2004 DAEWOO LACETTI oil level
[x] Cancel search: oil levelPage 248 of 2643

1F – 2IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–111. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clearing Trouble Codes 1F–111. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–111.
DTC P0107 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Low Voltage 1F–114. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0108 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
High Voltage 1F–117. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0112 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–120. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0113 Intake Air Temperature Sensor High
Voltage 1F–122. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor Low Voltage 1F–125. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor High Voltage 1F–128. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0122 Throttle Position Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–131. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0123 Throttle Position Sensor High
Voltage 1F–134. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0131 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–137. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0132 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor High
Voltage 1F–140. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0133 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor No
Activity 1F–142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0135 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater
Circuit Not Functioning 1F–145. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0137 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–148. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0138 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor High
Voltage 1F–151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0140 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor No
Activity 1F–153. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0141 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater
Malfunction 1F–156. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0171 Fuel Trim System Too Lean 1F–158. . . .
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Too Rich 1F–162. . . . .
DTC P0222 Main Throttle Idle Actuator (MTIA)
Low Voltage 1F–165. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0223 Main Throttle Idle Actuator (MTIA)
High Voltage 1F–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0261 Injector 1 Low Voltage 1F–171. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0262 Injector 1 High Voltage 1F–173. . . . . . . .
DTC P0264 Injector 2 Low Voltage 1F–175. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0265 Injector 2 High Voltage 1F–177. . . . . . . .
DTC P0267 Injector 3 Low Voltage 1F–179. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0268 Injector 3 High Voltage 1F–181. . . . . . . .
DTC P0270 Injector 4 Low Voltage 1F–183. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0271 Injector 4 High Voltage 1F–185. . . . . . . . DTC P0300 Multiple Cylinder Misfire(Catalyst
Damage) 1F–188. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0300 Multiple Cylinder Misfire(Increase
