2004 DAEWOO LACETTI hydraulic
[x] Cancel search: hydraulicPage 5 of 2643
v
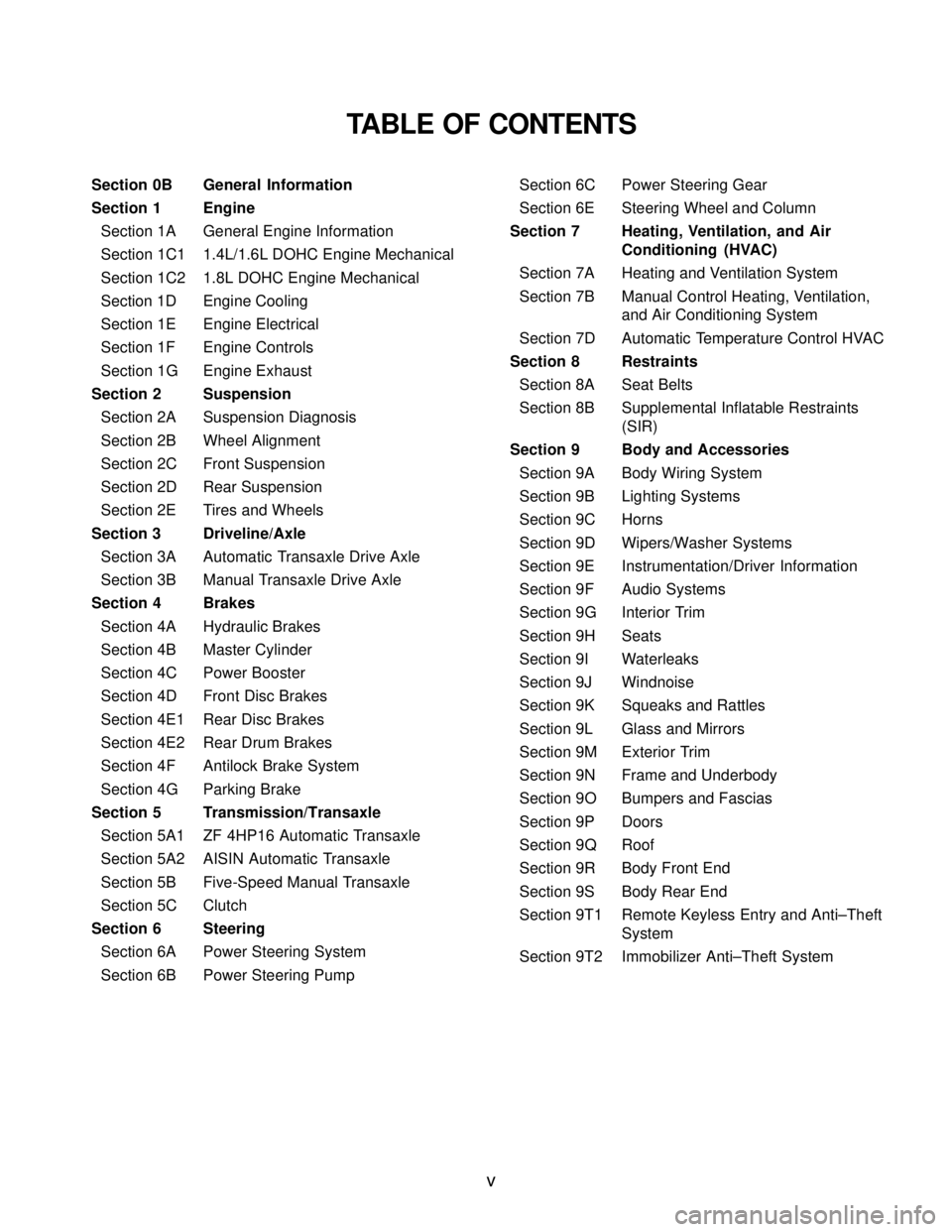
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section 0B General Information
Section 1 Engine
Section 1A General Engine Information
Section 1C1 1.4L/1.6L DOHC Engine Mechanical
Section 1C2 1.8L DOHC Engine Mechanical
Section 1D Engine Cooling
Section 1E Engine Electrical
Section 1F Engine Controls
Section 1G Engine Exhaust
Section 2 Suspension
Section 2A Suspension Diagnosis
Section 2B Wheel Alignment
Section 2C Front Suspension
Section 2D Rear Suspension
Section 2E Tires and Wheels
Section 3 Driveline/Axle
Section 3A Automatic Transaxle Drive Axle
Section 3B Manual Transaxle Drive Axle
Section 4 Brakes
Section 4A Hydraulic Brakes
Section 4B Master Cylinder
Section 4C Power Booster
Section 4D Front Disc Brakes
Section 4E1 Rear Disc Brakes
Section 4E2 Rear Drum Brakes
Section 4F Antilock Brake System
Section 4G Parking Brake
Section 5 Transmission/Transaxle
Section 5A1 ZF 4HP16 Automatic Transaxle
Section 5A2 AISIN Automatic Transaxle
Section 5B Five-Speed Manual Transaxle
Section 5C Clutch
Section 6 Steering
Section 6A Power Steering System
Section 6B Power Steering PumpSection 6C Power Steering Gear
Section 6E Steering Wheel and Column
Section 7 Heating, Ventilation, and Air
Conditioning (HVAC)
Section 7A Heating and Ventilation System
Section 7B Manual Control Heating, Ventilation,
and Air Conditioning System
Section 7D Automatic Temperature Control HVAC
Section 8 Restraints
Section 8A Seat Belts
Section 8B Supplemental Inflatable Restraints
(SIR)
Section 9 Body and Accessories
Section 9A Body Wiring System
Section 9B Lighting Systems
Section 9C Horns
Section 9D Wipers/Washer Systems
Section 9E Instrumentation/Driver Information
Section 9F Audio Systems
Section 9G Interior Trim
Section 9H Seats
Section 9I Waterleaks
Section 9J Windnoise
Section 9K Squeaks and Rattles
Section 9L Glass and Mirrors
Section 9M Exterior Trim
Section 9N Frame and Underbody
Section 9O Bumpers and Fascias
Section 9P Doors
Section 9Q Roof
Section 9R Body Front End
Section 9S Body Rear End
Section 9T1 Remote Keyless Entry and Anti–Theft
System
Section 9T2 Immobilizer Anti–Theft System
Page 38 of 2643
1A – 6IGENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
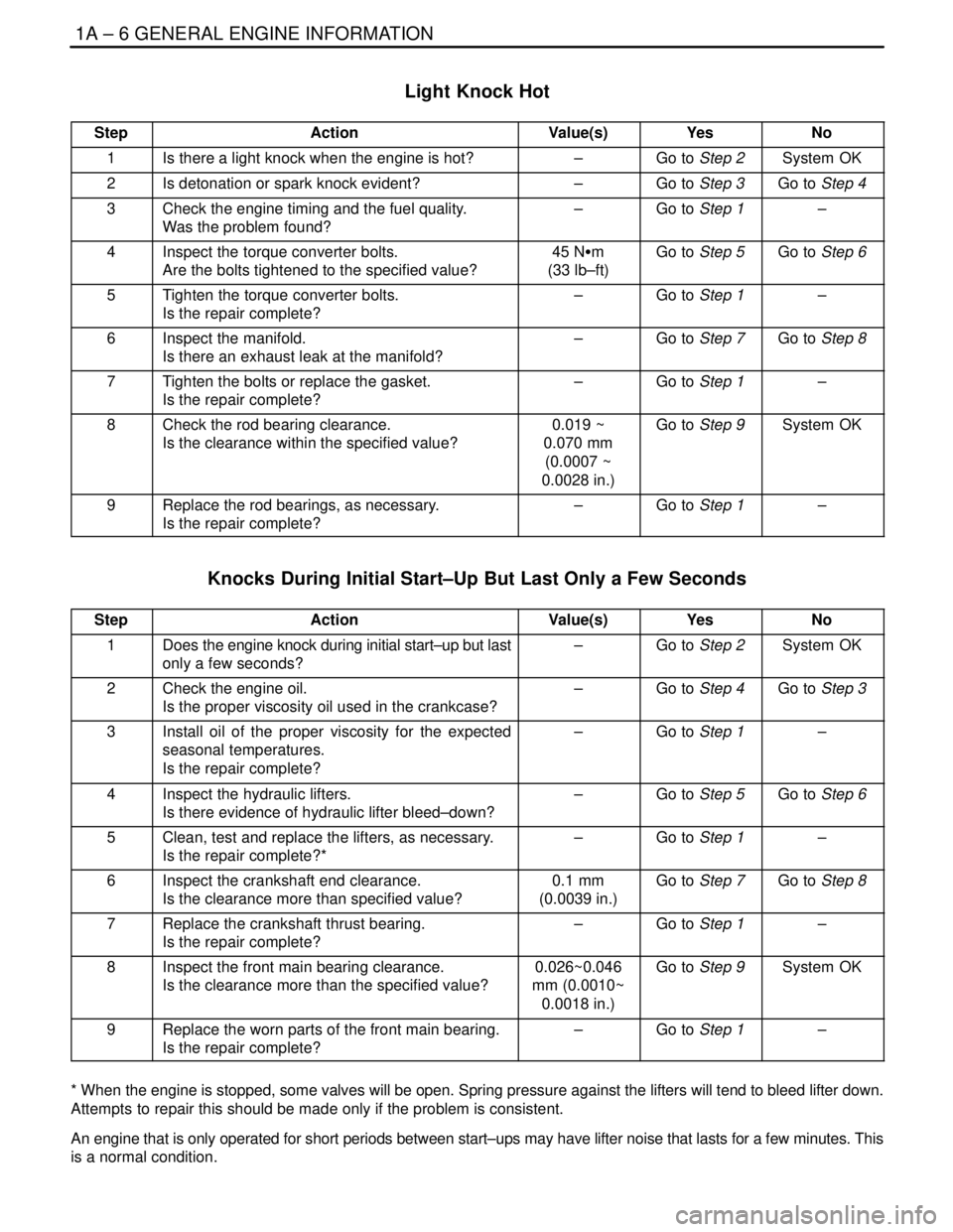
Light Knock Hot
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Is there a light knock when the engine is hot?–Go to Step 2System OK
2Is detonation or spark knock evident?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Check the engine timing and the fuel quality.
Was the problem found?–Go to Step 1–
4Inspect the torque converter bolts.
Are the bolts tightened to the specified value?45 NSm
(33 lb–ft)Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Tighten the torque converter bolts.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
6Inspect the manifold.
Is there an exhaust leak at the manifold?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Tighten the bolts or replace the gasket.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
8Check the rod bearing clearance.
Is the clearance within the specified value?0.019 ~
0.070 mm
(0.0007 ~
0.0028 in.)Go to Step 9System OK
9Replace the rod bearings, as necessary.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
Knocks During Initial Start–Up But Last Only a Few Seconds
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Does the engine knock during initial start–up but last
only a few seconds?–Go to Step 2System OK
2Check the engine oil.
Is the proper viscosity oil used in the crankcase?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
3Install oil of the proper viscosity for the expected
seasonal temperatures.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
4Inspect the hydraulic lifters.
Is there evidence of hydraulic lifter bleed–down?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Clean, test and replace the lifters, as necessary.
Is the repair complete?*–Go to Step 1–
6Inspect the crankshaft end clearance.
Is the clearance more than specified value?0.1 mm
(0.0039 in.)Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Replace the crankshaft thrust bearing.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
8Inspect the front main bearing clearance.
Is the clearance more than the specified value?0.026~0.046
mm (0.0010~
0.0018 in.)Go to Step 9System OK
9Replace the worn parts of the front main bearing.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
* When the engine is stopped, some valves will be open. Spring pressure against the lifters will tend to bleed lifter down.
Attempts to repair this should be made only if the problem is consistent.
An engine that is only operated for short periods between start–ups may have lifter noise that lasts for a few minutes. This
is a normal condition.
Page 46 of 2643
1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
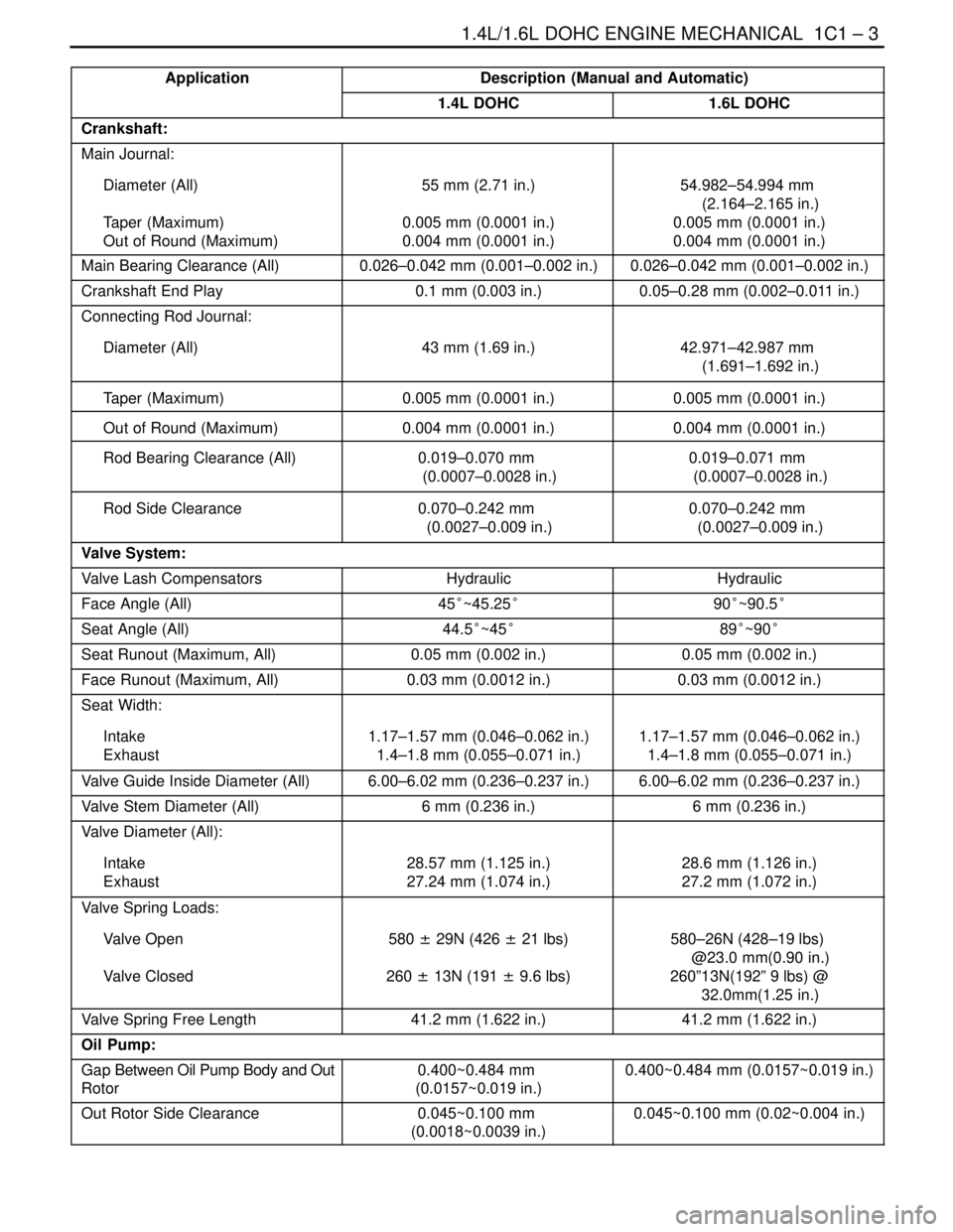
ApplicationDescription (Manual and Automatic)
1.4L DOHC1.6L DOHC
Crankshaft:
Main Journal:
Diameter (All)
Taper (Maximum)
Out of Round (Maximum)55 mm (2.71 in.)
0.005 mm (0.0001 in.)
0.004 mm (0.0001 in.)54.982–54.994 mm
(2.164–2.165 in.)
0.005 mm (0.0001 in.)
0.004 mm (0.0001 in.)
Main Bearing Clearance (All)0.026–0.042 mm (0.001–0.002 in.)0.026–0.042 mm (0.001–0.002 in.)
Crankshaft End Play0.1 mm (0.003 in.)0.05–0.28 mm (0.002–0.011 in.)
Connecting Rod Journal:
Diameter (All)43 mm (1.69 in.)
42.971–42.987 mm
(1.691–1.692 in.)
Taper (Maximum)0.005 mm (0.0001 in.)0.005 mm (0.0001 in.)
Out of Round (Maximum)0.004 mm (0.0001 in.)0.004 mm (0.0001 in.)
Rod Bearing Clearance (All)0.019–0.070 mm
(0.0007–0.0028 in.)0.019–0.071 mm
(0.0007–0.0028 in.)
Rod Side Clearance0.070–0.242 mm
(0.0027–0.009 in.)0.070–0.242 mm
(0.0027–0.009 in.)
Valve System:
Valve Lash CompensatorsHydraulicHydraulic
Face Angle (All)45°~45.25°90°~90.5°
Seat Angle (All)44.5°~45°89°~90°
Seat Runout (Maximum, All)0.05 mm (0.002 in.)0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
Face Runout (Maximum, All)0.03 mm (0.0012 in.)0.03 mm (0.0012 in.)
Seat Width:
Intake
Exhaust1.17–1.57 mm (0.046–0.062 in.)
1.4–1.8 mm (0.055–0.071 in.)1.17–1.57 mm (0.046–0.062 in.)
1.4–1.8 mm (0.055–0.071 in.)
Valve Guide Inside Diameter (All)6.00–6.02 mm (0.236–0.237 in.)6.00–6.02 mm (0.236–0.237 in.)
Valve Stem Diameter (All)6 mm (0.236 in.)6 mm (0.236 in.)
Valve Diameter (All):
Intake
Exhaust28.57 mm (1.125 in.)
27.24 mm (1.074 in.)28.6 mm (1.126 in.)
27.2 mm (1.072 in.)
Valve Spring Loads:
Valve Open
Valve Closed580 ± 29N (426 ± 21 lbs)
260 ± 13N (191 ± 9.6 lbs)580–26N (428–19 lbs)
@23.0 mm(0.90 in.)
260”13N(192” 9 lbs) @
32.0mm(1.25 in.)
Valve Spring Free Length41.2 mm (1.622 in.)41.2 mm (1.622 in.)
Oil Pump:
Gap Between Oil Pump Body and Out
Rotor0.400~0.484 mm
(0.0157~0.019 in.)0.400~0.484 mm (0.0157~0.019 in.)
Out Rotor Side Clearance0.045~0.100 mm
(0.0018~0.0039 in.)0.045~0.100 mm (0.02~0.004 in.)
