2004 DAEWOO LACETTI brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 952 of 2643

2D – 10IREAR SUSPENSION
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Installation Procedure
1. Install the rear knuckle into the vehicle and install
the brake line into the strut assembly bracket.
2. Install the knuckle–to–strut assembly bolts and
nuts. Do not tighten.
3. Install the clip securing the brake line to the strut
assembly.
4. Tighten the knuckle–to–strut assembly nuts.
Tighten
Tighten the knuckle–to–strut assembly nuts to 100
NSm (74 lb–ft).
5. Connect the rear trailing link to the rear knuckle.
Refer to ”Rear Trailing Link” in this section.
6. Connect the rear parallel link to the knuckle. Refer
to ”Rear Parallel Link” in this section.
7. Connect the front parallel link to the knuckle. Refer
to ”Front Parallel Link” in this section.
8. Connect the parking brake to the knuckle assembly.
Refer to Section 4G, Parking Brake.
9. On vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, con-
nect the brake line to the knuckle assembly. On
vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes, install the
rear brake caliper onto the knuckle assembly. Refer
to Section 4E1, Rear Disc Brakes.
10. On vehicles equipped with the antilock braking sys-
tem, install the ABS speed sensor. Refer to Section
4F, Antilock Brake System.
11. Install the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
12. Lower the vehicle.
TRAILING LINK
Removal Procedure
1. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
2. Remove the rear trailing link–to–rear knuckle nut.
3. Remove the rear trailing link–to–trailing link bracket
nut and the rear trailing link–to–knuckle bolt.
4. Remove the rear trailing link.
Page 957 of 2643

REAR SUSPENSION 2D – 15
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
5. Remove the crossmember–to–body bolts.
6. Remove the crossmember.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the crossmember.
2. Install the crossmember–to–body bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the crossmember–to–body bolts to 112 NSm
(83 lb–ft).
3. Route and install the rear wheel speed sensor wir-
ing.
4. Install the rear parallel link bolt onto the crossmem-
ber. Refer to ”Rear Parallel Link”in this section.
5. Install the front parallel link bolt onto the crossmem-
ber. Refer to ”Front Parallel Link” in this section.
6. Lower the vehicle.
HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
Removal Procedure
1. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
2. Remove the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
3. On vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, re-
move the rear brake drum detent screw and brake
drum. Refer to Section 4E2, Rear Drum Brakes.
4. On vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes, remove
the rear brake caliper and rear brake disc. Refer to
Section 4E1, Rear Disc Brakes.
5. Remove the hub bolts and hub assembly.
Page 958 of 2643
2D – 16IREAR SUSPENSION
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Installation Procedure
1. Install the hub assembly.
Tighten
Tighten the hub assembly bolts to 65 NSm (48 lb–ft).
2. Install the hub nut.
3. On vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes, install
the rear brake disc and rear brake caliper. Refer to
Section 4E1, Rear Disc Brakes.
4. On vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, install
the rear brake drum and the brake drum detent
screw. Refer to Section 4E2, Rear Drum Brakes.
5. Install the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
6. Lower the vehicle.
Page 960 of 2643
2D – 18IREAR SUSPENSION
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
5. Install the lock nut onto the strut dampener rod.
Tighten
Tighten the ball joint–to–control arm nuts to 100 NSm
(74 lb–ft). Tighten the strut dampener–to–strut mount
nut to 75 NSm (55 lb–ft).
6. Release the spring.
7. Remove the strut assembly from the spring com-
pressor and install the strut assembly into the ve-
hicle. Refer to ”Strut Assembly” in this section.
KNUCKLE
Disassembly Procedure
1. Remove the knuckle from the vehicle. Refer to
”Knuckle Assembly” in this section.
2. Remove the brake drum. Refer to Section 4E2,
Rear Drum Brakes.
3. Remove the wheel hub. Refer to ”Hub and Bearing
Assembly” in this section.
4. On vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, re-
move the rear drum brake assembly. On vehicles
equipped with rear disc brakes, remove the rear
disc brake assembly. Refer to Section 4E1, Rear
Disc Brakes.
5. Remove the brake splash shield. Refer to Section
4E2, Rear Drum Brakes.
Assembly Procedure
1. Install the brake splash shield. Refer to Section
4E1, Rear Disc Brakes.
2. On vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, install
the rear drum brake assembly. On vehicles
equipped with rear disc brakes, install the rear disc
brake assembly. Refer to Section 4E1, Rear Disc
Brakes.
3. Install the wheel hub. Refer to ”Hub and Bearing
Assembly” in this section.
4. Install the brake caliper and brake rotor or the
brake drum. Refer to Section 4E1, Rear Disc
Brakes and 4E2, Rear Drum Brakes.
5. Install the knuckle into the vehicle. Refer to
”Knuckle Assembly” in this section.
Page 965 of 2643

TIRES AND WHEELS 2E – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE
WHEEL
Removal Procedure
1. Loosen the wheel bolts.
2. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
3. Remove the wheel bolts.
Notice : Never use heat to loosen a tight wheel. It can
shorten the life of the wheel, the wheel nuts and the wheel
bearings. Excessive force, such as hammering the wheel
or tire, can also cause damage and is not recommended.
Slight tapping of the wheel sidewall with one’s hand or with
a rubber mallet is acceptable.
4. Remove the wheel.
Difficulty in removing the wheels from the vehicle can be
due to foreign material or to a tight fit between the wheel
centerhole and the hub or the rotor. These wheels can be
removed by
5. Retightening the wheel bolts on the affected wheel
and then loosening the wheel bolts by two turns.
6. Lowering the vehicle and rocking it from side to side
as hard as possible, using one or more person’s
body weight to loosen the wheel.
7. Raising the vehicle and removing the wheel.
CAUTION : Do not allow the penetrating oil to get on
the vertical surfaces between the wheel and the drum
(or rotor) because penetrating oil in this area could
cause the wheel to work loose as the vehicle is driven,
resulting in loss of control and an injury accident.
Penetrating oil is not effective in removing tight wheels. If
it is used, however, apply it sparingly and only to the
wheel’s centerhole area.
Installation Procedure
Notice : Before installing the wheels, remove any buildup
of corrosion on the wheel mounting surface and the brake
drum or the rotor mounting surface by scraping and brush-
ing them with a wire brush. Installing the wheels without
good metal–to–metal contact at the mounting surfaces
can cause the wheel nuts to loosen, which can later allow
a wheel to come off while the vehicle is moving. Wheel
bolts must be tightened in sequence and to the proper
torque to avoid bending the wheel, the brake drum or the
rotor.
1. Mount the wheel.
2. Install the wheel bolts in the sequence shown. Do
not tighten the wheel bolts.
3. Lower the vehicle.
Tighten
Tighten the wheel bolts to 100 NSm (74 lb–ft).
Page 966 of 2643
2E – 4ITIRES AND WHEELS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
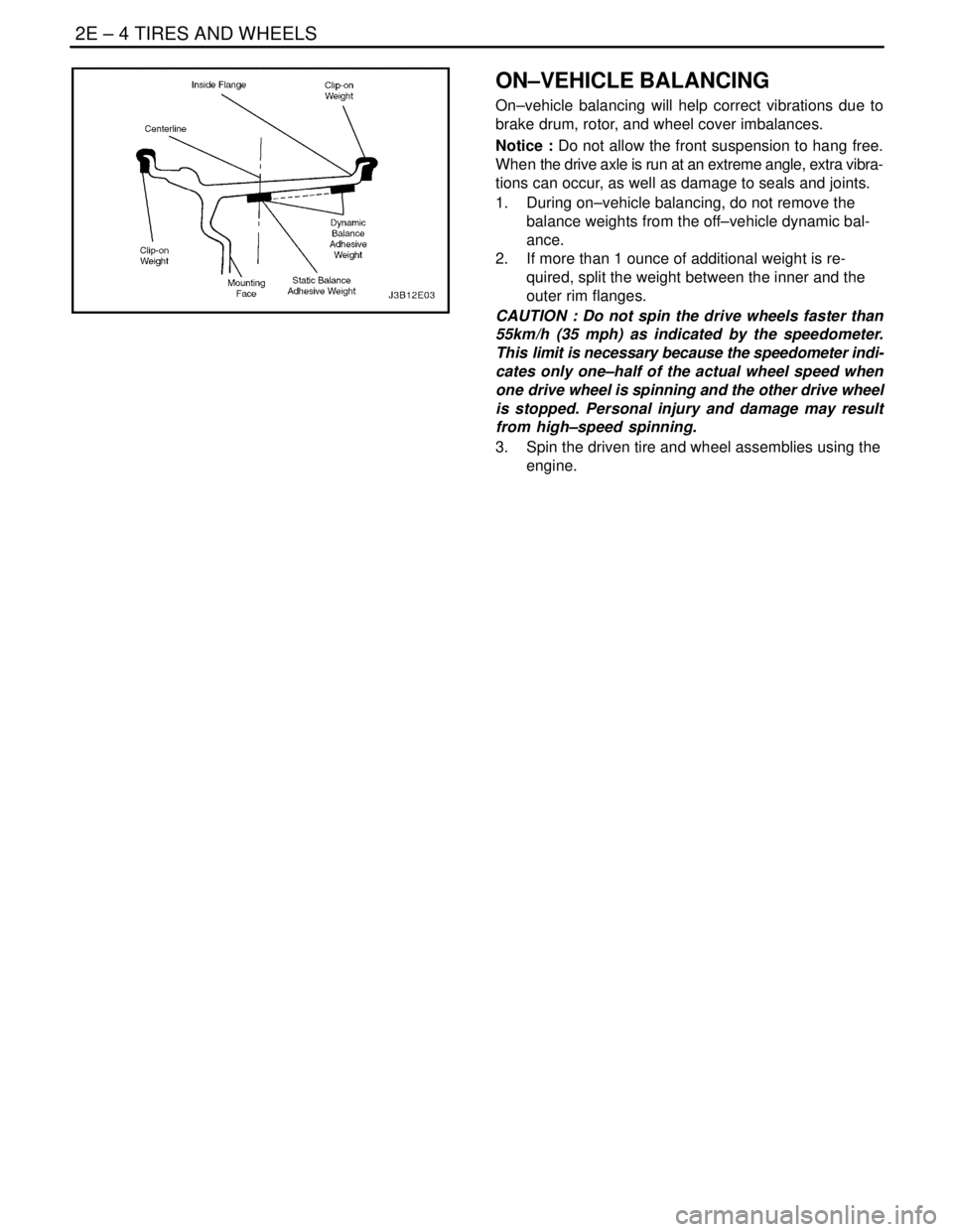
ON–VEHICLE BALANCING
On–vehicle balancing will help correct vibrations due to
brake drum, rotor, and wheel cover imbalances.
Notice : Do not allow the front suspension to hang free.
When the drive axle is run at an extreme angle, extra vibra-
tions can occur, as well as damage to seals and joints.
1. During on–vehicle balancing, do not remove the
balance weights from the off–vehicle dynamic bal-
ance.
2. If more than 1 ounce of additional weight is re-
quired, split the weight between the inner and the
outer rim flanges.
CAUTION : Do not spin the drive wheels faster than
55km/h (35 mph) as indicated by the speedometer.
This limit is necessary because the speedometer indi-
cates only one–half of the actual wheel speed when
one drive wheel is spinning and the other drive wheel
is stopped. Personal injury and damage may result
from high–speed spinning.
3. Spin the driven tire and wheel assemblies using the
engine.
