2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA gas
[x] Cancel search: gasPage 2052 of 2643
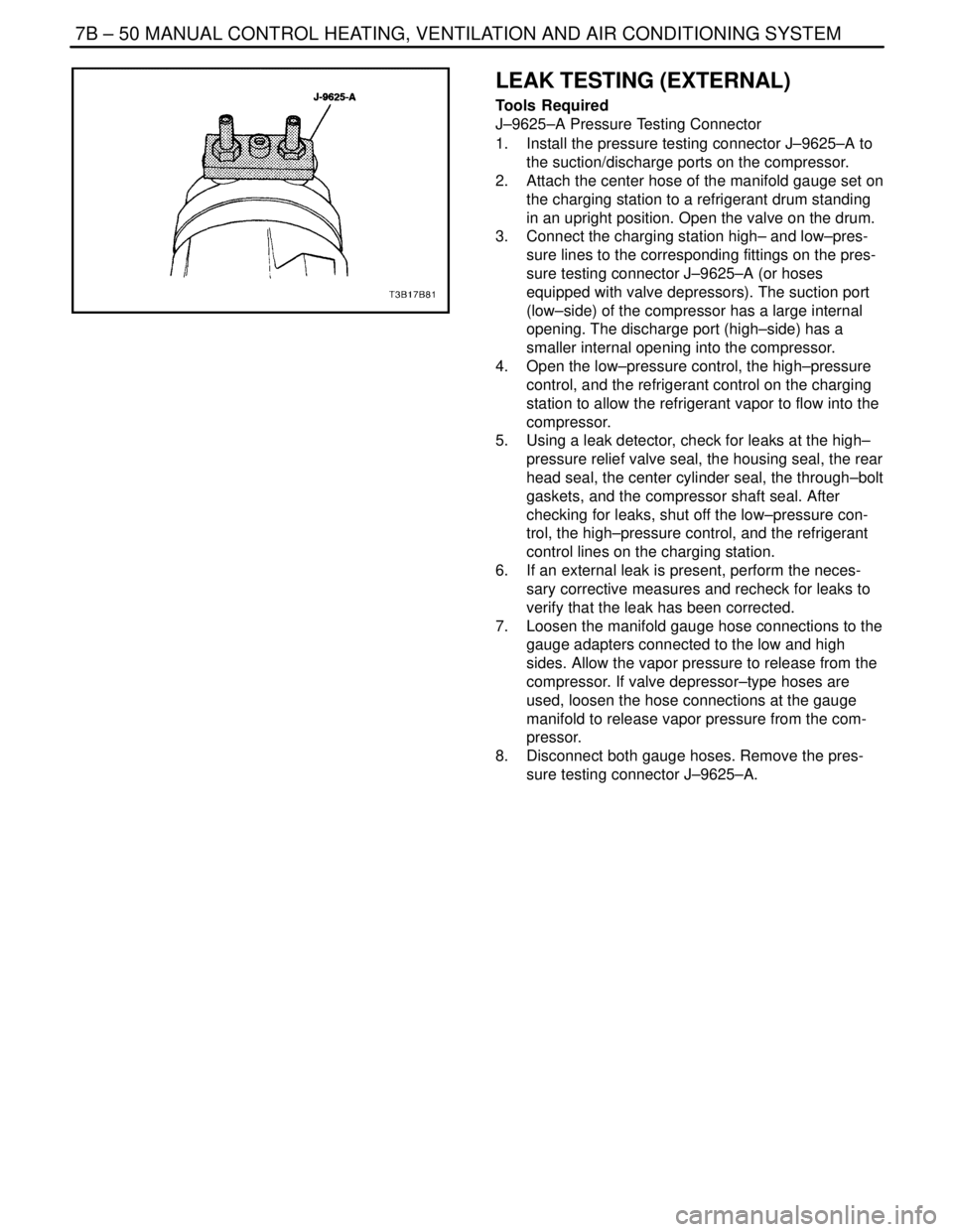

7B – 50IMANUAL CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
LEAK TESTING (EXTERNAL)
Tools Required
J–9625–A Pressure Testing Connector
1. Install the pressure testing connector J–9625–A to
the suction/discharge ports on the compressor.
