2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Section 6
[x] Cancel search: Section 6Page 1007 of 2643
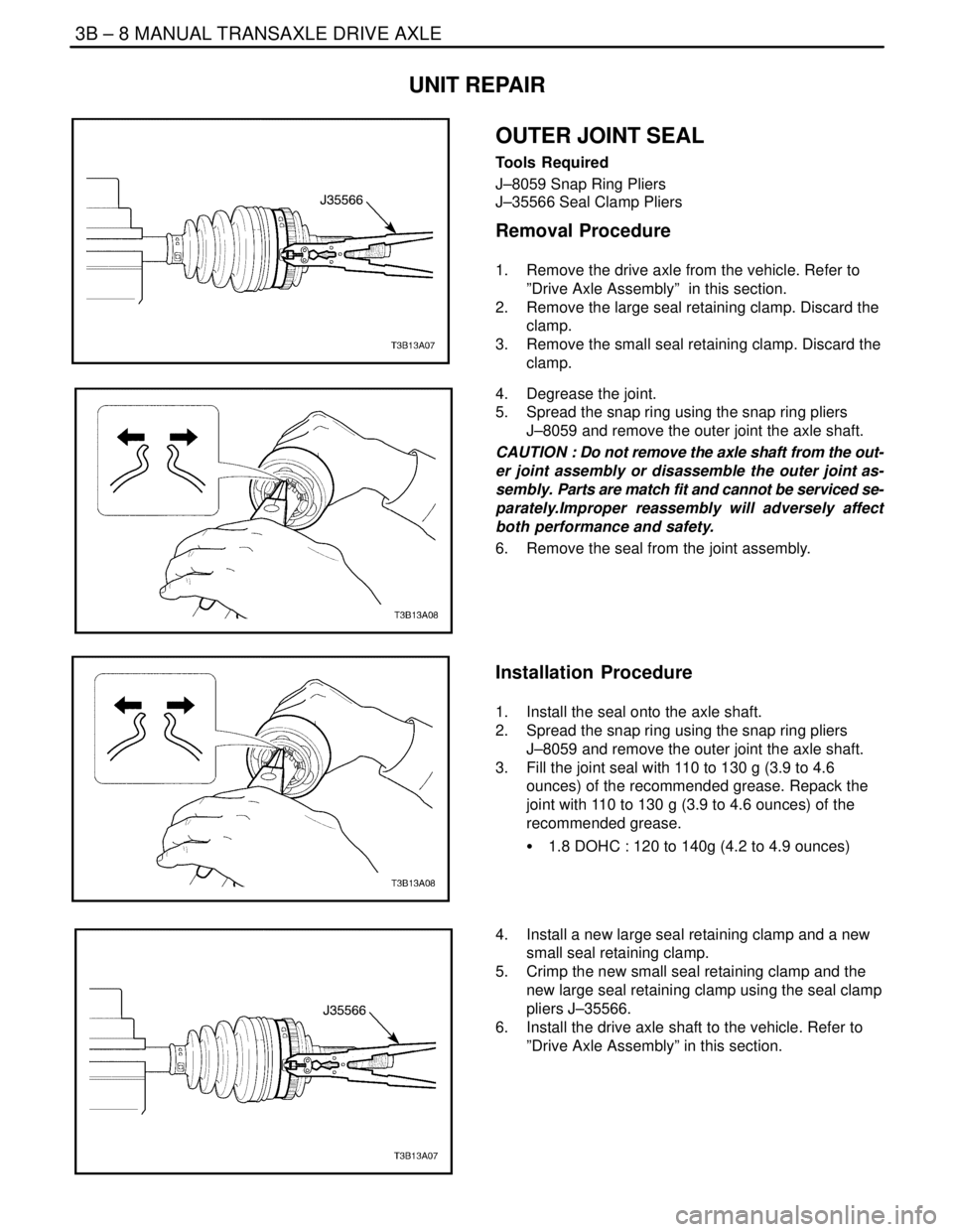
3B – 8IMANUAL TRANSAXLE DRIVE AXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
UNIT REPAIR
OUTER JOINT SEAL
Tools Required
J–8059 Snap Ring Pliers
J–35566 Seal Clamp Pliers
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the drive axle from the vehicle. Refer to
”Drive Axle Assembly” in this section.
