2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA automatic transaxle
[x] Cancel search: automatic transaxlePage 213 of 2643

1D – 18IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at
an efficient level during all engine operating conditions.
When the engine is cold, the cooling system cools the en-
gine slowly or not at all. This slow cooling of the engine al-
lows the engine to warm up quickly.
The cooling system includes a radiator and recovery sub-
system, cooling fans, a thermostat and housing, a coolant
pump, and a coolant pump drive belt. The timing belt
drives the coolant pump.
All components must function properly in order for the
cooling system to operate. The coolant pump draws the
coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates
through water jackets in the engine block, the intake man-
ifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches the
operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat
opens. The coolant then goes back to the radiator where
it cools.
This system directs some coolant through the hoses to the
heater core. This provides for heating and defrosting. The
surge tank is connected to the radiator to recover the cool-
ant displaced by expansion from the high temperatures.
The surge tank maintains the correct coolant level.
The cooling system for this vehicle has no radiator cap or
filler neck. The coolant is added to the cooling system
through the surge tank.
RADIATOR
This vehicle has a lightweight tube–and–fin aluminum ra-
diator. Plastic tanks are mounted on the right and the left
sides of the radiator core.
On vehicles equipped with automatic transaxles, the
transaxle fluid cooler lines run through the left radiator
tank. A radiator drain cock is on this radiator.
To drain the cooling system, open the drain cock.
SURGE TANK
The surge tank is a transparent plastic reservoir, similar to
the windshield washer reservoir.
The surge tank is connected to the radiator by a hose and
to the engine cooling system by another hose. As the ve-
hicle is driven, the engine coolant heats and expands. The
portion of the engine coolant displaced by this expansion
flows from the radiator and the engine into the surge tank.
The air trapped in the radiator and the engine is degassed
into the surge tank.When the engine stops, the engine coolant cools and con-
tracts. The displaced engine coolant is then drawn back
into the radiator and the engine. This keeps the radiator
filled with the coolant to the desired level at all times and
increases the cooling efficiency.
Maintain the coolant level between the MIN and the MAX
marks on the surge tank when the system is cold.
WATER PUMP
The belt–driven centrifugal water pump consists of an im-
peller, a drive shaft, and a belt pulley. The water pump is
mounted on the front of the transverse–mounted engine,
and is driven by the timing belt.
The impeller is supported by a completely sealed bearing.
The water pump is serviced as an assembly and, there-
fore, cannot be disassembled.
THERMOSTAT
A wax pellet–type thermostat controls the flow of the en-
gine coolant through the engine cooling system. The ther-
mostat is mounted in the thermostat housing to the front
of the cylinder head.
The thermostat stops the flow of the engine coolant from
the engine to the radiator in order to provide faster warm–
up, and to regulate the coolant temperature. The thermo-
stat remains closed while the engine coolant is cold, pre-
venting circulation of the engine coolant through the
radiator. At this point, the engine coolant is allowed to cir-
culate only throughout the heater core to warm it quickly
and evenly.
As the engine warms, the thermostat opens. This allows
the engine coolant to flow through the radiator, where the
heat is dissipated through the radiator. This opening and
closing of the thermostat permits enough engine coolant
to enter the radiator to keep the engine within proper en-
gine temperature operating limits.
The wax pellet in the thermostat is hermetically sealed in
a metal case. The wax element of the thermostat expands
when it is heated and contracts when it is cooled.
As the vehicle is driven and the engine warms, the engine
coolant temperature increases. When the engine coolant
reaches a specified temperature, the wax pellet element
in the thermostat expands and exerts pressure against the
metal case, forcing the valve open. This allows the engine
coolant to flow through the engine cooling system and cool
the engine.
As the wax pellet cools, the contraction allows a spring to
close the valve.
The thermostat begins to open at 87°C (189°F) and is fully
open at 102°C (216°F). The thermostat closes at 86°C
(187°F).
