2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Throttle body
[x] Cancel search: Throttle bodyPage 251 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS1F–574 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Important Preliminary Checks 1F–574. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intermittents 1F–574. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hard Start 1F–576. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Surges or Chuggles 1F–579. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lack of Power, Sluggishness, or Sponginess 1F–581
Hesitation, Sag, Stumble 1F–583. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cuts Out, Misses 1F–584. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Poor Fuel Economy 1F–587. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling 1F–588. .
Excessive Exhaust Emissions or Odors 1F–591. . . . .
Dieseling, Run–On 1F–592. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Backfire 1F–593. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR1F–594 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE 1F–594. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Pressure Relief 1F–594. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Tank 1F–594. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump 1F–596. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filter 1F–597. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Rail and Injectors (1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–598. . .
Fuel Rail and Injectors (1.8L DOHC) 1F–600. . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–602. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
(1.8L DOHC) 1F–602. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Position Sensor (1.8L DOHC) 1F–603. . . . . .
Throttle Body (1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–603. . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Body (1.8L DOHC) 1F–604. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S 1)
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–606. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S 1)
(1.8L DOHC) 1F–607. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S 2) 1F–607. . . . .
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–608. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (1.8L DOHC) 1F–609
Idle Air Control Valve (1.8L DOHC) 1F–609. . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–610. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(1.8L DOHC) 1F–611. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–611. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve (1.8L DOHC) 1F–612
Knock Sensor (1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–612. . . . . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (1.8L DOHC) 1F–613. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Evaporative Emission Canister 1F–614. . . . . . . . . . . . Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve 1
F–615
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–615. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
(1.8L DOHC) 1F–616. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Position Sensor (1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–618
Camshaft Position Sensor (1.8L DOHC) 1F–619. . . .
Engine Control Module (1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–620. . .
Engine Control Module (1.8L DOHC) 1F–621. . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–621. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil
(1.8L DOHC) 1F–622. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION1F–623 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition System Operation 1F–623. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil 1F–623. . . . . .
Crankshaft Position Sensor 1F–623. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Position Sensor 1F–623. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air System Operation 1F–623. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Control System Operation 1F–623. . . . . . . . . . . .
Evaporative Emission Control System
Operation 1F–624. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Evaporative Emission Canister 1F–625. . . . . . . . . . . .
Positive Crankcase Ventilation System
Operation 1F–625. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 1F–625. . . . . . .
Throttle Position Sensor 1F–625. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Catalyst Monitor Oxygen Sensors 1F–625. . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve 1F–626. . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Air Temperature Sensor 1F–626. . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control Valve 1F–626. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor 1F–626. . . . . . . .
Engine Control Module 1F–627. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injector 1F–627. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Knock Sensor 1F–627. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rough Road Sensor 1F–627. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Strategy–Based Diagnostics 1F–628. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EOBD Serviceability Issues 1F–628. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Data Communications 1F–629. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) 1F–629. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Comprehensive Component Monitor Diagnostic
Operation 1F–630. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common EOBD Terms 1F–630. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes 1F–632. . . . . . . . .
Primary System–Based Diagnostics 1F–633. . . . . . . .
Page 256 of 2643

1F – 10IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb–FtLb–In
Camshaft Position Sensor Bolts (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)7–62
Camshaft Position Sensor Bolts (1.8 DOHC)8–71
Crankshaft Position Sensor Retaining Bolt (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)6.5–58
Crankshaft Position Sensor Retaining Bolt (1.8 DOHC)8–71
Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil Retaining Bolts10–89
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Retaining Bolts3022–
Engine Control Module Bolts12–106
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Bolt (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)17.513–
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Bolt (1.8 DOHC)2015–
Evaporative Emission Canister Flange Bolt4–35
Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Bracket Bolt5–44
Fuel Filter Mounting Bracket Assembly Bolt4–35
Fuel Tank Retaining Bolts2015–
Fuel Rail Retaining Bolts2518–
Idle Air Control Valve Retaining Bolts (1.8 DOHC)3–27
Intake Air Temperature Sensor2216–
Knock Sensor Bolt2015–
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Bolts (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)8–71
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Bolts (1.8 DOHC)4–35
Oxygen Sensor Bolt4231–
Throttle Body Retaining Nuts (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)1511–
Throttle Body Retaining Nuts (1.8 DOHC)10–89
Throttle Position Sensor Retaining Bolts (1.8 DOHC)2–18
Page 276 of 2643

1F – 30IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS
If an intermittent problem is evident, follow the guidelines
below.
