2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Iat resistance
[x] Cancel search: Iat resistancePage 254 of 2643

1F – 8IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EGR Desired Position
The desired exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) position is
the commanded EGR position. The ECM calculates the
desired EGR position. The higher the percentage, the lon-
ger the ECM is commanding the EGR valve ON.
Engine Load
Indicates engine load based on manifold absolute pres-
sure. The higher the percentage, the more load the engine
is under.
Engine Run Time
The engine run time is a measure of how long the engine
has been running. When the engine stops running, the tim-
er resets to zero.
Engine Speed
Engine Speed is computed by the ECM from the fuel con-
trol reference input. It should remain close to desired idle
under the various engine loads with the engine idling.
Fan
The Fan Control (FC) Relay is commanded by the ECM.
The FC Relay displays the command as ON or OFF.
Fuel Level Sensor
The Fuel Level Sensor monitors the fuel level in the tank.
The Fuel Level Sensor monitors the rate of change of the
air pressure in the EVAP system. Several of the Enhanced
EVAP System diagnostics are dependent upon the correct
fuel level.
Fuel System Status
The Closed Loop is displayed indicating that the ECM is
controlling the fuel delivery according to the Front Heated
Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) voltage as close to an air/fuel ra-
tio of 14.7 to 1 as possible.
IAC Position
The scan tool displays the ECM command for the Idle Air
Control (IAC) pintle position in counts. The higher the
number of counts, the greater the commanded idle speed
reads. The Idle Air Control responds to changes in the en-
gine load in order to maintain the desired idle rpm.
Ignition 1 (Voltage)
The ignition volts represent the system voltage measured
by the ECM at the ignition feed circuit.
Intake Air Temperature
The ECM converts the resistance of the Intake Air Tem-
perature (IAT) sensor to degrees in the same manner as
the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor. In take air
temperature is used by the ECM to adjust fuel delivery and
spark timing according to incoming air density.Knock Present
The KS Noise Channel indicates when the ECM detects
the KS signal. The ECM should display NO at idle.
Long Term FT
The Long Term Fuel Trim (FT) is derived from the short
term fuel trim value. The Long Term FT is used for the long
term correction of the fuel delivery. A value of 128 counts
(0%) indicates that the fuel delivery requires no com-
pensation in order to maintain a 14.7:1 air to fuel ratio. A
value below 128 counts means that the fuel system is too
rich and the fuel delivery is being reduced. The ECM is de-
creasing the injector pulse width. A value above 128
counts indicates that a lean condition exists for which the
ECM is compensating.
MAP
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the change in the intake manifold pressure which results
from engine load and speed changes. As the intake man-
ifold pressure increases, the air density in the intake also
increases and the additional fuel is required.
Misfire History #1–4
Indicates the number of misfires that have occurred after
195 current misfires have been counted. The current mis-
fire counter will add its misfires to the history misfire count-
er after 195 total misfires have taken place. If 1 cylinder is
misfiring, the misfiring current counter will have 195 mis-
fires counted before adding to its history counter. If 2 cylin-
ders are misfiring, the misfiring current counter will add to
their history counters after 97 misfires. The counter incre-
ments only after a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
has been set.
Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
The pre–converter Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) reading represents the exhaust oxygen sensor
output voltage. This voltage will fluctuate constantly be-
tween 100 mv (lean exhaust) and 900 mv (rich exhaust)
when the system is operating in a Closed Loop.
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
The post–converter Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) represents the exhaust oxygen output voltage
past the catalytic converter. This voltage remains inactive,
or the voltage will appear lazy within a range of 100 mv
(lean exhaust) and 900 mv (rich exhaust) when operating
in a Closed Loop.
Short Term FT
The Short Term FT represents a short term correction to
fuel delivery by the ECM in response to the amount of time
the oxygen sensor voltage spends above or below the 450
mv threshold. If the oxygen sensor has mainly been below
450 mv, indicating a lean air/fuel mixture, short term fuel
trim will increase to tell the ECM to add fuel. If the oxygen
sensor voltage stays mainly above the threshold, the ECM
will reduce fuel delivery to compensate for the indicated
rich condition.