Page 220 of 2643
1E – 6IENGINE ELECTRICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
NO CRANK
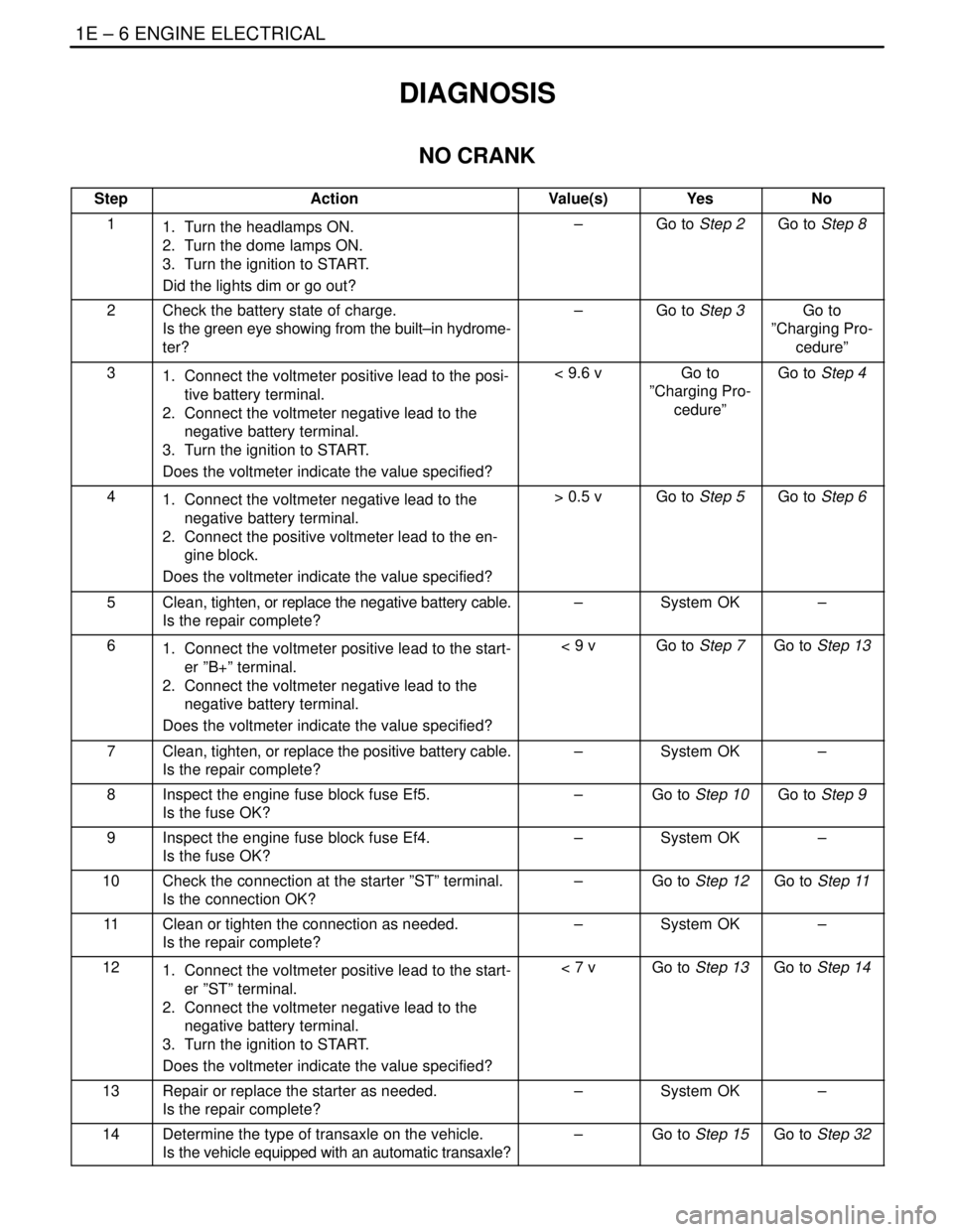
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the headlamps ON.
2. Turn the dome lamps ON.
3. Turn the ignition to START.
Did the lights dim or go out?–Go to Step 2Go to Step 8
2Check the battery state of charge.
Is the green eye showing from the built–in hydrome-
ter?–Go to Step 3Go to
”Charging Pro-
cedure”
31. Connect the voltmeter positive lead to the posi-
tive battery terminal.
