2004 DAEWOO LACETTI OBD port
[x] Cancel search: OBD portPage 816 of 2643
1F – 570IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1626
IMMOBILIZER NO RESPONSE
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is the control center of
the fuel injection system. It constantly looks at the informa-
tion from various sensors, and controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM also performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize opera-
tional problems, alert the driver through the Malfunction In-
dicator Lamp (MIL) (Check Engine), and store a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) or DTCs which identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs. The
ECM detects communication link failure with immobilizer
control unit.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S No immobilizer message identification for ECM re-
lease time window (1.5 or 2.0 seconds).S Ignition switch is turned to ON.
S ECM release time window expired.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Failure Records buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
DTC P1626 – Immobilizer No Response
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 3–
31. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
4Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 817 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 571
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1631
IMMOBILIZER INVALID RESPONSE
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is the control center of
the fuel injection system. It constantly looks at the informa-
tion from various sensors, and controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM also performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize opera-
tional problems, alert the driver through the Malfunction In-
dicator Lamp (MIL) (Check Engine), and store a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) or DTCs which identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs. The
ECM received incorrect message identification.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Wrong immobilizer message received.
S Ignition switch is turned to ON.
S Immobilizer option selected.S ECM release time window expired.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Failure Records buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
DTC P1631 – Immobilizer Invalid Response
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 3–
31. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
4Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 818 of 2643
1F – 572IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1650
SPI COMMUNICATION BETWEEN ERROR WITH SIDM
CHIP
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is the control center of
the fuel injection system. It constantly looks at the informa-
tion from various sensors, and controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM also performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize opera-
tional problems, alert the driver through the Malfunction In-
dicator Lamp (MIL) (Check Engine), and store a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) or DTCs which identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs. An
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
(EEPROM) is used to house the program information and
the calibrations required for engine, transmission, and
powertrain diagnostics operation. The Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will stored, when the ECM detects SPI com-
munication between main CPU and output driver I/C is
corrupted.
Conditions for Setting the DTCS Ignition switch is turned to ON.
S Battery voltage is greater than 11 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
DTC P1650 – SPI Communication Between Error with SIDM Chip
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 3–
31. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
4Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 819 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 573
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1655
SPI COMMUNICATION BETWEEN ERROR WITH PSVI
CHIP
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is the control center of
the fuel injection system. It constantly looks at the informa-
tion from various sensors, and controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM also performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize opera-
tional problems, alert the driver through the Malfunction In-
dicator Lamp (MIL) (Check Engine), and store a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) or DTCs which identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs. An
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
(EEPROM) is used to house the program information and
the calibrations required for engine, transmission, and
powertrain diagnostics operation. The Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will stored, when the ECM detects corrupted
serial peripheral interface (SPI) comunication between
main CPU and output driver I/C.
Conditions for Setting the DTCS Ignition switch is turned to ON.