Page 257 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
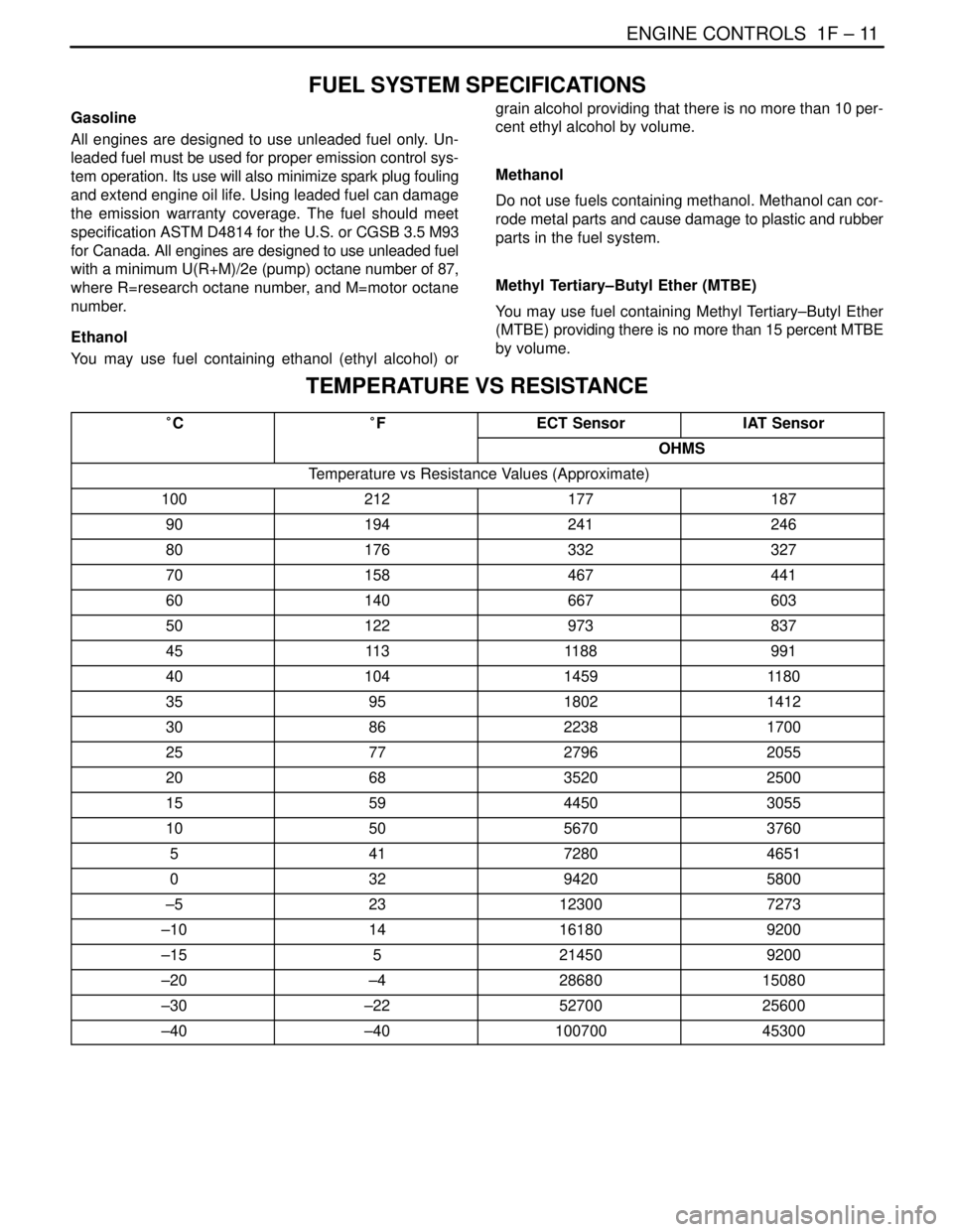
FUEL SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS
Gasoline
All engines are designed to use unleaded fuel only. Un-
leaded fuel must be used for proper emission control sys-
tem operation. Its use will also minimize spark plug fouling
and extend engine oil life. Using leaded fuel can damage
the emission warranty coverage. The fuel should meet
specification ASTM D4814 for the U.S. or CGSB 3.5 M93
for Canada. All engines are designed to use unleaded fuel
with a minimum U(R+M)/2e (pump) octane number of 87,
where R=research octane number, and M=motor octane
number.