2. Connect the voltmeter negative lead to the
negative battery terminal.
3. Turn the ignition to START.
Does the voltmeter indicate the value specified?< 9.6 vGo to
”Charging Pro-
cedure”Go to Step 4
41. Connect the voltmeter negative lead to the
negative battery terminal.
2. Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the en-
gine block.
Does the voltmeter indicate the value specified?> 0.5 vGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Clean, tighten, or replace the negative battery cable.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
61. Connect the voltmeter positive lead to the start-
er ”B+” terminal.
2. Connect the voltmeter negative lead to the
negative battery terminal.
Does the voltmeter indicate the value specified?< 9 vGo to Step 7Go to Step 13
7Clean, tighten, or replace the positive battery cable.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
8Inspect the engine fuse block fuse Ef5.
Is the fuse OK?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 9
9Inspect the engine fuse block fuse Ef4.
Is the fuse OK?–System OK–
10Check the connection at the starter ”ST” terminal.
Is the connection OK?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 11
11Clean or tighten the connection as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
121. Connect the voltmeter positive lead to the start-
er ”ST” terminal.
2. Connect the voltmeter negative lead to the
negative battery terminal.
3. Turn the ignition to START.
Does the voltmeter indicate the value specified?< 7 vGo to Step 13Go to Step 14
13Repair or replace the starter as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
14Determine the type of transaxle on the vehicle.
Is the vehicle equipped with an automatic transaxle?–Go to Step 15Go to Step 32
Page 245 of 2643

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 1E – 31
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
trolyte and the plates are at room temperature. A
battery that is extremely cold may not accept cur-
rent for several hours after starting the charger.
3. Charge the battery until the green dot appears. The
battery should be checked every half–hour while
charging. Tipping or shaking the battery may be
necessary to make the green dot appear.
4. After charging, the battery should be load tested.
Refer to ”Starter Motor” in this section.
CHARGING TIME REQUIRED
The time required to charge a battery will vary depending
upon the following factors:
S Size of Battery – A completely discharged large
heavy–duty battery requires more than twice the re-
charging time as a completely discharged small pas-
senger car battery.
S Temperature – A longer time will be needed to
charge any battery at –18°C (0°F) than at 27°C
(80°F). When a fast charger is connected to a cold
battery, the current accepted by the battery will be
very low at first. The battery will accept a higher cur-
rent rate as the battery warms.
S Charger Capacity – A charger which can supply only
5 amperes will require a much longer charging period
than a charger that can supply 30 amperes or more.
S State–of–Charge – A completely discharged battery
requires more than twice as much charge as a one–
half charged battery. Because the electrolyte is nearly
pure water and a poor conductor in a completely dis-
charged battery, the current accepted by the battery
is very low at first. Later, as the charging current
causes the electrolyte acid content to increase, the
charging current will likewise increase.
CHARGING A COMPLETELY
DISCHARGED BATTERY (OFF THE
VEHICLE)
Unless this procedure is properly followed, a perfectly
good battery may need to be replaced.
The following procedure should be used to recharge a
completely discharged battery:
1. Measure the voltage at the battery terminals with
an accurate voltmeter. If the reading is below 10
volts, the charge current will be very low, and it
could take some time before the battery accepts
the current in excess of a few milliamperes. Refer
to ””Charging Time Required” in this section, which
focuses on the factors affecting both the charging
time required and the rough estimates in the table
below. Such low current may not be detectable on
ammeters available in the field.
2. Set the battery charger on the high setting.Important : Some chargers feature polarity protection cir-
cuitry, which prevents charging unless the charger leads
are correctly connected to the battery terminals. A com-
pletely discharged battery may not have enough voltage
to activate this circuitry, even though the leads are con-
nected properly, making it appear that the battery will not
accept charging current. Therefore, follow the specific
charger manufacturer’s instruction for bypassing or over-
riding the circuitry so that the charger will turn on and
charge a low–voltage battery.