S Battery voltage is greater than 11 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
DTC P1655 – SPI Communication Between Error with PSVI Chip
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 3–
31. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
4Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 820 of 2643
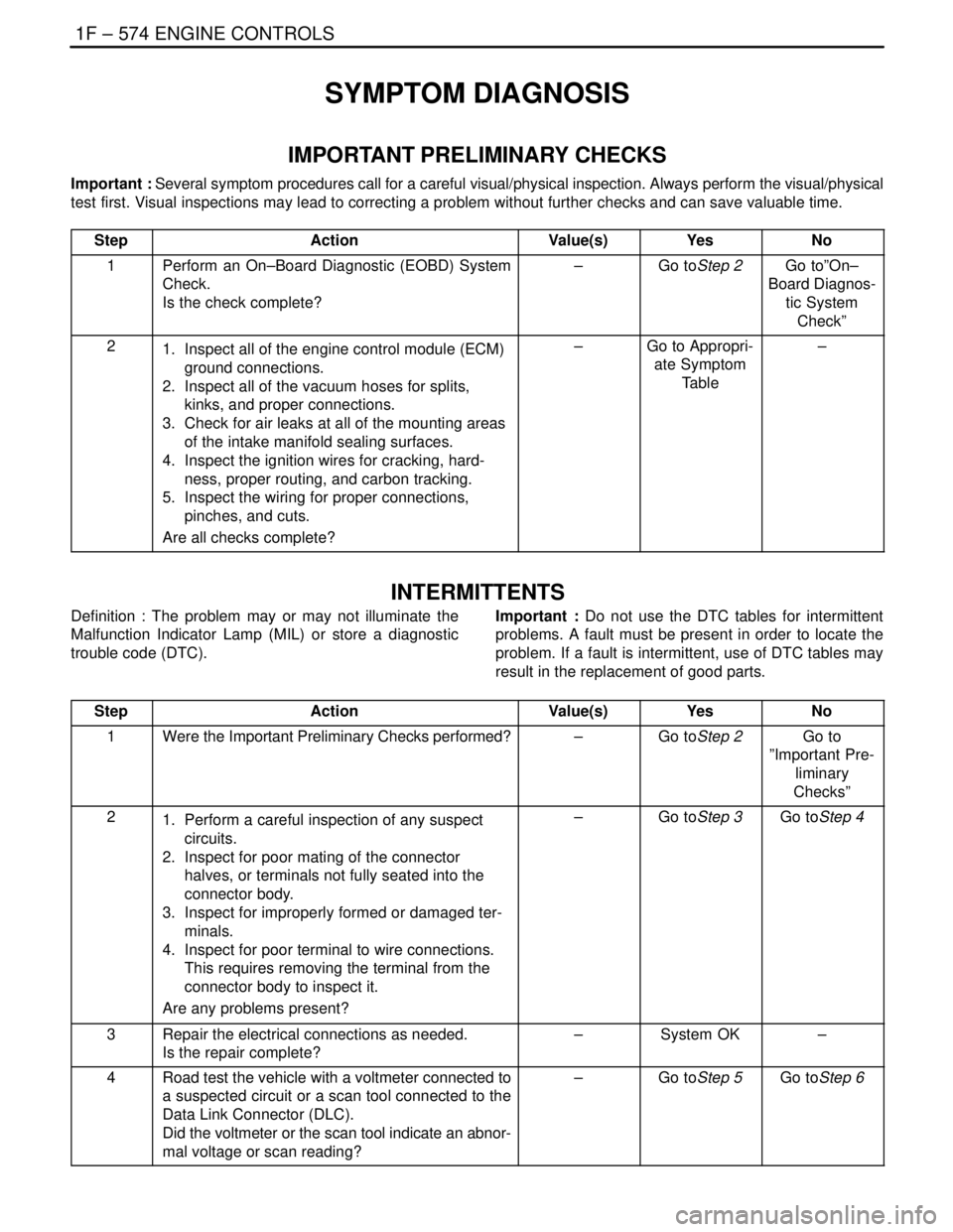
1F – 574IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
IMPORTANT PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Important : Several symptom procedures call for a careful visual/physical inspection. Always perform the visual/physical
test first. Visual inspections may lead to correcting a problem without further checks and can save valuable time.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the check complete?–Go toStep 2Go to”On–
Board Diagnos-
tic System
Check”
21. Inspect all of the engine control module (ECM)
ground connections.
2. Inspect all of the vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and proper connections.
3. Check for air leaks at all of the mounting areas
of the intake manifold sealing surfaces.
4. Inspect the ignition wires for cracking, hard-
ness, proper routing, and carbon tracking.
5. Inspect the wiring for proper connections,
pinches, and cuts.
Are all checks complete?–Go to Appropri-
ate Symptom
Table–
INTERMITTENTS
Definition : The problem may or may not illuminate the
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) or store a diagnostic
trouble code (DTC).Important : Do not use the DTC tables for intermittent
problems. A fault must be present in order to locate the
problem. If a fault is intermittent, use of DTC tables may
result in the replacement of good parts.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Perform a careful inspection of any suspect
circuits.