Ethanol
You may use fuel containing ethanol (ethyl alcohol) orgrain alcohol providing that there is no more than 10 per-
cent ethyl alcohol by volume.
Methanol
Do not use fuels containing methanol. Methanol can cor-
rode metal parts and cause damage to plastic and rubber
parts in the fuel system.
Methyl Tertiary–Butyl Ether (MTBE)
You may use fuel containing Methyl Tertiary–Butyl Ether
(MTBE) providing there is no more than 15 percent MTBE
by volume.
TEMPERATURE VS RESISTANCE
°C°FECT SensorIAT Sensor
OHMS
Temperature vs Resistance Values (Approximate)
100212177187
90194241246
80176332327
70158467441
60140667603
50122973837
4511 31188991
4010414591180
359518021412
308622381700
257727962055
206835202500
155944503055
105056703760
54172804651
03294205800
–523123007273
–1014161809200
–155214509200
–20–42868015080
–30–225270025600
–40–4010070045300
Page 294 of 2643

1F – 48IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
11Compare the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT).
Is the ECT relatively close to the IAT?–Go to Step 12Go to ”DTC
P0118 Engine
Coolant Tem-
perature High
Voltage
121. Check if the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor reading is over the specified reading.
2. Crank the engine while watching the MAP sen-
sor reading.
Does the MAP sensor read above the specified val-
ue and then change while cranking the engine?4 vGo to Step 13Go to Step 14
13Crank the engine.
Does the Crankshaft Position (CKP) Active Counter
increment while cranking?–Go to Step 16Go to Step 18
14Check the scan data for serial data.
Was serial data lost while cranking the engine?–Go to Step 15Go to ”MAP
Sensor Output
Check”
15Repair voltage loss to the engine control module
(ECM) from the ignition switch.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
16Check for the presence of spark from all of the igni-
tion wires while cranking the engine.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–Go to Step 41Go to Step 17
171. Measure the resistance of the ignition wires.
2. Replace any of the ignition wire(s) with a resist-
ance above the value specified.
3. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?30,000 WGo to Step 3Go to Step 18
181. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sen-
sor connector.
3. Measure the voltage between the CKP connec-
tor terminals 1 and 3.
4. Repair the wiring as needed.
Does the voltage measure near the value specified?1.4 v (2.5 v)*Go to Step 19Go to Step 20
19Measure the voltage between the CKP connector
terminals 2 and 3.
Does the voltage measure near the value specified1.4 v (2.5 v)*Go to Step 26Go to Step 21
20Measure the voltage between the CKP connector
terminals 1 and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the value specified?1.4 v (2.5 v)*Go to Step 22Go to Step 23
21Measure the voltage between the CKP connector
terminals 2 and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the value specified?1.4 v (2.5 v)*Go to Step 22Go to Step 24
22Check for an open or short in the wire between the
CKP connector terminal 3 and ground.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 25Go to Step 40
23Check for an open or short in the wire between the
CKP connector terminal 1 and the ECM connector
terminal M21
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 25Go to Step 40
Page 366 of 2643

1F – 120IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B11F51
BRNORN
/BLK
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0112
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor uses a thermis-
tor to control the signal voltage to the engine control mod-
ule (ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage
and a ground to the sensor. When the air is cold, the resist-
ance is high ; therefore IAT sensor signal voltage will be
high. If the intake air is warm, resistance is low ; therefore
the IAT sensor signal voltage will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT voltage is less than 0.01V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.S The ECM will default to 605C(1405F) for intake air
temperature. The scan tool will not show the de-
faulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare the IAT
sensor to the engine coolant temperature(ECT) sensor.
The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor should be relatively
close to each other. Use the temperature vs. Resistance
Values table to evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor.
