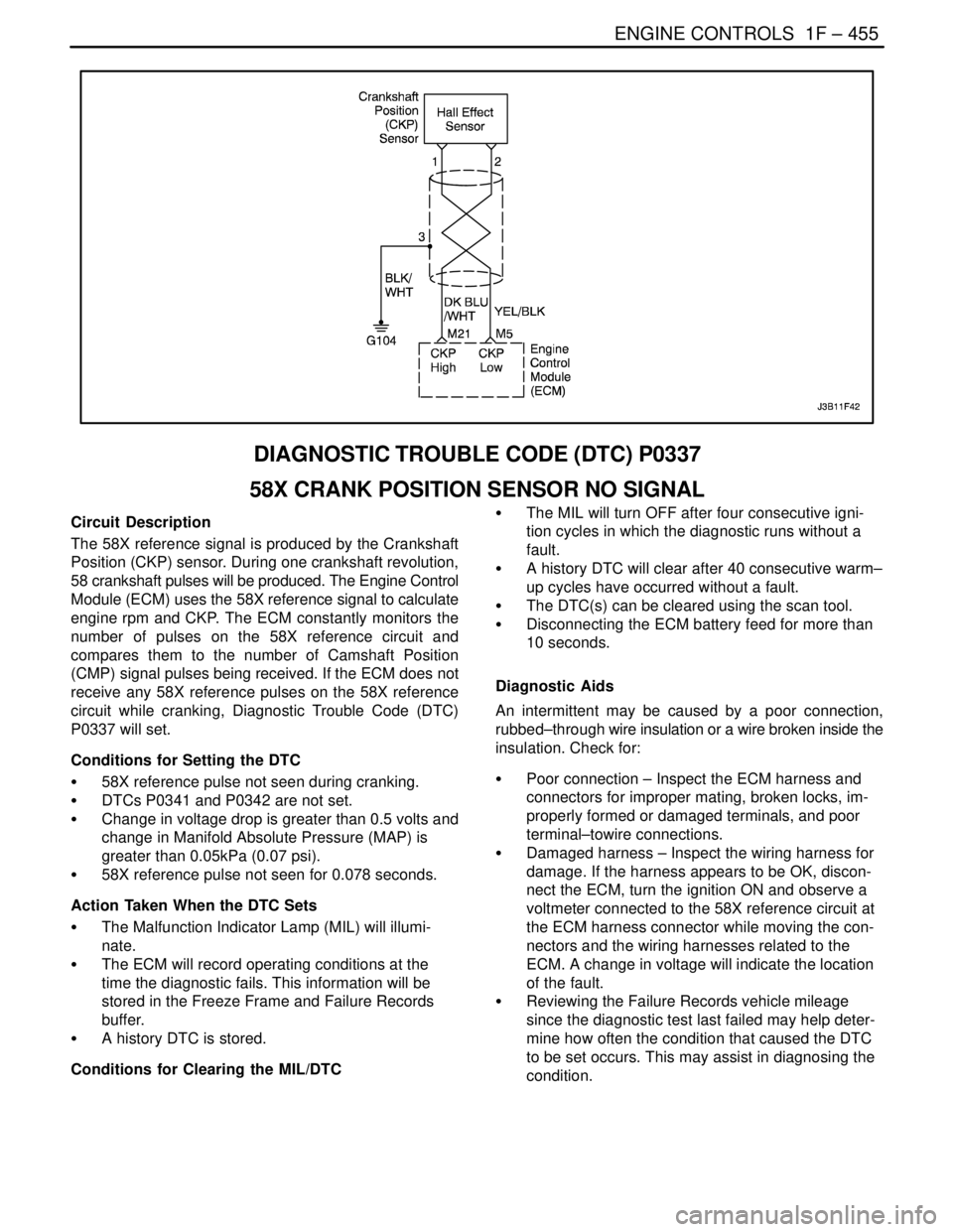
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the Crankshaft
Position (CKP) sensor. During one crankshaft revolution,
58 crankshaft pulses will be produced. The Engine Control
Module (ECM) uses the 58X reference signal to calculate
engine rpm and CKP. The ECM constantly monitors the
number of pulses on the 58X reference circuit and
compares them to the number of Camshaft Position
(CMP) signal pulses being received. If the ECM does not
receive any 58X reference pulses on the 58X reference
circuit while cranking, Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
P0337 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S 58X reference pulse not seen during cranking.
S DTCs P0341 and P0342 are not set.
S Change in voltage drop is greater than 0.5 volts and
change in Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) is
greater than 0.05kPa (0.07 psi).
S 58X reference pulse not seen for 0.078 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffer.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTCS The MIL will turn OFF after four consecutive igni-
tion cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a
fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles have occurred without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
S Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks, im-
properly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–towire connections.
S Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, discon-
nect the ECM, turn the ignition ON and observe a
voltmeter connected to the 58X reference circuit at
the ECM harness connector while moving the con-
nectors and the wiring harnesses related to the
ECM. A change in voltage will indicate the location
of the fault.
S Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage
since the diagnostic test last failed may help deter-
mine how often the condition that caused the DTC
to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
Page 704 of 2643