Page 52 of 2643

1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COMPONENT LOCATOR
CYLINDER HEAD
1. Oil Filler Cap
2. Engine Cover
3. Camshaft Cover
4. Camshaft Cover Gasket
5. Camshaft Cover Bolt
6. Hydraulic Tappet Adjuster
7. Valve Key
8. Valve Spring Cap
9. Valve Spring
10. Valve Stem Seal
11. EGR Vaccum Hose
12. EGR Valve
13. EGR Valve Gasket
14. EGR Valve Adaptor
15. EGR Valve Adaptor Gasket16. Cylinder Head
17. Front Camshaft Cap
18. Valve Guide
19. Plug
20. Freeze Plug
21. Oil Duct Cap
22. Intake Valve
23. Exhaust Valve
24. Cylinder Head Gasket
25. Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
26. Heat Take Off Pipe
27. Camshaft
28. Camshaft Seal
29. Thermostat
Page 123 of 2643
1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
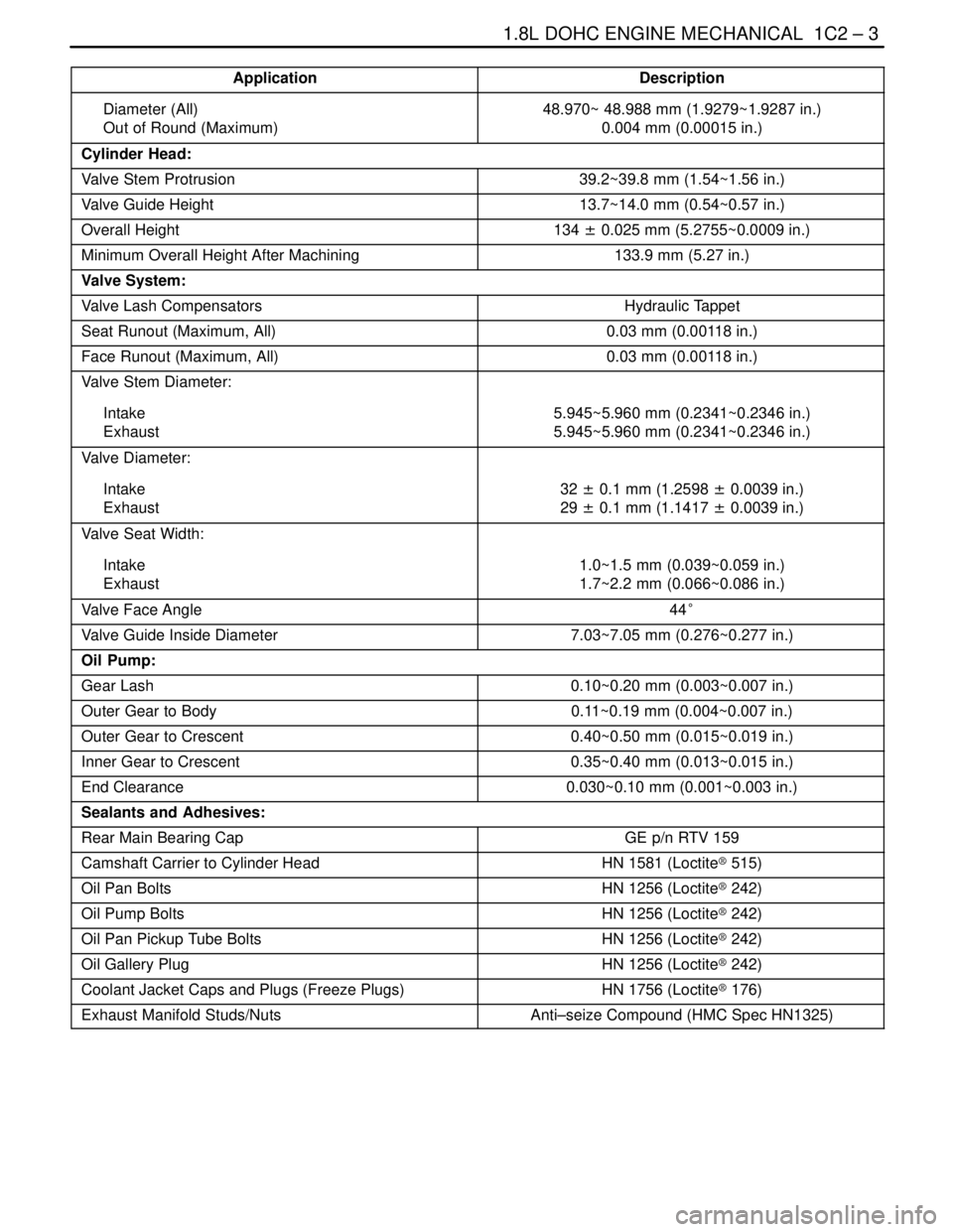
Application Description
Diameter (All)
Out of Round (Maximum)48.970~ 48.988 mm (1.9279~1.9287 in.)
0.004 mm (0.00015 in.)
Cylinder Head:
Valve Stem Protrusion39.2~39.8 mm (1.54~1.56 in.)
Valve Guide Height13.7~14.0 mm (0.54~0.57 in.)
Overall Height134 ± 0.025 mm (5.2755~0.0009 in.)