2. Attach the center hose of the manifold gauge set on
the charging station to a refrigerant drum standing
in an upright position. Open the valve on the drum.
3. Connect the charging station high– and low–pres-
sure lines to the corresponding fittings on the pres-
sure testing connector J–9625–A (or hoses
equipped with valve depressors). The suction port
(low–side) of the compressor has a large internal
opening. The discharge port (high–side) has a
smaller internal opening into the compressor.
4. Open the low–pressure control, the high–pressure
control, and the refrigerant control on the charging
station to allow the refrigerant vapor to flow into the
compressor.
5. Using a leak detector, check for leaks at the high–
pressure relief valve seal, the housing seal, the rear
head seal, the center cylinder seal, the through–bolt
gaskets, and the compressor shaft seal. After
checking for leaks, shut off the low–pressure con-
trol, the high–pressure control, and the refrigerant
control lines on the charging station.
6. If an external leak is present, perform the neces-
sary corrective measures and recheck for leaks to
verify that the leak has been corrected.
7. Loosen the manifold gauge hose connections to the
gauge adapters connected to the low and high
sides. Allow the vapor pressure to release from the
compressor. If valve depressor–type hoses are
used, loosen the hose connections at the gauge
manifold to release vapor pressure from the com-
pressor.
8. Disconnect both gauge hoses. Remove the pres-
sure testing connector J–9625–A.
Page 2053 of 2643

MANUAL CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM 7B – 51
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
GENERAL INFORMATION
THE V5 A/C SYSTEM
The V5 variable displacement compressor along with the
thermal expansion valve on the evaporator, constitutes a
largely self–regulating system. There is no pressure cycl-
ing switch, no high–pressure cut–off switch and no low–
pressure cut–off switch. The compressor clutch is con-
trolled by the electronic control module (ECM), which
receives data from various engine systems and from a
pressure transducer located in the high–pressure refriger-
ant pipe. In normal operation, the clutch is engaged contin-
uously. Should one of the monitored conditions become
abnormal, the ECM will disengage the compressor clutch
until normal operation is restored. These conditions in-
clude the following:
S Wide–open throttle.
S High engine coolant temperature.
S High engine RPM.
S Refrigerant low pressure.
S Refrigerant high pressure.
The compressor clutch will remain disengaged until nor-
mal operation is established.
SYSTEM
COMPONENTS–FUNCTIONAL
Compressor
All compressors are belt–driven from the engine crank-
shaft through the compressor clutch pulley. The compres-
sor pulley rotates without driving the compressor shaft un-
til an electromagnetic clutch coil is energized. When
voltage is applied to energize the clutch coil, the clutch
plate and hub assembly is drawn rearward toward the
pulley. The magnetic force locks the clutch plate and
pulley together as one unit to drive the compressor shaft.
As the compressor shaft is driven, it compresses the low–
pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator into a
high–pressure, high–temperature vapor. The refrigerant
oil which is used to lubricate the compressor is carried with
the refrigerant. Refer to ”V5 Air Conditioning Compressor
Overhaul” in this section.
Condenser Core
The condenser assembly in front of the radiator consists
of coils which carry the refrigerant, and cooling fins that
provide the rapid transfer of heat. The air passing through
the condenser cools the high–pressure refrigerant vapor
and causes it to condense into a liquid.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is located with the evaporator core,
on the front passenger side fire wall.
The expansion valve can fail in three different positions:
open, closed, or restricted.
An expansion valve that fails in the open position will result
in a noisy A/C compressor or no cooling. The cause can
be a broken spring, a broken ball, or excessive moisture
in the A/C system. If the spring or the ball are found to be
defective, replace the expansion valve. If excessive mois-
ture is found in the A/C system, recycle the refrigerant.
An expansion valve that fails in the closed position will re-
sult in low suction pressure and no cooling. This may be
caused by a failed power dome or excessive moisture in
the A/C system. If the power dome on the expansion valve
is found to be defective, replace the expansion valve. If ex-
cessive moisture is found in the A/C system, recycle the
refrigerant.
A restricted expansion valve will result in low suction pres-
sure and no cooling. This may be caused by debris in the
refrigerant system. If debris is believed to be the cause, re-
cycle the refrigerant, replace the expansion valve, and re-
place the receiver–dryer.