1F – 458IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0341
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR RATIONALITY
System Description
The Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor is used to correlate
crankshaft to camshaft position so that the Engine Control
Module (ECM) can determine which cylinder is ready to be
fueled by the injector. The CMP is also used to determine
which cylinder is misfiring when a misfire is present. When
the ECM cannot use the information from the CMP sensor,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is set, and the ECM will
fuel the engine using the Alternating Synchronous Double
Fire (ASDF) method.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S CMP Sensor reference pulse is not detected at the
correct interval every 4 cylinders.
S Engine is running.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the complaint,
should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Anytime a poor connection is present, the CMP Reference
Activity counter will stop incrementing.
Page 707 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 461
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0342
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR NO SIGNAL
System Description
The Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor is used to correlate
crankshaft to camshaft position so that the Engine Control
Module (ECM) can determine which cylinder is ready to be
fueled by the injector. The CMP is also used to determine
which cylinder is misfiring when a misfire is present. When
the ECM cannot use the information from the CMP sensor,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is set, and the ECM will
fuel the engine using the Alternating Synchronous Double
Fire (ASDF) method.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S CMP Sensor pulse is not detected at the correct
interval every 4 cylinders.
S Engine is running.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the complaint,
should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
Page 710 of 2643

1F – 464IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0351
IGNITION CONTROL CIRCUIT A FAULT (CYLINDER 1 & 4)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) provides a ground for
the electronic spark timing A circuit. When the ECM re-
moves the ground path of the ignition primary coil, the
magnetic field produced by the coil collapses. The collaps-
ing magnetic field produces a voltage in the secondary coil
which fires the spark plug.
The circuit between the ECM and the electronic ignition
system ignition coil is monitored for an open circuit, short
to voltage, and short to ground. When the ECM detects a
problem in the electronic spark timing A circuit, it will set
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Monitor fault feedback signal.
S Ignition ON.
S Fault flag increments fail count.
S Must receive more than 200 failures within 255 test
cycles.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S Low speed coolant fan turns on.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
S Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks, im-
properly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–towire connection.
Page 712 of 2643

1F – 466IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0352
IGNITION CONTROL CIRCUIT B FAULT (CYLINDER 2 & 3)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) provides a ground for
the electronic spark timing A circuit. When the ECM re-
moves the ground path of the ignition primary coil, the
magnetic field produced by the coil collapses. The collaps-
ing magnetic field produces a voltage in the secondary coil
which fires the spark plug.
The circuit between the ECM and the electronic ignition
system ignition coil is monitored for an open circuit, short
to voltage, and short to ground. When the ECM detects a
problem in the electronic spark timing A circuit, it will set
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Monitor fault feedback signal.
S Ignition ON.
S Fault flag increments fail count.
S Must receive more than 200 failures within 255 test
cycles.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S Low speed coolant fan turns on.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
S Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks, im-
properly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–towire connection.
Page 730 of 2643

