2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA automatic transaxle
[x] Cancel search: automatic transaxlePage 1387 of 2643
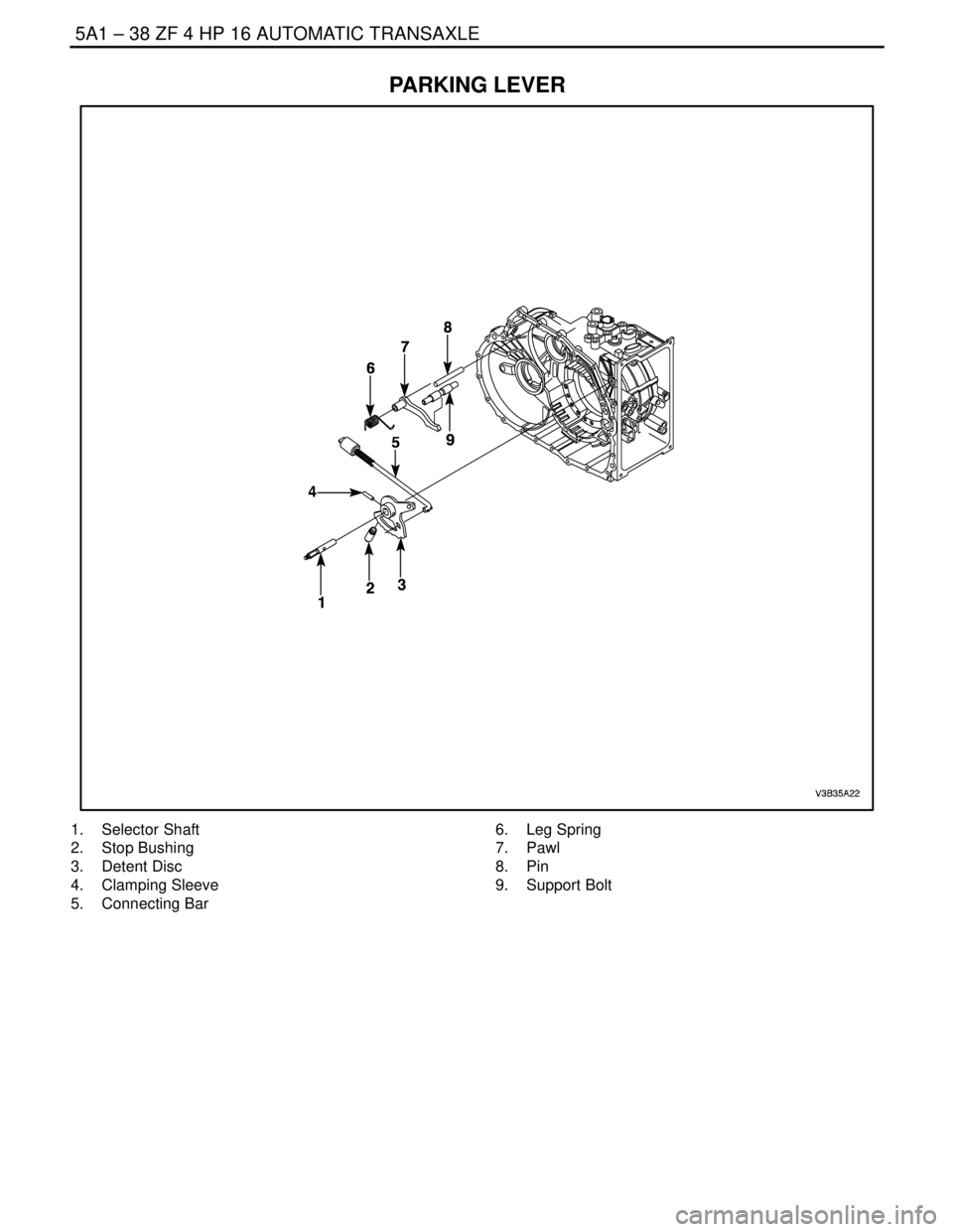
5A1 – 38IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
PARKING LEVER
1. Selector Shaft
2. Stop Bushing
3. Detent Disc
4. Clamping Sleeve
5. Connecting Bar6. Leg Spring
7. Pawl
8. Pin
9. Support Bolt
Page 1388 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 39
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
INPUT SHAFT & SHIFT GEAR
Page 1389 of 2643

5A1 – 40IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
1. Inner Disc Carrier F
2. Clutch Plate F
3. Line Clutch Disc F
4. Clutch Outer Disc F
5. Spring Disc
6. Stop Ring
7. Cup Spring
8. O–ring
9. O–ring
10. Piston D
11. Slotted Nut
12. Roller Bearing
13. Adjust Ring
14. Bearing Plate
15. Roller Bearing
16. Spur Gear
17. Piston D
18. Spring Disc
19. Snap Ring
20. Clutch Plate D
21. Cup Spring
22. Line Clutch Disc D
23. Spring Disc
24. Disc Carrier C/D
25. Pitting Key
26. Line Clutch Disc C
27. Clutch Outer Disc C
28. Cup Spring
29. Line Clutch Disc C
30. Snap Ring
31. Piston C
32. Cylinder C
33. Snap Ring
34. Front Ring Gear
35. Oil Tray
36. Front Planetary Gear
37. Front Sun Gear
38. Snap Ring
39. Needle Bearing40. Rear Planetary Gear Set
41. Snap Ring
42. Rear Sun Gear
43. Needle Bearing
44. Snap Ring
45. Piston B
46. Clutch Plate B
47. Clutch Outer Disc B
48. Line Clutch Disc B
49. Spring Disc
50. Piston Ring
51. Inner Disc Carrier E
52. Needle Bearing
53. Snap Ring
54. Clutch Plate Disc E
55. Line Clutch Disc E
56. Clutch Outer Disc E
57. Spring Disc
58. Retainer Ring
59. O–ring
60. Oil Dam
61. Cup Spring
62. O–ring
63. Piston E
64. O–ring
65. Input Shaft
66. O–ring
67. O–ring
68. Piston
69. Oil Dam
70. O–ring
71. Cup Spring
72. Stop Ring
73. Shim
74. Needle Bearing
75. O–ring
76. Piston Ring
77. Rear Cover
Page 1390 of 2643
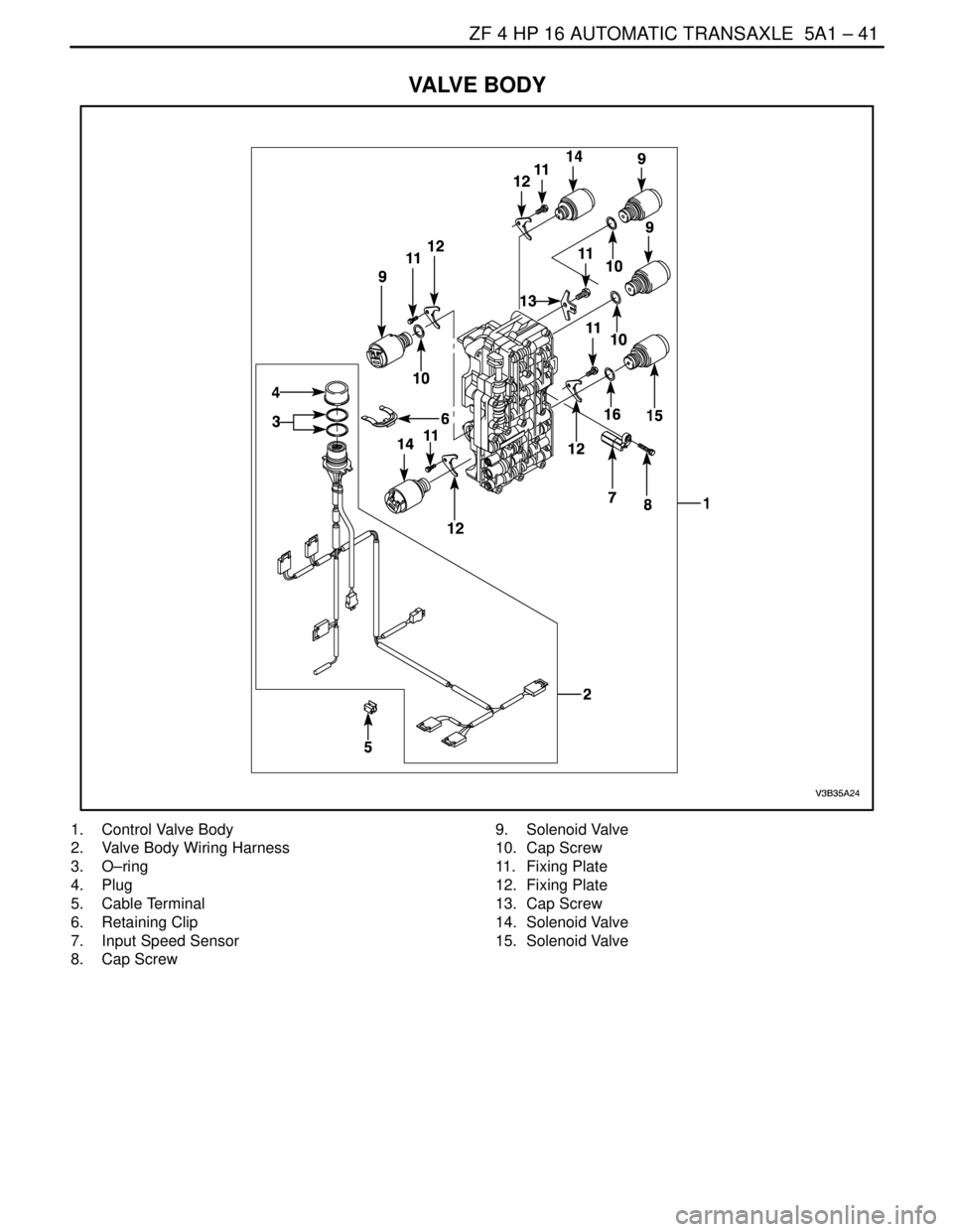
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 41
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
VALVE BODY
1. Control Valve Body
2. Valve Body Wiring Harness
3. O–ring
4. Plug
5. Cable Terminal
6. Retaining Clip
7. Input Speed Sensor
8. Cap Screw9. Solenoid Valve
10. Cap Screw
11. Fixing Plate
12. Fixing Plate
13. Cap Screw
14. Solenoid Valve
15. Solenoid Valve
Page 1391 of 2643
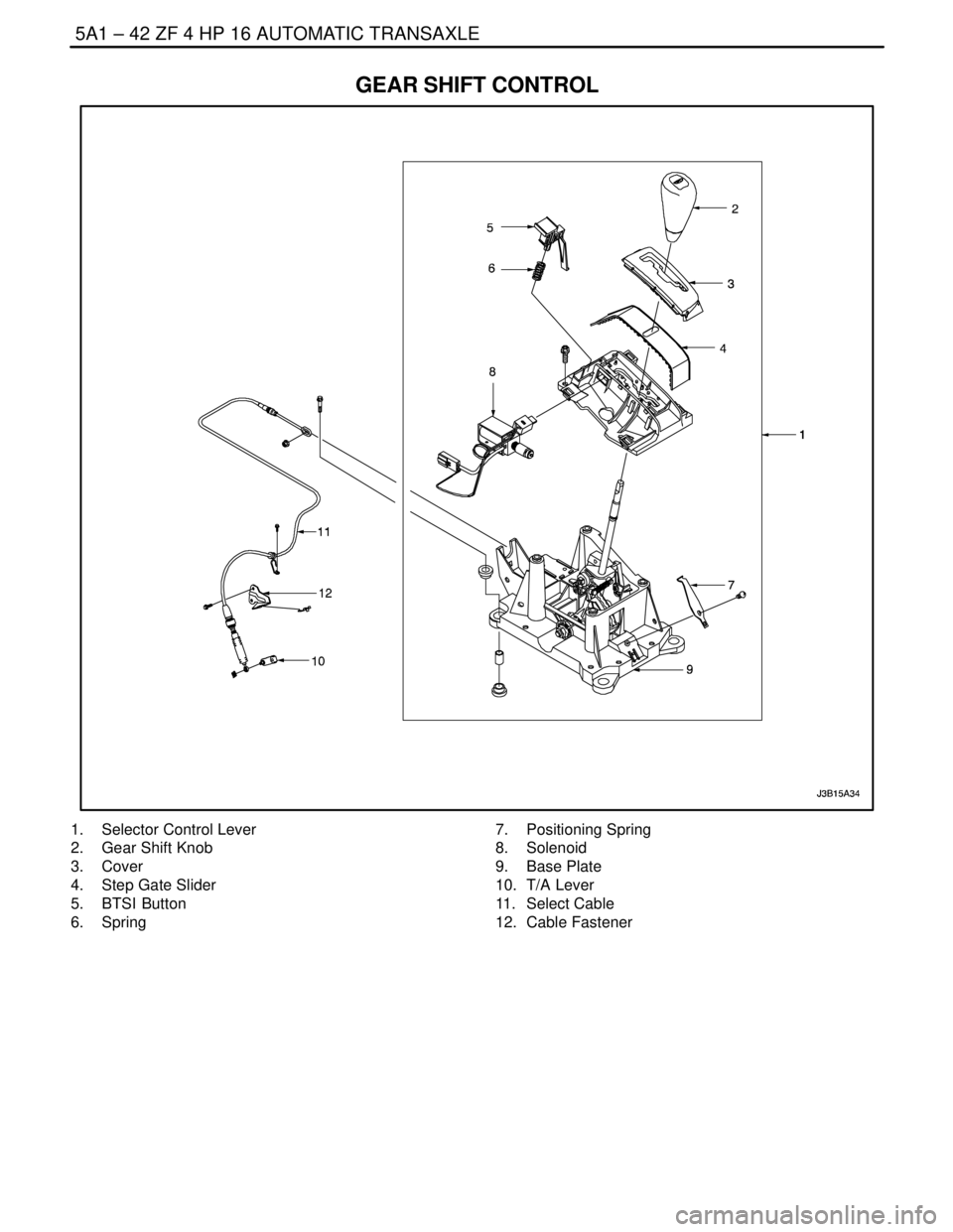
5A1 – 42IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GEAR SHIFT CONTROL
1. Selector Control Lever
2. Gear Shift Knob
3. Cover
4. Step Gate Slider
5. BTSI Button
6. Spring7. Positioning Spring
8. Solenoid
9. Base Plate
10. T/A Lever
11. Select Cable
12. Cable Fastener
Page 1392 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 43
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND
PROCEDURES DIAGNOSIS
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
You must be familiar with some basic electronics to use
this section of the Service Manual. They will help you to
follow diagnostic procedures.
Notice : Lack of the basic knowledge of this transaxle
when performing diagnostic procedures could result in in-
correct diagnostic performance or damage to transaxle
components.
Do not, under any circumstances, attempt to diagnose a
transaxle problem without this basic knowledge.
Notice : If a wire is probed with a sharp instrument and not
properly sealed afterward, the wire will corrode and an
open circuit will result.
Diagnostic test probes are now available that allow you to
probe individual wires without leaving the wire open to the
environment. These probe devices are inexpensive and
easy to install, and they permanently seal the wire from
corrosion.
Special Tools
You should be able to use a Digital Volt Meter (DVM), a cir-
cuit tester, jumper wires or leads and a line pressure gauge
set.
The functional check procedure is designed to verify the
correct operation of electronic components in the trans-
axle.
This will eliminate the unnecessary removal of transaxle
components.
FUNCTIONAL CHECK PROCEDURE
Begin with the Functional Check Procedure which pro-
vides a general outline of how to diagnose automatic
transaxle. The following functional check procedure will in-
dicate the proper path of diagnosing the transaxle by de-
scribing the basic checks and then referencing the loca-
tions of the specific checks.
S Check the fluid level according to the Fluid Level
Service Procedure.
S Check the transaxle for fluid leaks.
S Check if the transaxle fluid is not burnt by color and
smell.
S Ensure that the transaxle is not in Limp Home
Mode(LHM).
S Check the battery terminals and the ground con-
nections for corrosion or looseness.
S Check that the cooler flow is not restricted.S Check all electrical connections for tightness.
S Use on–board diagnostic tool or a scan tool to see
if any transaxle trouble codes have been set. Refer
to the appropriate ”Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)”
information and repair the vehicle as directed. After
repairing the vehicle, perform the road test and
verify that the code has not set again.
S Perform the Electrical/Garage Shift Tests.
S Perform the Road Test Procedure in this section.
S Inspect the oil and check for metal or other contam-
inants in the oil pan.
LINE PRESSURE CHECK
PROCEDURE
The 4HP 16 A/T uses a trochoid type oil pump to produce
hydraulic pressure, and a pressure control solenoid (sole-
noid 1) to control that pressure at the pressure regulator
valve, after it leaves the pump. The transaxle pressure
control solenoid is controlled by an electrical signal that
ranges from 0 to 12 volts corresponds to minimum line
pressure (approx. 89.9 to 124.7 psi (6.2 to 8.6 bar)) and
0 volt corresponds to a maximum line pressure (approx.
221.9 to 252.4 psi (15.3 to 17.4 bar)) in all range.
Line pressures are calculated for two sets of gear ranges
– Drive–Park–Neutral and Reverse. This allow the trans-
axle line pressure to be appropriate for different pressure
needs in different gear ranges:
Gear
Range
Solenoid
1RPMPressure
Drive,
ReverseOff2,500221.9~252.4psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
On2,50017.4~269.8psi
(1.2~18.6 bar)
Neutral,
ParkOff2,500221.9~252.4psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
On2,50089.9~269.8 psi
(6.2~18.6 bar)
Before performing a line pressure check, verify that the
pressure control solenoid is receiving the correct electrical
signal from the TCM:
1. Install a scan tool.
2. Start the engine and set parking brake.
3. Check for a stored pressure control solenoid diag-
nostic trouble code, and other diagnostic trouble
codes.
Page 1393 of 2643
5A1 – 44IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Repair vehicle, if necessary.
Inspect:
S Fluid level.
S Manual linkage.
Install or Connect:
S Scan tool (scanner)
S Oil pressure gauge at line pressure port (clutch B or
E ports on transaxle case)
5. Put gear selector in Park and set the parking brake.6. Start engine and allow it to warm up at idle.
7. Access the ”Solenoid 1 Control Mode” on the scan-
ner.
8. Switching solenoid 1 ON/OFF, accelerating the en-
gine to 2,500rpm, and then read the line pressure
at the each gear.
9. Compare data to the Drive–Park–Neutral line pres-
sure chart below.
Notice : Total test running time should not exceed 2 min-
utes, or transaxle damage could occur.
CAUTION : Brake must be applied at all times to pre-
vent unexpected vehicle motion.
If pressure readings differ greatly from the line pressure
chart, refer to the Diagnosis Charts contained in this sec-
tion.
Notice : Clutch damage may occur.
The scanner is only able to control the pressure control so-
lenoid in Park and Neutral with the vehicle stopped.
This protects the clutches from extremely high or low pres-
sures in Drive or Reverse rang.
Gear Range
SolenoidLine
Pressure B PortE Port
Park / NeutralONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 ps
i (15.3~17.4 bar)
ReverseONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
DriveONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH137.7~162.4 psi
(9.5~11.2 bar)
3ONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)137.7~162.4 psi
(9.5~11.2 bar)
2ONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH137.7~162.4 psi
(9.5~11.2 bar)
1ONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
Page 1394 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 45
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
CLUTCH PLATE DIAGNOSIS
Composition Plates
Dry the plate and inspect the plates for the following condi-
tions :
S Pitting
S Flaking
S Wear
S Glazing
S Cracking
S Charring
Chips or metal particles embedded in the lining
Replace a composition plate which shows any of these
conditions.
Steel Plates
Wipe the plates dry and check the plates for heat discolor-
ation. If the surfaces are smooth, even if colorsmear is in-
dicated, you can reuse the plate. If the plate is discolored
with hot spots or if the surface is scuffed, replace the plate.
Important : If the clutch shows evidence or extreme heat
or burning, replace the springs.
Causes of Burned Clutch Plates
The following conditions can result in a burned clutch
plate:
S Incorrect usage of clutch plates.
S Engine coolant in the transaxle fluid.
S A cracked clutch piston.
S Damaged or missing seals.
S Low line pressure.
S Valve problems.
– The valve body face is not flat
– Porosity between channels
– The valve bushing clips are improperly installed.
– The check balls are misplaced.
S The seal rings are worn or damaged
Engine Coolant in Transaxle
Notice : Antifreeze will deteriorate the O–ring seals and
the glue used to bond the clutch material to the pressure
plate. Both conditions may cause transaxle damage.
Perform the following steps if the transaxle oil cooler has
developed a leak, allowing engine coolant to enter the
transaxle:
1. Because the coolant will attach to the seal material
causing leakage, disassemble the transaxle and
replace all rubber type seals.
2. Because the facing material may become sepa-
rated from the steel center portion, replace the
composition faced clutch plate assemblies.
3. Replace all nylon parts including washers.
4. Replace the torque converter.
5. Thoroughly clean and rebuild the transaxle, using
new gaskets and oil filter.6. Flush the cooler lines after you have properly re-
paired or replaced the transaxle.
COOLER FLUSHING AND FLOW
TEST
Notice : You must flush the cooler whenever you receive
a transaxle for service. Cooler flushing is essential for
SRTA installation, major overhaul, whenever you replace
a pump or torque converter, or whenever you suspect that
the fluid has been contaminated.
After filling the transaxle with fluid, start the engine and run
for 30 seconds. This will remove any residual moisture
from the oil cooler. Disconnect the return line at the trans-
axle and observe the flow with the engine running. If the
fluid flow is insufficient, check the fluid flow by disconnect-
ing the feed line at the cooler. Observe the flow with the
engine running.
S If the flow from the cooler return line at the trans-
axle is insufficient, check the flow rate from the feed
line to the cooler. BLockage exists in the transaxle
or the cooler.
S If the flow from the transaxle feed line to the cooler
is insufficient, the transaxle is the cause of the fluid
flow problem.
S If the flow the transaxle feed line to the cooler is
insufficient, but flow from the cooler return line to
the transaxle is insufficient, inspect the cooler pipes
and fittings. Then repeat the cooler flushing proce-
dure. If the flow is still insufficient, replace the cool-
er.
TRANSAXLE FLUID LEVEL SERVICE
PROCEDURE
This procedure is to be used when checking a concern
with the fluid level in a vehicle. A low fluid level will result
in slipping and loss of drive/ reverse or delay on engage-
ment of drive/ reverse when the vehicle is cold.
The vehicle is first checked for transaxle diagnostic mes-
sages on the scan tool. If the oil level is low, it is possible
to register a vehicle speed signal fault.
The vehicle is to be test driven to determine if there is an
abnormal delay when selecting drive or reverse, or loss of
drive. One symptom of low fluid level is a momentary loss
of drive when driving the vehicle around a corner. Also
when the transaxle fluid level is low, a loss of drive may oc-
cur when the transaxle fluid temperature is low.
When adding or changing transaxle fluid use only ESSO
LT 71141 automatic transaxle fluid or other approved
fluids. The use of incorrect fluid will cause the performance
and durability of the transaxle to be severely degraded.
Fluid Level Diagnosis Procedure
1. If the vehicle is at operating temperature allow the
vehicle to cool down for two hours, but no greater
than four hours. Or if the vehicle is at cool status,
start the engine and allow the engine to idle for
approximately 5 minutes (825~875 rpm), if pos-