Evaporator Core
The evaporator is a device which cools and dehumidifies
the air before it enters the vehicle. High–pressure liquid re-
frigerant flows through the expansion tube orifice and be-
comes a low–pressure gas in the evaporator. The heat in
the air passing through the evaporator core is transferred
to the cooler surface of the core, which cools the air. As the
process of heat transfer from the air to the evaporator core
surface is taking place, any moisture or humidity in the air
condenses on the outside surface of the evaporator core
and is drained off as water.
Receiver–Dryer
The sealed receiver–dryer assembly is connected to the
condenser outlet pipe. It acts as a refrigerant storing con-
tainer, receiving liquid, vapor, and refrigerant oil from the
evaporator.
At the bottom of the receiver–dryer is the desiccant, which
acts as a drying agent for the moisture that may have en-
tered the system. An oil bleed hole is located near the bot-
tom of the receiver–dryer outlet pipe to provide an oil re-
turn path to the compressor. The receiver–dryer is
serviceable only as an assembly.
Heater Core
The heater core heats the air before it enters the vehicle.
Engine coolant is circulated through the core to heat the
outside air passing over the fins of the core. The core is
functional at all times and may be used to temper condi-
tioned air in the A/C mode as well as in the heat or the vent
modes.
Page 2054 of 2643

7B – 52IMANUAL CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SYSTEM COMPONENTS–CONTROL
Controller
The operation of the A/C system is controlled by the
switches and the lever on the control head. The compres-
sor clutch and the blower are connected electrically to the
control head by a wiring harness. The blower circuit is
open in the OFF mode. Airflow is provided by the four
blower speeds available in the remaining modes. Cooled
and dehumidified air is available in the MAX, NORMAL,
BI–LEVEL, and DEFROST modes.
The temperature is controlled by the position of the tem-
perature knob on the control head. A cable connects this
knob to the temperature door, which controls the airflow
through the heater core. As the temperature knob is
moved through its range of travel, a sliding clip on the
cable at the temperature valve connection should assume
a position ensuring that the temperature door will seat in
both extreme positions. The temperature door position is
independent of the mode control switch. The temperature
door on some models is controlled electrically, eliminating
the need for the temperature cable.
The electric engine cooling fan on some vehicles is not
part of the A/C control system; however, the fan is opera-
tional any time the A/C control is in the MAX, NORMAL,
or BI–LEVEL modes. Some models provide for engine
cooling fan operation when the controller is in the DE-
FROST mode. This added feature is part of the A/C con-
troller function and is aimed at preventing excessive com-
pressor head temperatures. It also allows the A/C system
to function more efficiently. On some models, the engine
cooling fan will be turned off during road speed conditions
above 56 km/h (35 mph), when the airflow though the con-
denser coil is adequate for efficient cooling. The operation
of the cooling fan is controlled by the powertrain control
module (PCM), or the engine control module (ECM),
through the cooling fan relay.
Pressure Transducer
The pressure transducer incorporates the functions of the
high–pressure and the low–pressure cutout switches
along with the fan cycling switch. The pressure transducer
is located in the high–side liquid refrigerant line near the
right front strut tower and the air filter assembly.
Wide–Open Throttle (WOT) Compressor
Cutoff
During full throttle acceleration on vehicles equipped with
multi–port injection (MPI), the throttle position sensor
(TPS) sends a signal to the PCM or the ECM, which then
controls the compressor clutch.
A/C Time Delay Relay
This relay on some vehicles controls the current to the en-
tire A/C system and provides a short delay of A/C opera-
tion upon start–up.
V5 COMPRESSOR–GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
Different vehicles with V5 compressors may exhibit differ-
ences in mounting and installation, but overhaul proce-
dures are similar.
Before removing the compressor or performing on–ve-
hicle repairs, clean the compressor connections and the
outside of the compressor.
Important : After removing a compressor from the vehicle
for servicing, drain the oil by removing the oil drain plug.
Also drain the oil from the suction and the discharge ports
to insure complete draining. Measure the amount of oil
drained, and record that amount. Discard the used oil and
add the same amount of new polyalkaline glycol (PAG) re-
frigerant oil to the compressor.
The compressor has been removed from the vehicle un-
less otherwise indicated.
Clean tools and a clean work area are important for proper
servicing. Keep dirt and foreign material from getting on or
into the compressor parts. Parts that are to be reassem-
bled should be cleaned with trichloroethane, naphtha,
stoddard solvent, kerosene, or equivalent solvents. Dry
the cleaned parts with clean dry air. Use only lint–free
cloths to wipe the parts.
V5 COMPRESSOR–DESCRIPTION OF
OPERATION
The V5 is a variable displacement compressor that can
match the automotive air conditioning (A/C) demand un-
der all conditions without cycling. The basic compressor
mechanism is a variable angle wobble–plate with five ax-
ially oriented cylinders. The center of control of the com-
pressor displacement is a bellows–actuated control valve
located in the rear head of the compressor. The control
valve senses compressor suction pressure.
The wobble–plate angle and the compressor displace-
ment are controlled by the crankcase suction pressure dif-
ferential. When the A/C capacity demand is high, the suc-
tion pressure will be above the control point. The valve will
maintain a bleed from crankcase to suction. With no
crankcase suction pressure differential, the compressor
will have maximum displacement.
When the A/C capacity demand is lower and the suction
pressure reaches the control point, the valve will bleed dis-
charge gas into the crankcase and close off a passage
from the crankcase to the suction plenum. The angle of the
wobble–plate is controlled by a force balance on the five
pistons. A slight elevation of the crankcase suction pres-
sure differential creates total force on the pistons resulting
in a movement about the wobbleplate pivot pin that re-
duces the plate angle.
The compressor has a unique lubrication system. The
crankcase suction bleed is routed through the rotating
wobble–plate for lubrication of the wobble–plate bearing.
The rotation acts as an oil separator which removes some
Page 2094 of 2643

IAUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION, AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM 7D – 39
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
UNIT REPAIR
V5 AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR OVERHAUL
COMPRESSOR OVERHAUL
Refer to Section 7B, Manual Control Heating, Ventilation,
and Air Conditioning System for details of the following
procedures:
S Clutch Coil.
S Clutch Plate and Hub Assembly.
S Clutch Rotor and Bearing.
S Component Locator V5 Compressor.
S Control Valve Assembly.
S Cylinder to Front Head O–Ring.
S Leak Testing (External).
S Pressure Relief Valve.
S Rear Head, Gasket, Valve Plate, Reed Plate, and
O–Ring.
S Shaft Seal Replacement.
Page 2104 of 2643

SEAT BELTS 8A – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
DRIVER SEAT BELT WARNING
The driver’s safety belt incorporates a safety belt reminder
light in the instrument cluster to remind the driver if the
safety belt is not fastened when the the ignition is turned
ON.
THREE–POINT ELR FRONT SEAT
BELT WITH PRETENSIONER
The three–point emergency locking retractor (ELR) front
seat belt pretensioner is always unlocked, allowing the
passenger freedom of movement, except in emergencies
such as rapid deceleration, rapid acceleration, or hard cor-
nering maneuvers.
The front seat belt pretensioner contains an ignitor charge
and a gas generator to inflate the pretensioner. The pre-
tensioner also includes wiring and a connector. The con-
nector of the pretensioner contains a shorting bar which
short–circuits the pretensioner high circuit to the preten-
sioner low circuit when the connector is disconnected. The
shorting bar prevents current from traveling through the
pretensioner during servicing. The shorting bar disen-
gaged when the connecotr is connected.
The pretensioner is an electronically controlled pyrotech-
nical reactor which reduce seat belt slack when it is actived
with air bags.
The front seat belt pretensioner must be replaced after an
accident that cause its activation.
THREE–POINT CLR (ELR) REAR
OUTBOARD SEAT BELT
The rear outboard seating positions use the three–point
child locking retractor (CLR) or emergency locking retrac-
tor (ELR) seat belts. The three–point CLR (ELR) seat beltis always unlocked, allowing the passenger freedom of
movement, except in emergencies such as rapid decel-
eration, rapid acceleration, or hard cornering maneuvers.
OPERATIONAL AND FUNCTIONAL
CHECKS
CAUTION :
S Keep sharp objects and potentially damaging
objects away from the seat belts.