1F – 484IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0420
CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR LOW EFFICIENCY
Circuit Description
In order to control exhaust emissions of Hydrocarbons
(HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Nitrogen Oxide (NOx),
a Three–Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) is used. The cat-
alyst within the converter promotes a chemical reaction
which oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas,
converting them into harmless water vapor and carbon
dioxide, it also reduces NOx, converting it into nitrogen.
The catalytic converter also has the ability to store oxygen.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has the capability to
monitor this process using a Heated
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2) located in the ex-
haust stream past the TWC. The HO2S2 produces an out-
put signal which indicates the oxygen storage capacity of
the catalyst; this in turn indicates the catalyst’s ability to
convert exhaust emissions effectively. The ECM monitors
the catalyst efficiency by first allowing the catalyst to heat
up, waiting for a stabilization period while the engine is id-
ling, and then adding and removing fuel while monitoring
the reaction of the HO2S2. When the catalyst is function-
ing properly, the HO2S2 response to the extra fuel is slow
compared to the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1).
When the HO2S2 response is close to that of the HO2S1,
the Oxygen storage capability or efficiency of the catalyst
is considered to be bad, and the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Oxygen storage capacity index time is less than 0.3
seconds.
S Before idle test, the vehicle needs to be driven for
at least:
S 15 seconds at airflow is greater than 9.2 g/sec.
for manual transaxle.
S 11 seconds at airflow is greater than 12 g/sec
for automatic transaxle.
S Oxygen Sensor Capacity test condition:
S Closed loop stoichiometry.
S Purge concentration learned.
S Engine is running more than 330 seconds.
S Airflow is between 2.5 and 7.25 g/sec.
S Throttle Position (TP) sensor is less than 1.5%.
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is between –7°C
(19.4°F) and 105°C (221°F).
S Barometric pressure (BARO) is greater than 72 kPa
(10.4 psi).
S Catalyst temperature is between 500°C (932°F)
and 850°C (1562°F) for automatic transaxle.
S Catalyst temperature is between 450°C (842°F)
and 850°C (1562°F) for automatic transaxle.
S Closed Loop integrator change is less than 0.03.
S Idle time is less than 1 minute.
S Vehicle speed is less than 3 km/h (1.9 mph).S Block Learn Mode is learned.
S Above condition is stabilized for 5 seconds.
Note : Test is aborted for this idle if:
S Change in engine speed is greater than 80 rpm.
S A/C status changed.
S Cooling fan status changed.
S Insufficient air/fuel shift.
S DTC(s) P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0133, P1133,
P0134, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141,
P1167, P1171, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0341,
P0342, P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404,
P0405, P0406, P0443, P0502, P0506, P0507, and
P0562 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
The catalyst test may abort due to a change in the engine
load. Do not change the engine load (i.e. A/C, coolant fan,
heater motor) while a catalyst test is in progress.
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent
complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
Page 735 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 489
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0461
FUEL LEVEL STUCK
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) uses the signal from
the fuel level sensor to calculate expected vapor pressure
within the fuel system. Vapor pressure varies as the fuel
level changes. The fuel level signal also used to determine
if the fuel level is too high or too low to be able to detect
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) system faults. This Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the fuel level stuck.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Change in fuel level sensor output is less than 3.5%
after 250 km (155 mile) driving.
S Ignition ON.
S DTCs P0462, P0463 and P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in Failure Records buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
rubber.
Check for a poor connection or damaged ECM harness.
Inspect the fuel level circuit terminal for the following con-
ditions:
S Improper mating.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed.
S Damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection.
S Damaged harness.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an
2. Determine if fault is present. Reviews Freeze
Frame data to determine when the DTC set. Al-
ways record this information.
Page 738 of 2643

1F – 492IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0462
FUEL LEVEL LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) uses the signal from
the fuel level sensor to calculate expected vapor pressure
within the fuel system. Vapor pressure varies as the fuel
level changes. The fuel level signal also used to determine
if the fuel level is too high or too low to be able to detect
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) system faults. This Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) detects a continuous short to
low or open in either the signal circuit or the fuel level sen-
sor.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Fuel level sensor output is less than 5% of sensor
reading scale.
S Ignition ON.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in Failure Records buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.Diagnostic Aids
Inspect harness connector for backed–out terminal, im-
proper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or dam-
aged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connection.
Inspect wiring harness for damage.
A stuck fuel level sensor may cause the DTC set.
If the DTC P0462 cannot be duplicate, the information in-
cluded on the Failure record data can be useful in deter-
mine vehicle conditions when the DTC was first set.
Resistance checks for fuel level sensor:
S Empty = 280 ohms or over.
S Half Full = about 90 ohms.
S Full = 38 ohms or less
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Determine if fault is present. Review Freeze Frame
data to determine when the DTC set. Always record
this information.