2. Remove the large seal retaining clamp. Discard the
clamp.
3. Remove the small seal retaining clamp. Discard the
clamp.
4. Degrease the joint.
5. Spread the snap ring using the snap ring pliers
J–8059 and remove the outer joint the axle shaft.
CAUTION : Do not remove the axle shaft from the out-
er joint assembly or disassemble the outer joint as-
sembly. Parts are match fit and cannot be serviced se-
parately.Improper reassembly will adversely affect
both performance and safety.
6. Remove the seal from the joint assembly.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the seal onto the axle shaft.
2. Spread the snap ring using the snap ring pliers
J–8059 and remove the outer joint the axle shaft.
3. Fill the joint seal with 110 to 130 g (3.9 to 4.6
ounces) of the recommended grease. Repack the
joint with 110 to 130 g (3.9 to 4.6 ounces) of the
recommended grease.
S 1.8 DOHC : 120 to 140g (4.2 to 4.9 ounces)
4. Install a new large seal retaining clamp and a new
small seal retaining clamp.
5. Crimp the new small seal retaining clamp and the
new large seal retaining clamp using the seal clamp
pliers J–35566.
6. Install the drive axle shaft to the vehicle. Refer to
”Drive Axle Assembly” in this section.
Page 1008 of 2643
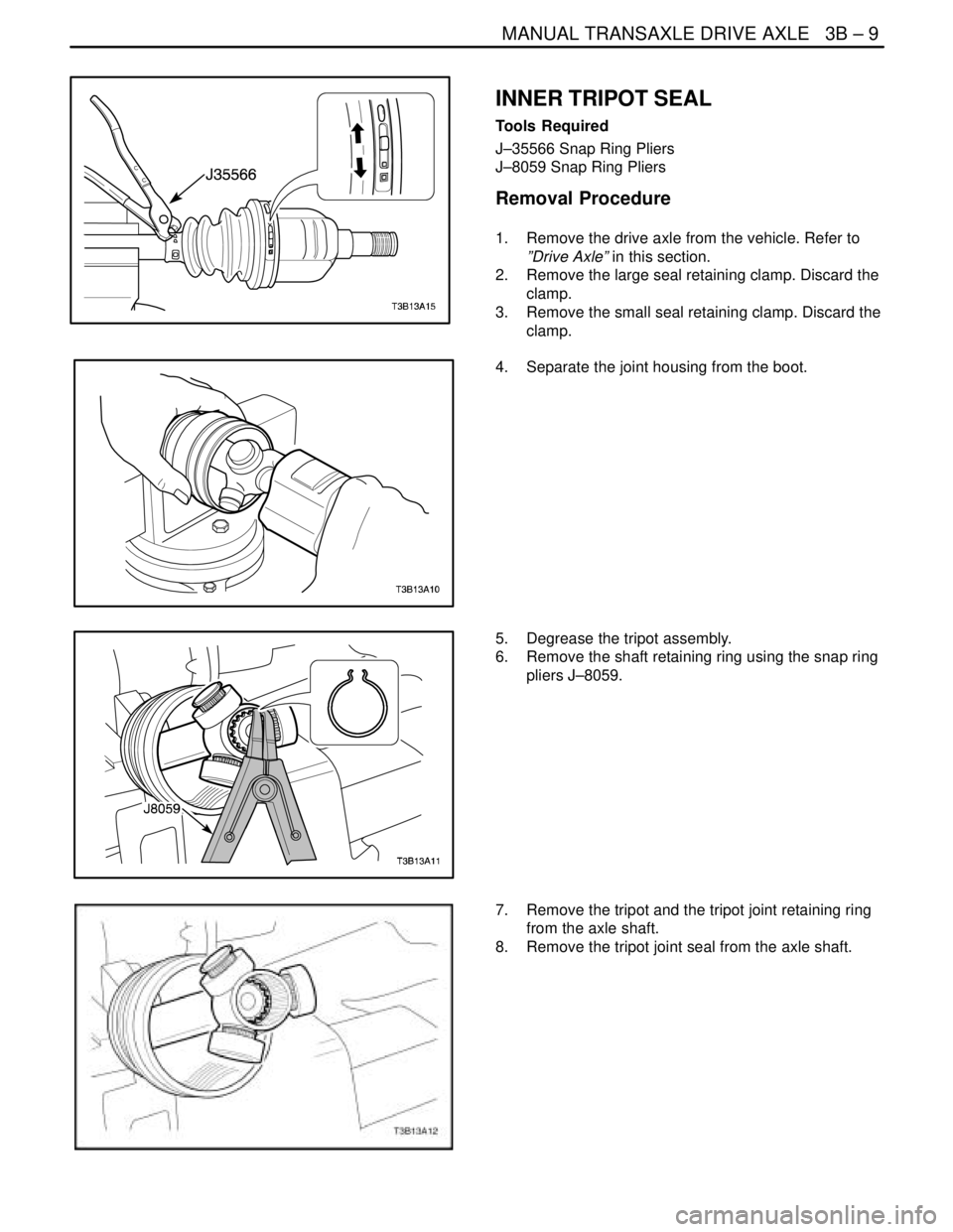
MANUAL TRANSAXLE DRIVE AXLE 3B – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
INNER TRIPOT SEAL
Tools Required
J–35566 Snap Ring Pliers
J–8059 Snap Ring Pliers
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the drive axle from the vehicle. Refer to
”Drive Axle” in this section.
2. Remove the large seal retaining clamp. Discard the
clamp.
3. Remove the small seal retaining clamp. Discard the
clamp.
4. Separate the joint housing from the boot.
5. Degrease the tripot assembly.
6. Remove the shaft retaining ring using the snap ring
pliers J–8059.
7. Remove the tripot and the tripot joint retaining ring
from the axle shaft.
8. Remove the tripot joint seal from the axle shaft.
Page 1009 of 2643
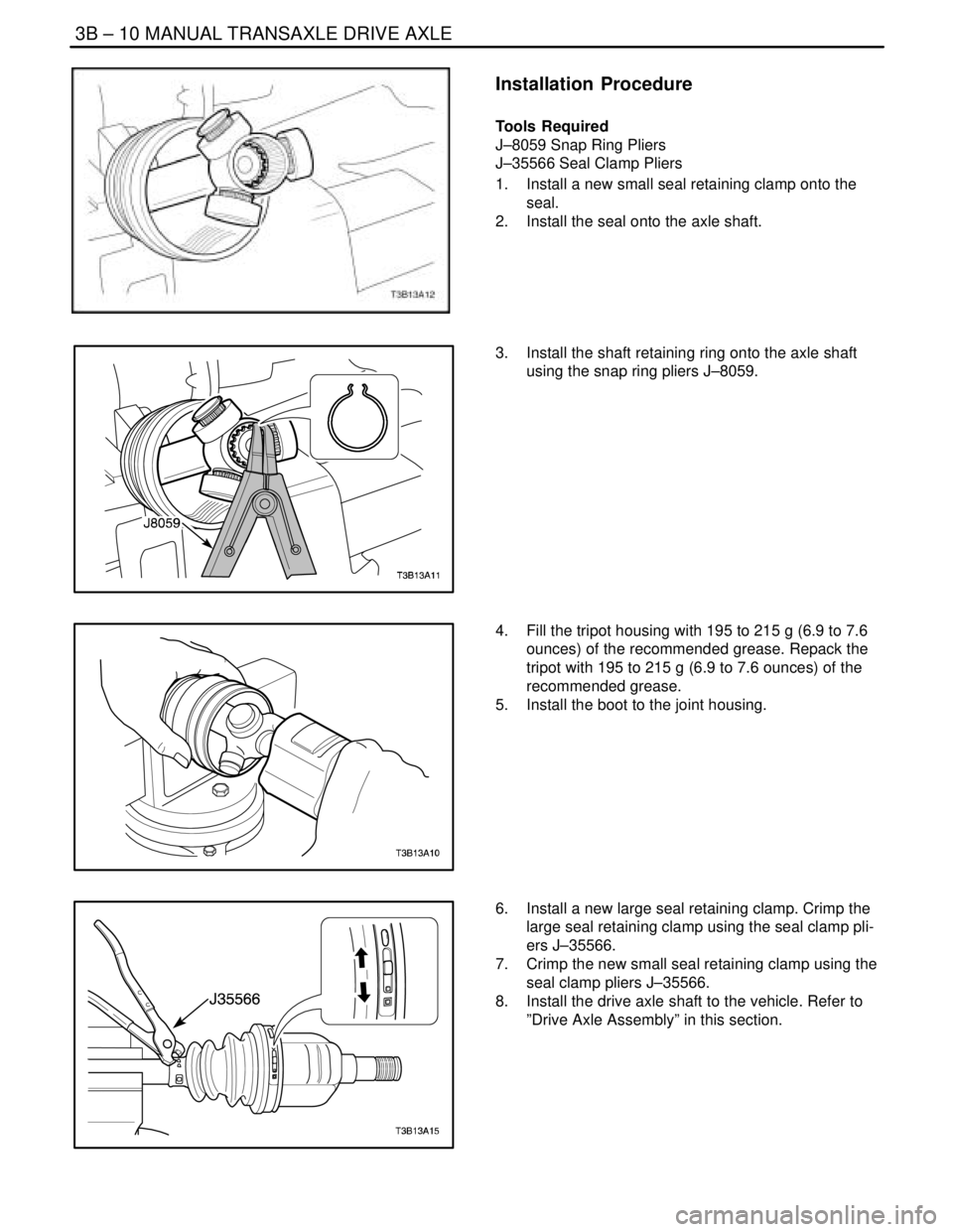
3B – 10IMANUAL TRANSAXLE DRIVE AXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Installation Procedure
Tools Required
J–8059 Snap Ring Pliers
J–35566 Seal Clamp Pliers
1. Install a new small seal retaining clamp onto the
seal.
2. Install the seal onto the axle shaft.
3. Install the shaft retaining ring onto the axle shaft
using the snap ring pliers J–8059.
4. Fill the tripot housing with 195 to 215 g (6.9 to 7.6
ounces) of the recommended grease. Repack the
tripot with 195 to 215 g (6.9 to 7.6 ounces) of the
recommended grease.
5. Install the boot to the joint housing.
6. Install a new large seal retaining clamp. Crimp the
large seal retaining clamp using the seal clamp pli-
ers J–35566.
7. Crimp the new small seal retaining clamp using the
seal clamp pliers J–35566.
8. Install the drive axle shaft to the vehicle. Refer to
”Drive Axle Assembly” in this section.
Page 1013 of 2643

SECTION 4
USAGE AND CAPACITY OF FUSES IN FUSE BLOCK
CONTENTS
1. ENGINE ROOM RELAY AND FUSE BLOCK 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2. I.P FUSE BLOCK4–3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. POSITION OF CONTROL UNIT, RELAY AND PART NUMBER 4–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1017 of 2643
SECTION : 4A
HYDRAULIC BRAKES
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS4A–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Specifcations 4A–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 4A–2. . . . . . . . . .