S Avoid bending or damaging any portion of the
buckle or the latch plate.
S Do not bleach or dye the belt webbing. Use
only mild soap and water in order to clean the
belts.
S When installing the seat belt anchor bolts and
the screws, start the bolts and the screws by
hand in order to prevent cross–threading.
S Do not attempt any repairs on the retractor
mechanisms or the covers. Replace any defec-
tive assemblies with new assemblies.
S Replace any belts that are cut or damaged in
any way.
1. Inspect all seat belt anchor bolts and the screws in
order to verify that they are secure.
2. Inspect the seat belt buckle. The buckle must lock
and unlock easily.
3. After inserting the latch into the buckle, tug sharply
on the belt. The buckle must remain locked.
4. Fully extend the shoulder belt portion to make sure
that there is no twisting or tears in the belt.
5. Let the shoulder belt retract fully. The belt should
retract easily.
CHILD SEAT TETHER ANCHOR
For notch back vehicle, there are three child seat tether
anchors located on the read deck lid sill plate. For hatch
back vehicle, there are three child seat fether anchors on
the lower rear tail member in the luggage compartment.
And there are 4 lower child anchors under the rear seat.
4 circular discs on the rear seat indicate the location of the
lower child anchors.
Page 2204 of 2643
8B – 100ISUPPLEMENTAL INFLATABLE RESTRAINTS (SIR)
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
SUPPLEMENTAL INFLATABLE
RESTRAINTS(SIR)
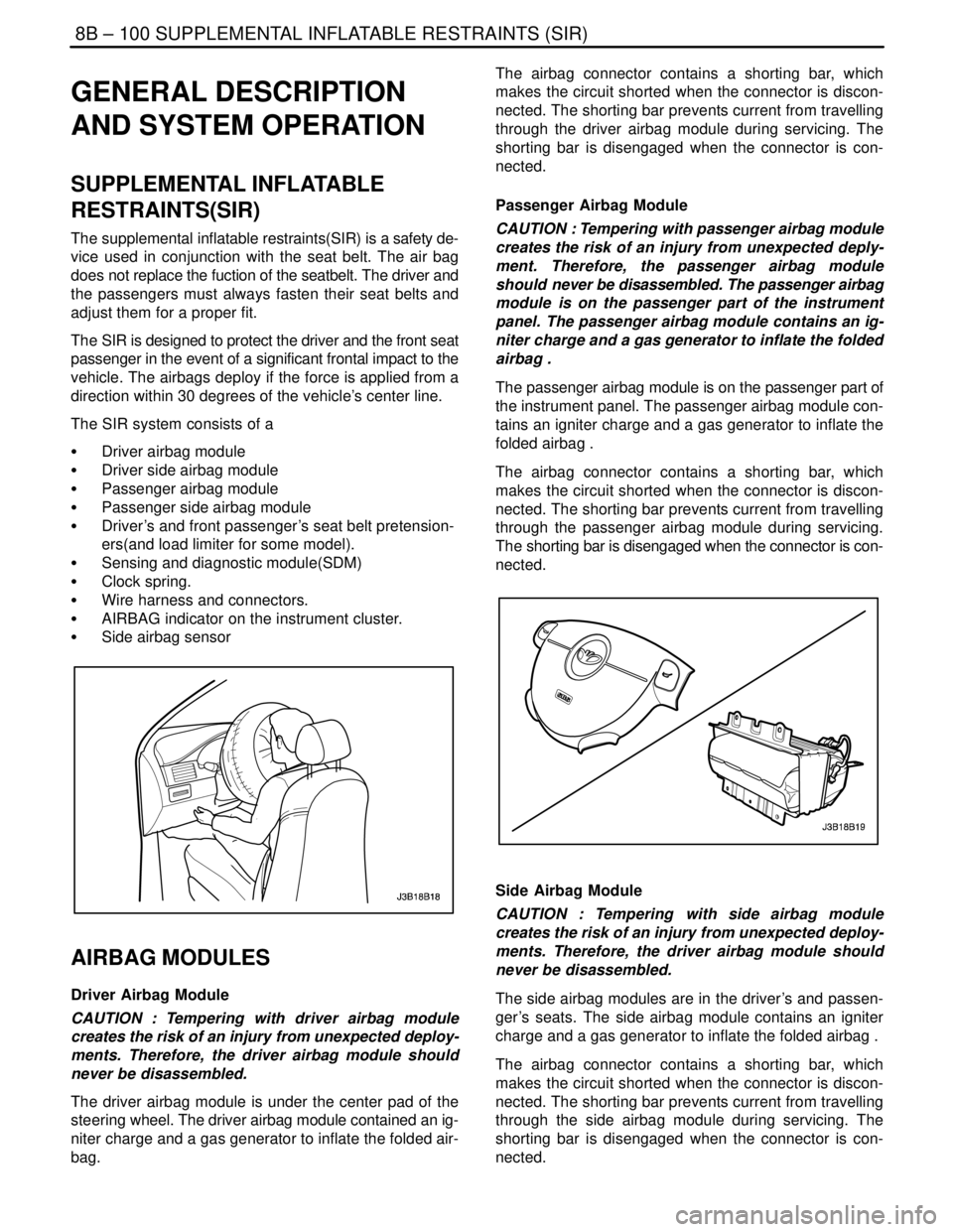
The supplemental inflatable restraints(SIR) is a safety de-
vice used in conjunction with the seat belt. The air bag
does not replace the fuction of the seatbelt. The driver and
the passengers must always fasten their seat belts and
adjust them for a proper fit.
The SIR is designed to protect the driver and the front seat
passenger in the event of a significant frontal impact to the
vehicle. The airbags deploy if the force is applied from a