Minimum Overall Height After Machining133.9 mm (5.27 in.)
Valve System:
Valve Lash CompensatorsHydraulic Tappet
Seat Runout (Maximum, All)0.03 mm (0.00118 in.)
Face Runout (Maximum, All)0.03 mm (0.00118 in.)
Valve Stem Diameter:
Intake
Exhaust5.945~5.960 mm (0.2341~0.2346 in.)
5.945~5.960 mm (0.2341~0.2346 in.)
Valve Diameter:
Intake
Exhaust32 ± 0.1 mm (1.2598 ± 0.0039 in.)
29 ± 0.1 mm (1.1417 ± 0.0039 in.)
Valve Seat Width:
Intake
Exhaust1.0~1.5 mm (0.039~0.059 in.)
1.7~2.2 mm (0.066~0.086 in.)
Valve Face Angle44°
Valve Guide Inside Diameter7.03~7.05 mm (0.276~0.277 in.)
Oil Pump:
Gear Lash0.10~0.20 mm (0.003~0.007 in.)
Outer Gear to Body0.11~0.19 mm (0.004~0.007 in.)
Outer Gear to Crescent0.40~0.50 mm (0.015~0.019 in.)
Inner Gear to Crescent0.35~0.40 mm (0.013~0.015 in.)
End Clearance0.030~0.10 mm (0.001~0.003 in.)
Sealants and Adhesives:
Rear Main Bearing CapGE p/n RTV 159
Camshaft Carrier to Cylinder HeadHN 1581 (Loctite® 515)
Oil Pan BoltsHN 1256 (Loctite® 242)
Oil Pump BoltsHN 1256 (Loctite® 242)
Oil Pan Pickup Tube BoltsHN 1256 (Loctite® 242)
Oil Gallery PlugHN 1256 (Loctite® 242)
Coolant Jacket Caps and Plugs (Freeze Plugs)HN 1756 (Loctite® 176)
Exhaust Manifold Studs/NutsAnti–seize Compound (HMC Spec HN1325)
Page 229 of 2643

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 1E – 15
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Position the starter electrical wire on the solenoid
terminals and the ground wire on the lower stud.
5. Install the starter solenoid nuts and the ground wire
nut.
Tighten
Tighten the starter solenoid terminal–to–battery cable
terminal nut to 5.5 NSm (49 lb–in), and the starter sole-
noid terminal–to–ignition solenoid terminal nut to 5.5
NSm (49 lb–in).
Tighten the starter lower mounting stud ground wire
nut to 12 NSm (106 lb–in).
BATTERY AND BATTERY TRAY
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable and then dis-
connect the positive battery cable.
2. Remove the nuts from the battery rods that fasten
the battery hold–down bar clamp.
3. Check the battery carrier tray for obvious cracks or
damage. Unclip the lead to the negative battery
cable from the side of the battery tray (if applica-
ble). Detach the carrier tray if necessary by remov-
ing the upper battery carrier tray bolts, and the side
bolt that connects the hydraulic clutch hose bracket
to the battery carrier tray (if applicable).
4. Remove the lower battery tray bolts.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the battery carrier by fastening the carrier
tray upper, lower, and side bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the battery carrier tray upper, lower and side
bolts (if applicable) to 20 NSm (15 lb–ft).
2. Push in the clip of the negative battery lead to the
hole in the side of the battery tray (if applicable and
as shown).
Page 903 of 2643

2A – 2ISUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Abnormal or Excessive Tire Wear
ChecksAction
Check the front–wheel and the rear–wheel alignment.Align the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for excessive toe on the front and the rear wheels.Adjust the toe on the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Inspect for out–of–balance tires.Balance the tires.
Inspect for worn strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Check for a failure to rotate tires.Rotate the tires. Replace the tires as needed.
Check for an overloaded vehicle.Maintain the proper load weight.
Inspect for low tire inflation.Inflate the tires to the proper pressure.
Scuffed Tires
ChecksAction
Inspect for incorrect toe on the front and the rear wheels.Adjust the toe on the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for a twisted or a bent suspension arm.Replace the suspension arm.
Wheel Tramp
ChecksAction
Inspect for an out–of–balance tire or wheel.Balance the tire or the wheel.
Inspect for improper strut dampener action.Replace the strut dampeners.
Shimmy, Shake, or Vibration
ChecksAction
Inspect for an out–of–balance tire or wheel.Balance the tire or the wheel.
Inspect for excessive wheel hub runout.Measure the hub flange runout. Replace the hub as need-
ed.
Inspect for excessive brake drum or brake rotor imbal-
ance.Adjust the brakes. Replace the brake rotor or the brake
drum as needed.
Inspect for worn tie rod ends.Replace the outer tie rods.
Inspect for wheel trim imbalance.Balance the wheel.
Inspect for a worn lower ball joint.Replace the lower ball joint.
Inspect for excessive wheel runout.Measure the wheel runout. Replace the wheel as needed.
Inspect for excessive loaded radial runout on the tire and
wheel assembly.Match–mount the tire and wheel assembly.
Hard Steering
ChecksAction
Check the steering gear preload adjustment.Perform a rack bearing preload adjustment.
Check the hydraulic system. Test the power steering sys-
tem pressure with a gauge.Replace the seals and the hoses as needed.
Inspect for binding or catching in the steering gear.Lubricate the steering gear. Repair or replace the steering
gear as needed.
Inspect for a loose steering gear mounting.Tighten the steering gear mounting bracket nuts.
Page 906 of 2643
SUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS 2A – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Steering Wheel Kickback
ChecksAction
Inspect for air in the power steering system.Purge the power steering system of air.
Inspect for a loose steering gear mounting.Tighten the steering gear mounting bracket nuts.
Inspect the joint from the column to the steering gear for
loose connections or wear.Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace the in-
termediate shaft as needed.
Inspect for loose tie rod ends.Tighten the tie rod ends. Replace the outer tie rods as
needed.
Inspect for loose or worn wheel bearings.Tighten the drive axle nut. Replace the wheel bearings as
needed.
Steering Wheel Surges or Jerks
ChecksAction
Check the hydraulic system. Test the power steering sys-
tem pressure with a gauge.Replace the seals and the hoses as needed.
Inspect for a sluggish steering gear valve.Clean the pinion valve assembly. Replace the pinion valve
assembly as needed.
Inspect for a loose power steering pump serpentine belt.Adjust the power steering pump serpentine belt.
Cupped Tires
ChecksAction
Check the front–wheel and the rear–wheel alignment.Align the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for worn strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Inspect for worn or loose wheel bearings.Tighten the drive axle nut. Replace the wheel bearings as
needed.
Inspect for excessive tire or wheel runout.Match–mount the tires. Replace the tires as needed. Re-
place the wheels as needed.
Inspect for a worn ball joint.Replace the ball joint.
Check the steering gear preload adjustment.Perform a rack bearing preload adjustment.
TORQUE STEER
A degree of torque steer to the right may be experienced
during the use of heavy throttle on some front–wheel drive
cars with drive axles of unequal length. This torque steer
to the right results from the right drive axle being longer
than the left drive axle, which creates a difference in the
drive axle angle. Cars with intermediate shaft assemblies
have axles of almost equal length.
A difference in the drive axle lengths results in more torque
toe–in in the left front wheel. You will notice the torque toe–
in when the vehicle accelerates from a standing start or at
lower speeds.
Inspection Procedure
1. Place a small piece of tape at the top center of the
steering wheel.2. Note the inches of steering wheel deflection re-
quired to keep the vehicle straight during heavy ac-
celeration.
3. Compare this finding with similar cars.
Factors that may cause torque steer to be more apparent
on a particular vehicle include:
S Variations in the tire and wheel assemblies. This
has the most significant effect on torque steer. A
slightly smaller diameter on the right front tire will
increase a right torque lead.
S Large differences in the right and the left front tire
pressure.
S Looseness in the control arm bushings, the tie rod
assemblies, or the steering gear mounting. This
looseness permits a front wheel to pull forward and
toe–in under a torque greater than the wheel on the
opposite side. A loose suspension component may
result in an opposite lead upon deceleration.