Refer to ”Temperature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 368 of 2643

1F – 122IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B11F51
BRNORN
/BLK
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0113
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor uses a thermis-
tor to control the signal voltage to the engine control mod-
ule (ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage
and a ground to the sensor . when the air is cold, the resist-
ance is high ; therefore IAT sensor signal voltage will be
high. If the intake air is warm, resistance is low ; therefore
the IAT sensor signal voltage will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT voltage is less than 4.99V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.S The ECM will default to 605C(1405F) for intake air
temperature. The scan tool will not show the de-
faulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
S If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare
the IAT sensor to the engine coolant temperature
(ECT) sensor. The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor
should be relatively close to each other.
S Use the temperature vs. Resistance Values table to
evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer
to ”Temperature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 482 of 2643
1F – 236IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
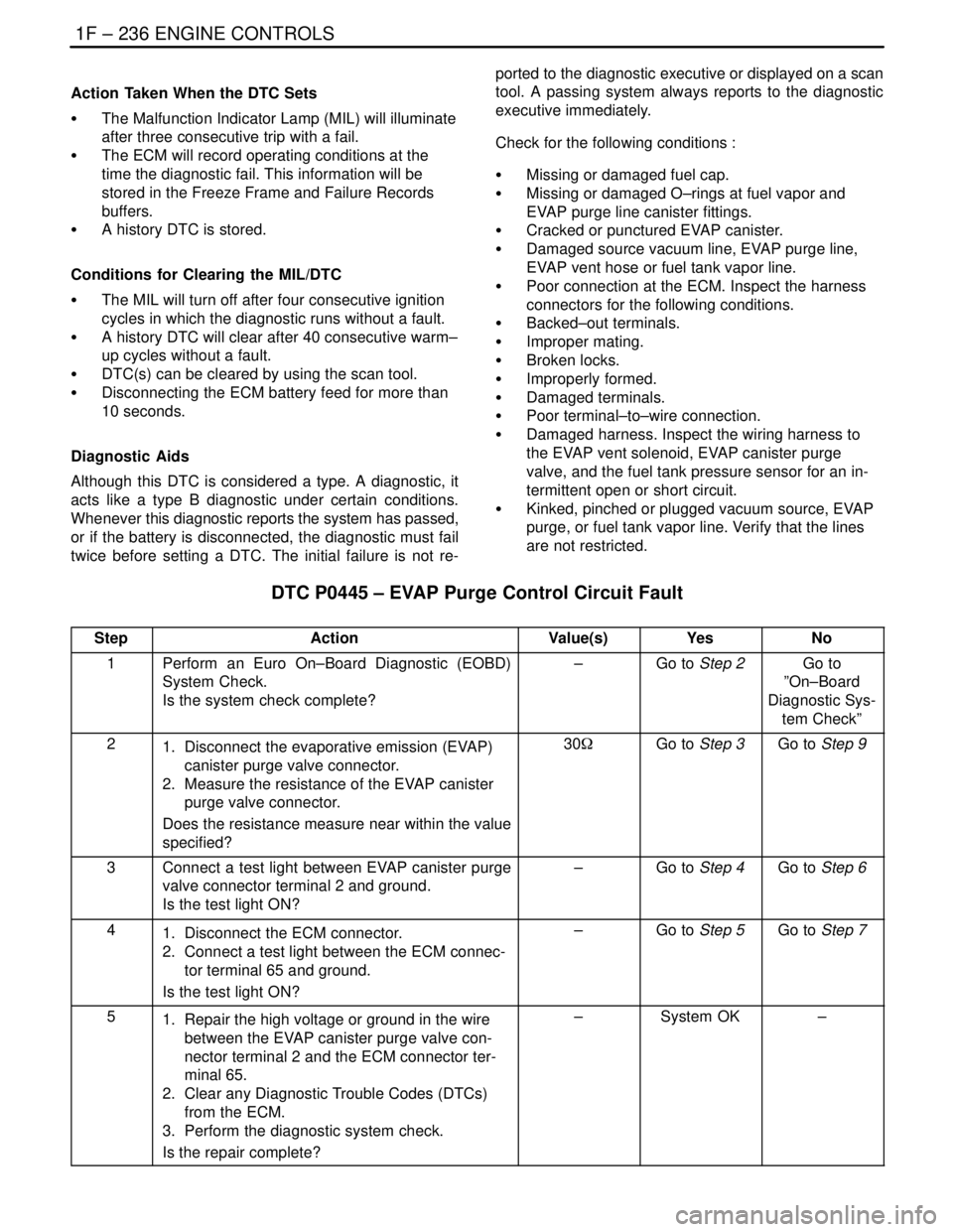
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Although this DTC is considered a type. A diagnostic, it
acts like a type B diagnostic under certain conditions.
