2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Rear switch
[x] Cancel search: Rear switchPage 274 of 2643

1F – 28IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COMPONENT LOCATOR
COMPONENT LOCATOR (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Components on ECM Harness
11. Engine Control Module (ECM)
12. Data Link Connector (DLC)
13. Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
14. ECM/ABS Harness Ground
15. Fuse Panel (2)
ECM Controlled Devices
20. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
21. Fuel Injector (4)
22. Main Throttle Idle Actuator (MTIA)
23. Fuel Pump Relay
24. Cooling Fan Relays (High)
25. Cooling Fan Control Relay (A/C Only)
26. Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil
27. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control Purge Sole-
noid
28. Main Relay
29. A/C Compressor Relay30. Cooling Fan Relays (Low)
Information Sensors
31. Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
32. Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
33. Variable Geometry Induction System (VGIS) Sole-
noid
34. Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
35. Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
36. Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
38. Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
39. Knock Sensor
40. Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2)
41. Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Not PCM/ECM Connected
42. Evaporative Emission Canister (under vehicle, be-
hind right rear wheel)
43. Engine Oil Pressure Switch
44. Air Cleaner
Page 275 of 2643
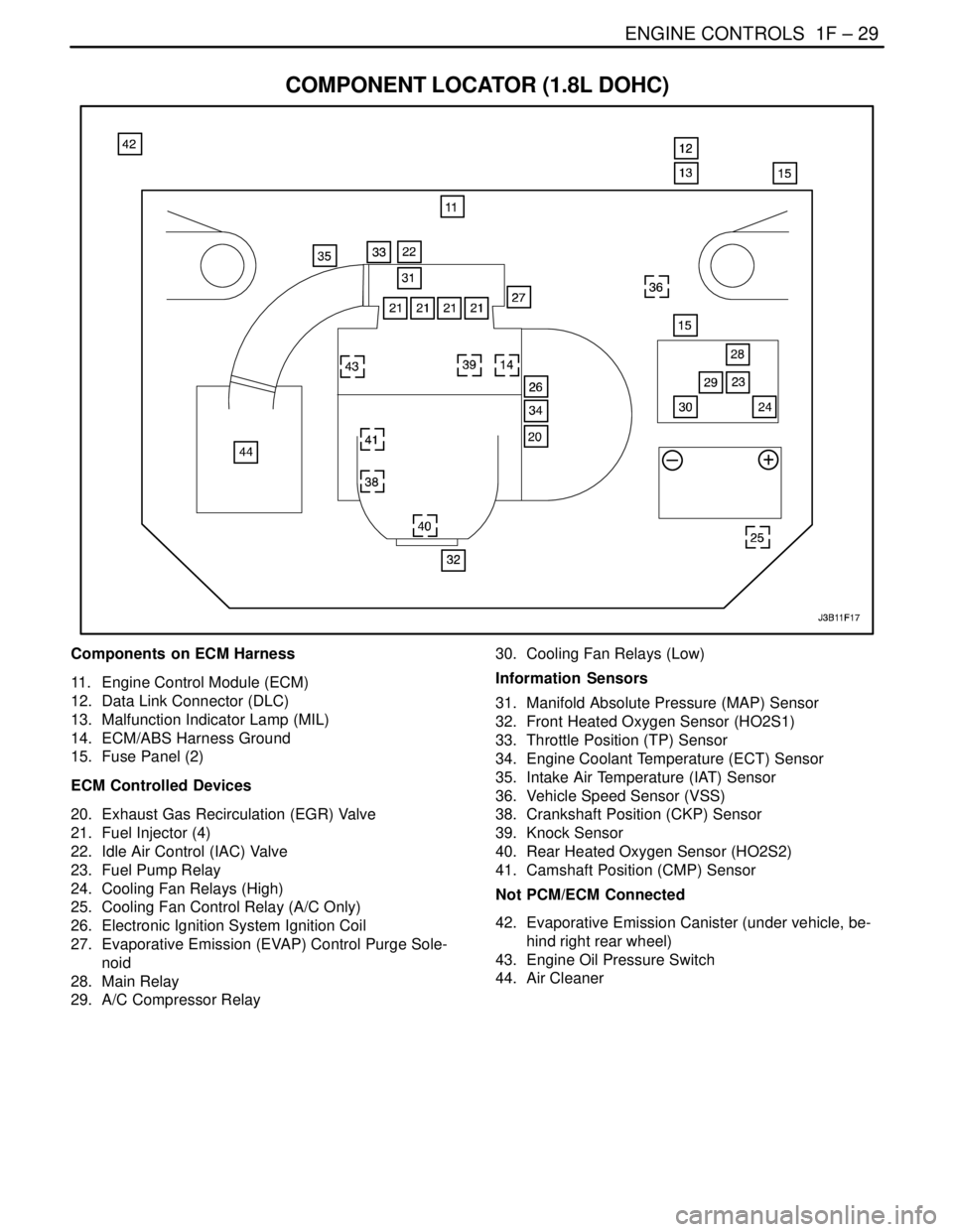
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 29
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COMPONENT LOCATOR (1.8L DOHC)
Components on ECM Harness
11. Engine Control Module (ECM)
12. Data Link Connector (DLC)
13. Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
14. ECM/ABS Harness Ground
15. Fuse Panel (2)
ECM Controlled Devices
20. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
21. Fuel Injector (4)
22. Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
23. Fuel Pump Relay
24. Cooling Fan Relays (High)
25. Cooling Fan Control Relay (A/C Only)
26. Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil
27. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control Purge Sole-
noid
28. Main Relay
29. A/C Compressor Relay30. Cooling Fan Relays (Low)
Information Sensors
31. Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
32. Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
33. Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
34. Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
35. Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
36. Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
38. Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
39. Knock Sensor
40. Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2)
41. Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Not PCM/ECM Connected
42. Evaporative Emission Canister (under vehicle, be-
hind right rear wheel)
43. Engine Oil Pressure Switch
44. Air Cleaner
Page 395 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 149
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Check for an intermittent ground in the wire be-
tween the O2 sensor and the engine control mod-
ule.
S Perform an injector 2alance test to determine if a