direction within 30 degrees of the vehicle’s center line.
The SIR system consists of a
S Driver airbag module
S Driver side airbag module
S Passenger airbag module
S Passenger side airbag module
S Driver’s and front passenger’s seat belt pretension-
ers(and load limiter for some model).
S Sensing and diagnostic module(SDM)
S Clock spring.
S Wire harness and connectors.
S AIRBAG indicator on the instrument cluster.
S Side airbag sensor
AIRBAG MODULES
Driver Airbag Module
CAUTION : Tempering with driver airbag module
creates the risk of an injury from unexpected deploy-
ments. Therefore, the driver airbag module should
never be disassembled.
The driver airbag module is under the center pad of the
steering wheel. The driver airbag module contained an ig-
niter charge and a gas generator to inflate the folded air-
bag.The airbag connector contains a shorting bar, which
makes the circuit shorted when the connector is discon-
nected. The shorting bar prevents current from travelling
through the driver airbag module during servicing. The
shorting bar is disengaged when the connector is con-
nected.
Passenger Airbag Module
CAUTION : Tempering with passenger airbag module
creates the risk of an injury from unexpected deply-
ment. Therefore, the passenger airbag module
should never be disassembled. The passenger airbag
module is on the passenger part of the instrument
panel. The passenger airbag module contains an ig-
niter charge and a gas generator to inflate the folded
airbag .
The passenger airbag module is on the passenger part of
the instrument panel. The passenger airbag module con-
tains an igniter charge and a gas generator to inflate the
folded airbag .
The airbag connector contains a shorting bar, which
makes the circuit shorted when the connector is discon-
nected. The shorting bar prevents current from travelling
through the passenger airbag module during servicing.
The shorting bar is disengaged when the connector is con-
nected.