Emission) 1F–192. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit Fault
(1.4L DOHC) 1F–195. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit Fault
(1.6L DOHC) 1F–198. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0335 Magnetic Crankshaft Position
Sensor Electrical Error 1F–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0336 58X Crankshaft Position Sensor
No Plausible Signal 1F–204. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0337 58X Crankshaft Position Sensor
No Signal 1F–207. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0341 Camshaft Position Sensor
Rationality 1F–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0342 Camshaft Position Sensor Signal 1F–212
DTC P0351 Ignition Signal Coil A Fault 1F–214. . . . .
DTC P0352 Ignition Signal Coil B Fault 1F–216. . . . .
DTC P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Out
Of Limit 1F–218. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Opened 1F–221. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0405 EGR Pintle Position Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–224. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0406 EGR Pintle Position Sensor High
Voltage 1F–227. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0420 Catalyst Low Efficiency 1F–230. . . . . . . .
DTC P0444 EVAP Purge Control Circuit No
Signal 1F–232. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0445 EVAP Purge Control Circuit Fault 1F–235
DTC P0462 Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage
(1.6L DOHC Only) 1F–238. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0463 Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage
(1.6L DOHC Only) 1F–241. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0480 Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC) 1F–245. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0480 Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC) 1F–248. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0481 High Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC) 1F–251. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0481 High Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC) 1F–254. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0501 Vehicle Speed No Signal
(M/T Only) 1F–257. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0510 Throttle Position Switch Circuit Fault
(1.4L DOHC) 1F–260. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0510 Throttle Position Switch Circuit
Fault (1.6L DOHC) 1F–262. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0532 A/C Pressure Sensor Low Voltage 1F–264
DTC P0533 A/C Pressure Sensor High
Voltage 1F–267. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 356 of 2643
1F – 110IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
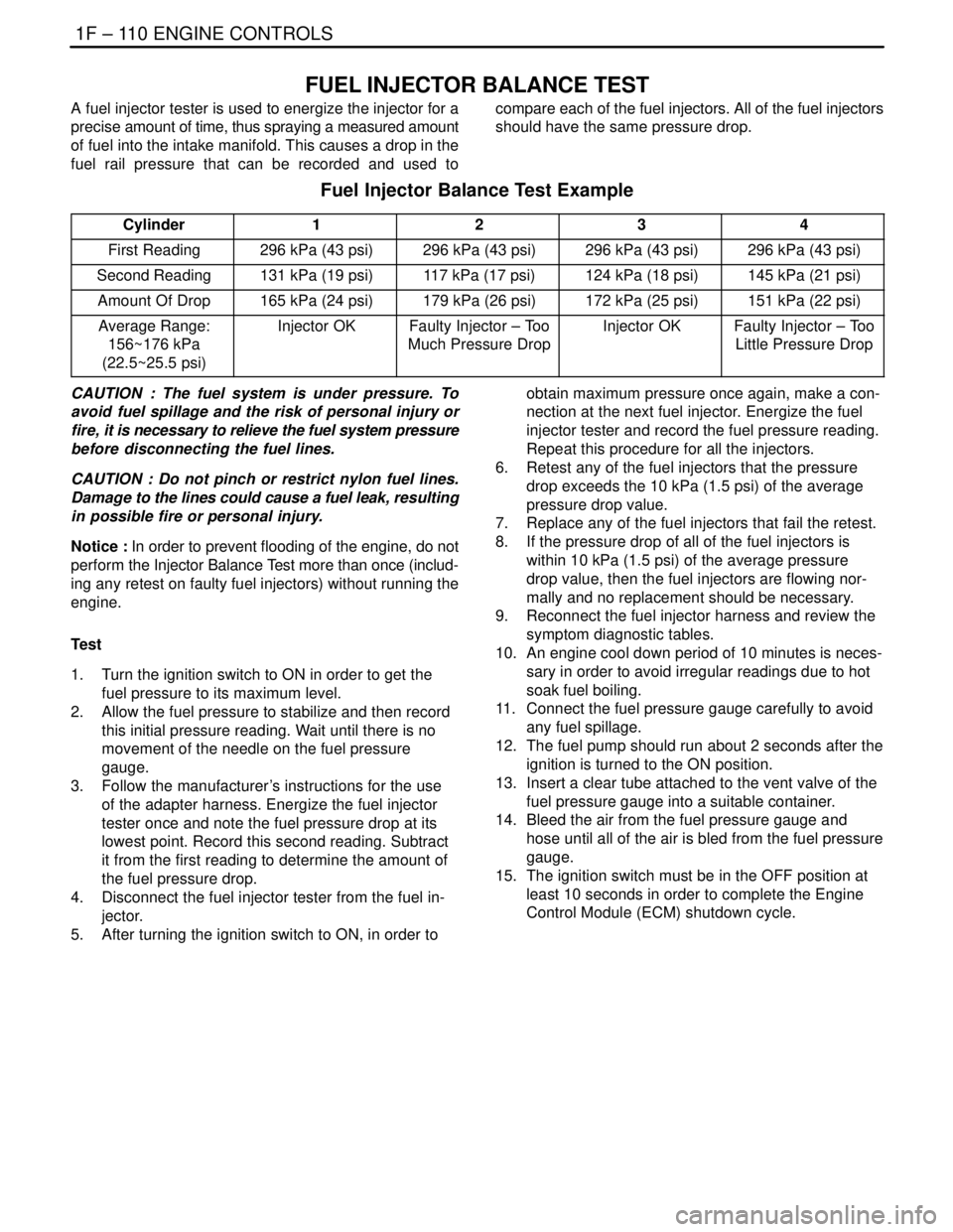
FUEL INJECTOR BALANCE TEST
A fuel injector tester is used to energize the injector for a
precise amount of time, thus spraying a measured amount
of fuel into the intake manifold. This causes a drop in the
fuel rail pressure that can be recorded and used tocompare each of the fuel injectors. All of the fuel injectors
should have the same pressure drop.