3. Continue to charge the battery until the charge cur-
rent is measurable. Battery chargers vary in the
amount of voltage and current provided. The time
required for the battery to accept a measurable
charge current at various voltages may be as fol-
lows:
Voltage
Hours
16.0 or moreUp to 4 hours
14.0–15.9Up to 8 hours
13.9 or lessUp to 16 hours
S If the charge current is not measurable at the
end of the above charging times, the battery
should be replaced.
S If the charge current is measurable during the
charging time, the battery is good, and charging
should be completed in the normal manner.
Important : It is important to remember that a completely
discharged battery must be recharged for a sufficient num-
ber of ampere hours (AH) to restore the battery to a usable
state. As a general rule, using the reserve capacity rating
(RC) as the number of ampere hours of charge usually
brings the green dot into view.
S If the charge current is still not measurable after
using the charging time calculated by the above
method, the battery should be replaced.
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
1. Position the vehicle with the good (charged) battery
so that the jumper cables will reach.
2. Turn off the ignition, all the lights, and all the electri-
cal loads in both vehicles. Leave the hazard flasher
on if jump starting where there may be other traffic
and any other lights needed for the work area.
3. In both vehicles, apply the parking brake firmly.
Notice : To avoid vehicle damage,Make sure the cables
are not on or near pulleys, fans, or other parts that will
move when the engine starts.
4. Shift an automatic transaxle to PARK, or a manual
transaxle to NEUTRAL.
CAUTION : In order to avoid injury, do not use cables
that have loose or missing insulation.
5. Clamp one end of the first jumper cable to the posi-
tive terminal on the battery. Make sure it does not
touch any other metal parts. Clamp the other end of
Page 276 of 2643

1F – 30IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS
If an intermittent problem is evident, follow the guidelines
below.
Preliminary Checks
Before using this section you should have already per-
formed the ”On–Board Diagnostic System Check.”
Perform a thorough visual inspection. This inspection can
often lead to correcting a problem without further checks
and can save valuable time. Inspect for the following con-
ditions:
S Engine control module (ECM) grounds for being
clean, tight, and in their proper location.
S Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, collapsing and prop-
er connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Control Information label. Inspect thoroughly for
any type of leak or restriction.
S Air leaks at the throttle body mounting area and the
intake manifold sealing surfaces.
S Ignition wires for cracks, hardness, proper routing,
and carbon tracking.
S Wiring for proper connections.
S Wiring for pinches or cuts.
Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables
Do not use the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) tables to
try to correct an intermittent fault. The fault must be pres-
ent to locate the problem.
Incorrect use of the DTC tables may result in the unneces-
sary replacement of parts.
Faulty Electrical Connections or Wiring
Most intermittent problems are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful inspection of sus-
pect circuits for the following:
S Poor mating of the connector halves.
S Terminals not fully seated in the connector body.
S Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All con-
nector terminals in a problem circuit should be care-
fully inspected, reformed, or replaced to insure con-
tact tension.S Poor terminal–to–wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body.
Road Test
If a visual inspection does not find the cause of the prob-
lem, the vehicle can be driven with a voltmeter or a scan
tool connected to a suspected circuit. An abnormal voltage
or scan tool reading will indicate that the problem is in that
circuit.
If there are no wiring or connector problems found and a
DTC was stored for a circuit having a sensor, except for
DTC P0171 and DTC P0172, replace the sensor.
Fuel System
Some intermittent driveability problems can be attributed
to poor fuel quality. If a vehicle is occasionally running
rough, stalling, or otherwise performing badly, ask the cus-
tomer about the following fuel buying habits:
S Do they always buy from the same source? If so,
fuel quality problems can usually be discounted.
S Do they buy their fuel from whichever fuel station
that is advertising the lowest price? If so, check the
fuel tank for signs of debris, water, or other contam-
ination.
IDLE LEARN PROCEDURE
Whenever the battery cables, the engine control module
(ECM), or the ECM fuse is disconnected or replaced, the
following idle learn procedure must be performed:
1. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition OFF for 5 seconds.
3. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
4. Start the engine in park/neutral.
5. Allow the engine to run until the engine coolant is
above 185° F (85°C ).
6. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
7. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
8. If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic trans-
axle, apply the parking brake. While pressing the
brake pedal, place the transaxle in D (drive).
9. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
10. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
11. Turn the ignition OFF. The idle learn procedure is
complete.
Page 328 of 2643

1F – 82IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls the engine idle
speed with the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve. To increase the
idle speed, the ECM pulls the IAC pintle away from its seat,
allowing more air to pass by the throttle body. To decrease
the idle speed, it extends the IAC valve pintle toward its
seat, reducing bypass air flow. A scan tool will read the
ECM commands to the IAC valve in counts. The higher
counts indicate more air bypass (higher idle). The lower
counts indicate less air is allowed to bypass (lower idle).
Diagnostic Aids
If the idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend the Idle
Air Control (IAC) valve with a IAC driver. Start the engine.
If the idle speed is above 800 rpm, locate and repair the
vacuum leak. Also, check for a binding throttle plate or
throttle linkage or an incorrect base idle setting.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. The IAC valve is extended and retracted by the IAC
driver. IAC valve movement is verified by an engine
speed change. If no change in engine speed oc-
curs, the valve can be removed from the throttle
body and tested. Connect the IAC driver to the re-
moved IAC valve and turn the ignition ON. Do not
start the engine.5. This step checks the quality of the IAC valve move-
ment in Step 2. Fully extending the IAC valve may
cause an engine stall. This may be normal.
6. Steps 2 and 5 verify proper IAC valve operation.
This step checks the IAC circuit for a wiring or ECM
fault.
Idle Air Control Valve Reset Procedure
Whenever the battery cable or the Engine Control Module
(ECM) connector or the ECM fuse Ef11 is disconnected or
replaced, the following idle learn procedure must be per-
formed:
1. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition OFF for 10 seconds.
3. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
4. Start the engine in park/neutral.
5. Allow the engine to run until the engine coolant is
above 185°F (85°C).
6. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
7. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
8. If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic trans-
axle, apply the parking brake. While pressing the
brake pedal, place the transaxle in D (drive).
9. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
10. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
11. Turn the ignition OFF. The idle learn procedure is
complete.
Page 714 of 2643

1F – 468IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0401
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION INSUFFICIENT FLOW
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position.
This diagnostic will determine if there is a reduction in EGR
flow.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204,
P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404, P0405,
P0406 and P0502 are not set.
S Test in Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) mode.
S Barometric Pressure (BARO) is greater than 72
kPa (10.4 psi).
S Vehicle speed is greater than 18 km/h (11.2
mph).
S A/C clutch/transmission clutch are unchanged.
S Rpm is between 1400 and 3000 for manual
transaxle.
S Rpm is between 1300 and 2900 for automatic
transaxle.
S Compensated MAP is with 10.3 to 32 kpa (1.5 to
4.6 psi) range.
S Start test
S Throttle position (TP) sensor is less then 1%.
S EGR is less than 1%.
S Change in MAP is less than 1.0 kpa (0.15 psi)Note : Test will be aborted when:
S Change in vehicle speed is greater than 5km/h (3.1
mph).
S Rpm is increased more than 75.
S EGR opened less than 90% commanded position.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC set as Failure Records data only.
This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
The EGR Decel Filter value can be a great aid in determin-
ing if a problem exists and to verify repairs. The EGR De-
cel Filter is an average of the difference in the expected
MAP change and the actual MAP change caused by open-
ing the EGR valve during a deceleration, and is used to de-
termine when the MIL is illuminated. By driving the vehicle
up to approximately 97 km/h (60 mph) and decelerating to
32 km/h (20 mph), it can be determined if the EGR system
is OK, partially restricted, or fully restricted.
A more negative number (less than –3) indicates that the
system is working normally, whereas a positive number in-
dicates that the system is being restricted and that the ex-
pected amount of EGR flow is was not seen. A number
that falls between negative 3 and positive 2 indicates that
the system is partially restricted but not restricted enough
to cause an emissions impact.