COMPONENT LOCATOR4A–3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake System (ABS) 4A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake System (NON–ABS) 4A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSIS4A–5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake System Testing 4A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake Hose Inspection 4A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Warning Lamp Operation 4A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stop Lamp Warning Circuit Diagnosis 4A–6. . . . . . . . MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR4A–10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE 4A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Bleeding the Brakes 4A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pressure Bleeding the Brakes 4A–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake Hose Rear 4A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake Hose Front 4A–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stoplamp Switch 4A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake Pedal 4A–16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION4A–17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Warning Lamp Operation 4A–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1021 of 2643

HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
BRAKE SYSTEM TESTING
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake perfor-
mance cannot be made if the roadway is wet, greasy, or
covered with loose dirt whereby all tires do not grip the
road equally. Testing will also be adversely affected if the
roadway is crowned so as to throw the weight so roughly
that the wheels tend to bounce.
Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both light
and heavy pedal pressure; however, avoid locking the
brakes and sliding the tires. Locked brakes and sliding
tires do not indicate brake efficiency since heavily braked,
but turning, wheels will stop the vehicle in less distance
than locked brakes. More tire–to–road friction is present
with a heavily–braked, turning tire than with a sliding tire.
Because of the high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
There are three major external conditions that affect brake
performance:
S Tires having unequal contact and grip of the road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated, and the tread pattern of the right and the
left tires must be approximately equal.
S Unequal loading of the vehicle can affect the brake
performance since the most heavily loaded wheels
require more braking power, and thus more braking
effort, than the others.
S Misalignment of the wheels, particularly conditions
of excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
To check for brake fluid leaks, hold constant foot pressure
on the pedal with the engine running at idle and the shift
lever in NEUTRAL. If the pedal gradually falls away with
the constant pressure, the hydraulic system may be leak-
ing. Perform a visual check to confirm any suspected
leaks.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight drop
in the reservoir level results from normal lining wear, an ab-
normally low level indicates a leak in the system. The hy-
draulic system may be leaking either internally or external-
ly. Refer to the procedure below to check the master
cylinder. Also, the system may appear to pass this test
while still having a slight leak. If the fluid level is normal,
check the vacuum booster pushrod length. If an incorrect
pushrod length is found, adjust or replace the rod.
Check the master cylinder using the following procedure:
S Check for a cracked master cylinder casting or
brake fluid leaking around the master cylinder.
Leaks are indicated only if there is at least one drop
of fluid. A damp condition is not abnormal.S Check for a binding pedal linkage and for an incor-
rect pushrod length. If both of these parts are in
satisfactory condition, disassemble the master cyl-
inder and check for an elongated or swollen primary
cylinder or piston seals. If swollen seals are found,
substandard or contaminated brake fluid should be
suspected. If contaminated brake fluid is found, all
the components should be disassembled and
cleaned, and all the rubber components should be
replaced. All of the pipes must also be flushed.
Improper brake fluid, or mineral oil or water in the fluid,
may cause the brake fluid to boil or cause deterioration of
the rubber components. If the primary piston cups in the
master cylinder are swollen, then the rubber parts have
deteriorated. This deterioration may also be evidenced by
swollen wheel cylinder piston seals on the drum brake
wheels.
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all the hy-
draulic parts and wash the parts with alcohol. Dry these
parts with compressed air before reassembly to keep alco-
hol out of the system. Replace all the rubber parts in the
system, including the hoses. Also, when working on the
brake mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings. If exces-
sive fluid is found, replace the linings.
If the master cylinder piston seals are in satisfactory condi-
tion, check for leaks or excessive heat conditions. If these
conditions are not found, drain the fluid, flush the master
cylinder with brake fluid, refill the master cylinder, and
bleed the system. Refer to ”Manual Bleeding the Brakes”
or”Pressure Bleeding the Brakes” in this section.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The hydraulic brake hoses should be inspected at least
twice a year. The brake hose assembly should be checked
for road hazard damage, cracks, chafing of the outer cov-
er, and for leaks or blisters. Inspect the hoses for proper
routing and mounting. A brake hose that rubs on a suspen-
sion component will wear and eventually fail. A light and
a mirror may be needed for an adequate inspection. If any
of the above conditions are observed on the brake hose,
adjust or replace the hose as necessary.
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
This brake system uses a BRAKE warning lamp located
in the instrument panel cluster. When the ignition switch
is in the START position, the BRAKE warning lamp should
glow and go OFF when the ignition switch returns to the
RUN position.
The following conditions will activate the BRAKE lamp:
S Parking brake applied. The light should be ON
whenever the parking brake is applied and the igni-
tion switch is ON.
S Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master cylin-
der will turn the BRAKE lamp ON.
S EBD system is disabled. The light should be ON
when the EBD system is malfunctioning.
Page 1027 of 2643
HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