Fuel Injector Balance Test Example
Cylinder1234
First Reading296 kPa (43 psi)296 kPa (43 psi)296 kPa (43 psi)296 kPa (43 psi)
Second Reading131 kPa (19 psi)117 kPa (17 psi)124 kPa (18 psi)145 kPa (21 psi)
Amount Of Drop165 kPa (24 psi)179 kPa (26 psi)172 kPa (25 psi)151 kPa (22 psi)
Average Range:
156~176 kPa
(22.5~25.5 psi)Injector OKFaulty Injector – Too
Much Pressure DropInjector OKFaulty Injector – Too
Little Pressure Drop
CAUTION : The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pressure
before disconnecting the fuel lines.
CAUTION : Do not pinch or restrict nylon fuel lines.
Damage to the lines could cause a fuel leak, resulting
in possible fire or personal injury.
Notice : In order to prevent flooding of the engine, do not
perform the Injector Balance Test more than once (includ-
ing any retest on faulty fuel injectors) without running the
engine.
Test
1. Turn the ignition switch to ON in order to get the
fuel pressure to its maximum level.
2. Allow the fuel pressure to stabilize and then record
this initial pressure reading. Wait until there is no
movement of the needle on the fuel pressure
gauge.
3. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the use
of the adapter harness. Energize the fuel injector
tester once and note the fuel pressure drop at its
lowest point. Record this second reading. Subtract
it from the first reading to determine the amount of
the fuel pressure drop.
4. Disconnect the fuel injector tester from the fuel in-
jector.
5. After turning the ignition switch to ON, in order toobtain maximum pressure once again, make a con-
nection at the next fuel injector. Energize the fuel
injector tester and record the fuel pressure reading.
Repeat this procedure for all the injectors.
6. Retest any of the fuel injectors that the pressure
drop exceeds the 10 kPa (1.5 psi) of the average
pressure drop value.
7. Replace any of the fuel injectors that fail the retest.
8. If the pressure drop of all of the fuel injectors is
within 10 kPa (1.5 psi) of the average pressure
drop value, then the fuel injectors are flowing nor-
mally and no replacement should be necessary.
9. Reconnect the fuel injector harness and review the
symptom diagnostic tables.
10. An engine cool down period of 10 minutes is neces-
sary in order to avoid irregular readings due to hot
soak fuel boiling.
11. Connect the fuel pressure gauge carefully to avoid
any fuel spillage.
12. The fuel pump should run about 2 seconds after the
ignition is turned to the ON position.
13. Insert a clear tube attached to the vent valve of the
fuel pressure gauge into a suitable container.
14. Bleed the air from the fuel pressure gauge and
hose until all of the air is bled from the fuel pressure
gauge.
15. The ignition switch must be in the OFF position at
least 10 seconds in order to complete the Engine
Control Module (ECM) shutdown cycle.
Page 358 of 2643

1F – 112IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTCIlluminate MIL Error
Type Function
P0300Multiple Cylinder Misfire (Increase Emission)EYES
P0327Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P0327Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)EYES
P0335Magnetic Crankshaft Position Sensor Electrical ErrorEYES
P033658X Crankshaft Position Sensor Extra/missing PulseEYES
P033758X Crankshaft Sensor No SignalEYES
P0341Camshaft Position Sensor RationalityEYES
P0342Camshaft Position Sensor No SignalEYES
P0351Ignition Signal Coil A FaultAYES
P0352Ignition Signal Coil B FaultAYES
P0400Exhaust Gas Recirculation Out of LimitEYES
P0404Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) PpendEYES
P0405EGR Pintle Position Sensor Low VoltageEYES
P0406EGR Pintle Position Sensor High voltageEYES
P0420Catalyst Low EfficiencyAYES
P0444EVAP Purge Control Circuit No SignalEYES
P0445EVAP Purge Control Circuit FaultEYES
P0462Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage (1.6L DOHC Only)CnlNO
P0463Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage (1.6L DOHC Only)CnlNO
P0480Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)EYES
P0480Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)CnlNO
P0481High Speed Cooling Fan Relay High Voltage (1.4L DOHC)EYES
P0481High Speed Cooling Fan Relay High Voltage (1.6L DOHC)CnlNO
P0501Vehicle Speed No Signal (M/T Only)AYES
P0510Throttle Positon Switch Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P0510Throttle Positon Switch Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P0532A/C Pressure Sensor Low VoltageCnlNO
P0533A/C Pressure Sensor High VoltageCnlNO