Preliminary Checks
Before using this section you should have already per-
formed the ”On–Board Diagnostic System Check.”
Perform a thorough visual inspection. This inspection can
often lead to correcting a problem without further checks
and can save valuable time. Inspect for the following con-
ditions:
S Engine control module (ECM) grounds for being
clean, tight, and in their proper location.
S Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, collapsing and prop-
er connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Control Information label. Inspect thoroughly for
any type of leak or restriction.
S Air leaks at the throttle body mounting area and the
intake manifold sealing surfaces.
S Ignition wires for cracks, hardness, proper routing,
and carbon tracking.
S Wiring for proper connections.
S Wiring for pinches or cuts.
Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables
Do not use the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) tables to
try to correct an intermittent fault. The fault must be pres-
ent to locate the problem.
Incorrect use of the DTC tables may result in the unneces-
sary replacement of parts.
Faulty Electrical Connections or Wiring
Most intermittent problems are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful inspection of sus-
pect circuits for the following:
S Poor mating of the connector halves.
S Terminals not fully seated in the connector body.
S Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All con-
nector terminals in a problem circuit should be care-
fully inspected, reformed, or replaced to insure con-
tact tension.S Poor terminal–to–wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body.
Road Test
If a visual inspection does not find the cause of the prob-
lem, the vehicle can be driven with a voltmeter or a scan
tool connected to a suspected circuit. An abnormal voltage
or scan tool reading will indicate that the problem is in that
circuit.
If there are no wiring or connector problems found and a
DTC was stored for a circuit having a sensor, except for
DTC P0171 and DTC P0172, replace the sensor.
Fuel System
Some intermittent driveability problems can be attributed
to poor fuel quality. If a vehicle is occasionally running
rough, stalling, or otherwise performing badly, ask the cus-
tomer about the following fuel buying habits:
S Do they always buy from the same source? If so,
fuel quality problems can usually be discounted.
S Do they buy their fuel from whichever fuel station
that is advertising the lowest price? If so, check the
fuel tank for signs of debris, water, or other contam-
ination.
IDLE LEARN PROCEDURE
Whenever the battery cables, the engine control module
(ECM), or the ECM fuse is disconnected or replaced, the
following idle learn procedure must be performed:
1. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition OFF for 5 seconds.
3. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
4. Start the engine in park/neutral.
5. Allow the engine to run until the engine coolant is
above 185° F (85°C ).
6. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
7. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
8. If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic trans-
axle, apply the parking brake. While pressing the
brake pedal, place the transaxle in D (drive).
9. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
10. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
11. Turn the ignition OFF. The idle learn procedure is
complete.
Page 325 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 79
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (0°C, 19°C). The char-
acteristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The main throttle idle actuator (MTIA) provides a voltagesignal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle.
The signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles
to about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is
one of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel
control and other functions such as idle, wide open
throttle, deceleration enleanment, and acceleration en-
richment.
Diagnostic Aids
If the idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend the main
throttle idle actuator (MTIA) with a IAC driver. Start the en-
gine. If the idle speed is above 800 rpm, locate and repair
the vacuum leak. Also, check for a binding throttle plate or
throttle linkage or an incorrect base idle setting.