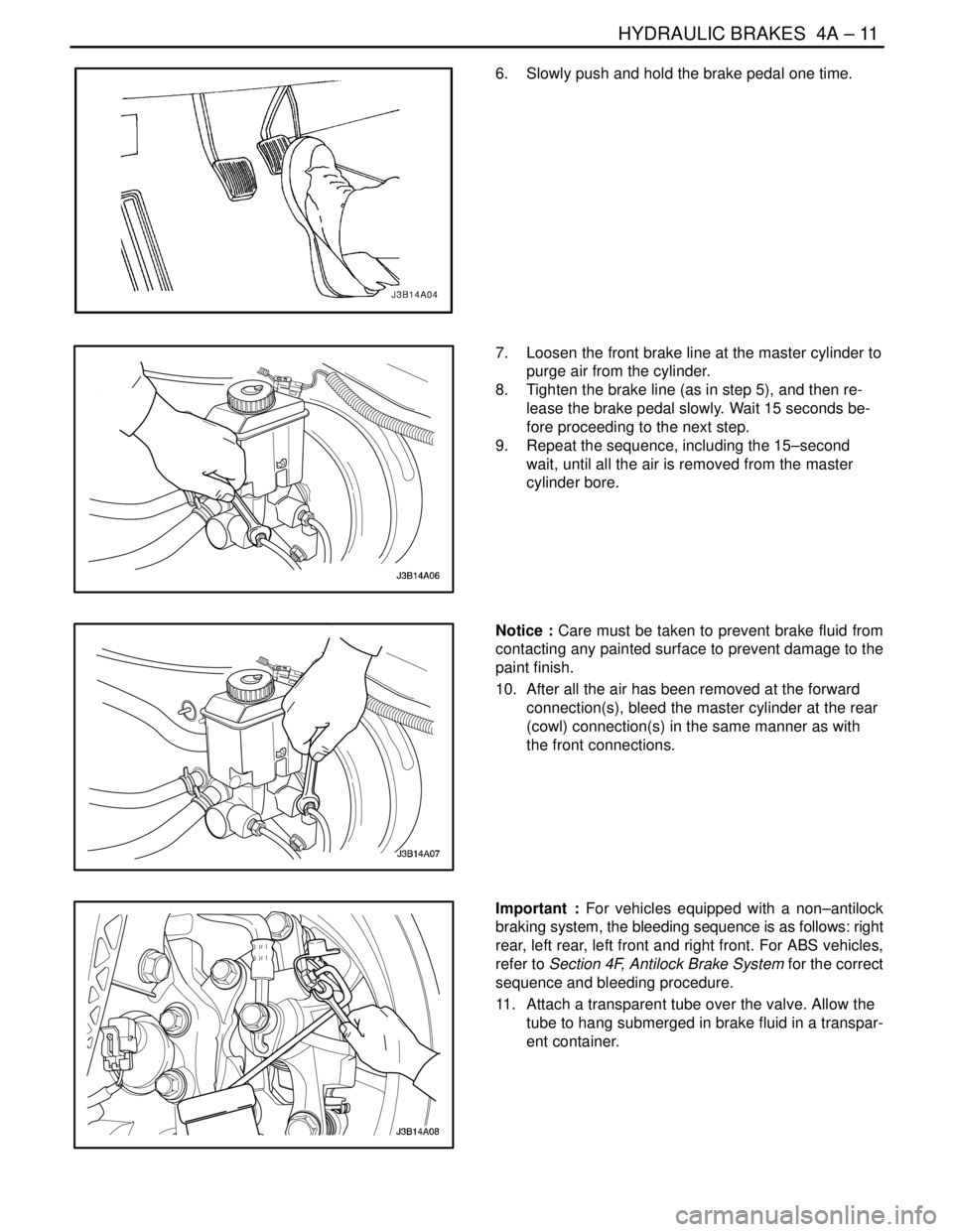
6. Slowly push and hold the brake pedal one time.
7. Loosen the front brake line at the master cylinder to
purge air from the cylinder.
8. Tighten the brake line (as in step 5), and then re-
lease the brake pedal slowly. Wait 15 seconds be-
fore proceeding to the next step.
9. Repeat the sequence, including the 15–second
wait, until all the air is removed from the master
cylinder bore.
Notice : Care must be taken to prevent brake fluid from
contacting any painted surface to prevent damage to the
paint finish.
10. After all the air has been removed at the forward
connection(s), bleed the master cylinder at the rear
(cowl) connection(s) in the same manner as with
the front connections.
Important : For vehicles equipped with a non–antilock
braking system, the bleeding sequence is as follows: right
rear, left rear, left front and right front. For ABS vehicles,
refer to Section 4F, Antilock Brake System for the correct
sequence and bleeding procedure.
11. Attach a transparent tube over the valve. Allow the
tube to hang submerged in brake fluid in a transpar-
ent container.
Page 1028 of 2643
4A – 12IHYDRAULIC BRAKES
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
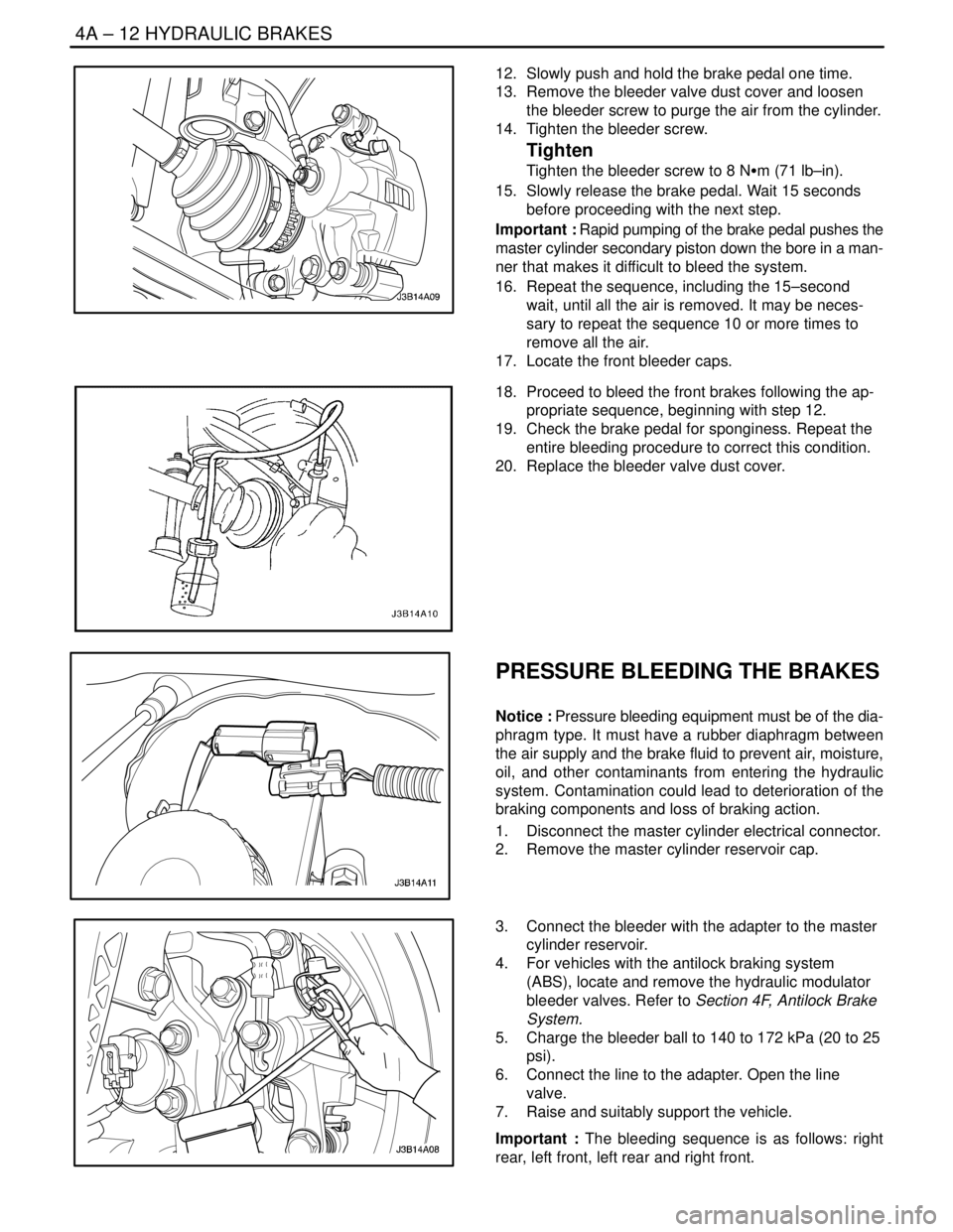
12. Slowly push and hold the brake pedal one time.
13. Remove the bleeder valve dust cover and loosen
the bleeder screw to purge the air from the cylinder.
14. Tighten the bleeder screw.
Tighten
Tighten the bleeder screw to 8 NSm (71 lb–in).
15. Slowly release the brake pedal. Wait 15 seconds