P0562System Voltage (Engine Side) Too LowCnlNO
P0563System Voltage (Engine Side) Too HighCnlNO
P0601Engine Control Module Checksum ErrorEYES
P0604Engine Control Module RAM ErrorEYES
P0605Engine Control Module INMVY Write ErrorEYES
P0656Fuel Level Gauge High Circuit FaultCnlNO
P1181Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid Low VoltageEYES
P1182Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid High VoltageEYES
P1230Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P1230Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P1231Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P1231Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P1320Crankshaft Segment Period Segment Adaptation At LimitEYES
Page 1021 of 2643

HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
BRAKE SYSTEM TESTING
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake perfor-
mance cannot be made if the roadway is wet, greasy, or
covered with loose dirt whereby all tires do not grip the
road equally. Testing will also be adversely affected if the
roadway is crowned so as to throw the weight so roughly
that the wheels tend to bounce.
Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both light
and heavy pedal pressure; however, avoid locking the
brakes and sliding the tires. Locked brakes and sliding
tires do not indicate brake efficiency since heavily braked,
but turning, wheels will stop the vehicle in less distance
than locked brakes. More tire–to–road friction is present
with a heavily–braked, turning tire than with a sliding tire.
Because of the high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
There are three major external conditions that affect brake
performance:
S Tires having unequal contact and grip of the road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated, and the tread pattern of the right and the
left tires must be approximately equal.
S Unequal loading of the vehicle can affect the brake
performance since the most heavily loaded wheels
require more braking power, and thus more braking
effort, than the others.
S Misalignment of the wheels, particularly conditions
of excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
To check for brake fluid leaks, hold constant foot pressure
on the pedal with the engine running at idle and the shift
lever in NEUTRAL. If the pedal gradually falls away with
the constant pressure, the hydraulic system may be leak-
ing. Perform a visual check to confirm any suspected
leaks.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight drop
in the reservoir level results from normal lining wear, an ab-
normally low level indicates a leak in the system. The hy-
draulic system may be leaking either internally or external-
ly. Refer to the procedure below to check the master
cylinder. Also, the system may appear to pass this test
while still having a slight leak. If the fluid level is normal,
check the vacuum booster pushrod length. If an incorrect
pushrod length is found, adjust or replace the rod.
Check the master cylinder using the following procedure:
S Check for a cracked master cylinder casting or
brake fluid leaking around the master cylinder.
Leaks are indicated only if there is at least one drop
of fluid. A damp condition is not abnormal.S Check for a binding pedal linkage and for an incor-
rect pushrod length. If both of these parts are in
satisfactory condition, disassemble the master cyl-
inder and check for an elongated or swollen primary
cylinder or piston seals. If swollen seals are found,
substandard or contaminated brake fluid should be
suspected. If contaminated brake fluid is found, all
the components should be disassembled and
cleaned, and all the rubber components should be
replaced. All of the pipes must also be flushed.
Improper brake fluid, or mineral oil or water in the fluid,
may cause the brake fluid to boil or cause deterioration of
the rubber components. If the primary piston cups in the
master cylinder are swollen, then the rubber parts have
deteriorated. This deterioration may also be evidenced by
swollen wheel cylinder piston seals on the drum brake
wheels.
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all the hy-
draulic parts and wash the parts with alcohol. Dry these
parts with compressed air before reassembly to keep alco-
hol out of the system. Replace all the rubber parts in the
system, including the hoses. Also, when working on the
brake mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings. If exces-
sive fluid is found, replace the linings.