Page 327 of 2643
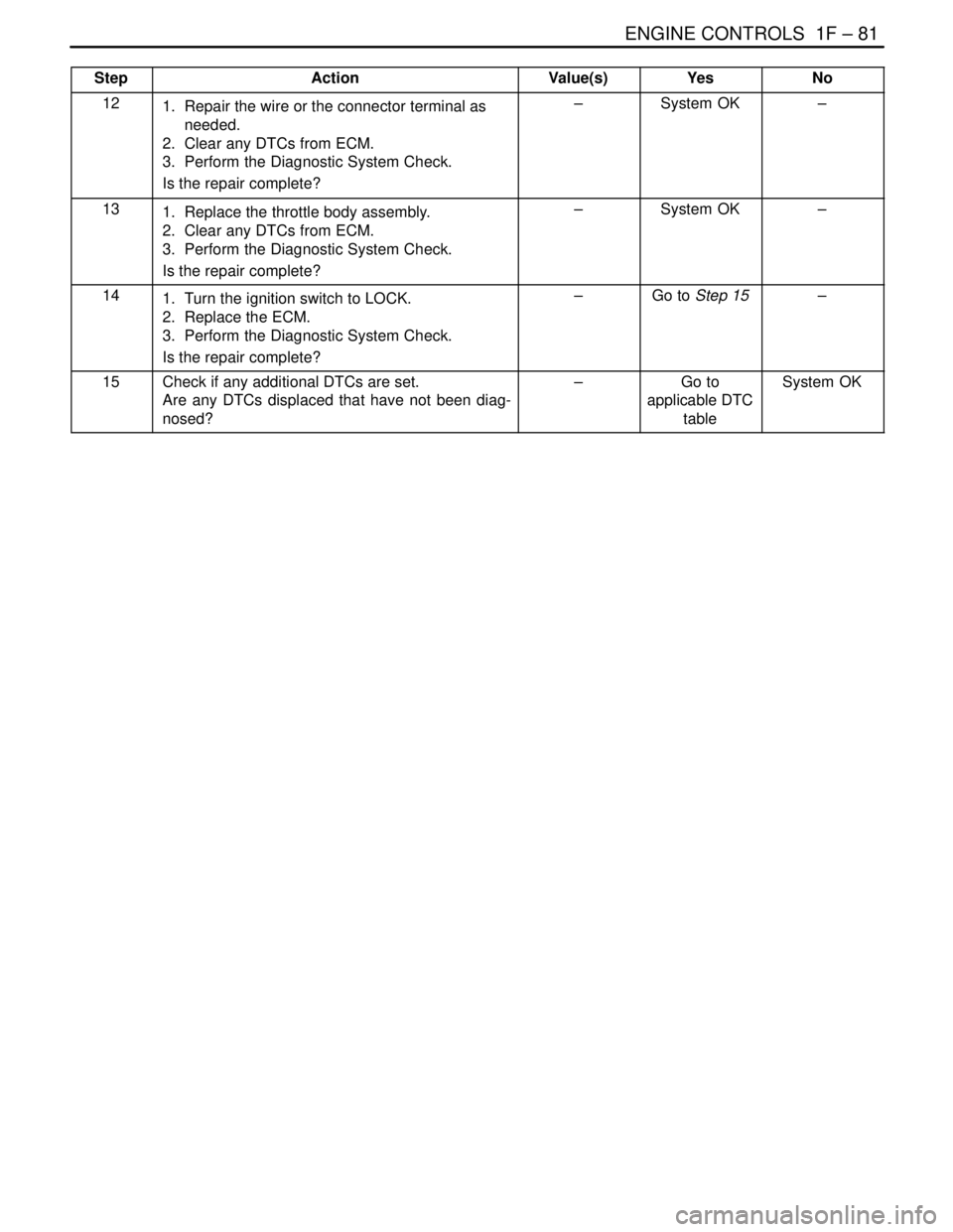
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 81
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
121. Repair the wire or the connector terminal as
needed.