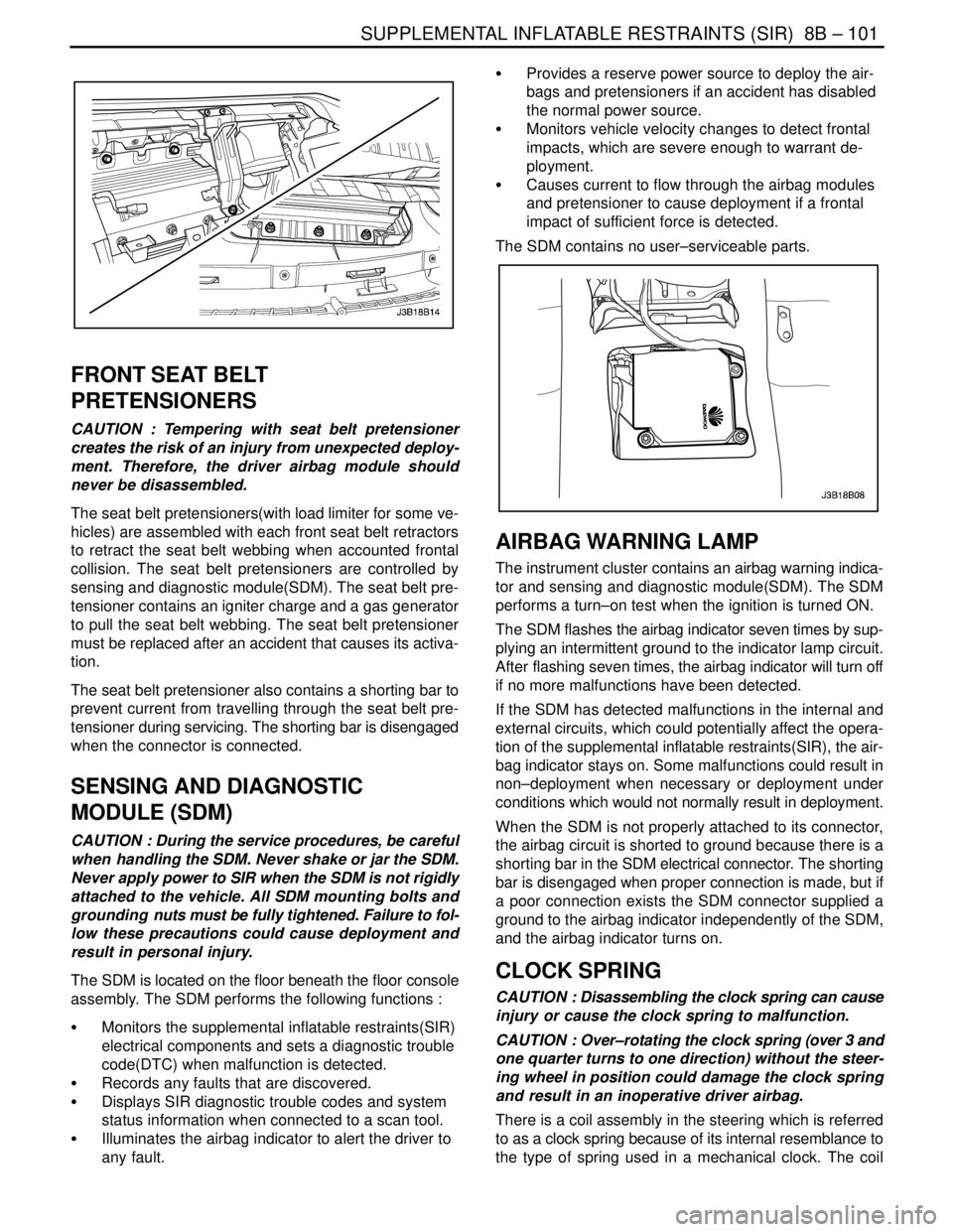
Side Airbag Module
CAUTION : Tempering with side airbag module
creates the risk of an injury from unexpected deploy-
ments. Therefore, the driver airbag module should
never be disassembled.
The side airbag modules are in the driver’s and passen-
ger’s seats. The side airbag module contains an igniter
charge and a gas generator to inflate the folded airbag .
The airbag connector contains a shorting bar, which
makes the circuit shorted when the connector is discon-
nected. The shorting bar prevents current from travelling
through the side airbag module during servicing. The
shorting bar is disengaged when the connector is con-
nected.
Page 2205 of 2643
SUPPLEMENTAL INFLATABLE RESTRAINTS (SIR) 8B – 101
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FRONT SEAT BELT
PRETENSIONERS
CAUTION : Tempering with seat belt pretensioner
creates the risk of an injury from unexpected deploy-
ment. Therefore, the driver airbag module should
never be disassembled.
The seat belt pretensioners(with load limiter for some ve-
hicles) are assembled with each front seat belt retractors
to retract the seat belt webbing when accounted frontal
collision. The seat belt pretensioners are controlled by
sensing and diagnostic module(SDM). The seat belt pre-
tensioner contains an igniter charge and a gas generator
to pull the seat belt webbing. The seat belt pretensioner
must be replaced after an accident that causes its activa-
tion.