If the master cylinder piston seals are in satisfactory condi-
tion, check for leaks or excessive heat conditions. If these
conditions are not found, drain the fluid, flush the master
cylinder with brake fluid, refill the master cylinder, and
bleed the system. Refer to ”Manual Bleeding the Brakes”
or”Pressure Bleeding the Brakes” in this section.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The hydraulic brake hoses should be inspected at least
twice a year. The brake hose assembly should be checked
for road hazard damage, cracks, chafing of the outer cov-
er, and for leaks or blisters. Inspect the hoses for proper
routing and mounting. A brake hose that rubs on a suspen-
sion component will wear and eventually fail. A light and
a mirror may be needed for an adequate inspection. If any
of the above conditions are observed on the brake hose,
adjust or replace the hose as necessary.
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
This brake system uses a BRAKE warning lamp located
in the instrument panel cluster. When the ignition switch
is in the START position, the BRAKE warning lamp should
glow and go OFF when the ignition switch returns to the
RUN position.
The following conditions will activate the BRAKE lamp:
S Parking brake applied. The light should be ON
whenever the parking brake is applied and the igni-
tion switch is ON.
S Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master cylin-
der will turn the BRAKE lamp ON.
S EBD system is disabled. The light should be ON
when the EBD system is malfunctioning.
Page 1042 of 2643

MASTER CYLINDER 4B – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
MASTER CYLINDER
The master cylinder is designed for use in a diagonal–split
system. One front and one diagonally opposite rear brake
are served by the primary piston. The opposite front and
rear brakes are served by the secondary piston. The mas-
ter cylinder incorporates the functions of the standard dual
master cylinder, plus a low fluid level indicator and the pro-
portioning valves in the non–antilock braking system. The
proportioning valves limit the outlet pressure to the rear
brakes after a predetermined master cylinder pressure
has been reached.
Important :
S Replace all the components included in the repair
kits used to service this master cylinder.S Lubricate rubber parts with clean brake fluid to ease
assembly.
S Do not use lubricated shop air on brake parts, as
this may damage rubber components.
S If any hydraulic component is removed or discon-
nected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of
the brake system.
S The torque values specified are for dry, unlubri-
cated fasteners.
S Perform all service operations on a clean bench,
free from all traces of mineral oil.
FLUID LEVEL SENSOR
The master cylinder is equipped with a fluid level sensor.
This sensor will activate the BRAKE light if a low fluid level
condition is detected. Once the fluid level is corrected, the
BRAKE light will go out.
Page 1137 of 2643
4F – 56IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F04
60A Ef230A Ef5
2
42
C107 C105
2
C110
G106
A19
A13 A1 A14
C110 C202
C202WHT LT GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
BLK
DK BLUDK BLU
PPL/WHT
PPL/WHT ABS
TCS Parking
Brake
Hot at all times
RED REDRED/WHT
Ignition
Switch
RED
RED
I/P Cluster
EBCM8
20
22 2216 41
1211
18 1621
1
C107
10A F410AF11
32 31
43
6 62 C201
C201 C201C201
C110 C202
Hot in Run and Start
30
4
1711
C202
15
B15
DLC
(Data Link
Connector)12
G106
BLK/WHTOil Feeding
Connector
”2” Ter.