2. Clear any DTCs from ECM.
3. Perform the Diagnostic System Check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
131. Replace the throttle body assembly.
2. Clear any DTCs from ECM.
3. Perform the Diagnostic System Check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
141. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Replace the ECM.
3. Perform the Diagnostic System Check.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 15–
15Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displaced that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 328 of 2643

1F – 82IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls the engine idle
speed with the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve. To increase the
idle speed, the ECM pulls the IAC pintle away from its seat,
allowing more air to pass by the throttle body. To decrease
the idle speed, it extends the IAC valve pintle toward its
seat, reducing bypass air flow. A scan tool will read the
ECM commands to the IAC valve in counts. The higher
counts indicate more air bypass (higher idle). The lower
counts indicate less air is allowed to bypass (lower idle).
Diagnostic Aids
If the idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend the Idle
Air Control (IAC) valve with a IAC driver. Start the engine.
If the idle speed is above 800 rpm, locate and repair the
vacuum leak. Also, check for a binding throttle plate or
throttle linkage or an incorrect base idle setting.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. The IAC valve is extended and retracted by the IAC
driver. IAC valve movement is verified by an engine
speed change. If no change in engine speed oc-
curs, the valve can be removed from the throttle
body and tested. Connect the IAC driver to the re-
moved IAC valve and turn the ignition ON. Do not
start the engine.5. This step checks the quality of the IAC valve move-
ment in Step 2. Fully extending the IAC valve may
cause an engine stall. This may be normal.
6. Steps 2 and 5 verify proper IAC valve operation.
This step checks the IAC circuit for a wiring or ECM
fault.
Idle Air Control Valve Reset Procedure
Whenever the battery cable or the Engine Control Module
(ECM) connector or the ECM fuse Ef11 is disconnected or
replaced, the following idle learn procedure must be per-
formed:
1. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition OFF for 10 seconds.
3. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
4. Start the engine in park/neutral.
5. Allow the engine to run until the engine coolant is
above 185°F (85°C).
6. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
7. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
8. If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic trans-
axle, apply the parking brake. While pressing the
brake pedal, place the transaxle in D (drive).
9. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
10. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