Whenever this diagnostic reports the system has passed,
or if the battery is disconnected, the diagnostic must fail
twice before setting a DTC. The initial failure is not re-ported to the diagnostic executive or displayed on a scan
tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic
executive immediately.
Check for the following conditions :
S Missing or damaged fuel cap.
S Missing or damaged O–rings at fuel vapor and
EVAP purge line canister fittings.
S Cracked or punctured EVAP canister.
S Damaged source vacuum line, EVAP purge line,
EVAP vent hose or fuel tank vapor line.
S Poor connection at the ECM. Inspect the harness
connectors for the following conditions.
S Backed–out terminals.
S Improper mating.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed.
S Damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection.
S Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness to
the EVAP vent solenoid, EVAP canister purge
valve, and the fuel tank pressure sensor for an in-
termittent open or short circuit.
S Kinked, pinched or plugged vacuum source, EVAP
purge, or fuel tank vapor line. Verify that the lines
are not restricted.
DTC P0445 – EVAP Purge Control Circuit Fault
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Disconnect the evaporative emission (EVAP)
canister purge valve connector.
2. Measure the resistance of the EVAP canister
purge valve connector.
Does the resistance measure near within the value
specified?30WGo to Step 3Go to Step 9
3Connect a test light between EVAP canister purge
valve connector terminal 2 and ground.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 6
41. Disconnect the ECM connector.
2. Connect a test light between the ECM connec-
tor terminal 65 and ground.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 7
51. Repair the high voltage or ground in the wire
between the EVAP canister purge valve con-
nector terminal 2 and the ECM connector ter-
minal 65.
2. Clear any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
from the ECM.
3. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 601 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 355
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0112
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor uses a thermistor
to control the signal voltage to the Engine Control Module
(ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference and a ground
to the sensor. When the air is cold, the resistance is high;
therefore the IAT signal voltage will be high. If the intake
air is warm, resistance is low; therefore the IAT signal volt-
age will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT is less than 149°C (300°F).
S Engine run time is greater than 120 seconds.
S Vehicles speed is greater than or equal to 50 km/h
(31 mph).
S DTC P0502 is not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The ECM will substitute a default value for intake
air temperature. The scan tool will not show the
defaulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare the IAT
sensor to the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor should be relatively
close to each other.
Use the Temperature vs. Resistance Values table to eval-
uate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer to ”Temper-
ature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
4. This step simulates a DTC P0113 condition. If the
scan tool displays the specified value, the IAT sig-
nal circuit, the ECM are OK.
8. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
Page 604 of 2643

1F – 358IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0113
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor uses a thermistor
to control the signal voltage to the Engine Control Module
(ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference and a ground
to the sensor. When the air is cold, the resistance is high;
therefore the IAT signal voltage will be high. If the intake
air is warm, resistance is low; therefore the IAT signal volt-
age will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT is less than –38°C (–36°F).
S Vehicles speed is less than 25 km/h (16 mph).
S Engine run time is greater than 120 seconds.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is above 70 °C
158 °F).
S Calculated air are flow is less than 15 g/second.
S DTC P0502, P0117, P0118 not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The ECM will substitute a default value for intake
air temperature. The scan tool will not show the
defaulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
S If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare
the IAT sensor to the Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) sensor. The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor
should be relatively close to each other.
S Use the Temperature vs. Resistance Values table
to evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Re-
fer to ”Temperature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
4. This step simulates a DTC P0112. If the ECM
senses the change, the ECM and wiring are OK.
5. This step will determine if the reason the ECM did
not sense the change was due to a open ground or
signal circuit or malfunctioning ECM.
11. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.