2004 DAEWOO LACETTI torque converter bolt
[x] Cancel search: torque converter boltPage 169 of 2643

1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 49
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
5. Install the right engine mount to the engine block
mount and the frame mount.
6. Install the right engine mount bracket retaining bolts
and nuts.
Tighten
Tighten the engine mount bracket retaining bolts and
nuts to 55 NSm (41 lb–ft).
7. Remove the floor jack used for support of the trans-
mission.
8. Remove the engine lifting device.
9. Install the transaxle torque converter bolts, if auto-
matic transaxle equipped.
Tighten
Tighten the transaxle torque converter bolts to 60
NSm (44 lb–ft).
10. Connect the vacuum lines at the CCP solenoid.
11. Connect the electrical connector to the CCP and
the EGR solenoid.
12. Connect the oil pressure switch connector.
13. Install the crankshaft pulley.
14. Install the crankshaft pulley bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the crankshaft pulley bolts to 20 NSm (15 lb–
ft) using a torque wrench.
15. Connect the CPS connector.
16. Install the exhaust flex pipe.
17. Install the exhaust flex pipe retaining nuts to the
exhaust manifold studs.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust flex pipe–to–exhaust manifold
retaining nuts to 35 NSm (26 lb–ft).
Page 1354 of 2643
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
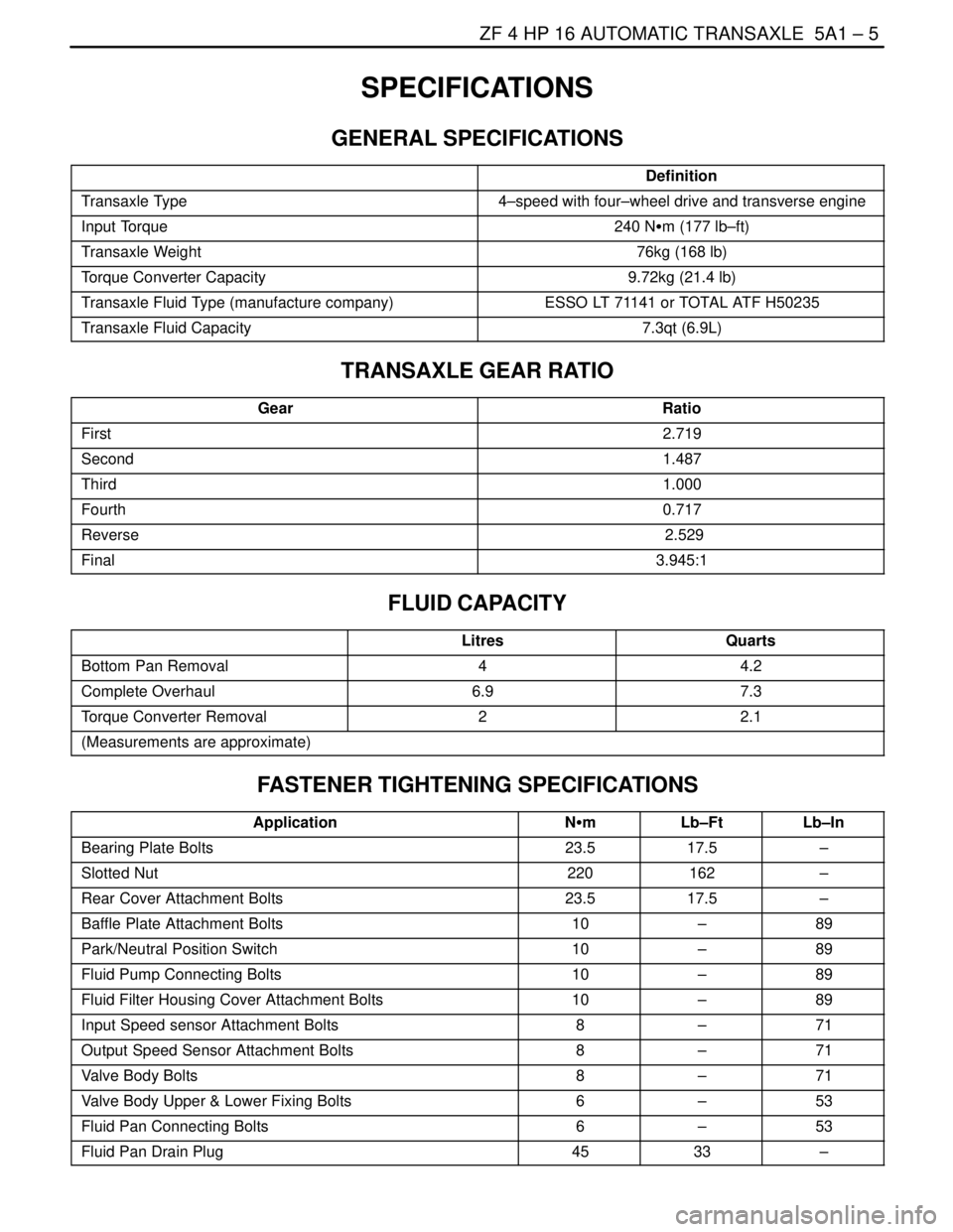
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Definition
Transaxle Type4–speed with four–wheel drive and transverse engine
Input Torque240 NSm (177 lb–ft)
Transaxle Weight76kg (168 lb)
Torque Converter Capacity9.72kg (21.4 lb)
Transaxle Fluid Type (manufacture company)ESSO LT 71141 or TOTAL ATF H50235
Transaxle Fluid Capacity7.3qt (6.9L)
TRANSAXLE GEAR RATIO
GearRatio
First2.719
Second1.487
Third1.000
Fourth0.717
Reverse 2.529
Final3.945:1
FLUID CAPACITY
LitresQuarts
Bottom Pan Removal44.2
Complete Overhaul6.97.3
Torque Converter Removal22.1
(Measurements are approximate)
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb–FtLb–In
Bearing Plate Bolts23.517.5–
Slotted Nut220162–
Rear Cover Attachment Bolts23.517.5–
Baffle Plate Attachment Bolts10–89
Park/Neutral Position Switch10–89
Fluid Pump Connecting Bolts10–89
Fluid Filter Housing Cover Attachment Bolts10–89
Input Speed sensor Attachment Bolts8–71
Output Speed Sensor Attachment Bolts8–71
Valve Body Bolts8–71
Valve Body Upper & Lower Fixing Bolts6–53
Fluid Pan Connecting Bolts6–53
Fluid Pan Drain Plug4533–
Page 1355 of 2643
5A1 – 6IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
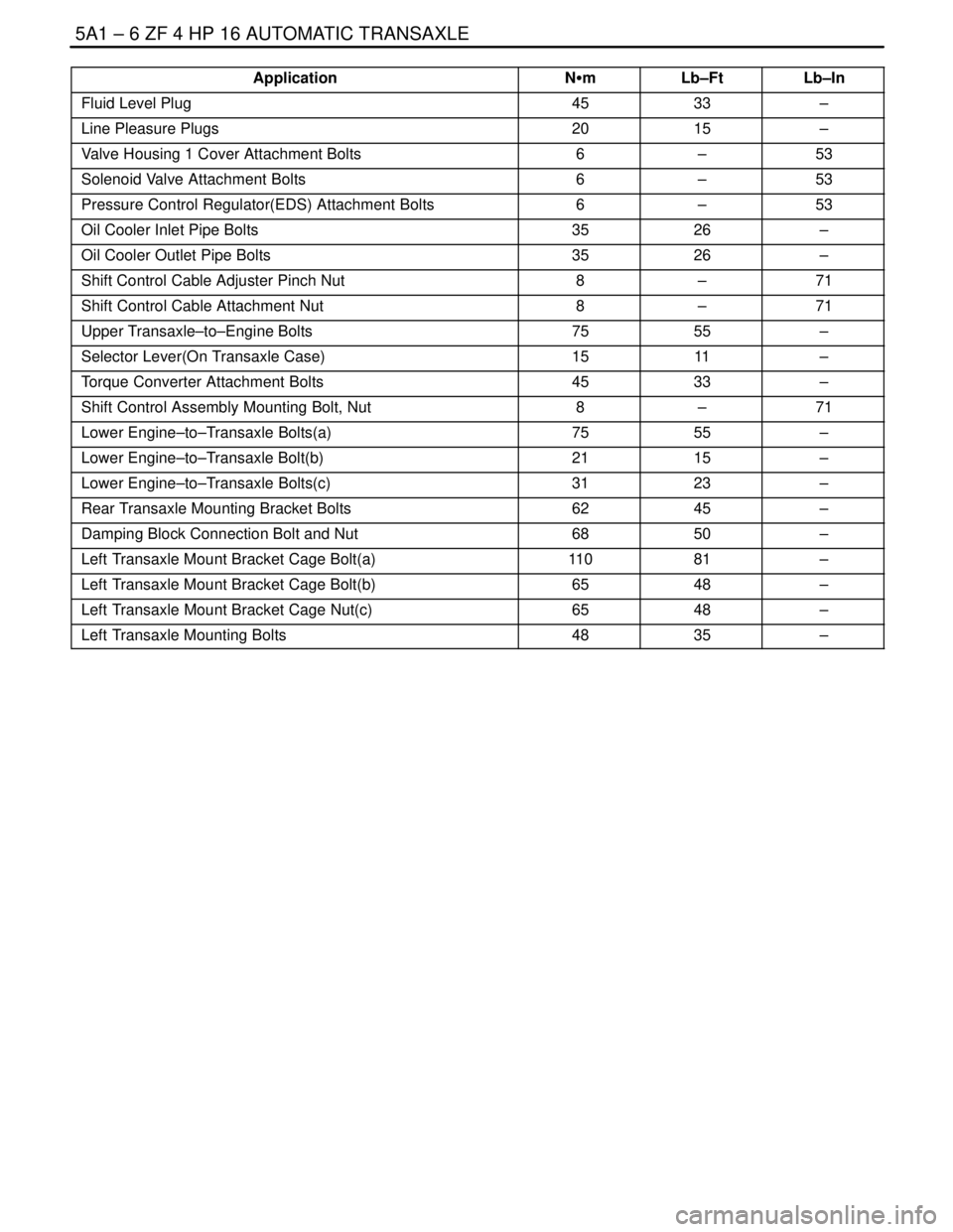
Application Lb–InLb–Ft NSm
Fluid Level Plug4533–
Line Pleasure Plugs2015–
Valve Housing 1 Cover Attachment Bolts6–53
Solenoid Valve Attachment Bolts6–53
Pressure Control Regulator(EDS) Attachment Bolts6–53
Oil Cooler Inlet Pipe Bolts3526–
Oil Cooler Outlet Pipe Bolts3526–
Shift Control Cable Adjuster Pinch Nut8–71
Shift Control Cable Attachment Nut8–71
Upper Transaxle–to–Engine Bolts7555–
Selector Lever(On Transaxle Case)1511–
Torque Converter Attachment Bolts4533–
Shift Control Assembly Mounting Bolt, Nut8–71
Lower Engine–to–Transaxle Bolts(a)7555–
Lower Engine–to–Transaxle Bolt(b)2115–
Lower Engine–to–Transaxle Bolts(c)3123–
Rear Transaxle Mounting Bracket Bolts6245–
Damping Block Connection Bolt and Nut6850–
Left Transaxle Mount Bracket Cage Bolt(a)11 081–
Left Transaxle Mount Bracket Cage Bolt(b)6548–
Left Transaxle Mount Bracket Cage Nut(c)6548–
Left Transaxle Mounting Bolts4835–
Page 1383 of 2643
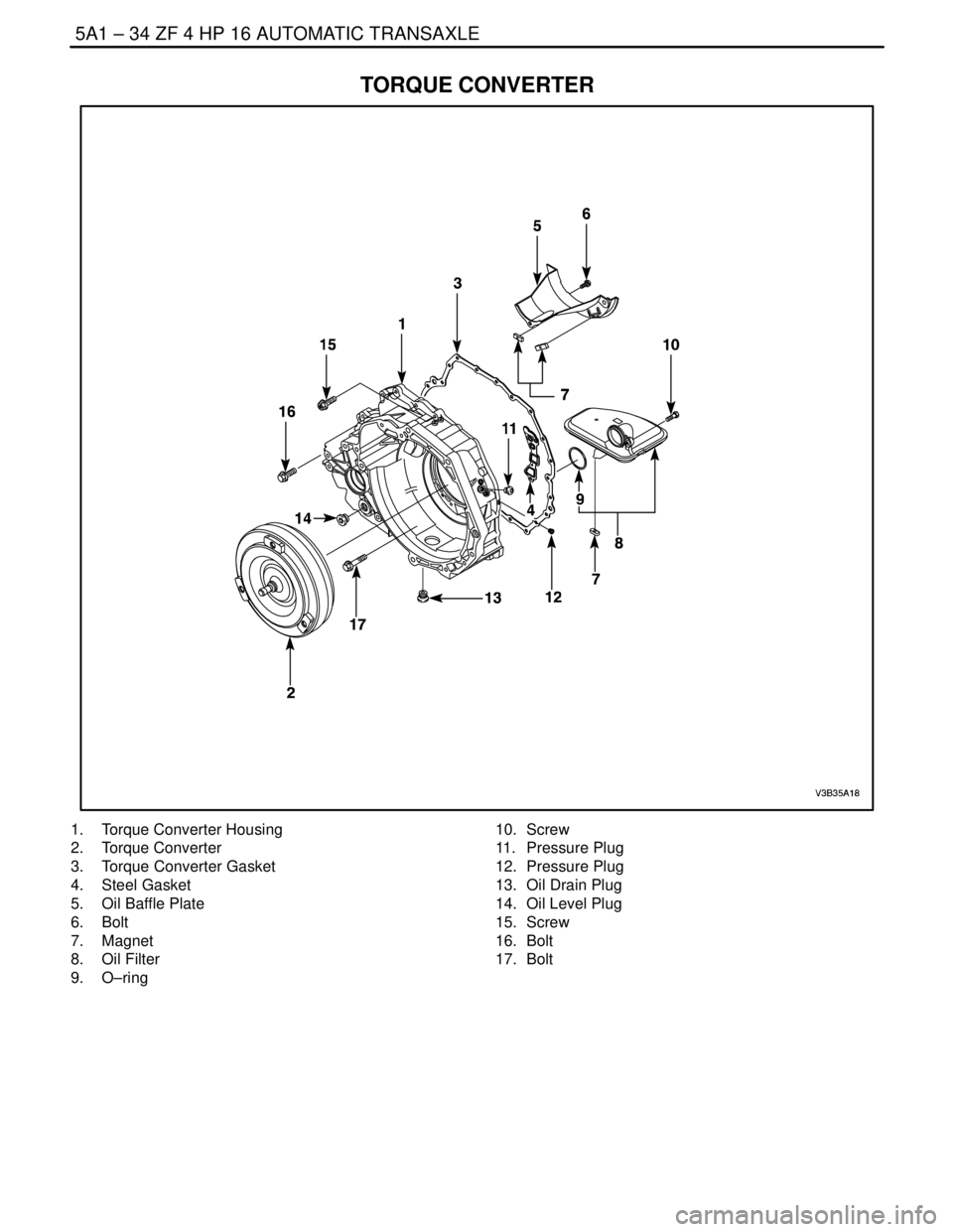
5A1 – 34IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TORQUE CONVERTER
1. Torque Converter Housing
2. Torque Converter
3. Torque Converter Gasket
4. Steel Gasket
5. Oil Baffle Plate
6. Bolt
7. Magnet
8. Oil Filter
9. O–ring10. Screw
11. Pressure Plug
12. Pressure Plug
13. Oil Drain Plug
14. Oil Level Plug
15. Screw
16. Bolt
17. Bolt
Page 1398 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 49
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Functional Check Procedure
Inspect
1. Install a tachometer or scan tool.
2. Operate the vehicle unit proper operating tempera-
ture is reached.
3. Drive the vehicle at 80 to 88km/h (50 to 55 mph)
with light throttle(road load).
4. Maintaining throttle position, lightly touch the brake
pedal and check for release of the TCC and a slight
increase in engine speed(rpm).
5. Release the brake slowly accelerate and check for
a reapply of the Lock up clutch and a slight de-
crease in engine speed(rpm).
Torque Converter Evaluation
Torque Converter Stator
The torque converter stator roller clutch can have one of
two different type malfunctions :
A. Stator assembly freewheels in both directions.
B. Stator assembly remains Locked up at all times.
Condition A – Poor Acceleration Low
Speed
The car tends to have poor acceleration from a stand still.
At speeds above 50 to 55km/h(30 to 35mph), the car may
act normal. If poor acceleration is noted, it should first be
determined that the exhaust system is not blocked, and
the transaxle is in 1st(First) gear when starting out.
If the engine freely accelerates to high rpm in N(Neutral),
it can be assumed that the engine and exhaust system are
normal. Checking for poor performance in ”Drive” and ”Re-
verse” will help determine if the stator is freewheeling at all
times.
Condition B – Poor Acceleration High
Speed
Engine rpm and car speed limited or restricted at high
speeds. Performance when accelerating from a standstill
is normal. Engine may overheat. Visual examination of the
converter may reveal a blue color from overheating.
If the converter has been removed, the stator roller clutch
can be checked by inserting two fingers into the splined in-
ner race of the roller clutch and trying to turn freely clock-
wise, but not turn or be very difficult to turn counter clock-
wise.
Noise
Torque converter whine is usually noticed when the ve-
hicle is stopped and the transaxle is in ”Drive” or ”Re-
verse”. The noise will increase when engine rpm is in-
creased. The noise will stop when the vehicle is moving or
when the torque converter clutch is applied because both
halves of the converter are turning at the same speed.
Perform a stall test to make sure the noise is actually com-
ing from the converter :1. Place foot on brake.
2. Put gear selector in ”Drive”.
3. Depress accelerator to approximately 1200rpm for
no more than six seconds.
Notice : If the accelerator is depressed for more than six
seconds, damage to the transaxle may occur.
A torque converter noise will increase under this load.
Important : This noise should not be confused with pump
whine noise which is usually noticeable in P (Park), N
(Neutral) and all other gear ranges. Pump whine will vary
with pressure ranges.
The torque converter should be replaced under any of the
following conditions:
S External leaks in the hub weld area.
S Converter hub is scored or damaged.
S Converter pilot is broken, damaged or fits poorly
into crankshaft.
S Steel particles are found after flushing the cooler
and cooler lines.
S Pump is damaged or steel particles are found in the
converter.
S Vehicle has TCC shudder and/or no TCC apply.
Replace only after all hydraulic and electrical diag-
noses have been made.(Lock up clutch material
may be glazed.)
S Converter has an imbalance which cannot be cor–
rected. (Refer To Converter Vibration Test Proce-
dure.)
S Converter is contaminated with engine coolant con-
taining antifreeze.
S Internal failure of stator roller clutch.
S Excess end play.
S Heavy clutch debris due to overheating (blue con-
verter).
S Steel particles or clutch lining material found in fluid
filter or on magnet when no internal parts in unit are
worn or damaged(indicates that lining material
came from converter).
The torque converter should not be replace if :
S The oil has an odor, is discolored, and there is no
evidence of metal or clutch facing particles.
S The threads in one or more of the converter bolt
holes are damaged.
–correct with thread insert.
S Transaxle failure did not display evidence of dam-
age or worn internal parts, steel particles or clutch
plate lining material in unit and inside the fluid filter.
S Vehicle has been exposed to high mileage(only).
The exception may be where the Lock up clutch
damper plate lining has seen excess wear by ve-
hicles operated in heavy and/or constant traffic,
such as taxi, delivery or police use.
Lock–Up Clutch Shudder Diagnosis
The key to diagnosing lock–up clutch(TCC) shudder is to
note when it happens and under what conditions.
Page 1399 of 2643

5A1 – 50IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TCC shudder should only occur during the APPLY and/or
RELEASE of the Lock up clutch.
While TCC Is Applying Or Releasing
If the shudder occurs while TCC is applying, the problem
can be within the transaxle or torque converter.
Something is not allowing the clutch to become fully en-
gaged, not allowing clutch to release, or is trying to release
and apply the clutch at the same time. This could be
caused by leaking turbine shaft seals, a restricted release
orifice, a distorted clutch or housing surface due to long
converter bolts, or defective friction material on the TCC
plate.
Shudder Occurs After TCC Has Applied :
In this case, most of the time there is nothing wrong with
the transaxle! As mentioned above, once the TCC has
been applied, it is very unlikely that will slip. Engine prob-
lems may go unnoticed under light throttle and load, but
become noticeable after TCC apply when going up a hill
or accelerating, due to the mechanical coupling between
engine and transaxle.
Important : Once TCC is applied there is no torque con-
verter assistance. Engine or driveline vibrations could be
unnoticeable before TCC engagement.
Inspect the following components to avoid misdiagnosis of
TCC shudder and possibly disassembling a transaxle and/
or replacing a torque converter unnecessarily :
S Spark plugs – Inspect for cracks, high resistance or
broken insulator.
S Plug wires – Lock in each end, if there is red dust
(ozone) or black substance (carbon) present, then
the wires are bad. Also look for a white discolor-
ation of the wire indicating arcing during hard accel-
eration.
S Distributor cap and rotor – look for broken or un–
crimped parts.
S Coil – look for black on bottom indication arcing
while engine is misfiring.
S Fuel injector – filter may be plugged.
S Vacuum leak – engine won’t get correct amount of
fuel. May run rich or lean depending on where the
leak is.S EGR valve – valve may let it too much unburnable
exhaust gas and cause engine to run lean.
S MAP sensor – like vacuum leak, engine won’t get
correct amount of fuel for proper engine operation.
S Carbon on intake valves – restricts proper flow or
air/fuel mixture into cylinders.
S Flat cam – valves don’t open enough to let proper
fuel/air mixture into cylinders.
S Oxygen sensor – may command engine too rich or
too lean for too long.
S Fuel pressure – may be too low.
S Engine mounts – vibration of mounts can be multi-
plied by TCC engagement.
S Axle joints – checks for vibration.
S TPS – TCC apply and release depends on the TPS
in many engines. If TPS is out of specification, TCC
may remain applied during initial engine starting.
S Cylinder balance – bad piston rings or poorly seal-
ing valves can cause low power in a cylinder.
S Fuel contamination – causes poor engine perfor-
mance.
TCM INITIALIZATION PROCEDURE
When one or more operations such as shown below are
performed, all learned contents which are stored in TCM
memory should be erased after the operations.
S When A/T H/W is replaced in a vehicle,
S When a used TCU is installed in other vehicle,
S When a vehicle condition is unstable (engine RPM
flare, TPS toggling and so on; at this kind of unsta-
ble conditions, mis–adaptation might be done).
1. Connect the Scan 100 with a DLC connector in a
vehicle.
2. Turn ignition switch ON.
3. Turn the power on for the Scan 100.
4. Follow the ”TCM LEARNED INITIALIZE” procedure
on the Scan 100 menu.
Notice : Before pushing ”Yes” Button for TCM initialization
on the Scan 100 screen, make sure that the condition is
as follows:
Condition :
1. Engine idle.
2. Select lever set ”P” range.
Page 1405 of 2643
5A1 – 56IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
Oil Leakage
Notice :
– Careful localization of leakage points may make it
possible to prevent incorrect or cost–intensive re-
pairs.
Test Steps :– Thoroughly clean the transaxle, engine, and sur-
rounding area(using a steam jet, for example).
– To locate leakage, use a suitable identifying spray
or similar product.
– Depending on the amount of leakage, take the
car for a short or a longer test drive – It may prove
sufficient to place the car on a hoist and run the
engine at idle speed to trace the leak.
– If possible, determine exactly which type of oil is
escaping.
Symptom
Possible CauseAction
Transaxle Oil Leak-
ageOil Pump(Torque Converter Sealing)S Visually check torque converter sealing.
S Replace the converter sealing as described in
the transaxle repair on the vehicle service.
Crankshaft Sealing RingS Check whether engine oil or TFT is leaking out.
S If leak is engine oil, replace the sealing ring as
described in the engine repair instruction.
Torque ConverterS Visual check.
S Fit an exchange converter as described in the
repair instruction.
Oil Content Too HighS Check oil level(TFT and axle oil) as described
in this chapter.
S Correct oil level, and recheck after a test drive.
Notice : Comply with the measuring procedure (fill-
ing procedure) in the repair instruction. Check the oil
level at the overflow plug adjust to proper level if nec-
essary.
O–ring at Bolt Head Damaged or Miss-
ingS Check O–ring.
S Replace O–ring as described in the repair in-
struction.
Shaft SealS Visually check the shaft seal.
S Replace the sealing ring as described in the
repair instruction.
Hose Clamp LooseS Check to ensure that the hose clamp fits tightly.
S If necessary, retighten clamp.
Oil Pan Gasket Not Installed ProperlyS Check to see if the gasket was positioned
properly.
S Install gasket properly as described in the re-
pair instruction.
Oil Pan Gasket DamagedS Check the gasket visually.
S Replace gasket as described in the repair in-
struction.
Bolt at Bracket LooseCheck the Tightening Torque
Retighten bolt
Sealing Ring at Oil DipstickS Check O–ring.
S If necessary, replace O–ring.
Sealing Ring Near End–Cover Connec-
tion DefectiveS Check sealing rings.
S Put in new sealing ring Check O–ring as de-
scribed in the repair instruction.
Page 1557 of 2643
5A1 – 208IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
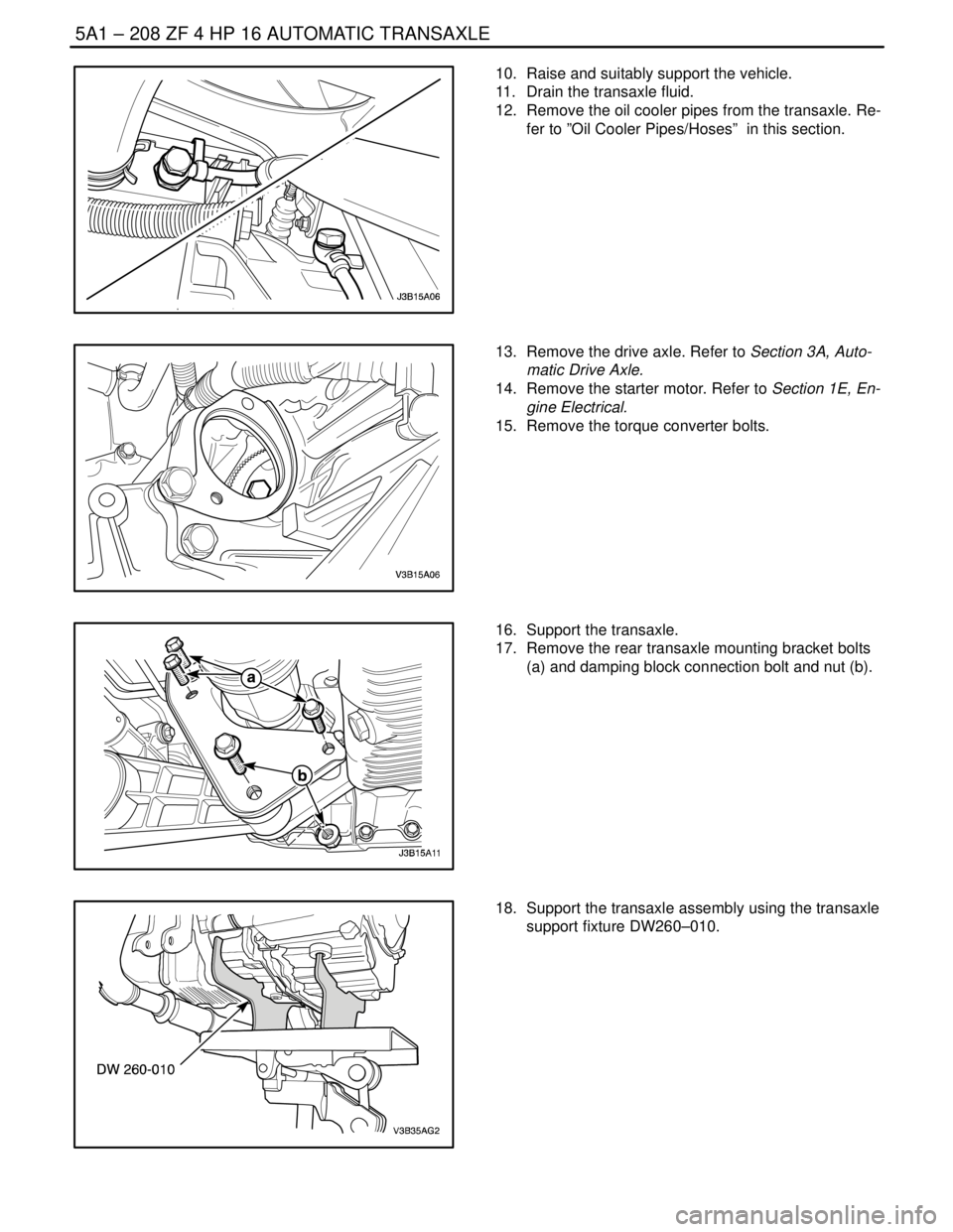
10. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
11. Drain the transaxle fluid.
12. Remove the oil cooler pipes from the transaxle. Re-
fer to ”Oil Cooler Pipes/Hoses” in this section.
13. Remove the drive axle. Refer to Section 3A, Auto-
matic Drive Axle.
14. Remove the starter motor. Refer to Section 1E, En-
gine Electrical.
15. Remove the torque converter bolts.
16. Support the transaxle.
17. Remove the rear transaxle mounting bracket bolts
(a) and damping block connection bolt and nut (b).
18. Support the transaxle assembly using the transaxle
support fixture DW260–010.