11. Turn the ignition OFF. The idle learn procedure is
complete.
Page 329 of 2643
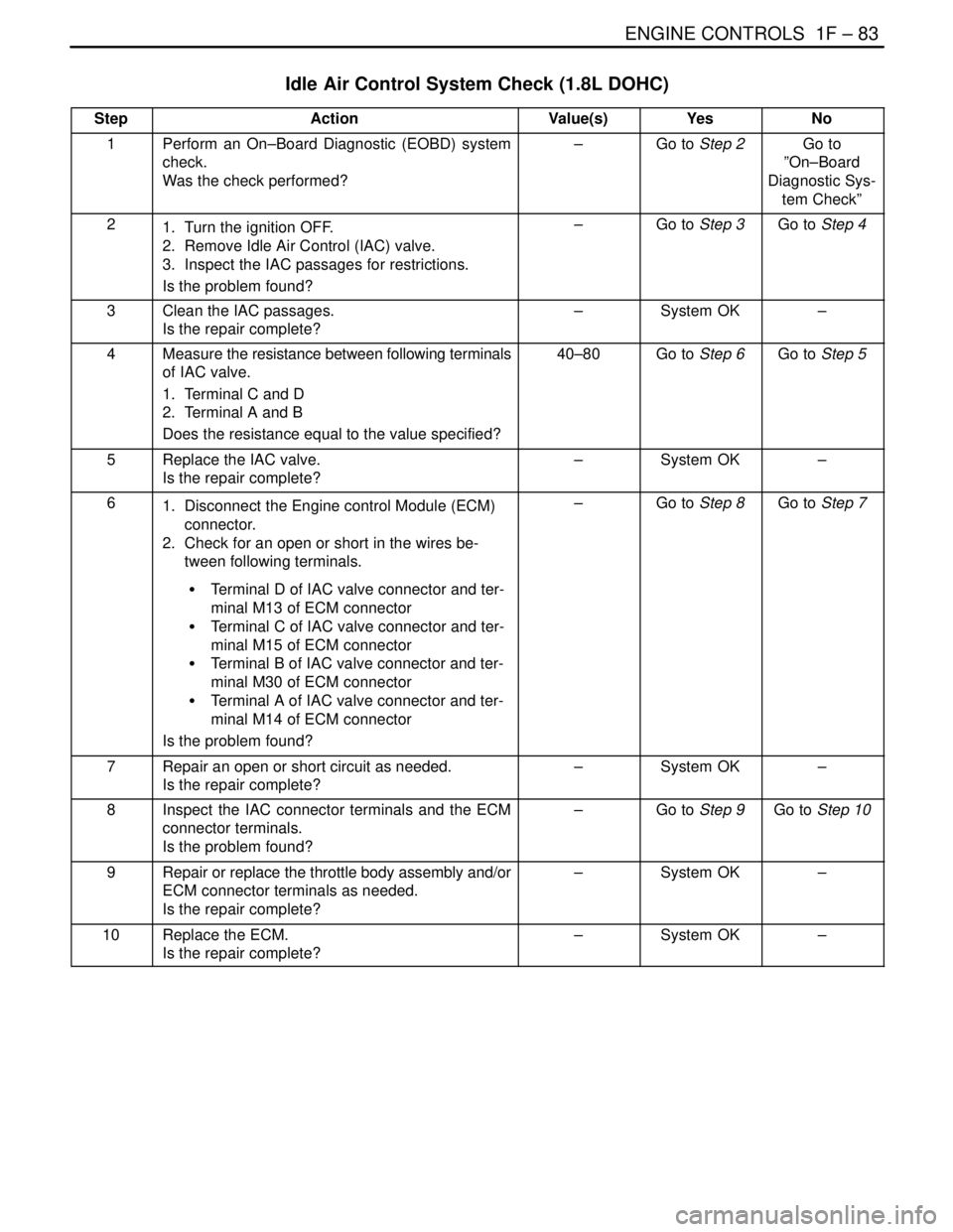
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 83
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Idle Air Control System Check (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system
check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Remove Idle Air Control (IAC) valve.
3. Inspect the IAC passages for restrictions.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Clean the IAC passages.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
4Measure the resistance between following terminals
of IAC valve.
1. Terminal C and D
2. Terminal A and B
Does the resistance equal to the value specified?40–80Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5Replace the IAC valve.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
61. Disconnect the Engine control Module (ECM)
connector.
2. Check for an open or short in the wires be-
tween following terminals.
S Terminal D of IAC valve connector and ter-
minal M13 of ECM connector
S Terminal C of IAC valve connector and ter-
minal M15 of ECM connector
S Terminal B of IAC valve connector and ter-
minal M30 of ECM connector
S Terminal A of IAC valve connector and ter-
minal M14 of ECM connector
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 7
7Repair an open or short circuit as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
8Inspect the IAC connector terminals and the ECM
connector terminals.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
9Repair or replace the throttle body assembly and/or
ECM connector terminals as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
10Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 377 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 131
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0122
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 195). The charac-
teristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage sig-
nal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles to
about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is one
of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel con-
trol and other functions such as idle, wide open throttle,
deceleration enleanment, and acceleration enrichment.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TPS voltage is less than 0.3V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will default to 20°C (68°F) for the first 60
seconds of the engine run time, and then 92 °C
(198 °F).
S The scan tool will not show the defaulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the DTC P0122 cannot be duplicated, the information in-
cluded in the Freeze Frame data can be useful. Use the
scan tool DTC information data to determine the status of
the DTC. If the DTC occurs intermittently, using the DTC
P0121 diagnostic table may help isolate the problem.