BRNBRN BRN
BRN PNK PNK PNK
19J1
59B1
ONStart Lock
Acc
IG1
19
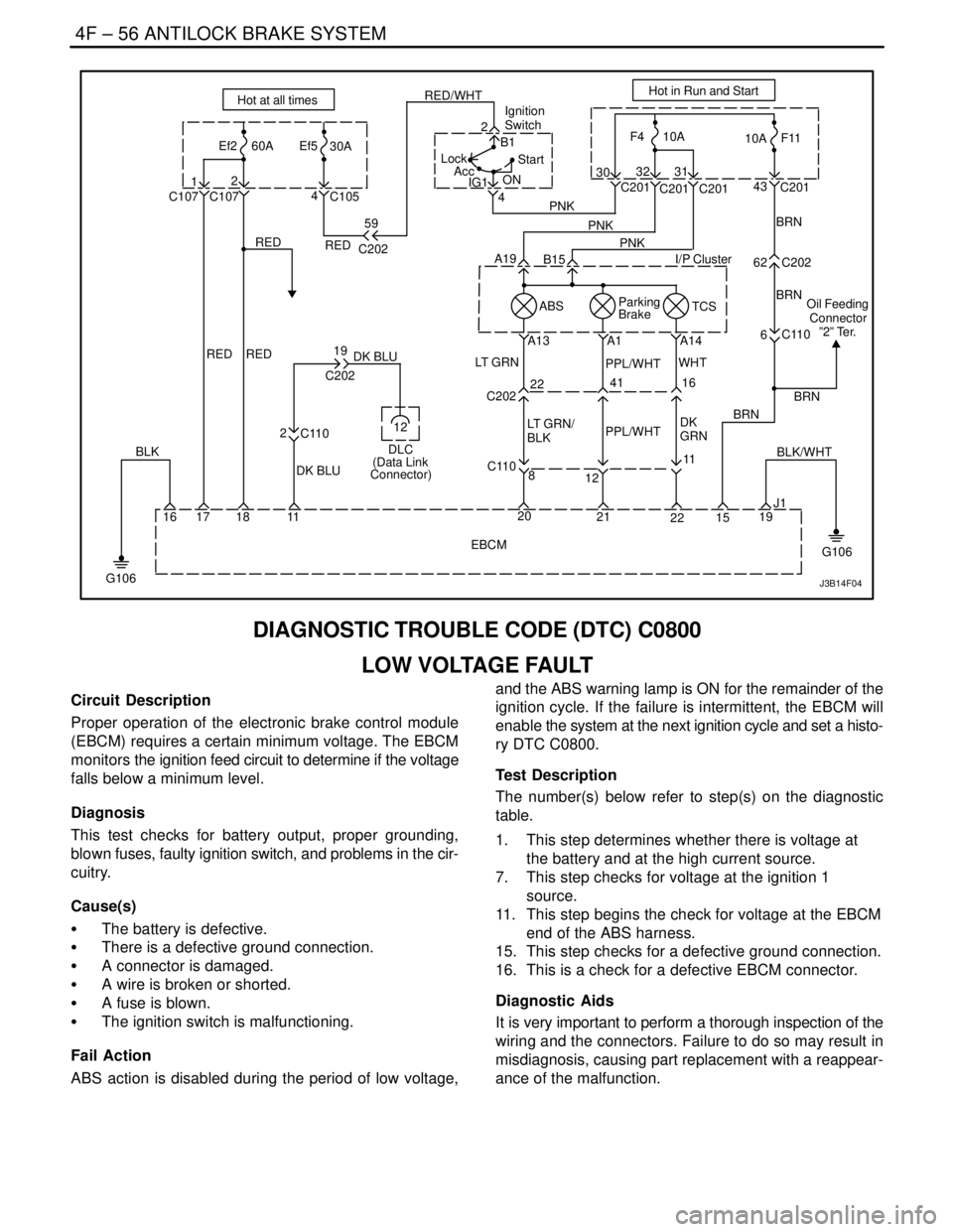
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0800
LOW VOLTAGE FAULT
Circuit Description
Proper operation of the electronic brake control module
(EBCM) requires a certain minimum voltage. The EBCM
monitors the ignition feed circuit to determine if the voltage
falls below a minimum level.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, faulty ignition switch, and problems in the cir-
cuitry.
Cause(s)
S The battery is defective.
S There is a defective ground connection.
S A connector is damaged.
S A wire is broken or shorted.
S A fuse is blown.
S The ignition switch is malfunctioning.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage,and the ABS warning lamp is ON for the remainder of the
ignition cycle. If the failure is intermittent, the EBCM will
enable the system at the next ignition cycle and set a histo-
ry DTC C0800.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and at the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
11. This step begins the check for voltage at the EBCM
end of the ABS harness.
