2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Rod
[x] Cancel search: RodPage 1143 of 2643
4F – 62IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
Removal Procedure
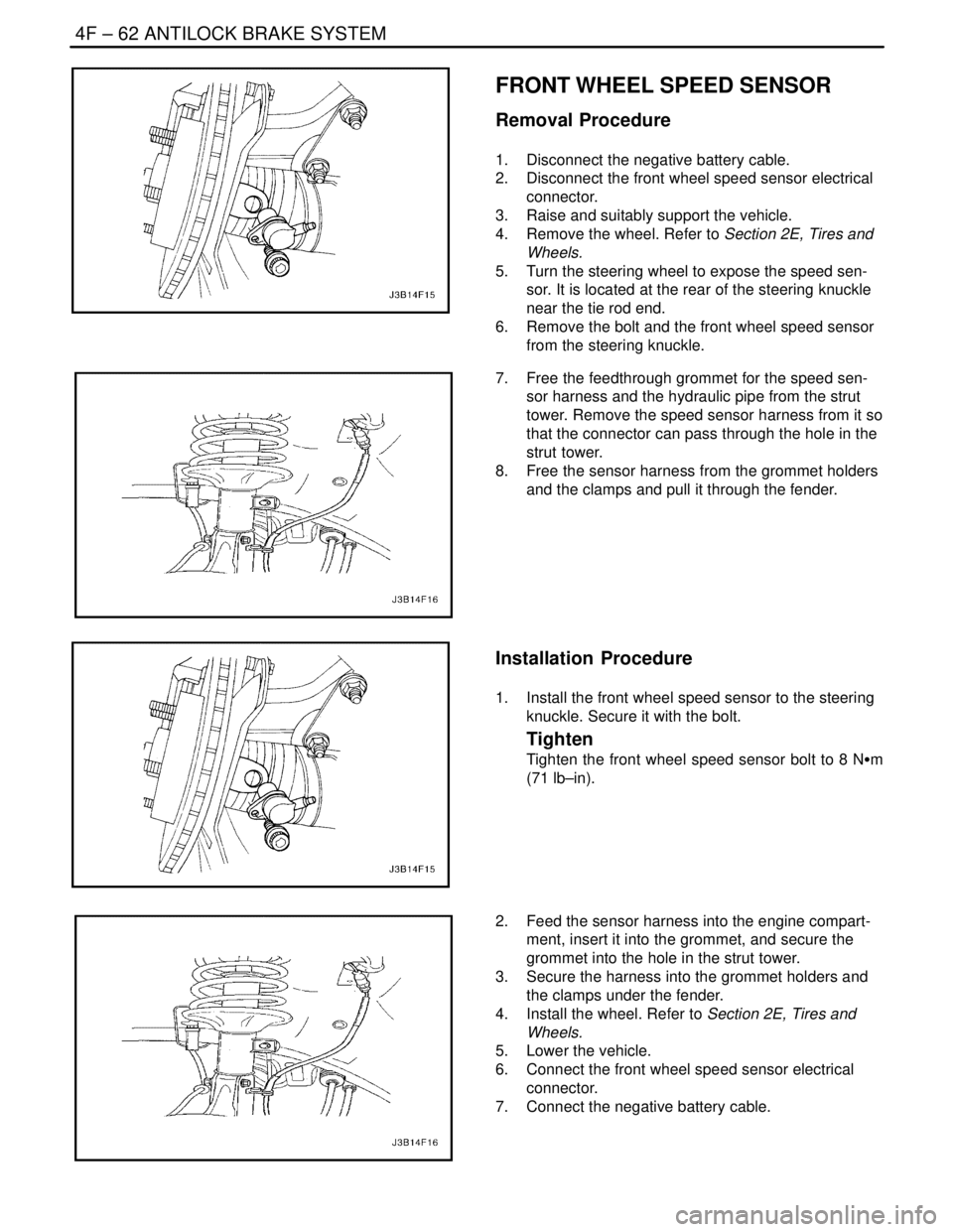
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the front wheel speed sensor electrical
connector.
3. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
4. Remove the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
5. Turn the steering wheel to expose the speed sen-
sor. It is located at the rear of the steering knuckle
near the tie rod end.
6. Remove the bolt and the front wheel speed sensor
from the steering knuckle.
7. Free the feedthrough grommet for the speed sen-
sor harness and the hydraulic pipe from the strut
tower. Remove the speed sensor harness from it so
that the connector can pass through the hole in the
strut tower.
8. Free the sensor harness from the grommet holders
and the clamps and pull it through the fender.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the front wheel speed sensor to the steering
knuckle. Secure it with the bolt.
Tighten
Tighten the front wheel speed sensor bolt to 8 NSm
(71 lb–in).
2. Feed the sensor harness into the engine compart-
ment, insert it into the grommet, and secure the
grommet into the hole in the strut tower.
3. Secure the harness into the grommet holders and
the clamps under the fender.
4. Install the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
5. Lower the vehicle.
6. Connect the front wheel speed sensor electrical
connector.
7. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 1150 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 69
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE FORCE
DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
As an add–on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD works
in a range in which the intervention thresholds for ABS
control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively moni-
tored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip is de-
tected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are switched to
pressure hold to prevent a further increase in pressure at
the rear–wheel breaks, thus electronically reproducing a
pressure–reduction function at the rear–wheel brakes.
THE BENEFITS OF EBD
S Elimination of conventional proportioning valve.
S EBD utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed
sensor to monitor rear wheel slip.
S Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure
hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle stabil-
ity.
S Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force distribu-
tion. (front to rear)
S Constant brake force distribution during vehicle life-
time.
S EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic.
(conventional proportioning valves are not monitor-
able)
S ”Keep alive” function.
Page 1155 of 2643
PARKING BRAKE 4G – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
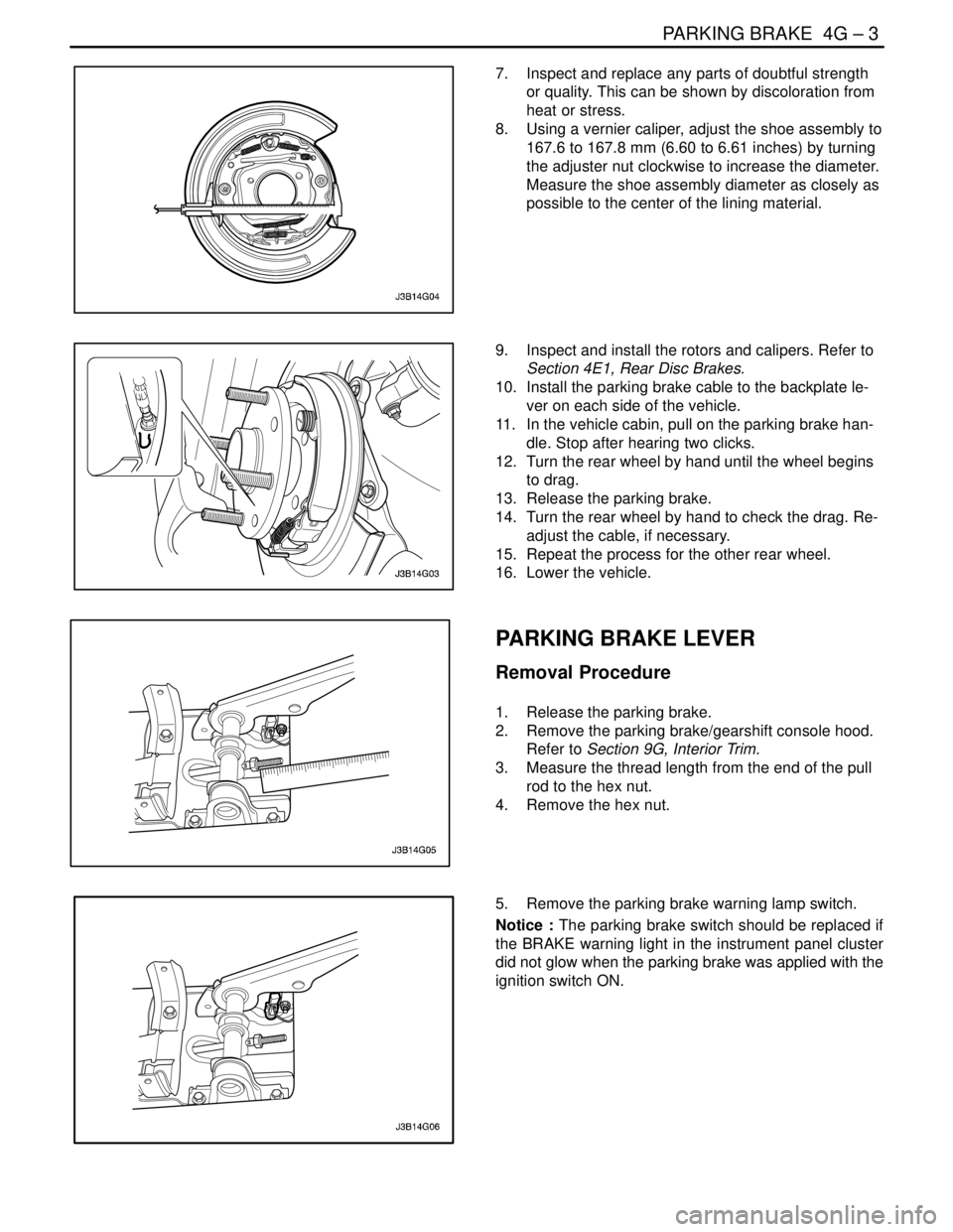
7. Inspect and replace any parts of doubtful strength
or quality. This can be shown by discoloration from
heat or stress.
8. Using a vernier caliper, adjust the shoe assembly to
167.6 to 167.8 mm (6.60 to 6.61 inches) by turning
the adjuster nut clockwise to increase the diameter.
Measure the shoe assembly diameter as closely as
possible to the center of the lining material.
9. Inspect and install the rotors and calipers. Refer to
Section 4E1, Rear Disc Brakes.
10. Install the parking brake cable to the backplate le-
ver on each side of the vehicle.
11. In the vehicle cabin, pull on the parking brake han-
dle. Stop after hearing two clicks.
12. Turn the rear wheel by hand until the wheel begins
to drag.
13. Release the parking brake.
14. Turn the rear wheel by hand to check the drag. Re-
adjust the cable, if necessary.
15. Repeat the process for the other rear wheel.
16. Lower the vehicle.
PARKING BRAKE LEVER
Removal Procedure
1. Release the parking brake.
2. Remove the parking brake/gearshift console hood.
Refer to Section 9G, Interior Trim.
3. Measure the thread length from the end of the pull
rod to the hex nut.
4. Remove the hex nut.
5. Remove the parking brake warning lamp switch.
Notice : The parking brake switch should be replaced if
the BRAKE warning light in the instrument panel cluster
did not glow when the parking brake was applied with the
ignition switch ON.
Page 1156 of 2643
4G – 4IPARKING BRAKE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
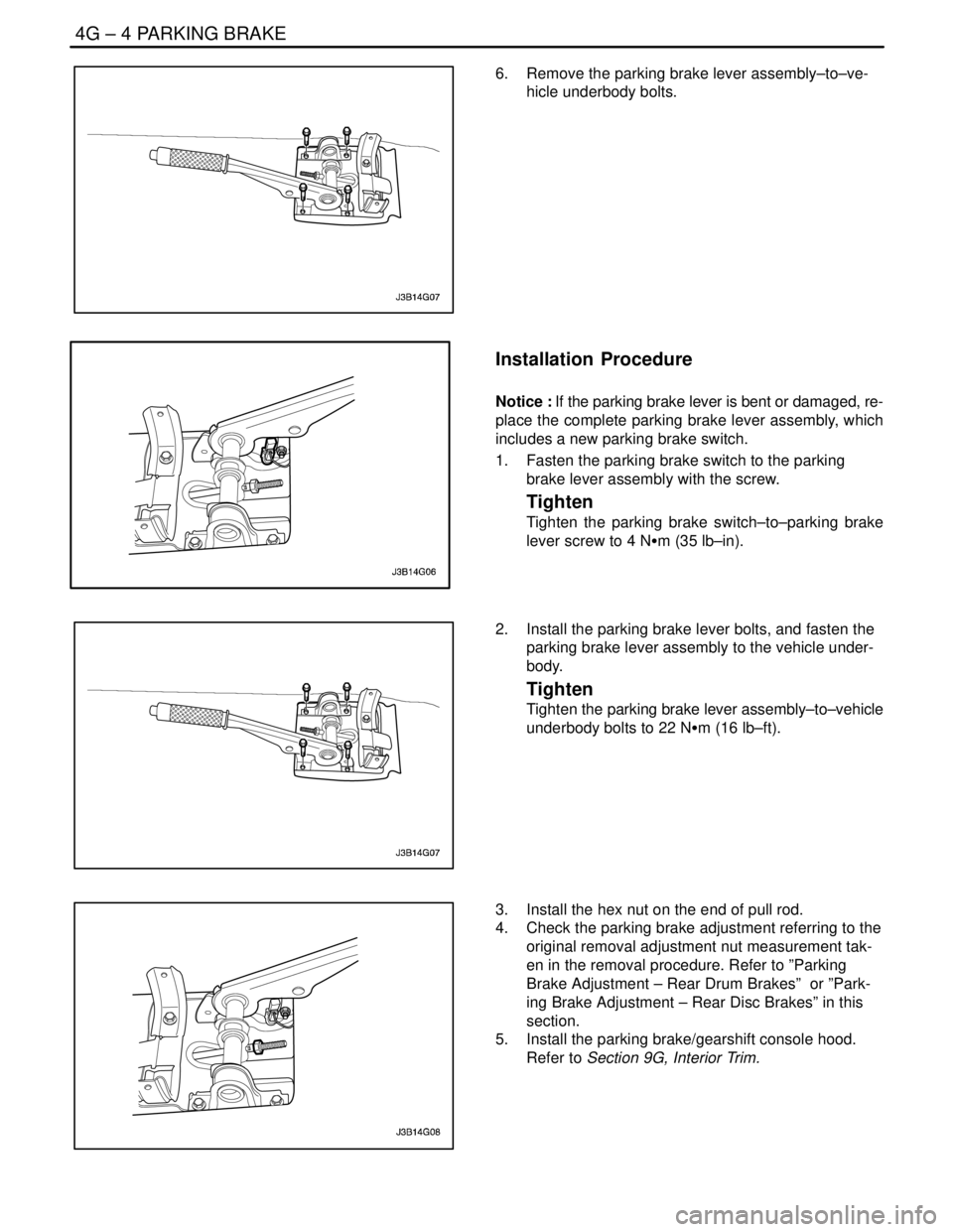
6. Remove the parking brake lever assembly–to–ve-
hicle underbody bolts.
Installation Procedure
Notice : If the parking brake lever is bent or damaged, re-
place the complete parking brake lever assembly, which
includes a new parking brake switch.
1. Fasten the parking brake switch to the parking
brake lever assembly with the screw.
Tighten
Tighten the parking brake switch–to–parking brake
lever screw to 4 NSm (35 lb–in).
2. Install the parking brake lever bolts, and fasten the
parking brake lever assembly to the vehicle under-
body.
Tighten
Tighten the parking brake lever assembly–to–vehicle
underbody bolts to 22 NSm (16 lb–ft).
3. Install the hex nut on the end of pull rod.
4. Check the parking brake adjustment referring to the
original removal adjustment nut measurement tak-
en in the removal procedure. Refer to ”Parking
Brake Adjustment – Rear Drum Brakes” or ”Park-
ing Brake Adjustment – Rear Disc Brakes” in this
section.
5. Install the parking brake/gearshift console hood.
Refer to Section 9G, Interior Trim.
Page 1157 of 2643
PARKING BRAKE 4G – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
PARKING BRAKE CABLE
Removal Procedure
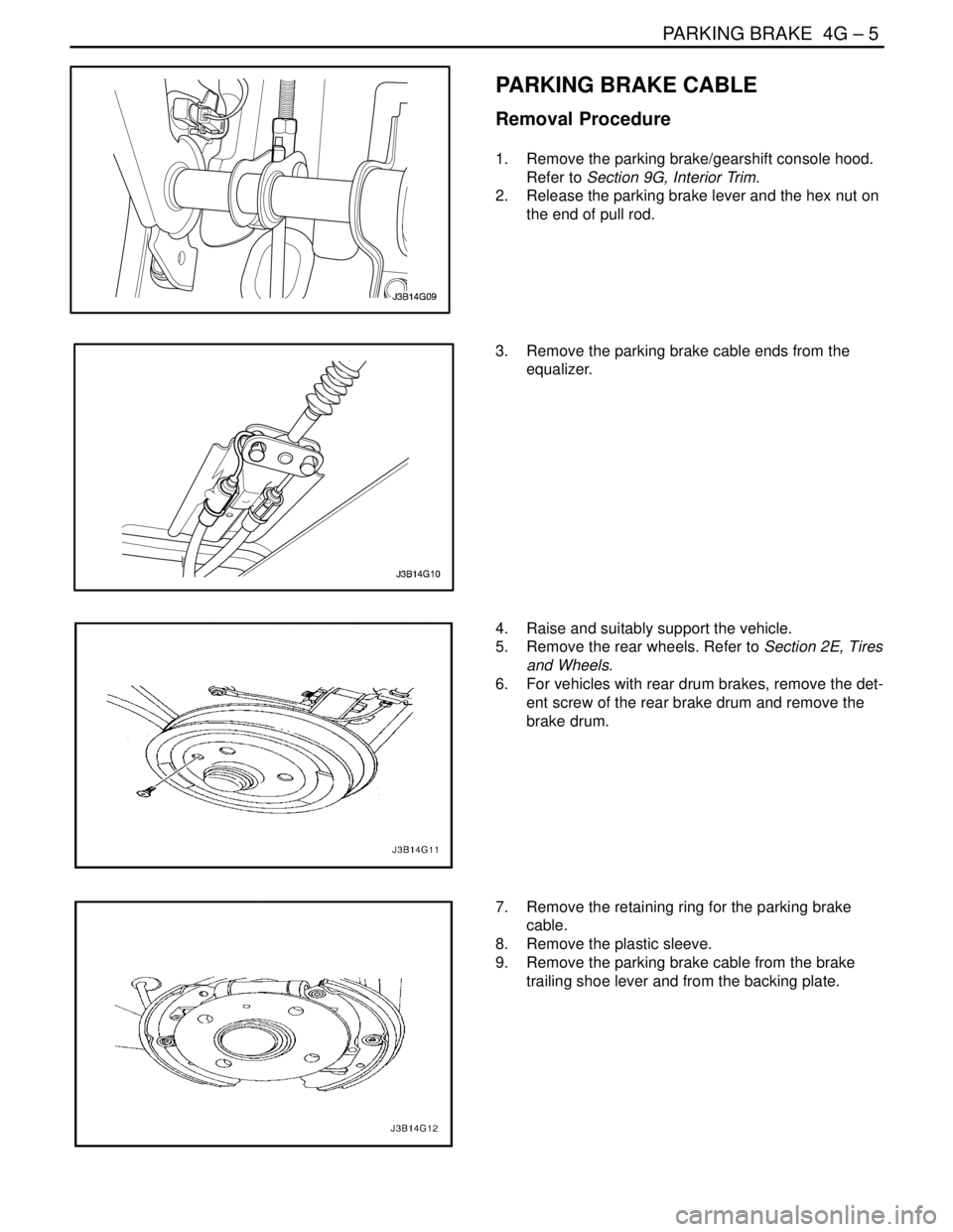
1. Remove the parking brake/gearshift console hood.
Refer to Section 9G, Interior Trim.
2. Release the parking brake lever and the hex nut on
the end of pull rod.
3. Remove the parking brake cable ends from the
equalizer.
4. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
5. Remove the rear wheels. Refer to Section 2E, Tires
and Wheels.
6. For vehicles with rear drum brakes, remove the det-
ent screw of the rear brake drum and remove the
brake drum.
7. Remove the retaining ring for the parking brake
cable.
8. Remove the plastic sleeve.
9. Remove the parking brake cable from the brake
trailing shoe lever and from the backing plate.
Page 1160 of 2643

4G – 8IPARKING BRAKE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
9. Attach the parking brake cable ends to the equaliz-
er.
10. Adjust the hex nut on the end of pull rod. Refer to
”Parking Brake Adjustment” in this section.
11. Install the parking brake/gearshift console hood.
Refer to Section 9G, Interior Trim.
PARKING BRAKE HANDLE
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the parking brake/gearshift console hood,
detaching the parking brake lever boot. Refer to
Section 9G, Interior Trim.
2. Slip the parking brake handle off of the parking
brake lever.
Installation Procedure
1. Push the parking brake handle as far as it will go on
the parking brake lever.
2. Install the parking brake/gearshift console hood
with the parking brake lever boot. Refer to Section
9G, Interior Trim.
Page 1350 of 2643

SECTION : 5A1
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION5A1–3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ZF 4HP 16 Automatic Transaxle 5A1–3. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Components 5A1–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIFICATIONS5A1–5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Specifications 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Gear Ratio 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fluid Capacity 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart 5A1–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure 5A1–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIAL TOOLS5A1–9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Tools Table 5A1–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SCHEMATIC AND ROUTING DIAGRAMS5A1–11 . . .
Transaxle Control Module (1 of 2) 5A1–11. . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Control Module (2 of 2) 5A1–12. . . . . . . . . .
Shift Mode Diagram 5A1–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Flow Diagram 5A1–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
COMPONENT LOCATOR5A1–33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Identification Information 5A1–33. . . . . . . .
Torque Converter 5A1–34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Housing 5A1–35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pump 5A1–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Cover & Oil Pan Cover 5A1–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parking Lever 5A1–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input Shaft & Shift Gear 5A1–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Valve Body 5A1–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Gear Shift Control 5A1–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
DIAGNOSIS5A1–43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Knowledge Required 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Check Procedure 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure Check Procedure 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . .
Clutch Plate Diagnosis 5A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cooler Flushing and Flow Test 5A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . Transaxle Fluid Level Service Procedure 5A1–45. . . .
Electrical/Garage Shift Test 5A1–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Road Test Procedure 5A1–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Converter Lock–Up Clutch(TCC)
Diagnosis 5A1–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TCM Initialization Procedure 5A1–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart 5A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Internal Wiring Harness Check 5A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Wiring Harness Connector 5A1–54. . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 5A1–56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS5A1–60
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Identification 5A1–60
DTC P0562 – System Voltage Low 5A1–68. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0563 – System Voltage High 5A1–71. . . . . . . .
DTC P0601 – Internal Control Module Memory
Checksum Error 5A1–74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0603 – Internal Control Module Keep
Alive Memory(KAM) Error 5A1–76. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0604 – Internal Control Module Random
Access Memory(RAM) Error 5A1–78. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0606 – Transaxle Control Module
Processor Fault 5A1–80. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0703 – Brake Switch Circuit
Malfunction 5A1–83. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0705 – Transmission Range Sensor
Circuit Malfunction(PRNDL Input) 5A1–86. . . . . . . .
DTC P0710 – Transmission Fluid Temperature
Sensor Circuit Malfunction 5A1–89. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0715 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
Malfunction 5A1–92. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0716 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
Range/Performance 5A1–95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0717 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
No Signal 5A1–98. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0720 – Output Speed Sensor(OSS)
Circuit Malfunction 5A1–101. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0721 – Output Speed Sensor(OSS)
Circuit Range/Performance 5A1–104. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1352 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Important Measurement/Adjustment 5A1–230. . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION5A1–232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mechanical Components 5A1–232. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronical Components 5A1–236. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TCM Inputs That Affect the 4HP 16
Transaxle 5A1–241. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
INTRODUCTION
ZF 4HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
The ZF 4 HP 16 is a four–speed automatic transaxle de-
signed for cars with front–wheel drive and a transversely
mounted engine.
The transaxle has a hydrodynamic torque converter with
a controlled slip lock–up clutch.
A planetary gear train establishes the mechanical gear ra-
tios. The integral constant ratio can be adapted to the en-
gine’s power output and the vehicle’s weight. The elec-
tronic–hydraulic control makes controlled power shifts and
various shift programs possible. In selector lever position
”P”, the output is locked mechanically.The special feature of this transaxle is that it operates with-
out freewheels. Shifting between individual gears takes
place by means of overlapping clutch engagement and re-
lease.
The advantage of overlap shifting is as follows:
– The transaxle can be of more compact design
and is lighter on account of the absence of free-
wheels and the lower number of shift elements
– Lower drag losses, i.e. higher efficiency
– Lower peak torques acting on the components
and driveline.
However, overlap shifting necessitates high–performance
hardware and software, and precision engine signals.