2. Inspect for poor mating of the connector
halves, or terminals not fully seated into the
connector body.
3. Inspect for improperly formed or damaged ter-
minals.
4. Inspect for poor terminal to wire connections.
This requires removing the terminal from the
connector body to inspect it.
Are any problems present?–Go toStep 3Go toStep 4
3Repair the electrical connections as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
4Road test the vehicle with a voltmeter connected to
a suspected circuit or a scan tool connected to the
Data Link Connector (DLC).
Did the voltmeter or the scan tool indicate an abnor-
mal voltage or scan reading?–Go toStep 5Go toStep 6
Page 874 of 2643

1F – 628IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
STRATEGY – BASED DIAGNOSTICS
Strategy–Based Diagnostics
The strategy–based diagnostic is a uniform approach to
repair all Electrical/Electronic (E/E) systems. The diag-
nostic flow can always be used to resolve an E/E system
problem and is a starting point when repairs are neces-
sary. The following steps will instruct the technician on
how to proceed with a diagnosis:
S Verify the customer complaint. To verify the cus-
tomer complaint, the technician should know the
normal operation of the system.
S Perform preliminary checks as follows:
S Conduct a thorough visual inspection.
S Review the service history.
S Detect unusual sounds or odors.
S Gather Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) informa-
tion to achieve an effective repair.
S Check bulletins and other service information. This
includes videos, newsletters, etc.
S Refer to service information (manual) system
check(s).
S Refer to service diagnostics.
No Trouble Found
This condition exists when the vehicle is found to operate
normally. The condition described by the customer may be
normal. Verify the customer complaint against another ve-
hicle that is operating normally. The condition may be in-
termittent. Verify the complaint under the conditions de-
scribed by the customer before releasing the vehicle.
Re–examine the complaint.
When the complaint cannot be successfully found or iso-
lated, a re–evaluation is necessary. The complaint should
be re–verified and could be intermittent as defined in ”In-
termittents,” or could be normal.
After isolating the cause, the repairs should be made. Vali-
date for proper operation and verify that the symptom has
been corrected. This may involve road testing or other
methods to verify that the complaint has been resolved un-
der the following conditions:
S Conditions noted by the customer.
S If a DTC was diagnosed, verify a repair by duplicat-
ing conditions present when the DTC was set as
noted in the Failure Records or Freeze Frame data.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of the vehicle repair will be more comprehen-
sive for vehicles with On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) sys-
tem diagnostics. Following a repair, the technician should
perform these steps:
Important : Follow the steps below when you verify re-
pairs on EOBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.S Review and record the Failure Records and the
Freeze Frame data for the DTC which has been
diagnosed (Freeze Fame data will only be stored
for an A or B type diagnostic and only if the MIL
has been requested).
S Clear the DTC(s).
S Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the
Failure Records and Freeze Frame data.
S Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
EOBD SERVICEABILITY ISSUES
Based on the knowledge gained from On–Board Diagnos-
tic (EOBD) experience in the 1994 and 1995 model years,
this list of non–vehicle faults that could affect the perfor-
mance of the EOBD system has been compiled. These
non–vehicle faults vary from environmental conditions to
the quality of fuel used. With the introduction of EOBD
diagnostics across the entire passenger car and light–duty
truck market in 1996, illumination of the MIL due to a non–
vehicle fault could lead to misdiagnosis of the vehicle, in-
creased warranty expense and customer dissatisfaction.
The following list of non–vehicle faults does not include ev-
ery possible fault and may not apply equally to all product
lines.
Fuel Quality
Fuel quality is not a new issue for the automotive industry,
but its potential for turning on the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) with EOBD systems is new.
Fuel additives such as ”dry gas” and ”octane enhancers”
may affect the performance of the fuel. If this results in an
incomplete combustion or a partial burn, it will set DTC
P0300. The Reed Vapor Pressure of the fuel can also
create problems in the fuel system, especially during the
spring and fall months when severe ambient temperature
swings occur. A high Reed Vapor Pressure could show up
as a Fuel Trim DTC due to excessive canister loading.
High vapor pressures generated in the fuel tank can also
affect the Evaporative Emission diagnostic as well.
Using fuel with the wrong octane rating for your vehicle
may cause driveability problems. Many of the major fuel
companies advertise that using ”premium” gasoline will
improve the performance of your vehicle. Most premium
fuels use alcohol to increase the octane rating of the fuel.
Although alcohol–enhanced fuels may raise the octane
rating, the fuel’s ability to turn into vapor in cold tempera-
tures deteriorates. This may affect the starting ability and
cold driveability of the engine.
Low fuel levels can lead to fuel starvation, lean engine op-
eration, and eventually engine misfire.
Non–OEM Parts
All of the EOBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts.
Something as simple as a high–performance exhaust sys-
tem that affects exhaust system back pressure could po-
Page 875 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 629
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
tentially interfere with the operation of the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and thereby turn on the MIL.
Small leaks in the exhaust system near the post catalyst
oxygen sensor can also cause the MIL to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones, stereos,
and anti–theft devices, may radiate electromagnetic inter-
ference (EMI) into the control system if they are improperly
installed. This may cause a false sensor reading and turn
on the MIL.
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain–soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL.
Refueling
A new EOBD diagnostic checks the integrity of the entire
Evaporative (EVAP) Emission system. If the vehicle is re-
started after refueling and the fuel cap is not secured cor-
rectly, the on–board diagnostic system will sense this as
a system fault, turn on the MIL, and set DTC P0440.
Vehicle Marshaling
The transportation of new vehicles from the assembly
plant to the dealership can involve as many as 60 key
cycles within 2 to 3 miles of driving. This type of operation
contributes to the fuel fouling of the spark plugs and will
turn on the MIL with a set DTC P0300.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of EOBD diagnostics will cause the MIL to
turn on if the vehicle is not maintained properly. Restricted
air filters, fuel filters, and crankcase deposits due to lack
of oil changes or improper oil viscosity can trigger actual
vehicle faults that were not previously monitored prior to
EOBD. Poor vehicle maintenance can not be classified as
a ”non–vehicle fault,” but with the sensitivity of EOBD
diagnostics, vehicle maintenance schedules must be
more closely followed.
Severe Vibration
The Misfire diagnostic measures small changes in the
rotational speed of the crankshaft. Severe driveline vibra-
tions in the vehicle, such as caused by an excessive
amount of mud on the wheels, can have the same effect
on crankshaft speed as misfire and, therefore, may set
DTC P0300.
Related System Faults
Many of the EOBD system diagnostics will not run if the
engine controlmodule (ECM) detects a fault on a related
system or component. One example would be that if the
ECM detected a Misfire fault, the diagnostics on the cata-
lytic converter would be suspended until the Misfire fault
was repaired. If the Misfire fault is severe enough, the cat-
alytic converter can be damaged due to overheating andwill never set a Catalyst DTC until the Misfire fault is re-
paired and the Catalyst diagnostic is allowed to run to
completion. If this happens, the customer may have to
make two trips to the dealership in order to repair the ve-
hicle.
SERIAL DATA COMMUNICATIONS
Class II Serial Data Communications
Government regulations require that all vehicle manufac-
turers establish a common communication system. This
vehicle utilizes the ”Class II” communication system. Each
bit of information can have one of two lengths: long or
short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by transmit-
ting and receiving multiple signals over a single wire. The
messages carried on Class II data streams are also priori-
tized. If two messages attempt to establish communica-
tions on the data line at the same time, only the message
with higher priority will continue. The device with the lower
priority message must wait. Themost significant result of
this regulation is that it provides scan tool manufacturers
with the capability to access data from any make or model
vehicle that is sold.
The data displayed on the other scan tool will appear the
same, with some exceptions. Some scan tools will only be
able to display certain vehicle parameters as values that
are a coded representation of the true or actual value. On
this vehicle the scan tool displays the actual values for ve-
hicle parameters. It will not be necessary to perform any
conversions from coded values to actual values.
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (EOBD)
On–Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When
a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not cur-
rently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is current-
ly active.
S The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
S The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Remember, a fuel trim Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
may be triggered by a list of vehicle faults. Make use of all
information available (other DTCs stored, rich or lean con-
dition, etc.) when diagnosing a fuel trim fault.
Page 877 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 631
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Barometric Pressure (BARO)
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
S Throttle Position (TP)
S High canister purge
S Fuel trim
S A/C on
Trip
Technically, a trip is a key–on run key–off cycle in which all
the enable criteria for a given diagnostic are met, allowing
the diagnostic to run. Unfortunately, this concept is not
quite that simple. A trip is official when all the enable crite-
ria for a given diagnostic are met. But because the enable
criteria vary from one diagnostic to another, the definition
of trip varies as well. Some diagnostics are run when the
vehicle is at operating temperature, some when the ve-
hicle first starts up; some require that the vehicle be cruis-
ing at a steady highway speed, some run only when the
vehicle is at idle; some diagnostics function with the
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) disabled. Some run only
immediately following a cold engine startup.
A trip then, is defined as a key–on run key–off cycle in
which the vehicle was operated in such a way as to satisfy
the enables criteria for a given diagnostic, and this diag-
nostic will consider this cycle to be one trip. However,
another diagnostic with a different set of enable criteria
(which were not met) during this driving event, would not
consider it a trip. No trip will occur for that particular diag-
nostic until the vehicle is driven in such a way as to meet
all the enable criteria
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the re-
quirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the time
of assembly and that there are not multiple faults present.
There is a continuous self–diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complimented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a malfunc-
tion is detected by the control module, a diagnostic trouble
code is set and the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is illu-
minated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is required by On–
Board Diagnostics (EOBD) that it illuminates under a strict
set of guide lines.
Basically, the MIL is turned on when the engine control
module (ECM) detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle
emissions.The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned on if an emissions–related diagnos-
tic test indicates a malfunction has occurred. It will stay on
until the system or component passes the same test, for
three consecutive trips, with no emissions related faults.
Extinguishing the MIL
When the MIL is on, the Diagnostic Executive will turn off
the MIL after three consecutive trips that a ”test passed”
has been reported for the diagnostic test that originally
caused the MIL to illuminate. Although the MIL has been
turned off, the DTC will remain in the ECM memory (both
Freeze Frame and Failure Records) until forty (40) warm–
up cycles after no faults have been completed.
If the MIL was set by either a fuel trim or misfire–related
DTC, additional requirements must be met. In addition to
the requirements stated in the previous paragraph, these
requirements are as follows:
S The diagnostic tests that are passed must occur
with 375 rpm of the rpm data stored at the time the
last test failed.
S Plus or minus ten percent of the engine load that
was stored at the time the last test failed. Similar
engine temperature conditions (warmed up or
warming up) as those stored at the time the last
test failed.
Meeting these requirements ensures that the fault which
turned on the MIL has been corrected.
The MIL is on the instrument panel and has the following
functions:
S It informs the driver that a fault that affects vehicle
emission levels has occurred and that the vehicle
should be taken for service as soon as possible.
S As a system check, the MIL will come on with the
key ON and the engine not running. When the en-
gine is started, the MIL will turn OFF.
S When the MIL remains ON while the engine is run-
ning, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, an EOBD System
Check must be performed. The procedures for
these checks are given in EOBD System Check.
These checks will expose faults which may not be
detected if other diagnostics are performed first.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communicating with the control module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). The DLC is used to con-
nect to a scan tool. Some common uses of the scan tool
are listed below:
S Identifying stored DTCs.
S Clearing DTCs.
S Performing output control tests.
S Reading serial data.