15. This step checks for a defective ground connection.
16. This is a check for a defective EBCM connector.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with a reappear-
ance of the malfunction.
Page 1350 of 2643

SECTION : 5A1
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION5A1–3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ZF 4HP 16 Automatic Transaxle 5A1–3. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Components 5A1–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIFICATIONS5A1–5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Specifications 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Gear Ratio 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fluid Capacity 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart 5A1–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure 5A1–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIAL TOOLS5A1–9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Tools Table 5A1–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SCHEMATIC AND ROUTING DIAGRAMS5A1–11 . . .
Transaxle Control Module (1 of 2) 5A1–11. . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Control Module (2 of 2) 5A1–12. . . . . . . . . .
Shift Mode Diagram 5A1–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Flow Diagram 5A1–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
COMPONENT LOCATOR5A1–33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Identification Information 5A1–33. . . . . . . .
Torque Converter 5A1–34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Housing 5A1–35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pump 5A1–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Cover & Oil Pan Cover 5A1–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parking Lever 5A1–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input Shaft & Shift Gear 5A1–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Valve Body 5A1–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Gear Shift Control 5A1–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
DIAGNOSIS5A1–43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Knowledge Required 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Check Procedure 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure Check Procedure 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . .
Clutch Plate Diagnosis 5A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cooler Flushing and Flow Test 5A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . Transaxle Fluid Level Service Procedure 5A1–45. . . .
Electrical/Garage Shift Test 5A1–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Road Test Procedure 5A1–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Converter Lock–Up Clutch(TCC)
Diagnosis 5A1–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TCM Initialization Procedure 5A1–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart 5A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Internal Wiring Harness Check 5A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Wiring Harness Connector 5A1–54. . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 5A1–56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS5A1–60
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Identification 5A1–60
DTC P0562 – System Voltage Low 5A1–68. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0563 – System Voltage High 5A1–71. . . . . . . .
DTC P0601 – Internal Control Module Memory
Checksum Error 5A1–74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0603 – Internal Control Module Keep
Alive Memory(KAM) Error 5A1–76. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0604 – Internal Control Module Random
Access Memory(RAM) Error 5A1–78. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0606 – Transaxle Control Module
Processor Fault 5A1–80. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0703 – Brake Switch Circuit
Malfunction 5A1–83. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0705 – Transmission Range Sensor
Circuit Malfunction(PRNDL Input) 5A1–86. . . . . . . .
DTC P0710 – Transmission Fluid Temperature
Sensor Circuit Malfunction 5A1–89. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0715 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
Malfunction 5A1–92. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0716 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
Range/Performance 5A1–95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0717 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
No Signal 5A1–98. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0720 – Output Speed Sensor(OSS)
Circuit Malfunction 5A1–101. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0721 – Output Speed Sensor(OSS)
Circuit Range/Performance 5A1–104. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1351 of 2643
5A1 – 2IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0722 – Output Speed Sensor(OSS)
Circuit No Signal 5A1–107. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0725 – Engine Speed Input Circuit
Malfunction 5A1–110. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0726 – Engine Speed Input Circuit
Range/Performance 5A1–112. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0727 – Engine Speed Input Circuit No
Signal 5A1–114. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0731 – Gear 1 Incorrect Ratio 5A1–116. . . . . .
DTC P0732 – Gear 2 Incorrect Ratio 5A1–118. . . . . .
DTC P0733 – Gear 3 Incorrect Ratio 5A1–120. . . . . .
DTC P0734 – Gear 4 Incorrect Ratio 5A1–122. . . . . .
DTC P0781 – 1–2 Shift Malfunction 5A1–124. . . . . . .
DTC P0782 – 2–3 Shift Malfunction 5A1–126. . . . . . .
DTC P0783 – 3–4 Shift Malfunction 5A1–128. . . . . . .