restricted fuel injector may be causing the lean con-
dition.S Vacuum of crankcase leaks will cause a lean run-
ning condition.
S An exhaust manifold gasket leak of a cracked ex-
haust manifold may cause outside air to be pulled
into the exhaust and past the sensor.
DTC P0137 – Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to ON, with the engine
OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Engine at operating temperature.
4. Run the engine at 1,200rpm.
Does the scan tool the downstream oxygen (O2)
sensor1 voltage within the value specified?0.07–0.52VGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
3Does the scan tool the heated oxygen (O2) sensor1
voltage within the value specified?0.1VGo to Step 9Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
41. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Heated O2 sensor connector
and engine control module (ECM) connector.
3. Check the Heated O2 sensor wire between the
Heated O2 sensor connector terminal 3 and
ECM connector terminal 36 for short to ground.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
51. Repair the wire of the connector terminal as
needed.
2. Clear the DTCs from the ECM.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
61. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Heated O2 sensor connector
and engine control module (ECM) connector.
3. Check the O2 sensor wire between the O2
sensor connector terminal 2 and ECM connec-
tor terminal 64 for short to ground.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
71. Repair the wire of the connector terminal as
needed.
2. Clear the DTCs from the ECM.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
81. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Replace the Heated O2 sensor.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 10–
Page 398 of 2643

1F – 152IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0138 – Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor High Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to ON, with the engine
OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Engine at operating temperature.
4. Run the engine at 1,200rpm.
Does the scan tool the Heated oxygen(O2) sensor
voltage within the value specified?More than
1.2VGo to Step 3Go to Step 6
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Heated O2 sensor connector
and engine control module (ECM) connector.
3. Check the Heated O2 sensor wire between the
Heated O2 sensor connector terminal 4 and
ECM connector terminal 64 for an open or
short to battery voltage.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Repair the wire of the connector terminal as
needed.
2. Clear the DTCs from the ECM.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
51. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Replace the Heated O2 sensor.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 7–
61. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Replace the ECM.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 7–
7Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displaced that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to applica-
ble DTC tableSystem OK
Page 400 of 2643

1F – 154IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Diagnostic Aids
Normal scan tool voltage varies between 0.15 to 8.5mV
while in Closed Loop. If DTC P0140 is intermittent, refer
to ”Intermittents” in this section.
DTC P0140 – Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor No Activity
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Run the engine to above the specified operat-
ing temperature.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Operate the engine above the specified rpm for
2 minuets.
Does the scan tool the indicate Closed Loop?80°C(176°F)
1,200rpmGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Turn the Turn the ignition switch to ON.
2. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within the freeze frame
conditions and Conditions for Setting the DTC
as noted?
Does the scan tool the indicate Closed Loop?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 4
4Disconnect the Heated O2 sensor connector and
jumper the Heated O2 sensor low circuit, terminal 3
to ground.
Is the HO2 voltage below the specified value and
does the scan tool indicate the heated oxygen sen-
sor heater voltage within the specified value?0.5VGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Check the Heated O2 sensor connector for malfunc-
tion terminals or poor connection and repair as nec-
essary.
Is repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 9
61. Turn the ignition switch to On.
2. Remove the jumper wire.
3. Using a digital voltmeter(DVM), measure the
voltage between the Heated O2 sensor signal
circuit, terminal 4 to ground.
Does the Heated O2 sensor voltage measure above
the specified value?0.6VGo to Step 10Go to Step 9
7Does the Heated O2 sensor voltage measure below
the specified value?0.3VGo to Step 11Go to Step 8
8Check the Heated O2 sensor ground circuit, termi-
nal 3 for an open or poor connection and repair as
necessary.
Is repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 8
9Check the Heated O2 sensor signal circuit, terminal
4 for an open or poor connection and repair as nec-
essary.
Is repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 8
Page 403 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 157
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S An exhaust manifold gasket leak of a cracked ex-
haust manifold may cause outside air to be pulled
into the exhaust and past the sensor.
DTC P0141 – Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater Malfunction
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Heated O2 sensor connector
and engine control module (ECM) connector.
3. Check the Heated O2 sensor heater wire be-
tween the Heated O2 sensor connector termi-
nal 3 and ECM connector terminal 16 for an
open or short to ground.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Repair the wire of the connector terminal as
needed.
2. Clear the DTCs from the ECM.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
41. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Replace the Heated O2 sensor.
3. Road tests the vehicle.
4. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 6–
5Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displaced that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to applica-
ble DTC tableSystem OK
Page 879 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 633
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Failed This Ig. (Failed This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the diagnostic test
has failed at least once during the current ignition cycle.
This message will clear when DTCs are cleared or the igni-
tion is cycled.
History
This message display indicates that the DTC has been
stored in memory as a valid fault. A DTC displayed as a
History fault may not mean that the fault is no longer pres-
ent. The history description means that all the conditions
necessary for reporting a fault have been met (maybe
even currently), and the information was stored in the con-
trol module memory.
MIL Requested
This message display indicates that the DTC is currently
causing the MIL to be turned ON. Remember that only
type A and type B DTCs can request the MIL. The MIL re-
quest cannot be used to determine if the DTC fault condi-
tions are currently being experienced. This is because the
diagnostic executive will require up to three trips during
which the diagnostic test passes to turn OFF the MIL.
Not Run Since CI (Not Run Since Cleared)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run since the last time DTCs were cleared.
Therefore, the diagnostic test status (passing or failing) is
unknown. After DTCs are cleared, this message will con-
tinue to be displayed until the diagnostic test runs.
Not Run This Ig. (Not Run This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run during this ignition cycle.
Test Ran and Passed
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has done the following:
S Passed the last test.
S Run and passed during this ignition cycle.
S Run and passed since DTCs were last cleared.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Test Ran and
Passed” after a repair verification, the vehicle is ready to
be released to the customer.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Failed This Ignition”
after a repair verification, then the repair is incomplete and
further diagnosis is required.
Prior to repairing a vehicle, status information can be used
to evaluate the state of the diagnostic test, and to help
identify an intermittent problem. The technician can con-
clude that although the MIL is illuminated, the fault condi-
tion that caused the code to set is not present. An intermit-
tent condition must be the cause.
PRIMARY SYSTEM – BASED
DIAGNOSTICS
There are primary system–based diagnostics which eval-
uate system operation and its effect on vehicle emissions.
The primary system–based diagnostics are listed below
with a brief description of the diagnostic function:
Oxygen Sensor Diagnosis
The fuel control Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) is
diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Slow response.
S Response time (time to switch R/L or L/R).
S Inactive signal (output steady at bias voltage
approx. 450 mv).
S Signal fixed high.
S Signal fixed low.
The catalyst monitor Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) is diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Heater performance (time to activity on cold start).
S Signal fixed low during steady state conditions or
power enrichment (hard acceleration when a rich-
mixture should be indicated).
S Signal fixed high during steady state conditions or
deceleration mode (deceleration when a lean mix-
ture should be indicated).
S Inactive sensor (output steady at approximately 438
mv).
If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal
are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must be
replaced. Do not attempt to repair the wiring, connector or
terminals. In order for the sensor to function properly, it
must have clean reference air provided to it. This clean air
reference is obtained by way of the oxygen sensor wire(s).
Any attempt to repair the wires, connector or terminals
could result in the obstruction of the reference air and de-
grade oxygen sensor performance.
Misfire Monitor Diagnostic Operation
The misfire monitor diagnostic is based on crankshaft
rotational velocity (reference period) variations. The en-
gine control module (ECM) determines crankshaft rota-
tional velocity using the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
and the Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor. When a cylinder
misfires, the crankshaft slows down momentarily. By mon-
itoring the CKP and CMP sensor signals, the ECM can cal-
culate when a misfire occurs.
For a non–catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic will be
required to monitor a misfire present for between
1000–3200 engine revolutions.
For catalyst–damaging misfire, the diagnostic will respond
to misfire within 200 engine revolutions.
Rough roads may cause false misfire detection. A rough
road will cause torque to be applied to the drive wheels and
drive train. This torque can intermittently decrease the
crankshaft rotational velocity. This may be falsely de-
tected as a misfire.
Page 902 of 2643

SECTION : 2A
SUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DIAGNOSIS2A–1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Diagnosis 2A–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Torque Steer 2A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tapered Roller Bearing 2A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSIS
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
Problems in the steering, the suspension, the tires, and
the wheels involve several systems. Consider all systems
when diagnosing a complaint. Some problems, such as
abnormal or excessive tire wear and scuffed tires, may be
the result of hard driving. Always road test the vehicle first.If possible, do this road test with the customer.
Proceed with the following preliminary checks. Correct
any substandard conditions.
Preliminary Checks
ChecksAction
Inspect the tires for improper pressure and uneven wear.Inflate the tires to the proper pressure.
Inspect the joint from the steering column to the steering
gear for loose connections or wear.Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace the in-
termediate shaft as needed.
Inspect the front and the rear suspension, the steering
gear, and the linkage for loose or damaged parts.Tighten the front and the rear suspension. Tighten the
steering gear mounting bracket bolts. Tighten the coupling
flange pinch bolts. Replace the front and the rear suspen-
sion as needed. Replace the steering gear as needed. Re-
place the intermediate shaft as needed.
Inspect for out–of–round tires.Perform a free runout test. Match–mount the tires.
Inspect for out–of–balance tires, bent wheels, and worn or
loose wheel bearings.Balance the wheels. Replace the wheels. Replace the
wheel bearings.
Check the power steering pump serpentine belt tension.Tighten the power steering pump serpentine belt.
Inspect the power steering system for leaks. Check the
power steering fluid level.Repair any leaks. Perform a power steering gear test. Add
power steering fluid.
Car Lead/Pull
ChecksAction
Inspect for mismatched or uneven tires.Replace the tires.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Inspect for a radial tire lateral force.Check the wheel alignment. Switch the wheels. Replace
the tires as needed.
Check the front–wheel alignment.Align the front wheels.
Inspect for an off–center steering gear.Reseat the pinion valve assembly. Replace the pinion
valve assembly as needed.
Inspect for front–brake dragging.Adjust the front brakes.