before proceeding with the next step.
Important : Rapid pumping of the brake pedal pushes the
master cylinder secondary piston down the bore in a man-
ner that makes it difficult to bleed the system.
16. Repeat the sequence, including the 15–second
wait, until all the air is removed. It may be neces-
sary to repeat the sequence 10 or more times to
remove all the air.
17. Locate the front bleeder caps.
18. Proceed to bleed the front brakes following the ap-
propriate sequence, beginning with step 12.
19. Check the brake pedal for sponginess. Repeat the
entire bleeding procedure to correct this condition.
20. Replace the bleeder valve dust cover.
PRESSURE BLEEDING THE BRAKES
Notice : Pressure bleeding equipment must be of the dia-
phragm type. It must have a rubber diaphragm between
the air supply and the brake fluid to prevent air, moisture,
oil, and other contaminants from entering the hydraulic
system. Contamination could lead to deterioration of the
braking components and loss of braking action.
1. Disconnect the master cylinder electrical connector.
2. Remove the master cylinder reservoir cap.
3. Connect the bleeder with the adapter to the master
cylinder reservoir.
4. For vehicles with the antilock braking system
(ABS), locate and remove the hydraulic modulator
bleeder valves. Refer to Section 4F, Antilock Brake
System.
5. Charge the bleeder ball to 140 to 172 kPa (20 to 25
psi).
6. Connect the line to the adapter. Open the line
valve.
7. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
Important : The bleeding sequence is as follows: right
rear, left front, left rear and right front.