DTC P1604 – Data Check of Internal &
Extended Ram Failed 5A1–130. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1606 – Failure Of External Watchdog 5A1–132
DTC P1671 – CAN Transmit Message
Failure 5A1–134. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1672 – CAN Bus Off Failure 5A1–136. . . . . . . .
DTC P1673 – CAN Receive ECM Message
Failure 5A1–138. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1839 – EDS 3 Output Shorted To
Ground 5A1–140. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1840 – EDS 3 Output Shorted To
Power 5A1–142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1841 – EDS 3 Output Open 5A1–144. . . . . . . .
DTC P1850 – Solenoid 1 Output Shorted To
Ground 5A1–146. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1851 – Solenoid 1 Output Shorted To
Power 5A1–148. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1852 – Solenoid 1 Output Open 5A1–150. . . .
DTC P1853 – Solenoid 2 Output Shorted To
Ground 5A1–152. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1854 – Solenoid 2 Output Shorted To
Power 5A1–154. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1855 – Solenoid 2 Output Open 5A1–156. . . .
DTC P1861 – EDS 4 Output Shorted To
Ground 5A1–158. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1862 – EDS 4 Output Shorted To
Power 5A1–160. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1863 – EDS 4 Output Open 5A1–162. . . . . . . .
DTC P1864 – EDS 5 Output Shorted To
Ground 5A1–164. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1865 – EDS 5 Output Shorted To
Power 5A1–166. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1866 – EDS 5 Output Open 5A1–168. . . . . . . .
DTC P1867 – EDS 6 Output Shorted To
Ground 5A1–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DTC P1868 – EDS 6 Output Shorted To
Power 5A1–172. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1869 – EDS 6 Output Open 5A1–174. . . . . . . .
DTC P1871 – EDS Valve Power Supply
Circuit Shorted to Power 5A1–176. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1874 – Solenoid Valve Power Supply
Circuit Shorted to Power 5A1–178. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1881 – 2–1 Shift Malfunction 5A1–180. . . . . . .
DTC P1883 – 3–2 Shift Malfunction 5A1–182. . . . . . .
DTC P1884 – 4–3 Shift Malfunction 5A1–184. . . . . . .
DTC P1885 – 3–1 Shift Malfunction 5A1–186. . . . . . .
DTC P1886 – 4–2 Shift Malfunction 5A1–188. . . . . . .
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR5A1–190 . . . . . . . . . . . .
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE 5A1–190. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Fluid Level Checking Procedure 5A1–190.
Changing the Fluid 5A1–191. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fluid Level Set After Service 5A1–192. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Repairing Fluid Leaks 5A1–192. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Case Porosity Repair 5A1–193. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Control Lever Assembly 5A1–193. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Control Cable 5A1–195. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Control Cable Adjustment 5A1–196. . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Control Module(TCM) 5A1–197. . . . . . . . . .
Park/Neutral Start Switch 5A1–198. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Cooler Pipes/Hoses 5A1–199. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Drive Axle Oil Seal 5A1–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pan, Oil Pan Gasket 5A1–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Valve Body Assembly 5A1–203. . . . . . . . . . . .
Left Transaxle Mounting Bracket 5A1–205. . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Assembly 5A1–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UNIT REPAIR 5A1–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Converter 5A1–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Holding Fixture Assembly 5A1–212. . . . . . .
Valve Body 5A1–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Cover 5A1–213. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clutch B/E 5A1–214. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clutch B/E Measurement Procedure 5A1–217. . . . . .
Planetary Gear Set 5A1–220. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake C/D 5A1–221. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Differential 5A1–224. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Side Shaft 5A1–224. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake F, Slotted Nut 5A1–225. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Converter Housing 5A1–227. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Mechanism 5A1–228. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parking Lock System 5A1–229. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bearing Plate(With Spur Gear) Assembly 5A1–229. .
Oil Pump Assembly 5A1–229. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Differential/Side Shaft Outer Race, Bearing
Shim 5A1–230. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .