2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Map sensor
[x] Cancel search: Map sensorPage 768 of 2643

1F – 522IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1106
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE INTERMITTENT HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP signal voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above
4 volts with the key in the ON position, engine not running
or at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) (low vacuum).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used. This is calculated using inputs from the MAP sensor,
the rpm (58X), and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sen-
sor. The MAP sensor is the main sensor used in this cal-
culation, and measuring engine load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold pres-
sure changes while the linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) flow test diagnostic is being run (refer to DTC
P0401). This determines the engine vacuum level for
some other diagnostics and determines Barometric Pres-
sure (BARO). The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal
to calculated MAP based on Throttle Position (TP) and
various other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is intermittently above the calcu-
lated value, DTC P1106 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The MAP is greater than 103 kPa (15 psi).
S No TP sensor fail conditions present.
S Engine running more than 10 seconds
S TP sensor is less than 15 % if rpm is less than
2500.
S TP sensor less than 35% if rpm is greater than
2500.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Leaking or plugged vacuum supply line to the MAP
sensor.
S Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed–out
terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improper-
ly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–
towire connection.
S Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the har-
ness appears to be OK, observe the MAP display
on the scan tool while moving connectors and wir-
ing harnesses related to the sensor. A change in
the display will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 769 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 523
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P1106 – Manifold Absolute Pressure Intermittent High Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON, with the engine
not running.
3. Select diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) informa-
tion.
4. Check Last Test Fail and note any other DTCs
set.
Is DTC P0108 also set?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableGo to Step 3
3Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal 3
connection at the Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 4
4Check the MAP signal circuit between the MAP sen-
sor connector and Engine Control Module (ECM) for
an intermittent short to voltage.
Is a problem found?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 5
5Check for an intermittent short to voltage on the 5
volt reference M16 circuit between the MAP sensor
and ECM.
Is a problem found?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 6
6Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal M48
connection at the ECM.
Is a problem found?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 9
7Repair the faulty harness connector terminal for
sensor ground circuit or replace it.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 9–
8Locate and repair intermittent open or short circuit in
the wiring harness as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 9–
91. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 2
10Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 770 of 2643

1F – 524IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE INTERMITTENT LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP signal voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above
4 volts with the key in the ON position, engine not running
or at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) (low vacuum).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used. This is calculated using inputs from the MAP sensor,
the rpm (58X), and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sen-
sor. The MAP sensor is the main sensor used in this cal-
culation, and measuring engine load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold pres-
sure changes while the linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) flow test diagnostic is being run (refer to DTC
P0401). This determines the engine vacuum level for
some other diagnostics and determines Barometric Pres-
sure (BARO). The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal
to calculated MAP based on Throttle Position (TP) and
various other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is intermittently below the calcu-
lated value, DTC P1107 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The MAP is less than 12 kPa (1.7 psi).
S No TP sensor fail conditions present.
S TP sensor is greater than 0% if rpm is less than
1000.
S TP sensor less than 5% if rpm is greater than 1000.
S System voltage is between 11–11.5 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Leaking or plugged vacuum supply line to the MAP
sensor.
S Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed–out
terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improper-
ly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–
to–wire connection.
S Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the har-
ness appears to be OK, observe the MAP display
on the scan tool while moving connectors and wir-
ing harnesses related to the sensor. A change in
the display will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 771 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 525
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P1107 – Manifold Absolute Pressure Intermittent Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON, with the engine
not running.
3. Select diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) informa-
tion.
4. Check Last Test Fail and note any other DTCs
set.
Is DTC P0107 also set?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableGo to Step 3
31. Check for a poor 5 volt reference circuit or
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) signal cir-
cuit terminal connection at the MAP sensor.
2. Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
4Check the MAP signal circuit between the MAP sen-
sor connector and Engine Control Module (ECM) for
an intermittent short to ground.
Is a problem found?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
5Replace the faulty harness connector terminal for
the 5 volt reference circuit and/or the MAP signal cir-
cuit.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
6Repair intermittent open/short circuit in the wiring
harness.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
71. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 2
8Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 786 of 2643

1F – 540IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P1133 is most likely caused by one of the following
items:
S Fuel Pressure – The system will go rich if the fuel
pressure is too high. The ECM can compensate for
some increase. However, if it gets too high, a DTC
P1133 may set. Refer to ”Fuel System Diagnosis”
in this section.
S Leaking injector – A leaking or malfunctioning injec-
tor can cause the system to go rich.
S Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor – An
output that causes the ECM to sense a higher than
normal manifold pressure (low vacuum) can cause
the system to go rich. Disconnecting the MAP sen-
sor will allow the ECM to set a fixed value for the
MAP sensor. Substitute a different MAP sensor if
the rich condition is gone while the sensor is dis-
connected.
S Pressure regulator – Check for a leaking fuel pres-
sure regulator diaphragm by checking for the pres-
ence of liquid fuel in the vacuum line to the pres-
sure regulator.
S Throttle Position (TP) sensor – An intermittent TP
sensor output can cause the system to go rich due
to a false indication of the engine accelerating.S HO2S1 contamination – Inspect the HO2S1 for sili-
cone contamination from fuel or improper use of
Room Temperature Vulcanizing (RTV) sealant. The
sensor may have a white powdery coating and re-
sult in a high but false voltage signal (rich exhaust
indication). The ECM will then reduce the amount
of fuel delivered to the engine causing a severe
surge or driveability problem.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Chart.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
14. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
16. If no malfunctions have been found at this point and
no additional DTCs are set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids” in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
DTC P1133 – Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) Too Few
Transition
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
Are any additional Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs) set?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableGo to Step 3
31. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
2. Operate the vehicle within the specified param-
eter under the Conditions For Setting the DTC.
3. Monitor the lean–to–rich transition and rich–to–
lean transition and note the number of
switches.
Does the parameter show fewer transitions than the
specified value within 90 seconds.15Go to Step 4Go to Step 18
Page 822 of 2643
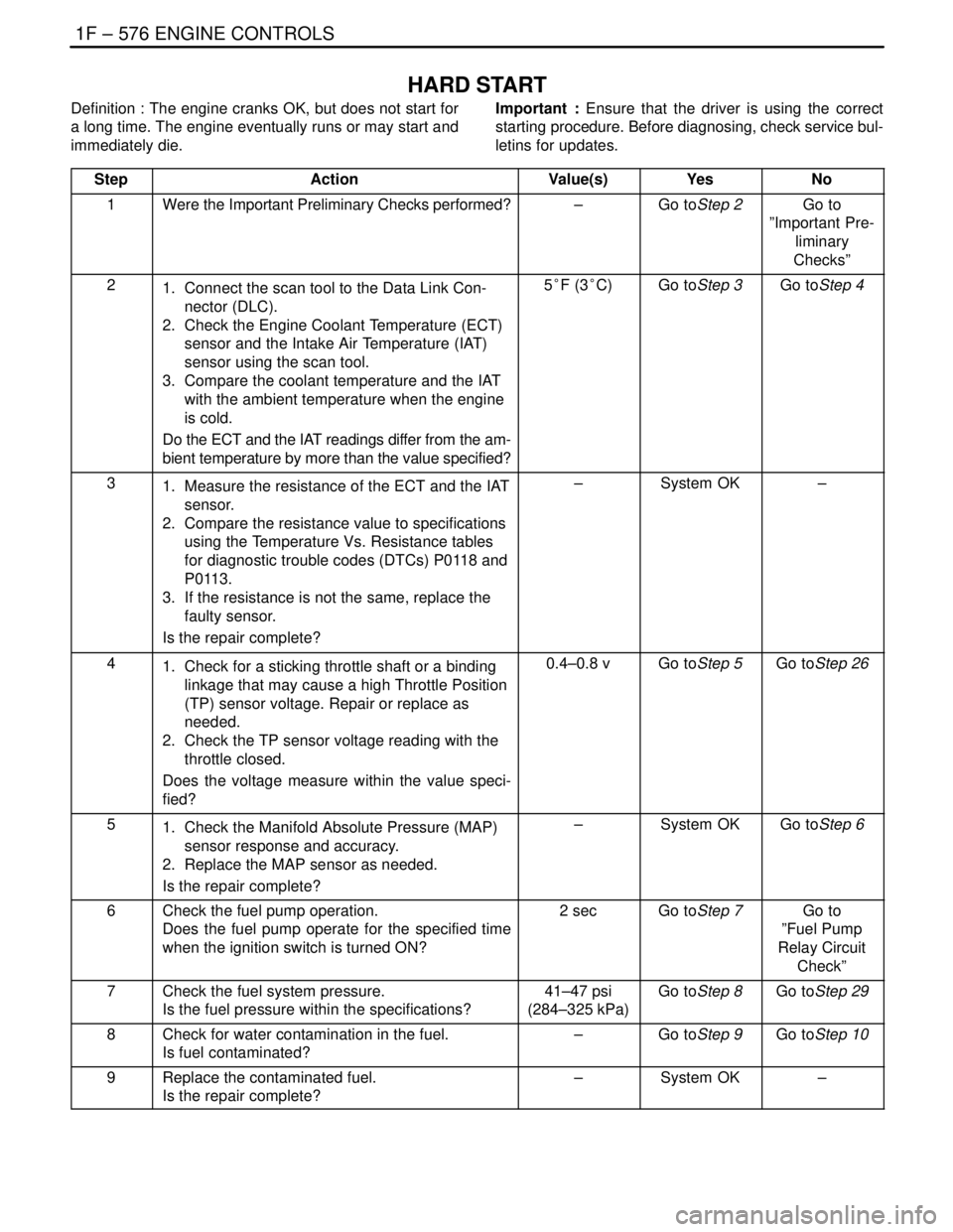
1F – 576IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
HARD START
Definition : The engine cranks OK, but does not start for
a long time. The engine eventually runs or may start and
immediately die.Important : Ensure that the driver is using the correct
starting procedure. Before diagnosing, check service bul-
letins for updates.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Connect the scan tool to the Data Link Con-
nector (DLC).
2. Check the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
sensor and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
sensor using the scan tool.
3. Compare the coolant temperature and the IAT
with the ambient temperature when the engine
is cold.
Do the ECT and the IAT readings differ from the am-
bient temperature by more than the value specified?5°F (3°C)Go toStep 3Go toStep 4
31. Measure the resistance of the ECT and the IAT
sensor.
2. Compare the resistance value to specifications
using the Temperature Vs. Resistance tables
for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) P0118 and
P0113.
3. If the resistance is not the same, replace the
faulty sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
41. Check for a sticking throttle shaft or a binding
linkage that may cause a high Throttle Position
(TP) sensor voltage. Repair or replace as
needed.
2. Check the TP sensor voltage reading with the
throttle closed.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?0.4–0.8 vGo toStep 5Go toStep 26
51. Check the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor response and accuracy.
2. Replace the MAP sensor as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OKGo toStep 6
6Check the fuel pump operation.
Does the fuel pump operate for the specified time
when the ignition switch is turned ON?2 secGo toStep 7Go to
”Fuel Pump
Relay Circuit
Check”
7Check the fuel system pressure.
Is the fuel pressure within the specifications?41–47 psi
(284–325 kPa)Go toStep 8Go toStep 29
8Check for water contamination in the fuel.
Is fuel contaminated?–Go toStep 9Go toStep 10
9Replace the contaminated fuel.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 829 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 583
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
HESITATION, SAG, STUMBLE
Definition : Involves a momentary lack of response as the
accelerator is pushed down. This can occur at any vehicle
speed. It is usually the most severe when first trying to
make the vehicle move, as from a stop. Hesitation, sag,
or stumble may cause the engine to stall if severe enough.Important : Before diagnosing this condition, check ser-
vice bulletins for Programmable Read–Only Memory
(PROM) updates.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Check the fuel system pressure. If the pres-
sure is not within the value specified, service
the fuel system as needed.
2. Inspect the Throttle Position (TP) sensor for
binding or sticking. The TP sensor voltage
should increase at a steady rate as the throttle
is moved toward Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
Is the problem found?41–47 psi
(284–325 kPa)Go toStep 3Go toStep 4
3Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
41. Check the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor response and accuracy.
2. Inspect the fuel for water contamination.
3. Check the Evaporative (EVAP) Emission canis-
ter purge system for proper operation.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 5Go toStep 6
5Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
61. Disconnect all of the fuel injector harness con-
nectors.
2. Connect an injector test light between the har-
ness terminals of each fuel injector.
3. Note the test light while cranking the engine.
Does the test light blink on all connectors?–Go toStep 8Go toStep 7
71. Repair or replace the faulty fuel injector drive
harness, the connector, or the connector termi-
nal.
2. If the connections and the harnesses are good,
replace the engine control module (ECM) for
an internal open in the fuel injector driver cir-
cuit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
8Measure the resistance of each fuel injector. The re-
sistance will increase slightly at higher tempera-
tures.
Is the fuel injector resistance within the value speci-
fied?11.6–12.4 ΩGo toStep 10Go toStep 9
9Replace any of the fuel injectors with a resistance
that is out of specifications.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
10Perform an injector balance test.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 11Go toStep 12
Page 834 of 2643
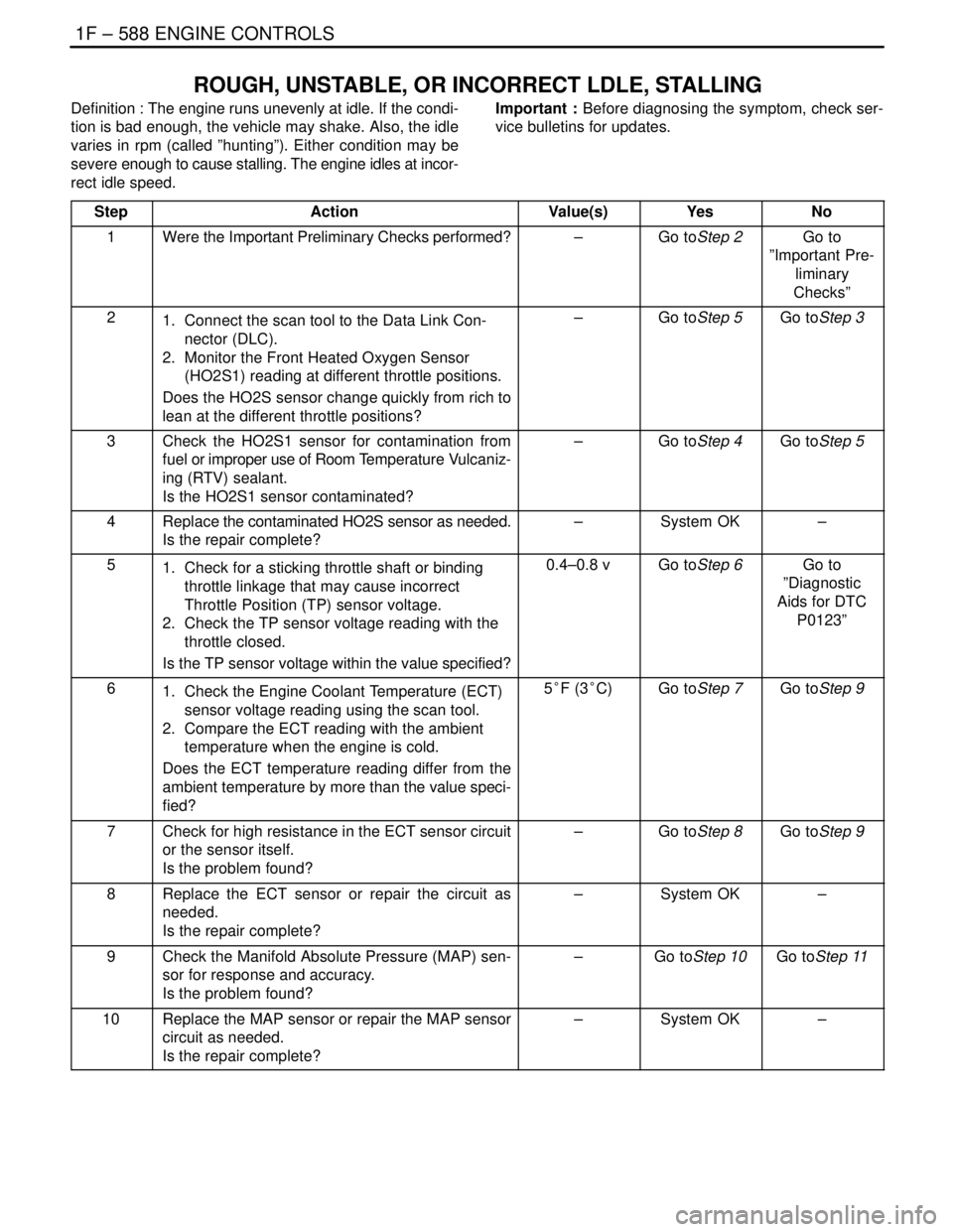
1F – 588IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ROUGH, UNSTABLE, OR INCORRECT LDLE, STALLING
Definition : The engine runs unevenly at idle. If the condi-
tion is bad enough, the vehicle may shake. Also, the idle
varies in rpm (called ”hunting”). Either condition may be
severe enough to cause stalling. The engine idles at incor-
rect idle speed.Important : Before diagnosing the symptom, check ser-
vice bulletins for updates.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Connect the scan tool to the Data Link Con-
nector (DLC).
2. Monitor the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) reading at different throttle positions.
Does the HO2S sensor change quickly from rich to
lean at the different throttle positions?–Go toStep 5Go toStep 3
3Check the HO2S1 sensor for contamination from
fuel or improper use of Room Temperature Vulcaniz-
ing (RTV) sealant.
Is the HO2S1 sensor contaminated?–Go toStep 4Go toStep 5
4Replace the contaminated HO2S sensor as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
51. Check for a sticking throttle shaft or binding
throttle linkage that may cause incorrect
Throttle Position (TP) sensor voltage.
2. Check the TP sensor voltage reading with the
throttle closed.
Is the TP sensor voltage within the value specified?0.4–0.8 vGo toStep 6Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids for DTC
P0123”
61. Check the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
sensor voltage reading using the scan tool.
2. Compare the ECT reading with the ambient
temperature when the engine is cold.
Does the ECT temperature reading differ from the
ambient temperature by more than the value speci-
fied?5°F (3°C)Go toStep 7Go toStep 9
7Check for high resistance in the ECT sensor circuit
or the sensor itself.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 8Go toStep 9
8Replace the ECT sensor or repair the circuit as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
9Check the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sor for response and accuracy.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 10Go toStep 11
10Replace the MAP sensor or repair the MAP sensor
circuit as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–