The EGR Decel Filter value should always be at –3 or low-
er. If the EGR Decel Filter number becomes more positive
(towards 0 or more), then the EGR system is becoming re-
stricted. Look for possible damage to the EGR pipe or for
a restriction caused by carbon deposits in the EGR pas-
sages or on the EGR valve.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
Page 730 of 2643

1F – 484IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0420
CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR LOW EFFICIENCY
Circuit Description
In order to control exhaust emissions of Hydrocarbons
(HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Nitrogen Oxide (NOx),
a Three–Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) is used. The cat-
alyst within the converter promotes a chemical reaction
which oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas,
converting them into harmless water vapor and carbon
dioxide, it also reduces NOx, converting it into nitrogen.
The catalytic converter also has the ability to store oxygen.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has the capability to
monitor this process using a Heated
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2) located in the ex-
haust stream past the TWC. The HO2S2 produces an out-
put signal which indicates the oxygen storage capacity of
the catalyst; this in turn indicates the catalyst’s ability to
convert exhaust emissions effectively. The ECM monitors
the catalyst efficiency by first allowing the catalyst to heat
up, waiting for a stabilization period while the engine is id-
ling, and then adding and removing fuel while monitoring
the reaction of the HO2S2. When the catalyst is function-
ing properly, the HO2S2 response to the extra fuel is slow
compared to the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1).
When the HO2S2 response is close to that of the HO2S1,
the Oxygen storage capability or efficiency of the catalyst
is considered to be bad, and the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Oxygen storage capacity index time is less than 0.3
seconds.
S Before idle test, the vehicle needs to be driven for
at least:
S 15 seconds at airflow is greater than 9.2 g/sec.
for manual transaxle.
S 11 seconds at airflow is greater than 12 g/sec
for automatic transaxle.
S Oxygen Sensor Capacity test condition:
S Closed loop stoichiometry.
S Purge concentration learned.
S Engine is running more than 330 seconds.
S Airflow is between 2.5 and 7.25 g/sec.
S Throttle Position (TP) sensor is less than 1.5%.
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is between –7°C
(19.4°F) and 105°C (221°F).
S Barometric pressure (BARO) is greater than 72 kPa
(10.4 psi).
S Catalyst temperature is between 500°C (932°F)
and 850°C (1562°F) for automatic transaxle.
S Catalyst temperature is between 450°C (842°F)
and 850°C (1562°F) for automatic transaxle.
S Closed Loop integrator change is less than 0.03.
S Idle time is less than 1 minute.
S Vehicle speed is less than 3 km/h (1.9 mph).S Block Learn Mode is learned.
S Above condition is stabilized for 5 seconds.
Note : Test is aborted for this idle if:
S Change in engine speed is greater than 80 rpm.
S A/C status changed.
S Cooling fan status changed.
S Insufficient air/fuel shift.
S DTC(s) P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0133, P1133,
P0134, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141,
P1167, P1171, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0341,
P0342, P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404,
P0405, P0406, P0443, P0502, P0506, P0507, and
P0562 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
The catalyst test may abort due to a change in the engine
load. Do not change the engine load (i.e. A/C, coolant fan,
heater motor) while a catalyst test is in progress.
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent
complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
Page 814 of 2643

1F – 568IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1601
SPI COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN ECM AND TCM
Circuit Description
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) communication is
used internally by the Engine Control Module (ECM) to
send message between the engine processor and the au-
tomatic transaxle processor. Included in each message
sent between the two processor is a checksum of the mes-
sage. Both the engine processor automatic transaxle
processor will compare this checksum value with calcu-
lated checksum. If the checksum do not match, the proc-
essor will review the new data as being corrupted and ig-
nore the value. The processor then use the previous
message. The receiving processor will then send a mes-
sage to the sending processor informing it that its last mes-
sage was corrupted.
The ECM monitor periodic TCM status message and if
message is not received fail counter incremented and
Diagnostic trouble Code (DTC) will stored.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Ignition switch is turned to ON.S Ignition voltage is greater than 11 volts.
S Engine is running more than 2 seconds.
S Device Control not active.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
DTC P1601 SPI Communications Between ECM and TCM
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 3–
31. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
4Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK