2004 DAEWOO LACETTI oxygen sensor
[x] Cancel search: oxygen sensorPage 871 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 625
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CANISTER
The Evaporative (EVAP) Emission canister is an emission
control device containing activated charcoal granules.
The EVAP emission canister is used to store fuel vapors
from the fuel tank. Once certain conditions are met, the en-
gine control module (ECM) activates the EVAP canister
purge solenoid, allowing the fuel vapors to be drawn into
the engine cylinders and burned.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE
VENTILATION SYSTEM OPERATION
A Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system is used to
provide complete use of the crankcase vapors. Fresh air
from the air cleaner is supplied to the crankcase. The fresh
air is mixed with blowby gases which are then passed
through a vacuum hose into the intake manifold.
Periodically inspect the hoses and the clamps. Replace
any crankcase ventilation components as required.
A restricted or plugged PCV hose may cause the following
conditions:
S Rough idle
S Stalling or low idle speed
S Oil leaks
S Oil in the air cleaner
S Sludge in the engine
A leaking PCV hose may cause the following conditions:
S Rough idle
S Stalling
S High idle speed
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor (a resistor which changes value based on tem-
perature) mounted in the engine coolant stream. Low cool-
ant temperature produces a high resistance (100,000
ohms at –40 °F [–40 °C]) while high temperature causes
low resistance (70 ohms at 266 °F [130 °C]).
The engine control module (ECM) supplies 5 volts to the
ECT sensor through a resistor in the ECM and measures
the change in voltage. The voltage will be high when the
engine is cold, and low when the engine is hot. By measur-
ing the change in voltage, the ECM can determine the
coolant temperature. The engine coolant temperature af-
fects most of the systems that the ECM controls. A failure
in the ECT sensor circuit should set a diagnostic trouble
code P0117 or P0118. Remember, these diagnostic
trouble codes indicate a failure in the ECT sensor circuit,
so proper use of the chart will lead either to repairing a wir-
ing problem or to replacing the sensor to repair a problem
properly.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer con-
nected to the throttle shaft of the throttle body. The TP sen-
sor electrical circuit consists of a 5 volt supply line and a
ground line, both provided by the engine control module
(ECM). The ECM calculates the throttle position by moni-
toring the voltage on this signal line. The TP sensor output
changes as the accelerator pedal is moved, changing the
throttle valve angle. At a closed throttle position, the output
of the TP sensor is low, about 0.5 volt. As the throttle valve
opens, the output increases so that, at Wide Open Throttle
(WOT), the output voltage will be about 5 volts.
The ECM can determine fuel delivery based on throttle
valve angle (driver demand). A broken or loose TP sensor
can cause intermittent bursts of fuel from the injector and
an unstable idle, because the ECM thinks the throttle is
moving. A problem in any of the TP sensor circuits should
set a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0121 or P0122.
Once the DTC is set, the ECM will substitute a default val-
ue for the TP sensor and some vehicle performance will
return. A DTC P0121 will cause a high idle speed.
CATALYST MONITOR OXYGEN
SENSORS
Three–way catalytic converters are used to control emis-
sions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and
oxides of nitrogen (NOx). The catalyst within the convert-
ers promotes a chemical reaction. This reaction oxidizes
the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas and converts
them into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide. The
catalyst also reduces NOx by converting it to nitrogen. The
engine control module (ECM) can monitor this process us-
ing the HO2S1 and HO2S2 sensor. These sensors pro-
duce an output signal which indicates the amount of oxy-
gen present in the exhaust gas entering and leaving the
three–way converter. This indicates the catalyst’s ability to
efficiently convert exhaust gasses. If the catalyst is operat-
ing efficiently, the HO2S1 sensor signals will be more ac-
tive than the signals produced by the HO2S2 sensor. The
catalyst monitor sensors operate the same way as the fuel
control sensors. The sensor’s main function is catalyst
monitoring, but they also have a limited role in fuel control.
If a sensor output indicates a voltage either above or below
the 450 mv bias voltage for an extended period of time, the
ECM will make a slight adjustment to fuel trim to ensure
that fuel delivery is correct for catalyst monitoring.