The seat belt pretensioner also contains a shorting bar to
prevent current from travelling through the seat belt pre-
tensioner during servicing. The shorting bar is disengaged
when the connector is connected.
SENSING AND DIAGNOSTIC
MODULE (SDM)
CAUTION : During the service procedures, be careful
when handling the SDM. Never shake or jar the SDM.
Never apply power to SIR when the SDM is not rigidly
attached to the vehicle. All SDM mounting bolts and
grounding nuts must be fully tightened. Failure to fol-
low these precautions could cause deployment and
result in personal injury.
The SDM is located on the floor beneath the floor console
assembly. The SDM performs the following functions :
S Monitors the supplemental inflatable restraints(SIR)
electrical components and sets a diagnostic trouble
code(DTC) when malfunction is detected.
S Records any faults that are discovered.
S Displays SIR diagnostic trouble codes and system
status information when connected to a scan tool.
S Illuminates the airbag indicator to alert the driver to
any fault.S Provides a reserve power source to deploy the air-
bags and pretensioners if an accident has disabled
the normal power source.
S Monitors vehicle velocity changes to detect frontal
impacts, which are severe enough to warrant de-
ployment.
S Causes current to flow through the airbag modules
and pretensioner to cause deployment if a frontal
impact of sufficient force is detected.
The SDM contains no user–serviceable parts.
AIRBAG WARNING LAMP
The instrument cluster contains an airbag warning indica-
tor and sensing and diagnostic module(SDM). The SDM
performs a turn–on test when the ignition is turned ON.
The SDM flashes the airbag indicator seven times by sup-
plying an intermittent ground to the indicator lamp circuit.
After flashing seven times, the airbag indicator will turn off
if no more malfunctions have been detected.
If the SDM has detected malfunctions in the internal and
external circuits, which could potentially affect the opera-
tion of the supplemental inflatable restraints(SIR), the air-
bag indicator stays on. Some malfunctions could result in
non–deployment when necessary or deployment under
conditions which would not normally result in deployment.
When the SDM is not properly attached to its connector,
the airbag circuit is shorted to ground because there is a
shorting bar in the SDM electrical connector. The shorting
bar is disengaged when proper connection is made, but if
a poor connection exists the SDM connector supplied a
ground to the airbag indicator independently of the SDM,
and the airbag indicator turns on.
CLOCK SPRING
CAUTION : Disassembling the clock spring can cause
injury or cause the clock spring to malfunction.
CAUTION : Over–rotating the clock spring (over 3 and
one quarter turns to one direction) without the steer-
ing wheel in position could damage the clock spring
and result in an inoperative driver airbag.
There is a coil assembly in the steering which is referred
to as a clock spring because of its internal resemblance to
the type of spring used in a mechanical clock. The coil
Page 2472 of 2643
SECTION : 9S
BODY REAR END
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS9S–1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 9S–1. . . . . . . . . . .
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR9S–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE 9S–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filler Door 9S–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filler Door Remote Handle and Cable 9S–2. . . .
Rear Deck Lid 9S–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Deck Lid Torque Rods 9S–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Luggage Compartment Lock Cylinder 9S–5. . . . . . . .
Luggage Compartment Lock Striker 9S–6. . . . . . . . . .
Luggage Compartment Lock 9S–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Weatherstrip 9S–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hatchback Weatherstrip 9S–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hatchback Door 9S–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Gas Support Assemblies 9S–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hatchback Door Lock Striker 9S–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hatchback Door Lock 9S–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION9S–10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filler Door 9S–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Deck Lid (Notchback) 9S–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hatchback Door 9S–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIFICATIONS
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb–FtLb–In
Fuel Filler Door Screws4–35
Fuel Filler Door Remote Cable Handle Cover Screw3–27
Fuel Filler Door Remote Cable Handle Screws10–89
Lower B–Pillar Seat Belt Anchor Bolt3828–
Luggage Compartment Lock Cylinder Nuts8–71
Luggage Compartment Lock Screws6–53
Luggage Compartment Lock Striker Bolts8–71
Rear Deck Lid Bolts10–89