Page 968 of 2643
2E – 6ITIRES AND WHEELS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Amchem Alodine No. 1001. Stock No. DX50T or
equivalent coating chemical for alloys.
S Ditzler Delclear Acrylic Urethane Clear, Stock No.
DAU–75 or equivalent.
S Ditzler Delthane Ultra–Urethane Additive, Stock No.
DXR–80 or equivalent.
Before repairing the alloy damage or the clear coat dam-
age, prepare the wheels and the tires.
1. Remove the wheel from the vehicle.
2. Mark the location of the outboard weights and re-
move them.
3. Wash the wheel inside and out with a water–based,
all–purpose cleaner. Remove the grease and oil
with a solvent cleaner.
4. Mask the tire prior to painting.
5. Using a 400–grit wet or dry sandpaper, sand over
the painted areas that will not require recoloring.
Sanding will promote the adhesion of the clear coat.
Alloy Damage on Wheel Surface
1. Mount the wheel on a brake lathe and spin the as-
sembly slowly.
2. Sand the wheel with a backing block or pad. Hold
the backing block or pad flat to the surface of the
wheel and sand slowly back and forth from the cen-
ter to the outer edge of the tire to remove the dam-
age. Use the following sandpaper grits in the order
listed:
1) 80 grit.
2) 150 grit.
3) 240 grit.
Clear Coat Damage on Unpainted Wheels
1. Apply the chemical stripper Amchem Alumi Prep
No. 33. Use a small 1/4–inch detail brush to apply
the stripper around the perimeter and spoke–like
areas.
2. Remove the stripper according to the manufactur-
er’s recommendations.
CAUTION : To avoid serious personal injury, do not
use engine power to rotate the wheel while sanding.
3. Sand the wheel with 240–grit sandpaper by rotating
the wheel on a slow–spinning brake lathe or by
mounting the wheel on the car and spinning it by
hand. Sanding restores the machined appearance
and promotes adhesion.
After repairing the alloy or clear coat damage, the wheels
must be recoated.
Page 973 of 2643

TIRES AND WHEELS 2E – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
pacity, diameter, rim width, offset, and mounting configu-
ration. A wheel of improper size or type may affect wheel
and bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer/odometer
calibration, vehicle ground clearance, and tire clearance
to the body and the chassis. The wheel offset is 49 ± 1 mm
(1.93 ± 0.04 inches). Steel wheels may be identified by a
two– or three–letter code stamped into the rim near the
valve stem. Alloy wheels should have the code, the part
number, and the manufacturer ID cast into the back side.
INFLATION O TIRES
The pressure recommended for any vehicle line is careful-
ly calculated to give a satisfactory ride, handling, tread life,
and load–carrying capacity.
Tire pressure should be checked monthly or before any
extended trip. Check the tires when they are cold, after the
vehicle has sat for 3 hours or more, or has been driven less
than 1 mile. Set the tire pressure to the specifications on
the tire label located on the rear face of the driver’s door.
Tire inflation pressure is also given under ”Tire Size and
Pressure Specifications” in this section.
Valve caps or extensions should be on the valves to keep
dust and water out.
For sustained driving at speeds up to 140 km/h (85 mph),
inflate the tires to the pressure recommended on the tire.
Sustained driving at speeds faster than 140 km/h (85mph), even if permitted by law, is not advised unless the
vehicle has special high–speed tires available from many
tire dealers. Tire pressures may increase as much as 41
kPa (6 psi) when the tires are hot.
Higher than recommended tire pressure can cause
S Hard ride.
S Tire bruising or damage.
S Rapid tread wear at the center of the tire.
Lower than recommended pressure can cause
S Tire squeal on turns.
S Hard steering.
S Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread.
S Tire rim bruises and rupture.
S Tire cord breakage.
S High tire temperatures.
Unequal tire pressures on same axle can cause
S Uneven braking.
S Steering lead.
S Reduced handling.
S Swerve on acceleration.
S Torque steer.