A problem with the HO2S1 sensor circuit will set DTC
P0131, P0132, P0133 or P0134 depending, on the special
condition. A problem with the HO2S2 sensor signal will set
DTC P0137, P0138, P0140 or P0141, depending on the
special condition.
A fault in the Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2) heat-
er element or its ignition feed or ground will result in lower
oxygen sensor response. This may cause incorrect cata-
lyst monitor diagnostic results.
Page 875 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 629
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
tentially interfere with the operation of the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and thereby turn on the MIL.
Small leaks in the exhaust system near the post catalyst
oxygen sensor can also cause the MIL to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones, stereos,
and anti–theft devices, may radiate electromagnetic inter-
ference (EMI) into the control system if they are improperly
installed. This may cause a false sensor reading and turn
on the MIL.
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain–soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL.
Refueling
A new EOBD diagnostic checks the integrity of the entire
Evaporative (EVAP) Emission system. If the vehicle is re-
started after refueling and the fuel cap is not secured cor-
rectly, the on–board diagnostic system will sense this as
a system fault, turn on the MIL, and set DTC P0440.
Vehicle Marshaling
The transportation of new vehicles from the assembly
plant to the dealership can involve as many as 60 key
cycles within 2 to 3 miles of driving. This type of operation
contributes to the fuel fouling of the spark plugs and will
turn on the MIL with a set DTC P0300.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of EOBD diagnostics will cause the MIL to
turn on if the vehicle is not maintained properly. Restricted
air filters, fuel filters, and crankcase deposits due to lack
of oil changes or improper oil viscosity can trigger actual
vehicle faults that were not previously monitored prior to
EOBD. Poor vehicle maintenance can not be classified as
a ”non–vehicle fault,” but with the sensitivity of EOBD
diagnostics, vehicle maintenance schedules must be
more closely followed.
Severe Vibration
The Misfire diagnostic measures small changes in the
rotational speed of the crankshaft. Severe driveline vibra-
tions in the vehicle, such as caused by an excessive
amount of mud on the wheels, can have the same effect
on crankshaft speed as misfire and, therefore, may set
DTC P0300.
Related System Faults
Many of the EOBD system diagnostics will not run if the
engine controlmodule (ECM) detects a fault on a related
system or component. One example would be that if the
ECM detected a Misfire fault, the diagnostics on the cata-
lytic converter would be suspended until the Misfire fault
was repaired. If the Misfire fault is severe enough, the cat-
alytic converter can be damaged due to overheating andwill never set a Catalyst DTC until the Misfire fault is re-
paired and the Catalyst diagnostic is allowed to run to
completion. If this happens, the customer may have to
make two trips to the dealership in order to repair the ve-
hicle.
SERIAL DATA COMMUNICATIONS
Class II Serial Data Communications
Government regulations require that all vehicle manufac-
turers establish a common communication system. This
vehicle utilizes the ”Class II” communication system. Each
bit of information can have one of two lengths: long or
short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by transmit-
ting and receiving multiple signals over a single wire. The
messages carried on Class II data streams are also priori-
tized. If two messages attempt to establish communica-
tions on the data line at the same time, only the message
with higher priority will continue. The device with the lower
priority message must wait. Themost significant result of
this regulation is that it provides scan tool manufacturers
with the capability to access data from any make or model
vehicle that is sold.
The data displayed on the other scan tool will appear the
same, with some exceptions. Some scan tools will only be
able to display certain vehicle parameters as values that
are a coded representation of the true or actual value. On
this vehicle the scan tool displays the actual values for ve-
hicle parameters. It will not be necessary to perform any
conversions from coded values to actual values.
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (EOBD)
On–Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When
a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not cur-
rently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is current-
ly active.
S The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
S The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Remember, a fuel trim Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
may be triggered by a list of vehicle faults. Make use of all
information available (other DTCs stored, rich or lean con-
dition, etc.) when diagnosing a fuel trim fault.
Page 876 of 2643

1F – 630IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENT
MONITOR DIAGNOSTIC OPERATION
Comprehensive component monitoring diagnostics are
required to monitor emissions–related input and output
powertrain components.
Input Components
Input components are monitored for circuit continuity and
out–of–range values. This includes rationality checking.
Rationality checking refers to indicating a fault when the
signal from a sensor does not seem reasonable, i.e.
Throttle Position (TP) sensor that indicates high throttle
position at low engine loads or Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) voltage. Input components may include, but are not
limited to, the following sensors:
S Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS).
S Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor.
S Throttle Position (TP) sensor.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor.
S Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
In addition to the circuit continuity and rationality check,
the ECT sensor is monitored for its ability to achieve a
steady state temperature to enable closed loop fuel con-
trol.
Output Components
Output components are diagnosed for proper response to
control module commands. Components where functional
monitoring is not feasible will be monitored for circuit conti-
nuity and out–of–range values if applicable. Output com-
ponents to be monitored include, but are not limited to the
following circuit:
S Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor.
S Control module controlled EVAP Canister Purge
Valve.
S A/C relays.
S Cooling fan relay.
S VSS output.
S MIL control.
Refer to ”Engine Control Module” and Sensors in this sec-
tion.
Passive and Active Diagnostic Tests
A passive test is a diagnostic test which simply monitors
a vehicle system or component. Conversely, an active
test, actually takes some sort of action when performing
diagnostic functions, often in response to a failed passive
test. For example, the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
diagnostic active test will force the EGR valve open during
closed throttle deceleration and/or force the EGR valve
closed during a steady state. Either action should result in
a change in manifold pressure.
Intrusive Diagnostic Tests
This is any on–board test run by the Diagnostic Manage-
ment System which may have an effect on vehicle perfor-
mance or emission levels.
Warm–Up Cycle
A warm–up cycle means that engine temperature must
reach aminimum of 160°F (70°C) and rise at least 72°F
(22°C) over the course of a trip.
Freeze Frame
Freeze Frame is an element of the Diagnostic Manage-
ment System which stores various vehicle information at
the moment an emissions–related fault is stored in
memory and when the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
is commanded on. These data can help to identify the
cause of a fault.
Failure Records
Failure Records data is an enhancement of the EOBD
Freeze Frame feature. Failure Records store the same ve-
hicle information as does Freeze Frame, but it will store
that information for any fault which is stored in onboard
memory, while Freeze Frame stores information only for
emission–related faults that command the MIL on.
COMMON EOBD TERMS
Diagnostic
When used as a noun, the word diagnostic refers to any
on–board test run by the vehicle’s Diagnostic Manage-
ment System. A diagnostic is simply a test run on a system
or component to determine if the system or component is
operating according to specification. There are many diag-
nostics, shown in the following list:
S Misfire
S Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
S Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2)
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
S Catalyst monitoring
Enable Criteria
The term ”enable criteria” is engineering language for the
conditions necessary for a given diagnostic test to run.
Each diagnostic has a specific list of conditions which
must be met before the diagnostic will run.
”Enable criteria” is another way of saying ”conditions re-
quired.”
The enable criteria for each diagnostic is listed on the first
page of the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) description
under the heading ”Conditions for Setting the DTC.” En-
able criteria varies with each diagnostic and typically in-
cludes, but is not limited to, the following items:
S Engine speed.
S Vehicle speed
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
S Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Page 879 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 633
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Failed This Ig. (Failed This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the diagnostic test
has failed at least once during the current ignition cycle.
This message will clear when DTCs are cleared or the igni-
tion is cycled.
History
This message display indicates that the DTC has been
stored in memory as a valid fault. A DTC displayed as a
History fault may not mean that the fault is no longer pres-
ent. The history description means that all the conditions
necessary for reporting a fault have been met (maybe
even currently), and the information was stored in the con-
trol module memory.
MIL Requested
This message display indicates that the DTC is currently
causing the MIL to be turned ON. Remember that only
type A and type B DTCs can request the MIL. The MIL re-
quest cannot be used to determine if the DTC fault condi-
tions are currently being experienced. This is because the
diagnostic executive will require up to three trips during
which the diagnostic test passes to turn OFF the MIL.
Not Run Since CI (Not Run Since Cleared)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run since the last time DTCs were cleared.
Therefore, the diagnostic test status (passing or failing) is
unknown. After DTCs are cleared, this message will con-
tinue to be displayed until the diagnostic test runs.
Not Run This Ig. (Not Run This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run during this ignition cycle.
Test Ran and Passed
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has done the following:
S Passed the last test.
S Run and passed during this ignition cycle.
S Run and passed since DTCs were last cleared.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Test Ran and
Passed” after a repair verification, the vehicle is ready to
be released to the customer.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Failed This Ignition”
after a repair verification, then the repair is incomplete and
further diagnosis is required.
Prior to repairing a vehicle, status information can be used
to evaluate the state of the diagnostic test, and to help
identify an intermittent problem. The technician can con-
clude that although the MIL is illuminated, the fault condi-
tion that caused the code to set is not present. An intermit-
tent condition must be the cause.
PRIMARY SYSTEM – BASED
DIAGNOSTICS
There are primary system–based diagnostics which eval-
uate system operation and its effect on vehicle emissions.
The primary system–based diagnostics are listed below
with a brief description of the diagnostic function:
Oxygen Sensor Diagnosis
The fuel control Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) is
diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Slow response.
S Response time (time to switch R/L or L/R).
S Inactive signal (output steady at bias voltage
approx. 450 mv).
S Signal fixed high.
S Signal fixed low.
The catalyst monitor Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) is diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Heater performance (time to activity on cold start).
S Signal fixed low during steady state conditions or
power enrichment (hard acceleration when a rich-
mixture should be indicated).
S Signal fixed high during steady state conditions or
deceleration mode (deceleration when a lean mix-
ture should be indicated).
S Inactive sensor (output steady at approximately 438
mv).
If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal
are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must be
replaced. Do not attempt to repair the wiring, connector or
terminals. In order for the sensor to function properly, it
must have clean reference air provided to it. This clean air
reference is obtained by way of the oxygen sensor wire(s).
Any attempt to repair the wires, connector or terminals
could result in the obstruction of the reference air and de-
grade oxygen sensor performance.
Misfire Monitor Diagnostic Operation
The misfire monitor diagnostic is based on crankshaft
rotational velocity (reference period) variations. The en-
gine control module (ECM) determines crankshaft rota-
tional velocity using the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
and the Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor. When a cylinder
misfires, the crankshaft slows down momentarily. By mon-
itoring the CKP and CMP sensor signals, the ECM can cal-
culate when a misfire occurs.
For a non–catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic will be
required to monitor a misfire present for between
1000–3200 engine revolutions.
For catalyst–damaging misfire, the diagnostic will respond
to misfire within 200 engine revolutions.
Rough roads may cause false misfire detection. A rough
road will cause torque to be applied to the drive wheels and
drive train. This torque can intermittently decrease the
crankshaft rotational velocity. This may be falsely de-
tected as a misfire.
Page 883 of 2643
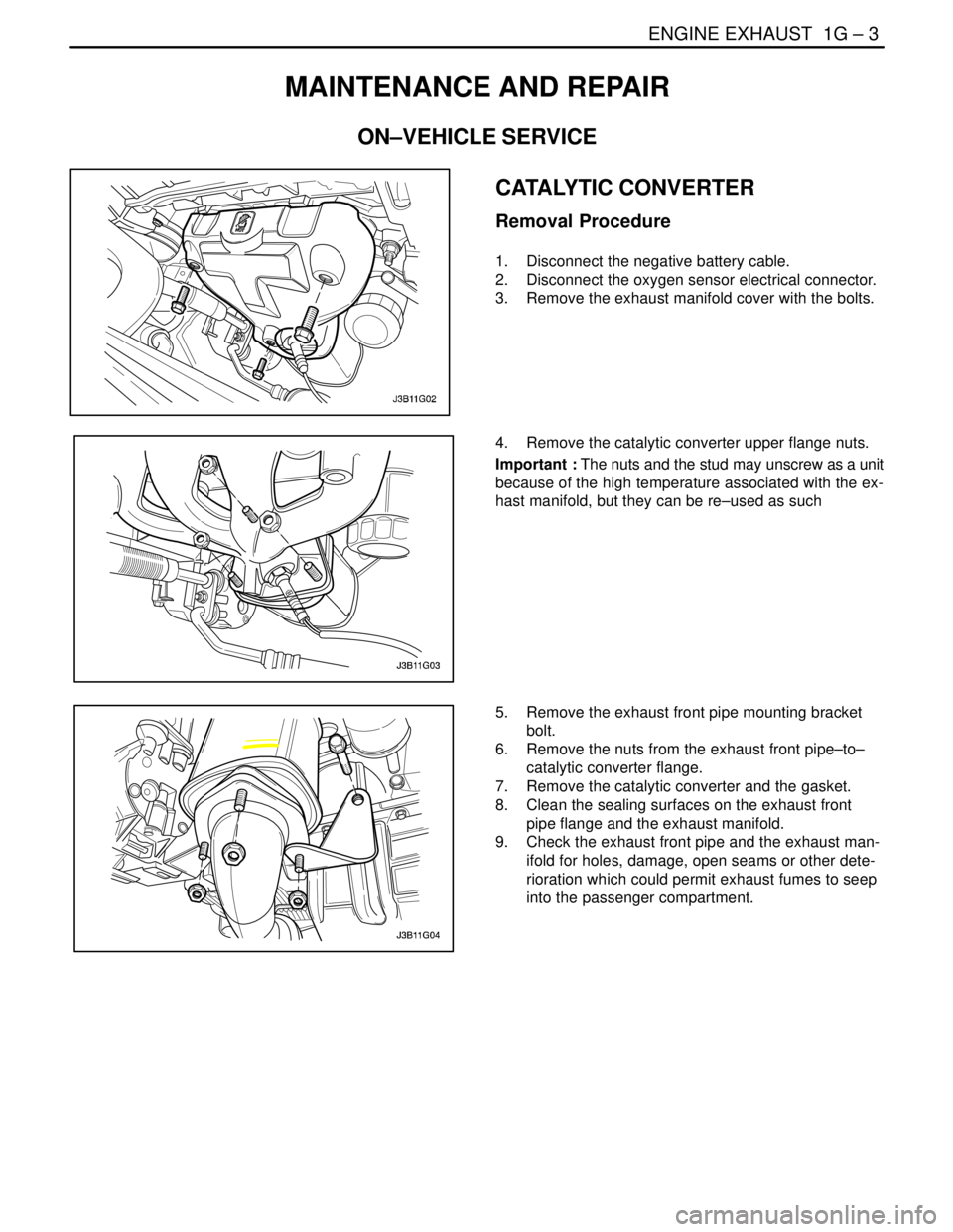
ENGINE EXHAUST 1G – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the oxygen sensor electrical connector.
3. Remove the exhaust manifold cover with the bolts.
4. Remove the catalytic converter upper flange nuts.
Important : The nuts and the stud may unscrew as a unit
because of the high temperature associated with the ex-
hast manifold, but they can be re–used as such
5. Remove the exhaust front pipe mounting bracket
bolt.
6. Remove the nuts from the exhaust front pipe–to–
catalytic converter flange.
7. Remove the catalytic converter and the gasket.
8. Clean the sealing surfaces on the exhaust front
pipe flange and the exhaust manifold.
9. Check the exhaust front pipe and the exhaust man-
ifold for holes, damage, open seams or other dete-
rioration which could permit exhaust fumes to seep
into the passenger compartment.
Page 884 of 2643

1G – 4IENGINE EXHAUST
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Installation Procedure
1. Install the catalytic converter and the gasket to the
exhaust front pipe flange.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust front pipe–to–catalytic converter
nuts to 40 NSm (30 lb–ft).
Tighten the exhaust front pipe–to–cylinder block bolt
to 50 NSm (37 lb–ft).
2. Install the catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
nuts and the gasket.
Tighten
Tighten the catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
nuts to 40 NSm (30 lb–ft).
3. Install the exhaust manifold conver bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust manifold cover bolts to 15 NSm
(11 lb–ft).
4. Connect the oxygen sensor electrical connector.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
EXHAUST FRONT PIPE
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the crossmember lower bracket with the
bolts.
Page 885 of 2643

ENGINE EXHAUST 1G – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
2. Disconnect the oxygen sensor connector.
3. Remove the exhaust front pipe mounting bracket
bolt.
4. Remove the nuts from the exhaust front pipe–to–
catalytic converter flange.
5. Remove the nuts from the exhaust front pipe–to–
exhaust front muffler.
6. Remove the exhaust front pipe and the gasket.
7. Clean the sealing surfaces on the exhaust front
muffler pipe flange and the exhaust front pipe.
8. Check the exhaust front pipe for holes, damage,
open seams or other deterioration which could per-
mit exhaust fumes to seep into the passenger
compartment.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the exhaust front pipe and the gasket.
2. Install the nuts from the exhaust front pipe–to–ex-
hasut front muffler.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust front pipe–to–exhaust front muf-
fler nets to 30 NSm (22 lb–ft).
3. Install the nuts from the exhaust front pipe–to–cata-
lytic converter flange.
4. Install the exhaust front pipe mounting bracket bolt.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust front pipe–to–catalytic converter
nuts to 40 NSm (30 lb–ft).
Tighten the exhaust front pipe–to–cylinder block bolt
to 50 NSm (37 lb–ft).
5. Connect the oxygen sensor connector.
Page 1399 of 2643

5A1 – 50IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TCC shudder should only occur during the APPLY and/or
RELEASE of the Lock up clutch.
While TCC Is Applying Or Releasing
If the shudder occurs while TCC is applying, the problem
can be within the transaxle or torque converter.
Something is not allowing the clutch to become fully en-
gaged, not allowing clutch to release, or is trying to release
and apply the clutch at the same time. This could be
caused by leaking turbine shaft seals, a restricted release
orifice, a distorted clutch or housing surface due to long
converter bolts, or defective friction material on the TCC
plate.
Shudder Occurs After TCC Has Applied :
In this case, most of the time there is nothing wrong with
the transaxle! As mentioned above, once the TCC has
been applied, it is very unlikely that will slip. Engine prob-
lems may go unnoticed under light throttle and load, but
become noticeable after TCC apply when going up a hill
or accelerating, due to the mechanical coupling between
engine and transaxle.
Important : Once TCC is applied there is no torque con-
verter assistance. Engine or driveline vibrations could be
unnoticeable before TCC engagement.
Inspect the following components to avoid misdiagnosis of
TCC shudder and possibly disassembling a transaxle and/
or replacing a torque converter unnecessarily :
S Spark plugs – Inspect for cracks, high resistance or
broken insulator.
S Plug wires – Lock in each end, if there is red dust
(ozone) or black substance (carbon) present, then
the wires are bad. Also look for a white discolor-
ation of the wire indicating arcing during hard accel-
eration.
S Distributor cap and rotor – look for broken or un–
crimped parts.
S Coil – look for black on bottom indication arcing
while engine is misfiring.
S Fuel injector – filter may be plugged.
S Vacuum leak – engine won’t get correct amount of
fuel. May run rich or lean depending on where the
leak is.S EGR valve – valve may let it too much unburnable
exhaust gas and cause engine to run lean.
S MAP sensor – like vacuum leak, engine won’t get
correct amount of fuel for proper engine operation.
S Carbon on intake valves – restricts proper flow or
air/fuel mixture into cylinders.
S Flat cam – valves don’t open enough to let proper
fuel/air mixture into cylinders.
S Oxygen sensor – may command engine too rich or
too lean for too long.
S Fuel pressure – may be too low.
S Engine mounts – vibration of mounts can be multi-
plied by TCC engagement.
S Axle joints – checks for vibration.
S TPS – TCC apply and release depends on the TPS
in many engines. If TPS is out of specification, TCC
may remain applied during initial engine starting.
S Cylinder balance – bad piston rings or poorly seal-
ing valves can cause low power in a cylinder.
S Fuel contamination – causes poor engine perfor-
mance.
TCM INITIALIZATION PROCEDURE
When one or more operations such as shown below are
performed, all learned contents which are stored in TCM
memory should be erased after the operations.
S When A/T H/W is replaced in a vehicle,
S When a used TCU is installed in other vehicle,
S When a vehicle condition is unstable (engine RPM
flare, TPS toggling and so on; at this kind of unsta-
ble conditions, mis–adaptation might be done).
1. Connect the Scan 100 with a DLC connector in a
vehicle.
2. Turn ignition switch ON.
3. Turn the power on for the Scan 100.
4. Follow the ”TCM LEARNED INITIALIZE” procedure
on the Scan 100 menu.
Notice : Before pushing ”Yes” Button for TCM initialization
on the Scan 100 screen, make sure that the condition is
as follows:
Condition :
1. Engine idle.
2. Select lever set ”P” range.